A simple or regular continued fraction is a continued fraction with numerators all equal one, and denominators built from a sequence of integer numbers. The sequence can be finite or infinite, resulting in a finite (or terminated) continued fraction like
or an infinite continued fraction like
Typically, such a continued fraction is obtained through an iterative process of representing a number as the sum of its integer part and the reciprocal of another number, then writing this other number as the sum of its integer part and another reciprocal, and so on. In the finite case, the iteration/recursion is stopped after finitely many steps by using an integer in lieu of another continued fraction. In contrast, an infinite continued fraction is an infinite expression. In either case, all integers in the sequence, other than the first, must be positive. The integers are called the coefficients or terms of the continued fraction.
Simple continued fractions have a number of remarkable properties related to the Euclidean algorithm for integers or real numbers. Every rational number / has two closely related expressions as a finite continued fraction, whose coefficients ai can be determined by applying the Euclidean algorithm to . The numerical value of an infinite continued fraction is irrational; it is defined from its infinite sequence of integers as the limit of a sequence of values for finite continued fractions. Each finite continued fraction of the sequence is obtained by using a finite prefix of the infinite continued fraction's defining sequence of integers. Moreover, every irrational number is the value of a unique infinite regular continued fraction, whose coefficients can be found using the non-terminating version of the Euclidean algorithm applied to the incommensurable values and 1. This way of expressing real numbers (rational and irrational) is called their continued fraction representation.
Motivation and notation
Consider, for example, the rational number 415/93, which is around 4.4624. As a first approximation, start with 4, which is the integer part; 415/93 = 4 + 43/93. The fractional part is the reciprocal of 93/43 which is about 2.1628. Use the integer part, 2, as an approximation for the reciprocal to obtain a second approximation of 4 + 1/2 = 4.5. Now, 93/43 = 2 + 7/43; the remaining fractional part, 7/43, is the reciprocal of 43/7, and 43/7 is around 6.1429. Use 6 as an approximation for this to obtain 2 + 1/6 as an approximation for 93/43 and 4 + 1/2 + 1/6, about 4.4615, as the third approximation. Further, 43/7 = 6 + 1/7. Finally, the fractional part, 1/7, is the reciprocal of 7, so its approximation in this scheme, 7, is exact (7/1 = 7 + 0/1) and produces the exact expression for 415/93.
That expression is called the continued fraction representation of 415/93. This can be represented by the abbreviated notation 415/93 = . (It is customary to replace only the first comma by a semicolon to indicate that the preceding number is the whole part.) Some older textbooks use all commas in the (n + 1)-tuple, for example, .
If the starting number is rational, then this process exactly parallels the Euclidean algorithm applied to the numerator and denominator of the number. In particular, it must terminate and produce a finite continued fraction representation of the number. The sequence of integers that occur in this representation is the sequence of successive quotients computed by the Euclidean algorithm. If the starting number is irrational, then the process continues indefinitely. This produces a sequence of approximations, all of which are rational numbers, and these converge to the starting number as a limit. This is the (infinite) continued fraction representation of the number. Examples of continued fraction representations of irrational numbers are:
- √19 = (sequence A010124 in the OEIS). The pattern repeats indefinitely with a period of 6.
- e = (sequence A003417 in the OEIS). The pattern repeats indefinitely with a period of 3 except that 2 is added to one of the terms in each cycle.
- π = (sequence A001203 in the OEIS). No pattern has ever been found in this representation.
- Φ = (sequence A000012 in the OEIS). The golden ratio, the irrational number that is the "most difficult" to approximate rationally (see § A property of the golden ratio φ below).
- γ = (sequence A002852 in the OEIS). The Euler–Mascheroni constant, which is expected but not known to be irrational, and whose continued fraction has no apparent pattern.
Continued fractions are, in some ways, more "mathematically natural" representations of a real number than other representations such as decimal representations, and they have several desirable properties:
- The continued fraction representation for a real number is finite if and only if it is a rational number. In contrast, the decimal representation of a rational number may be finite, for example 137/1600 = 0.085625, or infinite with a repeating cycle, for example 4/27 = 0.148148148148...
- Every rational number has an essentially unique simple continued fraction representation. Each rational can be represented in exactly two ways, since = . Usually the first, shorter one is chosen as the canonical representation.
- The simple continued fraction representation of an irrational number is unique. (However, additional representations are possible when using generalized continued fractions; see below.)
- The real numbers whose continued fraction eventually repeats are precisely the quadratic irrationals. For example, the repeating continued fraction is the golden ratio, and the repeating continued fraction is the square root of 2. In contrast, the decimal representations of quadratic irrationals are apparently random. The square roots of all (positive) integers that are not perfect squares are quadratic irrationals, and hence are unique periodic continued fractions.
- The successive approximations generated in finding the continued fraction representation of a number, that is, by truncating the continued fraction representation, are in a certain sense (described below) the "best possible".
Formulation
A continued fraction in canonical form is an expression of the form
where ai are integer numbers, called the coefficients or terms of the continued fraction.
When the expression contains finitely many terms, it is called a finite continued fraction. When the expression contains infinitely many terms, it is called an infinite continued fraction. When the terms eventually repeat from some point onwards, the continued fraction is called periodic.
Thus, all of the following illustrate valid finite simple continued fractions:
| Formula | Numeric | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| All integers are a degenerate case | ||
| Simplest possible fractional form | ||
| First integer may be negative | ||
| First integer may be zero |
For simple continued fractions of the form
the term can be calculated using the following recursive formula:
where and
from which it can be understood that the sequence stops if .
Notations
Consider a continued fraction expressed as
Because such a continued fraction expression may take a significant amount of vertical space, a number of methods have been tried to shrink it.
Gottfried Leibniz sometimes used the notation
and later the same idea was taken even further with the nested fraction bars drawn aligned, for example by Alfred Pringsheim as
or in more common related notations as
or
Carl Friedrich Gauss used a notation reminiscent of summation notation,
or in cases where the numerator is always 1, eliminated the fraction bars altogether, writing a list-style
Sometimes list-style notation uses angle brackets instead,
The semicolon in the square and angle bracket notations is sometimes replaced by a comma.
One may also define infinite simple continued fractions as limits:
This limit exists for any choice of and positive integers .
Calculating continued fraction representations
Consider a real number . Let and let . When , the continued fraction representation of is , where is the continued fraction representation of . When , then is the integer part of , and is the fractional part of .
In order to calculate a continued fraction representation of a number , write down the floor of . Subtract this value from . If the difference is 0, stop; otherwise find the reciprocal of the difference and repeat. The procedure will halt if and only if is rational. This process can be efficiently implemented using the Euclidean algorithm when the number is rational.
The table below shows an implementation of this procedure for the number :
Step Real
NumberInteger
partFractional
partSimplified Reciprocal
of f1 2 3 4 STOP
The continued fraction for is thus or, expanded:
Reciprocals
The continued fraction representations of a positive rational number and its reciprocal are identical except for a shift one place left or right depending on whether the number is less than or greater than one respectively. In other words, the numbers represented by and are reciprocals.
For instance if is an integer and then
- and .
If then
- and .
The last number that generates the remainder of the continued fraction is the same for both and its reciprocal.
For example,
- and .
Finite continued fractions
Every finite continued fraction represents a rational number, and every rational number can be represented in precisely two different ways as a finite continued fraction, with the conditions that the first coefficient is an integer and the other coefficients are positive integers. These two representations agree except in their final terms. In the longer representation the final term in the continued fraction is 1; the shorter representation drops the final 1, but increases the new final term by 1. The final element in the short representation is therefore always greater than 1, if present. In symbols:
- = .
- = .
Infinite continued fractions and convergents
Every infinite continued fraction is irrational, and every irrational number can be represented in precisely one way as an infinite continued fraction.
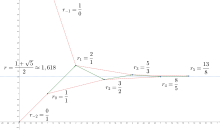
An infinite continued fraction representation for an irrational number is useful because its initial segments provide rational approximations to the number. These rational numbers are called the convergents of the continued fraction. The larger a term is in the continued fraction, the closer the corresponding convergent is to the irrational number being approximated. Numbers like π have occasional large terms in their continued fraction, which makes them easy to approximate with rational numbers. Other numbers like e have only small terms early in their continued fraction, which makes them more difficult to approximate rationally. The golden ratio Φ has terms equal to 1 everywhere—the smallest values possible—which makes Φ the most difficult number to approximate rationally. In this sense, therefore, it is the "most irrational" of all irrational numbers. Even-numbered convergents are smaller than the original number, while odd-numbered ones are larger.
For a continued fraction , the first four convergents (numbered 0 through 3) are
The numerator of the third convergent is formed by multiplying the numerator of the second convergent by the third coefficient, and adding the numerator of the first convergent. The denominators are formed similarly. Therefore, each convergent can be expressed explicitly in terms of the continued fraction as the ratio of certain multivariate polynomials called continuants.
If successive convergents are found, with numerators h1, h2, ... and denominators k1, k2, ... then the relevant recursive relation is that of Gaussian brackets:
The successive convergents are given by the formula
Thus to incorporate a new term into a rational approximation, only the two previous convergents are necessary. The initial "convergents" (required for the first two terms) are ⁄1 and ⁄0. For example, here are the convergents for .
n −2 −1 0 1 2 3 4 an 0 1 5 2 2 hn 0 1 0 1 5 11 27 kn 1 0 1 1 6 13 32
When using the Babylonian method to generate successive approximations to the square root of an integer, if one starts with the lowest integer as first approximant, the rationals generated all appear in the list of convergents for the continued fraction. Specifically, the approximants will appear on the convergents list in positions 0, 1, 3, 7, 15, ... , 2−1, ... For example, the continued fraction expansion for is . Comparing the convergents with the approximants derived from the Babylonian method:
n −2 −1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 an 1 1 2 1 2 1 2 1 hn 0 1 1 2 5 7 19 26 71 97 kn 1 0 1 1 3 4 11 15 41 56
- x0 = 1 = 1/1
- x1 = 1/2(1 + 3/1) = 2/1 = 2
- x2 = 1/2(2 + 3/2) = 7/4
- x3 = 1/2(7/4 + 3/7/4) = 97/56
Properties
The Baire space is a topological space on infinite sequences of natural numbers. The infinite continued fraction provides a homeomorphism from the Baire space to the space of irrational real numbers (with the subspace topology inherited from the usual topology on the reals). The infinite continued fraction also provides a map between the quadratic irrationals and the dyadic rationals, and from other irrationals to the set of infinite strings of binary numbers (i.e. the Cantor set); this map is called the Minkowski question-mark function. The mapping has interesting self-similar fractal properties; these are given by the modular group, which is the subgroup of Möbius transformations having integer values in the transform. Roughly speaking, continued fraction convergents can be taken to be Möbius transformations acting on the (hyperbolic) upper half-plane; this is what leads to the fractal self-symmetry.
The limit probability distribution of the coefficients in the continued fraction expansion of a random variable uniformly distributed in (0, 1) is the Gauss–Kuzmin distribution.
Some useful theorems
If is an infinite sequence of positive integers, define the sequences and recursively:
Theorem 1. For any positive real number
Theorem 2. The convergents of are given by
or in matrix form,
Theorem 3. If the th convergent to a continued fraction is then
or equivalently
Corollary 1: Each convergent is in its lowest terms (for if and had a nontrivial common divisor it would divide which is impossible).
Corollary 2: The difference between successive convergents is a fraction whose numerator is unity:
Corollary 3: The continued fraction is equivalent to a series of alternating terms:
Corollary 4: The matrix
has determinant , and thus belongs to the group of unimodular matrices
Corollary 5: The matrix has determinant , or equivalently,meaning that the odd terms monotonically decrease, while the even terms monotonically increase.
Corollary 6: The denominator sequence satisfies the recurrence relation , and grows at least as fast as the Fibonacci sequence, which itself grows like where is the golden ratio.
Theorem 4. Each (th) convergent is nearer to a subsequent (th) convergent than any preceding (th) convergent is. In symbols, if the th convergent is taken to be then
for all
Corollary 1: The even convergents (before the th) continually increase, but are always less than
Corollary 2: The odd convergents (before the th) continually decrease, but are always greater than
Theorem 5.
Corollary 1: A convergent is nearer to the limit of the continued fraction than any fraction whose denominator is less than that of the convergent.
Corollary 2: A convergent obtained by terminating the continued fraction just before a large term is a close approximation to the limit of the continued fraction.
Theorem 6: Consider the set of all open intervals with end-points . Denote it as . Any open subset of is a disjoint union of sets from .
Corollary: The infinite continued fraction provides a homeomorphism from the Baire space to .
Semiconvergents
If
are consecutive convergents, then any fractions of the form
where is an integer such that , are called semiconvergents, secondary convergents, or intermediate fractions. The -st semiconvergent equals the mediant of the -th one and the convergent . Sometimes the term is taken to mean that being a semiconvergent excludes the possibility of being a convergent (i.e., ), rather than that a convergent is a kind of semiconvergent.
It follows that semiconvergents represent a monotonic sequence of fractions between the convergents (corresponding to ) and (corresponding to ). The consecutive semiconvergents and satisfy the property .
If a rational approximation to a real number is such that the value is smaller than that of any approximation with a smaller denominator, then is a semiconvergent of the continued fraction expansion of . The converse is not true, however.
Best rational approximations
See also: Diophantine approximation and Padé approximantOne can choose to define a best rational approximation to a real number x as a rational number n/d, d > 0, that is closer to x than any approximation with a smaller or equal denominator. The simple continued fraction for x can be used to generate all of the best rational approximations for x by applying these three rules:
- Truncate the continued fraction, and reduce its last term by a chosen amount (possibly zero).
- The reduced term cannot have less than half its original value.
- If the final term is even, half its value is admissible only if the corresponding semiconvergent is better than the previous convergent. (See below.)
For example, 0.84375 has continued fraction . Here are all of its best rational approximations.
Continued fraction Rational approximation 1 3/4 4/5 5/6 11/13 16/19 27/32 Decimal equivalent 1 0.75 0.8 ~0.83333 ~0.84615 ~0.84211 0.84375 Error +18.519% −11.111% −5.1852% −1.2346% +0.28490% −0.19493% 0%

