 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
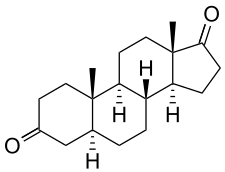
| IUPAC name (5S,8R,9S,10S,13S,14S)-10,13-dimethyl-2,4,5,6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16-dodecahydro-1H-cyclopentaphenanthrene-3,17-dione | |
| Other names Dihydroandrostenedione; 5α-Androstanedione; 5α-Androstane-3,17-dione | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C19H28O2 |
| Molar mass | 288.431 g/mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa). Infobox references | |
Androstanedione, also known as 5α-androstanedione or as 5α-androstane-3,17-dione, is a naturally occurring androstane (5α-androstane) steroid and an endogenous metabolite of androgens like testosterone, dihydrotestosterone (DHT), dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), and androstenedione. It is the C5 epimer of etiocholanedione (5β-androstanedione). Androstanedione is formed from androstenedione by 5α-reductase and from DHT by 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. It has some androgenic activity.
In female genital skin, the conversion of androstenedione into DHT through 5α-androstanedione appears to be more important than the direct conversion of testosterone into DHT.
References
- ^ "Human Metabolome Database: Showing metabocard for Androstanedione (HMDB0000899)".
- Kenneth L. Becker (2001). Principles and Practice of Endocrinology and Metabolism. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 994–. ISBN 978-0-7817-1750-2.
- Eric S. Orwoll; John P. Bilezikian; Dirk Vanderschueren (30 November 2009). Osteoporosis in Men: The Effects of Gender on Skeletal Health. Academic Press. pp. 296–. ISBN 978-0-08-092346-8.
- Charles D. Kochakian (6 December 2012). Anabolic-Androgenic Steroids. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 171–. ISBN 978-3-642-66353-6.
- Stanczyk FZ (June 2006). "Diagnosis of hyperandrogenism: biochemical criteria". Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 20 (2): 177–91. doi:10.1016/j.beem.2006.03.007. PMID 16772150.
External links
| Androgen receptor modulators | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ARTooltip Androgen receptor |
| ||||||
| GPRC6A |
| ||||||
This article about a steroid is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |
This biochemistry article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |