 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Rheumox |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Elimination half-life | 20 hours |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.033.543 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
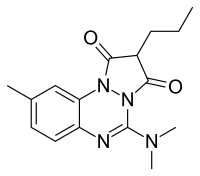
| Formula | C16H20N4O2 |
| Molar mass | 300.362 g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Chirality | Racemic mixture |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (what is this?) (verify) | |
Azapropazone is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). It is manufactured by Goldshield under the tradename Rheumox.
It was available in the UK as a prescription-only drug, with restrictions due to certain contra-indications and side-effects. Azopropazone has now been discontinued in the British National Formulary.
Azapropazone has a half-life of approximately 20 hours in humans and is not extensively metabolized.
References
- "Rheumox Capsules". South Africa Electronic Package Inserts. Archived from the original on 2008-05-15. Retrieved 2008-08-18.
- "Azapropazone". Patient UK. Archived from the original on 12 April 2009.
- Jones CJ (1976). "The pharmacology and pharmacokinetics of azapropazone - a review". Current Medical Research and Opinion. 4 (1): 3–16. doi:10.1185/03007997609109277. PMID 770078.
| Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) (primarily M01A and M02A, also N02BA) | |
|---|---|
| pyrazolones / pyrazolidines | |
| salicylates | |
| acetic acid derivatives and related substances | |
| oxicams | |
| propionic acid derivatives (profens) |
|
| n-arylanthranilic acids (fenamates) | |
| COX-2 inhibitors (coxibs) | |
| other | |
| NSAID combinations | |
| Key: underline indicates initially developed first-in-class compound of specific group; WHO-Essential Medicines; withdrawn drugs; veterinary use. | |
| Prostanoid signaling modulators | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Receptor (ligands) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Enzyme (inhibitors) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Others | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This drug article relating to the musculoskeletal system is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |