| 𒌔𒆠 | |
  | |
| Location | Uncertain; somewhere in the Diyala Governorate of the Republic of Iraq |
|---|---|
| Region | Mesopotamia |
| Coordinates | 33°5′40″N 44°31′20″E / 33.09444°N 44.52222°E / 33.09444; 44.52222 |
| Type | City |
| History | |
| Founded | c. 2900 BC |
| Abandoned | c. 1595 BC |
| Periods | Early Dynastic I, II, and III, Akkadian, Ur III, Isin-Larsa, Old Babylonian |
| Cultures | Sumer |
| Associated with | Sumerians |
| Site notes | |
| Condition | Lost city |
Akshak (Sumerian: 𒌔𒆠, akšak) (pre-Sargonic - u4kúsu.KI, Ur III - kúsu.KI, Phonetic - ak-su-wa-ak) was a city of ancient Sumer, situated on the northern boundary of Akkad, sometimes identified with Babylonian Upi (Greek Opis). It is known, based on an inscription "‘Ur-kisala, the sangu-priest of Sin of Akshak, son of Na-ti, pasisu-priest of Sin to Salam presented ." that there was a temple of the god Sin in Akshak.
History

Akshak first appears in a Sumerian literary composition Dumuzid's dream, where Dumuzid king of Uruk is said to have been toppled from his opulence by a hungry mob composed of men from the major cities of Sumer, including Akshak. The partially literary Sumerian king list mentions Unzi, Undalulu, Urur, Puzur-Nirah, Ishu-Il and Shu-Sin as kings of Akshak. Puzur-Nirah is also mentioned in the millennia later literary composition Weidner Chronicle as reigning in Akshak when a female tavern-keeper, Kug-bau of Kish, was appointed overlordship over Sumer.
Moving into actual archaeological sources, a king of Uruk, Enshakushanna, is recorded on a stone vessel from Nippur as attacking Akshak saying "The leader of Kish and the leader of Akshak, (when) both their cities were destroyed ...". Following this, Akshak was at war with Lagash, and was captured by Eannatum, who claims in one inscription (on Boulder A v 4-5) to have smitten its king, Zuzu.
"For the god Ningirsu, E-anatum, ruler of Lagash, ... In the year of the offensive of Akshak, E-anatum, nominee of the god Ningirsu, crushed Zuzu, king of Akshak, (all the way) from Antasur of Ningirsu to Akshak, and killed him. ... Kish trembled before E-anatum. drove the king of Akshak back to his own land. ... He defeated Kish, Akshak, and Mari at Antasur of the god Ningirsu."
The town of Antasur featured in several conflicts between Lagash and nearby Girsu. Akshak was also mentioned in tablets found at Ebla. In ca. 2350 BC, Akshak fell into the hands of Lugalzagesi of Umma. The Akkadian king Shar-Kali-Sharri reports defeating the Elamites in a battle at Akshak in his year name "In the year in which Szarkaliszarri brought the battle against Elam and Zahara in front of Akszak and ... and was victorious". A year name of an undetermined ruler of the Akkadian Empire reads "Year in which the Akszak canal in Nippur was split". The city was also mentioned in an Old Babylonian period tablet found at Sippar-Amnanum. A fragmentary year name of a ruler of that period, Itur-Shamash, mentions Akshak, "Year Itur-Szamasz built the temple of ... in Akszak". Itur-Shamash, son of Idinilu, is thought to have been ruler of the city of Kisurra.
There are no records for Akshak after the Old Babylonian period.
