| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Bell-shaped function" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (December 2018) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
A bell-shaped function or simply 'bell curve' is a mathematical function having a characteristic "bell"-shaped curve. These functions are typically continuous or smooth, asymptotically approach zero for large negative/positive x, and have a single, unimodal maximum at small x. Hence, the integral of a bell-shaped function is typically a sigmoid function. Bell shaped functions are also commonly symmetric.
Many common probability distribution functions are bell curves.
Some bell shaped functions, such as the Gaussian function and the probability distribution of the Cauchy distribution, can be used to construct sequences of functions with decreasing variance that approach the Dirac delta distribution. Indeed, the Dirac delta can roughly be thought of as a bell curve with variance tending to zero.
Some examples include:
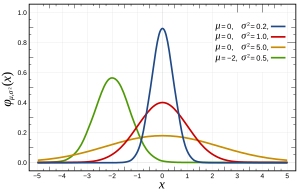
- Gaussian function, the probability density function of the normal distribution. This is the archetypal bell shaped function and is frequently encountered in nature as a consequence of the central limit theorem.
- Fuzzy Logic generalized membership bell-shaped function
- Hyperbolic secant. This is also the derivative of the Gudermannian function.
- Witch of Agnesi, the probability density function of the Cauchy distribution. This is also a scaled version of the derivative of the arctangent function.
- Raised cosines type like the raised cosine distribution or the raised-cosine filter
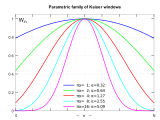
- Most of the window functions like the Kaiser window
- The derivative of the logistic function. This is a scaled version of the derivative of the hyperbolic tangent function.
- Some algebraic functions. For example
Gallery
References
- Weisstein, Eric W. "Delta Function". mathworld.wolfram.com. Retrieved 2020-09-21.
- "Fuzzy Logic Membership Function". Retrieved 2018-12-29.
- "Generalized bell-shaped membership function". Retrieved 2018-12-29.