The strictly monotonic increase in the denominators as additional terms are included permits an algorithm to impose a limit, either on size of denominator or closeness of approximation.
The "half rule" mentioned above requires that when ak is even, the halved term ak/2 is admissible if and only if |x − | > |x − | This is equivalent to: Shoemake (1995).
- > .
The convergents to x are "best approximations" in a much stronger sense than the one defined above. Namely, n/d is a convergent for x if and only if |dx − n| has the smallest value among the analogous expressions for all rational approximations m/c with c ≤ d; that is, we have |dx − n| < |cx − m| so long as c < d. (Note also that |dkx − nk| → 0 as k → ∞.)
Best rational within an interval
A rational that falls within the interval (x, y), for 0 < x < y, can be found with the continued fractions for x and y. When both x and y are irrational and
- x =
- y =
where x and y have identical continued fraction expansions up through ak−1, a rational that falls within the interval (x, y) is given by the finite continued fraction,
- z(x,y) =
This rational will be best in the sense that no other rational in (x, y) will have a smaller numerator or a smaller denominator.
If x is rational, it will have two continued fraction representations that are finite, x1 and x2, and similarly a rational y will have two representations, y1 and y2. The coefficients beyond the last in any of these representations should be interpreted as +∞; and the best rational will be one of z(x1, y1), z(x1, y2), z(x2, y1), or z(x2, y2).
For example, the decimal representation 3.1416 could be rounded from any number in the interval [3.14155, 3.14165). The continued fraction representations of 3.14155 and 3.14165 are
- 3.14155 = =
- 3.14165 = =
and the best rational between these two is
- = 355/113 = 3.1415929....
Thus, 355/113 is the best rational number corresponding to the rounded decimal number 3.1416, in the sense that no other rational number that would be rounded to 3.1416 will have a smaller numerator or a smaller denominator.
Interval for a convergent
A rational number, which can be expressed as finite continued fraction in two ways,
- z = = = pk/qk
will be one of the convergents for the continued fraction expansion of a number, if and only if the number is strictly between (see this proof)
- x = = 2pk - pk-1/2qk - qk-1 and
- y = = pk + pk-1/qk + qk-1
The numbers x and y are formed by incrementing the last coefficient in the two representations for z. It is the case that x < y when k is even, and x > y when k is odd.
For example, the number 355/113 has the continued fraction representations
- 355/113 = =
and thus 355/113 is a convergent of any number strictly between
= 688/219 ≈ 3.1415525 = 377/120 ≈ 3.1416667
Legendre's theorem on continued fractions
See also: Dirichlet's approximation theoremIn his Essai sur la théorie des nombres (1798), Adrien-Marie Legendre derives a necessary and sufficient condition for a rational number to be a convergent of the continued fraction of a given real number. A consequence of this criterion, often called Legendre's theorem within the study of continued fractions, is as follows:
Theorem. If α is a real number and p, q are positive integers such that , then p/q is a convergent of the continued fraction of α.
| Proof |
|---|
|
Proof. We follow the proof given in An Introduction to the Theory of Numbers by G. H. Hardy and E. M. Wright. Suppose α, p, q are such that , and assume that α > p/q. Then we may write , where 0 < θ < 1/2. We write p/q as a finite continued fraction , where due to the fact that each rational number has two distinct representations as finite continued fractions differing in length by one (namely, one where an = 1 and one where an ≠ 1), we may choose n to be even. (In the case where α < p/q, we would choose n to be odd.) Let p0/q0, ..., pn/qn = p/q be the convergents of this continued fraction expansion. Set , so that and thus,where we have used the fact that pn−1 qn - pn qn−1 = (-1) and that n is even. Now, this equation implies that α = . Since the fact that 0 < θ < 1/2 implies that ω > 1, we conclude that the continued fraction expansion of α must be , where is the continued fraction expansion of ω, and therefore that pn/qn = p/q is a convergent of the continued fraction of α. |
This theorem forms the basis for Wiener's attack, a polynomial-time exploit of the RSA cryptographic protocol that can occur for an injudicious choice of public and private keys (specifically, this attack succeeds if the prime factors of the public key n = pq satisfy p < q < 2p and the private key d is less than (1/3)n).
Comparison
Consider x = and y = . If k is the smallest index for which ak is unequal to bk then x < y if (−1)(ak − bk) < 0 and y < x otherwise.
If there is no such k, but one expansion is shorter than the other, say x = and y = with ai = bi for 0 ≤ i ≤ n, then x < y if n is even and y < x if n is odd.
Continued fraction expansion of π and its convergents
To calculate the convergents of π we may set a0 = ⌊π⌋ = 3, define u1 = 1/π − 3 ≈ 7.0625 and a1 = ⌊u1⌋ = 7, u2 = 1/u1 − 7 ≈ 15.9966 and a2 = ⌊u2⌋ = 15, u3 = 1/u2 − 15 ≈ 1.0034. Continuing like this, one can determine the infinite continued fraction of π as
The fourth convergent of π is = 355/113 = 3.14159292035..., sometimes called Milü, which is fairly close to the true value of π.
Let us suppose that the quotients found are, as above, . The following is a rule by which we can write down at once the convergent fractions which result from these quotients without developing the continued fraction.
The first quotient, supposed divided by unity, will give the first fraction, which will be too small, namely, 3/1. Then, multiplying the numerator and denominator of this fraction by the second quotient and adding unity to the numerator, we shall have the second fraction, 22/7, which will be too large. Multiplying in like manner the numerator and denominator of this fraction by the third quotient, and adding to the numerator the numerator of the preceding fraction, and to the denominator the denominator of the preceding fraction, we shall have the third fraction, which will be too small. Thus, the third quotient being 15, we have for our numerator (22 × 15 = 330) + 3 = 333, and for our denominator, (7 × 15 = 105) + 1 = 106. The third convergent, therefore, is 333/106. We proceed in the same manner for the fourth convergent. The fourth quotient being 1, we say 333 times 1 is 333, and this plus 22, the numerator of the fraction preceding, is 355; similarly, 106 times 1 is 106, and this plus 7 is 113. In this manner, by employing the four quotients , we obtain the four fractions:
- 3/1, 22/7, 333/106, 355/113, ....