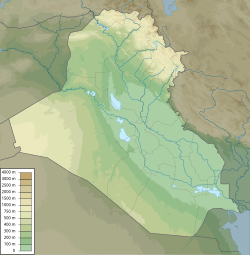
Location
Its exact location is uncertain. Classical writers located it where the Tigris and Euphrates rivers are closest together and it was mentioned along with Kish and Girsu in early records. Archaeologists in the 1900s placed Akshak at the site of Tel Omar (or Tel Umar) where a pair of sites straddles the Tigris, but that turned out to be Seleucia (possibly earlier Upi/Opis) when it was excavated by LeRoy Waterman of the American Schools of Oriental Research. Initially it was thought that two inscriptions bearing the name of Akshak were found there but after examination that proved not the case. Michael C. Astour placed it on the Tigris, on what is now the southern outskirts of Baghdad. A survey of the Diyala area showed no early remains in the area of Seleucia or Cteshiphon, apparently precluding that location.
Surveyed sites marked as possible locations of Akshak were Tell Mohammad, Tell Rishad, and Tell Abu Jawan. Tulul Mujaili' (also Tulül al-Mugeli' and el-Mjel'aat), which lies 15 kilometers northeast of Cteshiphon, has also been suggested as Akshak and also Opis. The site is 500 meters by 200 meters in area with a height of 6.5 meters. A surface survey showed occupation in Early Dynastic through Neo-Babylonian periods, mainly beginning in Kassite times. A kudurru of Marduk-nadin-ahhe (c. 1095–1078 BC), sixth king of the Second Dynasty of Isin and the 4th Dynasty of Babylon, was found there. Based on an early geographical list the site of Tell Sinker (N 56 ̧24' and E 44 ̧14'), on ancient bed of the Tigris river northwest of Baghdad, has also been proposed. Tell Sinker is site 16 (primarily Early Dynastic, 600 meters by 300 meters with a 250m x 100m x 10m central mound) in the Akkad Survey.
List of rulers
The Sumerian King List (SKL) lists only six rulers for Akshak. The following list should not be considered complete:
| Portrait or inscription | Ruler | Approx. date and length of reign (Middle Chronology) | Comments, notes, and references for mentions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Early Dynastic IIIb period (c. 2500 – c. 2340 BC) | |||
| Zuzu 𒍪𒍪 |
Uncertain, fl. c. 2500 – c. 2340 BC | ||
| Akshak dynasty of Sumer (c. 2459 – c. 2360 BC) | |||
| |||

|
Unzi 𒌦𒍣 |
reigned c. 2459 – c. 2429 BC (30 years) |
|
| Undalulu 𒌦𒁕𒇻𒇻 |
r. c. 2429 – c. 2417 BC (6 or 12 years) |
| |
| Urur 𒌨𒌨 |
r. c. 2417 – c. 2411 BC (6 years) |
| |
| Puzur-Nirah 𒅤𒊭𒀭𒈲 |
r. c. 2411 – c. 2391 BC (20 years) |
| |
| Ishu-Il 𒄿𒋗𒅋 |
r. c. 2391 – c. 2367 BC (24 years) |
| |
| Shu-Suen 𒋗𒀭𒂗𒍪 |
r. c. 2367 – c. 2360 BC (7 or 24 years) |
| |
| |||
See also
References
- Schmandt-Besserat, Denise, "Six Votive and Dedicatory Inscriptions", in When Writing Met Art: From Symbol to Story, New York, USA: University of Texas Press, pp. 71-86, 2007
- Ansky, S., "Dumuzi's Dream", The Harps that Once..., edited by David G. Roskies, New Haven: Yale University Press, pp. 28-46, 1992
- "Dumuzid's Dream". Electronic Text Corpus of Sumerian Literature."Those who come for the king are a motley crew, who know not food, who know not drink, who eat no sprinkled flour, who drink no poured water, who accept no pleasant gifts, who do not enjoy a wife's embraces, who never kiss dear little children, who never chew sharp-tasting garlic, who eat no fish, who eat no leeks. There were two men of Adab who came for the king. They were thistles in dried-up waters, they were thorns in stinking waters -- 'his hand was on the table, his tongue was in the palace' (Alludes to a proverb) . Then there were two men of Akšak who came for the king, with …… carried on their shoulders. Then there were two men of Unug who came for the king. With head-smashing clubs tied to their waists, there were two men of Urim who came for the king. "
- Thorkild Jacobsen, "The Sumerian King List", Assyriological Studies 11, Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1939
- A.K. Grayson, "Assyrian and Babylonian Chronicles", Eisenbrauns, 2000 ISBN 978-1575060491
- Frayne, Douglas, "Uruk", Pre-Sargonic Period: Early Periods Volume 1 (2700-2350 BC), University of Toronto Press, pp. 409-440, 2008 ISBN 978-0802035868
- Curchin, Leonard, "Eannatum and the Kings of Adab", Revue d’Assyriologie et d’archéologie Orientale, vol. 71, no. 1, pp. 93–95, 1977
- Jacobsen, Thorkild, "Early Political Development in Mesopotamia", Zeitschrift für Assyriologie und Vorderasiatische Archäologie, vol. 52, no. Jahresband, pp. 91-140, 1957
- Hamblin, William James (2007). Warfare in the ancient Near East to c. 1600 BC. London: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-25588-2. OCLC 255477145.
