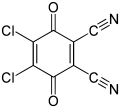
| |||
 | |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name 4,5-Dichloro-3,6-dioxocyclohexa-1,4-diene-1,2-dicarbonitrile | |||
Other names
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
| CAS Number | |||
| 3D model (JSmol) | |||
| Abbreviations | DDQ | ||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.402 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| PubChem CID | |||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |||
InChI
| |||
SMILES
| |||
| Properties | |||
| Chemical formula | C8Cl2N2O2 | ||
| Molar mass | 227.00 g·mol | ||
| Appearance | yellow to orange powder | ||
| Density | 1.7g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | 210–215 °C (410–419 °F; 483–488 K) (decomposes) | ||
| Boiling point | 301.8 °C (575.2 °F; 575.0 K) at 760mmHg | ||
| Solubility in water | reacts | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
| Pictograms | 
| ||
| Signal word | Danger | ||
| Hazard statements | H301 | ||
| Precautionary statements | P264, P270, P301+P310, P321, P330, P405, P501 | ||
| Flash point | 136.3 °C (277.3 °F; 409.4 K) | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |||
2,3-Dichloro-5,6-dicyano-1,4-benzoquinone (or DDQ) is the chemical reagent with formula C6Cl2(CN)2O2. This oxidant is useful for the dehydrogenation of alcohols, phenols, and steroid ketones. DDQ decomposes in water, but is stable in aqueous mineral acid.
Preparation
Synthesis of DDQ involves cyanation of chloranil. J. Thiele and F. Günther first reported a 6-step preparation in 1906. The substance did not receive interest until its potential as a dehydrogenation agent was discovered. A single-step chlorination from 2,3-dicyanohydroquinone was reported in 1965.
Reactions
The reagent removes pairs of H atoms from organic molecules. The stoichiometry of its action is illustrated by the conversion of tetralin to naphthalene:
- 2 C6Cl2(CN)2O2 + C10H12 → 2 C6Cl2(CN)2(OH)2 + C10H8
The resulting hydroquinone is poorly soluble in typical reaction solvents (dioxane, benzene, alkanes), which facilitates workup.
Solutions of DDQ in benzene are red, due to the formation of a charge-transfer complex.
Dehydrogenation
Aromatization
Cross-Dehydrogenative Coupling
Safety
DDQ reacts with water to release highly toxic hydrogen cyanide (HCN).
References
- 2,3-Dichloro-5,6-dicyano-p-benzoquinone at Sigma-Aldrich
- Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry : IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. p. 50. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-FP001. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- Braude, E. A.; Linstead, R. P.; Wooldridge, K. R. H. (1956). "593. Hydrogen Transfer. Part IX The Selective Dehydrogenation of Unsaturated Alcohols by High-potential Quinones". Journal of the Chemical Society (Resumed). 1956: 3070–3074. doi:10.1039/JR9560003070.
- Becker, H. D. (1965). "Quinone Dehydrogenation. I. Oxidation of Monohydric Phenols". Journal of Organic Chemistry. 30 (4): 982–989. doi:10.1021/jo01015a006.
- Turner, A. B.; Ringold, H. J. (1967). "Applications of High-potential Quinones. Part I. The Mechanism of Dehydrogenation of Steroidal Ketones by 2,3-Dichloro-5,6-Dicyanobenzoquinone". Journal of the Chemical Society C: Organic. 1967: 1720–1730. doi:10.1039/J39670001720.
- ^ Buckle, Derek R.; Collier, Steven J.; McLaws, Mark D. (2005). "2,3-Dichloro-5,6-dicyano-1,4-benzoquinone". e-EROS Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rd114.pub2. ISBN 0471936235.
- Thiele, J.; Günther, F. (1906). "Ueber Abkömmlinge des Dicyanhydrochinons". Justus Liebig's Annalen der Chemie. 349 (1): 45–66. doi:10.1002/jlac.19063490103.
- Walker, D.; Waugh, T. D. (1965). "2,3-Dichloro-5,6-Dicyanobenzoquinone (DDQ). A New Preparation". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 30 (9): 3240. doi:10.1021/jo01020a529.
- Rathore, Rajendra; Kochi, Jay K. (2000), "Donor/acceptor organizations and the electron-transfer paradigm for organic reactivity", Advances in Physical Organic Chemistry, Elsevier, pp. 193–318, doi:10.1016/s0065-3160(00)35014-6, ISBN 9780120335350
- Brown, W.; Turner, A. B. (1971). "Application of High-potential Quinones. 7. Synthesis of Steroidal Phenanthrenes by Double Methyl Migration". Journal of the Chemical Society C: Organic. 1971: 2566–2572. doi:10.1039/J39710002566. PMID 5167256.
- Zhang, Y.; Li, C. J. (2006). "DDQ-Mediated Direct Cross-Dehydrogenative-Coupling (CDC) between Benzyl Ethers and Simple Ketones". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 128 (13): 4242–4243. doi:10.1021/ja060050p. PMID 16568995.