To sum up, the pattern is
These convergents are alternately smaller and larger than the true value of π, and approach nearer and nearer to π. The difference between a given convergent and π is less than the reciprocal of the product of the denominators of that convergent and the next convergent. For example, the fraction 22/7 is greater than π, but 22/7 − π is less than 1/7 × 106 = 1/742 (in fact, 22/7 − π is just more than 1/791 = 1/7 × 113).
The demonstration of the foregoing properties is deduced from the fact that if we seek the difference between one of the convergent fractions and the next adjacent to it we shall obtain a fraction of which the numerator is always unity and the denominator the product of the two denominators. Thus the difference between 22/7 and 3/1 is 1/7, in excess; between 333/106 and 22/7, 1/742, in deficit; between 355/113 and 333/106, 1/11978, in excess; and so on. The result being, that by employing this series of differences we can express in another and very simple manner the fractions with which we are here concerned, by means of a second series of fractions of which the numerators are all unity and the denominators successively be the product of every two adjacent denominators. Instead of the fractions written above, we have thus the series:
- 3/1 + 1/1 × 7 − 1/7 × 106 + 1/106 × 113 − ...
The first term, as we see, is the first fraction; the first and second together give the second fraction, 22/7; the first, the second and the third give the third fraction 333/106, and so on with the rest; the result being that the series entire is equivalent to the original value.
Non-simple continued fraction
Main article: Continued fraction (non-simple)A non-simple continued fraction is an expression of the form
where the an (n > 0) are the partial numerators, the bn are the partial denominators, and the leading term b0 is called the integer part of the continued fraction.
To illustrate the use of non-simple continued fractions, consider the following example. The sequence of partial denominators of the simple continued fraction of π does not show any obvious pattern:
or
However, several non-simple continued fractions for π have a perfectly regular structure, such as:
The first two of these are special cases of the arctangent function with π = 4 arctan (1) and the fourth and fifth one can be derived using the Wallis product.
The continued fraction of above consisting of cubes uses the Nilakantha series and an exploit from Leonhard Euler.
Other continued fraction expansions
Periodic continued fractions
Main article: Periodic continued fractionThe numbers with periodic continued fraction expansion are precisely the irrational solutions of quadratic equations with rational coefficients; rational solutions have finite continued fraction expansions as previously stated. The simplest examples are the golden ratio φ = and √2 = , while √14 = and √42 = . All irrational square roots of integers have a special form for the period; a symmetrical string, like the empty string (for √2) or 1,2,1 (for √14), followed by the double of the leading integer.
A property of the golden ratio φ
Because the continued fraction expansion for φ doesn't use any integers greater than 1, φ is one of the most "difficult" real numbers to approximate with rational numbers. Hurwitz's theorem states that any irrational number k can be approximated by infinitely many rational m/n with
While virtually all real numbers k will eventually have infinitely many convergents m/n whose distance from k is significantly smaller than this limit, the convergents for φ (i.e., the numbers 5/3, 8/5, 13/8, 21/13, etc.) consistently "toe the boundary", keeping a distance of almost exactly away from φ, thus never producing an approximation nearly as impressive as, for example, 355/113 for π. It can also be shown that every real number of the form a + bφ/c + dφ, where a, b, c, and d are integers such that a d − b c = ±1, shares this property with the golden ratio φ; and that all other real numbers can be more closely approximated.
Regular patterns in continued fractions
While there is no discernible pattern in the simple continued fraction expansion of π, there is one for e, the base of the natural logarithm:
which is a special case of this general expression for positive integer n:
Another, more complex pattern appears in this continued fraction expansion for positive odd n:
with a special case for n = 1:
Other continued fractions of this sort are
where n is a positive integer; also, for integer n:
with a special case for n = 1:
If In(x) is the modified, or hyperbolic, Bessel function of the first kind, we may define a function on the rationals p/q by
which is defined for all rational numbers, with p and q in lowest terms. Then for all nonnegative rationals, we have
with similar formulas for negative rationals; in particular we have
Many of the formulas can be proved using Gauss's continued fraction.
Typical continued fractions
Most irrational numbers do not have any periodic or regular behavior in their continued fraction expansion. Nevertheless, for almost all numbers on the unit interval, they have the same limit behavior.
The arithmetic average diverges: , and so the coefficients grow arbitrarily large: . In particular, this implies that almost all numbers are well-approximable, in the sense thatKhinchin proved that the geometric mean of ai tends to a constant (known as Khinchin's constant):Paul Lévy proved that the nth root of the denominator of the nth convergent converges to Lévy's constant Lochs' theorem states that the convergents converge exponentially at the rate of