- Douglas Frayne, "Lagas", in Presargonic Period: Early Periods, Volume 1 (2700-2350 BC), RIM The Royal Inscriptions of Mesopotamia Volume 1, Toronto: University of Toronto Press, pp. 77-293, 2008 ISBN 9780802035868
- ^ Gordon, Cyrus Herzl (1992). Eblaitica: essays on the Ebla archives and Eblaite language 3. 3. Winona Lake, Ind.: Eisenbrauns. p. 58. ISBN 978-0-931464-77-5. OCLC 642922991.
- Kramer, Samuel N., "New Tablets from Fara", Journal of the American Oriental Society, vol. 52, no. 2, pp. 110–32, 1932
- Yuhong, Wu, and Stephanie Dalley, "The Origins of the Manana Dynasty at Kish, and the Assyrian King List", Iraq, vol. 52, pp. 159–65, 1990
- Kramer, Samuel N., "New Tablets from Fara", Journal of the American Oriental Society, vol. 52, no. 2, pp. 110–32, 1932
- George A. Barton, Dr. Waterman's Excavation at Tel Omar (Ctesiphon), Bulletin of the American Schools of Oriental Research, no. 30, pp. 6-8, (Apr., 1928)
- Howard C. Hollis, Material from Seleucia, The Bulletin of the Cleveland Museum of Art, vol. 20, No. 8, pp. 129-131, 1933
- Professor Waterman's Work at Seleucia, Bulletin of the American Schools of Oriental Research, no. 35, pp. 25-27, 1929
- Barnett, R. D. “Xenophon and the Wall of Media.” The Journal of Hellenic Studies, vol. 83, 1963, pp. 1–26
- ^ Adams, Robert M., "Land Behind Baghdad: A History of Settlement on the Diyala Plains", Chicago and London: University of Chicago Press, 1965
- Frame, Grant, "A Kudurru Fragment from the Reign of Adad-apla-iddina", Altorientalische Forschungen", vol. 13, no. 1-2, pp. 206-211, 1986
- K. al-Admi, "Kudurru of Maroduk-nadin-ahhe, IM 90585", Sumer 38, Sumer 38, pp. 121-133, 1982
- Frayne, D. R., "The Early Dynastic List of Geographical Names.", American Oriental Series 74. New Haven: American Oriental Society, 1992 ISBN 978-0940490741
- McGuire Gibson, The city and area of Kish, Field Research Projects, 1972
Further reading
- L Waterman, "Preliminary report upon the excavation at Tel Umar, Iraq: conducted by the University of Michigan and the Toledo museum of art", University of Michigan press, 1931
- L Waterman, "Second preliminary report upon the excavations at Tel Umar, Iraq: conducted by the University of Michigan, the Toledo Museum of Art and the Cleveland Museum of Art", University of Michigan press, 1933