| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name 2-Phenylpyridine | |||
| Other names 2-Azabiphenyl | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| CAS Number | |||
| 3D model (JSmol) | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.012.512 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| MeSH | C058324 | ||
| PubChem CID | |||
| UNII | |||
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |||
InChI
| |||
SMILES
| |||
| Properties | |||
| Chemical formula | C11H9N | ||
| Molar mass | 155.200 g·mol | ||
| Appearance | Colorless oil | ||
| Density | 1.086 g/mL | ||
| Boiling point | 268–270 °C (514–518 °F; 541–543 K) | ||
| Solubility in water | Low | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa). Infobox references | |||
2-Phenylpyridine is an organic compound with the formula C6H5C5H4N (or C11H9N). It is a colourless viscous liquid. The compound and related derivatives have attracted interest as precursors to highly fluorescent metal complexes of possible value as organic light emitting diodes (OLEDs).
The compound is prepared by the reaction of phenyl lithium with pyridine:
- C6H5Li + C5H5N → C6H5-C5H4N + LiH
The reaction of iridium trichloride with 2-phenylpyridine proceeds via cyclometallation to give the chloride-bridged complex:
- 4 C6H5-C5H4N + 2 IrCl3(H2O)3 → Ir2Cl2(C6H4-C5H4N)4 + 4 HCl
This complex can be converted to the pictured tris(cyclometallated) derivative tris(2-phenylpyridine)iridium.
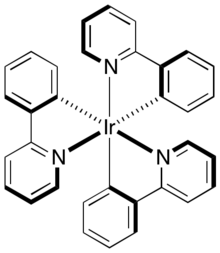
The degree and regiochemistry of fluorination of metalated 2-phenylpyridine ligands in platinum(II) complexes significantly modifies the emission properties of the complexes.
References
- Eli Zysman-Colman, ed. (2017). Iridium(III) in Optoelectronic and Photonics Applications. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-1-119-00713-5.
- Evans, J. C. W.; Allen, C. F. H. (1938). "2-Phenylpyridine". Organic Syntheses. 18: 70. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.018.0070.
- Lamansky, S.; Djurovich, P.; Murphy, D.; et al. (2001). "Synthesis and Characterization of Phosphorescent Cyclometalated Iridium Complexes". Inorganic Chemistry. 40 (7): 1704–1711. doi:10.1021/ic0008969. PMID 11261983.
- Kip A. Teegardin, Jimmie D. Weaver (2018). "Preparation of Fac-Tris(2-Phenylpyridinato) Iridium(III)". Org. Synth. 95: 29–45. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.095.0029. PMC 6022758. PMID 29962554.
- Thompson ME, Djurovich PE, Barlow S, Marder S (2007). "Organometallic Complexes for Optoelectronic Applications". Comprehensive Organometallic Chemistry III. Vol. 12. pp. 101–194. doi:10.1016/B0-08-045047-4/00169-2. ISBN 978-0-08-045047-6.
Further reading
- Zhou, Guijiang; Wong, Wai-Yeung; Yang, Xiaolong (2011). "New Design Tactics in OLEDs Using Functionalized 2-Phenylpyridine-Type Cyclometalates of Iridium(III) and Platinum(II)". Chemistry: An Asian Journal. 6 (7): 1706–1727. doi:10.1002/asia.201000928. PMID 21557486.