Applications
Pell's equation
Continued fractions play an essential role in the solution of Pell's equation. For example, for positive integers p and q, and non-square n, it is true that if p − nq = ±1, then p/q is a convergent of the regular continued fraction for √n. The converse holds if the period of the regular continued fraction for √n is 1, and in general the period describes which convergents give solutions to Pell's equation.
Dynamical systems
Continued fractions also play a role in the study of dynamical systems, where they tie together the Farey fractions which are seen in the Mandelbrot set with Minkowski's question-mark function and the modular group Gamma.
The backwards shift operator for continued fractions is the map h(x) = 1/x − ⌊1/x⌋ called the Gauss map, which lops off digits of a continued fraction expansion: h() = . The transfer operator of this map is called the Gauss–Kuzmin–Wirsing operator. The distribution of the digits in continued fractions is given by the zero'th eigenvector of this operator, and is called the Gauss–Kuzmin distribution.
History
- 300 BCE Euclid's Elements contains an algorithm for the greatest common divisor, whose modern version generates a continued fraction as the sequence of quotients of successive Euclidean divisions that occur in it.
- 499 The Aryabhatiya contains the solution of indeterminate equations using continued fractions
- 1572 Rafael Bombelli, L'Algebra Opera – method for the extraction of square roots which is related to continued fractions
- 1613 Pietro Cataldi, Trattato del modo brevissimo di trovar la radice quadra delli numeri – first notation for continued fractions
- Cataldi represented a continued fraction as & & & with the dots indicating where the following fractions went.
- 1695 John Wallis, Opera Mathematica – introduction of the term "continued fraction"
- 1737 Leonhard Euler, De fractionibus continuis dissertatio – Provided the first then-comprehensive account of the properties of continued fractions, and included the first proof that the number e is irrational.
- 1748 Euler, Introductio in analysin infinitorum. Vol. I, Chapter 18 – proved the equivalence of a certain form of continued fraction and a generalized infinite series, proved that every rational number can be written as a finite continued fraction, and proved that the continued fraction of an irrational number is infinite.
- 1761 Johann Lambert – gave the first proof of the irrationality of π using a continued fraction for tan(x).
- 1768 Joseph-Louis Lagrange – provided the general solution to Pell's equation using continued fractions similar to Bombelli's
- 1770 Lagrange – proved that quadratic irrationals expand to periodic continued fractions.
- 1813 Carl Friedrich Gauss, Werke, Vol. 3, pp. 134–138 – derived a very general complex-valued continued fraction via a clever identity involving the hypergeometric function
- 1892 Henri Padé defined Padé approximant
- 1972 Bill Gosper – First exact algorithms for continued fraction arithmetic.
See also
- Complete quotient
- Computing continued fractions of square roots – Algorithms for calculating square roots
- Egyptian fraction – Finite sum of distinct unit fractions
- Engel expansion – decomposition of a positive real number into a series of unit fractions, each an integer multiple of the next onePages displaying wikidata descriptions as a fallback
- Euler's continued fraction formula – Connects a very general infinite series with an infinite continued fraction.
- Iterated binary operation – Repeated application of an operation to a sequence
- Klein polyhedron – Concept in the geometry of numbers
- Mathematical constants by continued fraction representation
- Restricted partial quotients – Analytic series
- Stern–Brocot tree – Ordered binary tree of rational numbers
Notes
- ^ Pettofrezzo & Byrkit 1970, p. 150.
- ^ Long 1972, p. 173.
- ^ Pettofrezzo & Byrkit 1970, p. 152.
- ^ Weisstein 2022.
- Collins 2001.
- Cajori, Florian (1925). "Leibniz, the Master-Builder of Mathematical Notations". Isis. 7 (3): 412–429. doi:10.1086/358328.
- Swanson, Ellen (1999) . Mathematics into Type (PDF). Updated by O'Sean, Arlene; Schleyer, Antoinette (Updated ed.). American Mathematical Society. 2.4.1c "Continued fractions", p. 18.
- Long 1972, p. 183.
- Pettofrezzo & Byrkit 1970, p. 158.
- Long 1972, p. 177.
- Pettofrezzo & Byrkit 1970, pp. 162–163.
- ^ Thill 2008.
- Gosper, R. W. (1977). "Appendix 2: Continued Fraction Arithmetic". See "simplest intervening rational", pp. 29–31.
- Murakami, Hiroshi (February 2015). "Calculation of rational numbers in an interval whose denominator is the smallest by using FP interval arithmetic". ACM Communications in Computer Algebra. 48 (3/4): 134–136. doi:10.1145/2733693.2733711.
- Legendre, Adrien-Marie (1798). Essai sur la théorie des nombres (in French). Paris: Duprat. pp. 27–29.
- Barbolosi, Dominique; Jager, Hendrik (1994). "On a theorem of Legendre in the theory of continued fractions". Journal de Théorie des Nombres de Bordeaux. 6 (1): 81–94. doi:10.5802/jtnb.106. JSTOR 26273940 – via JSTOR.
- Hardy, G. H.; Wright, E. M. (1938). An Introduction to the Theory of Numbers. London: Oxford University Press. pp. 140–141, 153.
- Wiener, Michael J. (1990). "Cryptanalysis of short RSA secret exponents". IEEE Transactions on Information Theory. 36 (3): 553–558. doi:10.1109/18.54902 – via IEEE.
- Bunder & Tonien 2017.
- Scheinerman, Pickett & Coleman 2008.
- Foster 2015.
- Hardy & Wright 2008, Theorem 193.
- Niven, Zuckerman & Montgomery 1991.
- Sandifer 2006.
- Euler 1748.
References
- Bunder, Martin W.; Tonien, Joseph (2017). "Closed form expressions for two harmonic continued fractions". The Mathematical Gazette. 101 (552): 439–448. doi:10.1017/mag.2017.125. S2CID 125489697.
- Chen, Chen-Fan; Shieh, Leang-San (1969). "Continued fraction inversion by Routh's Algorithm". IEEE Trans. Circuit Theory. 16 (2): 197–202. doi:10.1109/TCT.1969.1082925.
- Collins, Darren C. (2001). "Continued Fractions" (PDF). MIT Undergraduate Journal of Mathematics. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2001-11-20.
- Cuyt, A.; Brevik Petersen, V.; Verdonk, B.; Waadeland, H.; Jones, W. B. (2008). Handbook of Continued fractions for Special functions. Springer Verlag. ISBN 978-1-4020-6948-2.
- Encyclopædia Britannica (2013). "Continued fraction – mathematics". Retrieved 26 April 2022.
- Euler, Leonhard (1748). "E101 – Introductio in analysin infinitorum, volume 1". The Euler Archive. Retrieved 26 April 2022.
- Foster, Tony (22 June 2015). "Theorem of the Day: Theorem no. 203" (PDF). Robin Whitty. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2013-12-11. Retrieved 26 April 2022.
- Gragg, William B. (1974). "Matrix interpretations and applications of the continued fraction algorithm". Rocky Mountain J. Math. 4 (2): 213. doi:10.1216/RMJ-1974-4-2-213. S2CID 121378061.
- Hardy, Godfrey H.; Wright, Edward M. (December 2008) . An Introduction to the Theory of Numbers (6 ed.). Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780199219865.
- Heilermann, J. B. H. (1846). "Ueber die Verwandlung von Reihen in Kettenbrüche". Journal für die reine und angewandte Mathematik. 33: 174–188.
- Jones, William B.; Thron, W. J. (1980). Continued Fractions: Analytic Theory and Applications. Encyclopedia of Mathematics and its Applications. Vol. 11. Reading. Massachusetts: Addison-Wesley Publishing Company. ISBN 0-201-13510-8.
- Long, Calvin T. (December 1972). Elementary Introduction to Number Theory (2nd ed.). Lexington: D. C. Heath and Company. ISBN 9780669627039.
- Magnus, Arne (1962). "Continued fractions associated with the Padé Table". Math. Z. 78: 361–374. doi:10.1007/BF01195180. S2CID 120535167.
- Niven, Ivan; Zuckerman, Herbert S.; Montgomery, Hugh L. (1991). An introduction to the theory of numbers (Fifth ed.). New York: Wiley. ISBN 0-471-62546-9.
- Perron, Oskar (1950). Die Lehre von den Kettenbrüchen. New York, NY: Chelsea Publishing Company.
- Pettofrezzo, Anthony J.; Byrkit, Donald R. (December 1970). Elements of Number Theory. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice Hall. ISBN 9780132683005.
- Rieger, Georg Johann (1982). "A new approach to the real numbers (motivated by continued fractions)" (PDF). Abhandlungen der Braunschweigischen Wissenschaftlichen Gesellschaft. 33: 205–217. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2020-12-10.
- Rockett, Andrew M.; Szüsz, Peter (1992). Continued Fractions. World Scientific Press. ISBN 981-02-1047-7.
- Sandifer, C. Edward (2006). "Chapter 32: Who proved e is irrational?". How Euler Did It (PDF). Mathematical Association of America. pp. 185–190. ISBN 978-0-88385-563-8. LCCN 2007927658. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2014-03-19.
- Scheinerman, Ed; Pickett, Thomas J.; Coleman, Ann (2008). "Another Continued Fraction for π". The American Mathematical Monthly. 115 (10): 930–933. doi:10.1080/00029890.2008.11920610. JSTOR 27642639. S2CID 11914017.
- Shoemake, Ken (1995). "I.4: Rational Approximation". In Paeth, Alan W. (ed.). Graphics Gems V (IBM Version). San Diego, California: Academic Press. pp. 25–31. ISBN 0-12-543455-3.
- Siebeck, H. (1846). "Ueber periodische Kettenbrüche". Journal für die reine und angewandte Mathematik. 33: 68–70.
- Thill, M. (2008). "A more precise rounding algorithm for rational numbers". Computing. 82 (2–3): 189–198. doi:10.1007/s00607-008-0006-7. S2CID 45166490.
- Thurston, Ben (2012). "Estimating square roots, generalized continued fraction expression for every square root". The Ben Paul Thurston Blog. Retrieved 26 April 2022.
- Wall, Hubert Stanley (1948). Analytic Theory of Continued Fractions. D. Van Nostrand Company, Inc. ISBN 0-8284-0207-8.
- Weisstein, Eric Wolfgang (2022). MathWorld (ed.). "Periodic Continued Fraction". Retrieved 26 April 2022.
External links
- "Continued fraction", Encyclopedia of Mathematics, EMS Press, 2001
- Knott, Ron (2018). "Continued fractions (An online Combined Continued Fraction Calculator is available)". Retrieved 26 April 2022.
- Linas Vepstas Continued Fractions and Gaps (2004) reviews chaotic structures in continued fractions.
- Continued Fractions on the Stern-Brocot Tree at cut-the-knot
- The Antikythera Mechanism I: Gear ratios and continued fractions Archived 2009-05-04 at the Wayback Machine
- Continued fraction calculator, WIMS.
- Continued Fraction Arithmetic Gosper's first continued fractions paper, unpublished. Cached on the Internet Archive's Wayback Machine
- Weisstein, Eric W. "Continued Fraction". MathWorld.
- Continued Fractions by Stephen Wolfram and Continued Fraction Approximations of the Tangent Function by Michael Trott, Wolfram Demonstrations Project.
- OEIS sequence A133593 ("Exact" continued fraction for pi)
- A view into "fractional interpolation" of a continued fraction {1; 1, 1, 1, ...}
- Best rational approximation through continued fractions
- CONTINUED FRACTIONS by C. D. Olds
| Fractions and ratios | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 | Division and ratio |  | |
| Fraction |
| ||
 of integer numbers. The sequence can be finite or infinite, resulting in a finite (or terminated) continued fraction like
of integer numbers. The sequence can be finite or infinite, resulting in a finite (or terminated) continued fraction like


 are called the
are called the  /
/ has two closely related expressions as a finite continued fraction, whose coefficients ai can be determined by applying the Euclidean algorithm to
has two closely related expressions as a finite continued fraction, whose coefficients ai can be determined by applying the Euclidean algorithm to  . The numerical value of an infinite continued fraction is
. The numerical value of an infinite continued fraction is  is the value of a unique infinite regular continued fraction, whose coefficients can be found using the non-terminating version of the Euclidean algorithm applied to the
is the value of a unique infinite regular continued fraction, whose coefficients can be found using the non-terminating version of the Euclidean algorithm applied to the  for 415/93.
for 415/93.










 term can be calculated using the following recursive formula:
term can be calculated using the following recursive formula:

 and
and 
 .
.









 and positive integers
and positive integers  .
.
 .
Let
.
Let  and let
and let  .
When
.
When  , the continued fraction representation of
, the continued fraction representation of  , where
, where  is the continued fraction representation of
is the continued fraction representation of  . When
. When  , then
, then  is the
is the  is the
is the  :
:


















 is thus
is thus  or, expanded:
or, expanded:

 and
and  are reciprocals.
are reciprocals.
 is an integer and
is an integer and  then
then
 and
and  .
. then
then
 and
and  .
. and its reciprocal.
and its reciprocal.
 and
and  .
.






 is an infinite sequence of positive integers, define the sequences
is an infinite sequence of positive integers, define the sequences  and
and  recursively:
recursively:









![{\displaystyle \ldots \ ]\ }](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/f28bcc28d8f19cfd10ba8688e2dabc22dd3c7bcc) are given by
are given by


 th convergent to a continued fraction is
th convergent to a continued fraction is  then
then


 which is impossible).
which is impossible).


 , and thus belongs to the group of
, and thus belongs to the group of


 has determinant
has determinant  , or equivalently,
, or equivalently, meaning that the odd terms monotonically decrease, while the even terms monotonically increase.
meaning that the odd terms monotonically decrease, while the even terms monotonically increase.
 satisfies the recurrence relation
satisfies the recurrence relation  , and grows at least as fast as the
, and grows at least as fast as the  where
where  is the
is the  th) convergent is nearer to a subsequent (
th) convergent is nearer to a subsequent ( th) convergent is. In symbols, if the
th) convergent is. In symbols, if the  then
then




 . Denote it as
. Denote it as  . Any open subset of
. Any open subset of  is a disjoint union of sets from
is a disjoint union of sets from 

 is an integer such that
is an integer such that  , are called semiconvergents, secondary convergents, or intermediate fractions. The
, are called semiconvergents, secondary convergents, or intermediate fractions. The  -st semiconvergent equals the
-st semiconvergent equals the  . Sometimes the term is taken to mean that being a semiconvergent excludes the possibility of being a convergent (i.e.,
. Sometimes the term is taken to mean that being a semiconvergent excludes the possibility of being a convergent (i.e.,  ), rather than that a convergent is a kind of semiconvergent.
), rather than that a convergent is a kind of semiconvergent.
 (corresponding to
(corresponding to  ) and
) and  (corresponding to
(corresponding to  ). The consecutive semiconvergents
). The consecutive semiconvergents  and
and  satisfy the property
satisfy the property  .
.
 to a real number
to a real number  is smaller than that of any approximation with a smaller denominator, then
is smaller than that of any approximation with a smaller denominator, then  , then p/q is a convergent of the continued fraction of α.
, then p/q is a convergent of the continued fraction of α.
 , where 0 < θ < 1/2. We write p/q as a finite continued fraction , where due to the fact that each rational number has two distinct representations as finite continued fractions differing in length by one (namely, one where an = 1 and one where an ≠ 1), we may choose n to be even. (In the case where α < p/q, we would choose n to be odd.)
, where 0 < θ < 1/2. We write p/q as a finite continued fraction , where due to the fact that each rational number has two distinct representations as finite continued fractions differing in length by one (namely, one where an = 1 and one where an ≠ 1), we may choose n to be even. (In the case where α < p/q, we would choose n to be odd.)
 , so that
, so that  and thus,
and thus, where we have used the fact that pn−1 qn - pn qn−1 = (-1) and that n is even.
where we have used the fact that pn−1 qn - pn qn−1 = (-1) and that n is even.









 above consisting of cubes uses the Nilakantha series and an exploit from Leonhard Euler.
above consisting of cubes uses the Nilakantha series and an exploit from Leonhard Euler.

 away from φ, thus never producing an approximation nearly as impressive as, for example,
away from φ, thus never producing an approximation nearly as impressive as, for example, 









 , and so the coefficients grow arbitrarily large:
, and so the coefficients grow arbitrarily large:  . In particular, this implies that almost all numbers are well-approximable, in the sense that
. In particular, this implies that almost all numbers are well-approximable, in the sense that



 &
&  &
&  with the dots indicating where the following fractions went.
with the dots indicating where the following fractions went.