 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /brɪˈmoʊnɪdiːn/ bri-MOH-nid-een |
| Trade names | Alphagan, Mirvaso, Lumify, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a601232 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Topical |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | Primarily liver |
| Elimination half-life | 3 hours (ocular), 12 hours (topical) |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.149.042 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
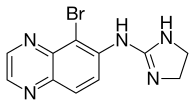
| Formula | C11H10BrN5 |
| Molar mass | 292.140 g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 252 °C (486 °F) |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
Brimonidine is an α2 agonist medication used to treat open-angle glaucoma, ocular hypertension, and rosacea. In rosacea it improves the redness. It is used as eye drops or applied to the skin. It is also available in the fixed-dose combination medication brimonidine/timolol along with timolol maleate.
Common side effects when used in the eyes include itchiness, redness, and a dry mouth. Common side effects when used on the skin include redness, burning, and headaches. More significant side effects may include allergic reactions and low blood pressure. Use in pregnancy appears to be safe. When applied to the eye it works by decreasing the amount of aqueous humor made while increasing the amount that drains from the eye. When applied to the skin it works by causing blood vessels to contract.
Brimonidine was patented in 1972 and came into medical use in 1996. It is available as a generic medication. In 2022, it was the 199th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 2 million prescriptions.
Medical uses
Brimonidine is indicated for the lowering of intraocular pressure in people with open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension. It is also used to reduce redness of the eye. The gel is indicated for the topical treatment of persistent (nontransient) facial erythema of rosacea in adults 18 years of age or older.
A 2017 Cochrane review found insufficient evidence to determine if brimonidine slows optic nerve damage.
Mechanism of action
Brimonidine is an α2 adrenergic agonist.
Peripheral α2 agonist activity results in vasoconstriction of blood vessels (as opposed to central α2 agonist activity that decreases sympathetic tone, as can be seen by the medication clonidine). This vasoconstriction may explain the acute reduction in aqueous humor flow. The increased uveoscleral outflow from prolonged use may be explained by increased prostaglandin release due to α adrenergic stimulation. This may lead to relaxed ciliary muscle and increased uveoscleral outflow.
Society and culture
Names
It is sold under the brand names Alphagan, Alphagan-P, Mirvaso, Lumify, Brymont, and others.
References
- ^ "Alphagan P- brimonidine tartrate solution/ drops". DailyMed. 27 June 2024. Retrieved 11 November 2024.
- ^ "Mirvaso- brimonidine tartrate gel". DailyMed. 24 October 2024. Retrieved 11 November 2024.
- ^ "Lumify Redness Reliever Eye Drops- brimonidine tartrate solution/ drops". DailyMed. 6 November 2023. Retrieved 11 November 2024.
- ^ "Brimonidine Tartrate eent Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Retrieved 17 March 2019.
- ^ "Brimonidine Tartrate topical Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Retrieved 17 March 2019.
- "COMBIGAN- brimonidine tartrate, timolol maleate solution/ drops". DailyMed. 26 July 2024. Retrieved 11 November 2024.
- Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 550. ISBN 9783527607495.
- "Competitive Generic Therapy Approvals". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 29 June 2023. Archived from the original on 29 June 2023. Retrieved 29 June 2023.
- British national formulary : BNF 76 (76 ed.). Pharmaceutical Press. 2018. p. 1153. ISBN 9780857113382.
- "The Top 300 of 2022". ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 30 August 2024. Retrieved 30 August 2024.
- "Brimonidine Drug Usage Statistics, United States, 2013 - 2022". ClinCalc. Retrieved 30 August 2024.
- Sena DF, Lindsley K (January 2017). "Neuroprotection for treatment of glaucoma in adults". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 1 (1): CD006539. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006539.pub4. PMC 5370094. PMID 28122126.
- Toris CB, Camras CB, Yablonski ME (July 1999). "Acute versus chronic effects of brimonidine on aqueous humor dynamics in ocular hypertensive patients". American Journal of Ophthalmology. 128 (1): 8–14. doi:10.1016/s0002-9394(99)00076-8. PMID 10482088.
Further reading
- Oh DJ, Chen JL, Vajaranant TS, Dikopf MS (January 2019). "Brimonidine tartrate for the treatment of glaucoma". Expert Opin Pharmacother. 20 (1): 115–122. doi:10.1080/14656566.2018.1544241. PMID 30407890. S2CID 53240954.
| Drugs used for glaucoma preparations and miosis (S01E) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sympathomimetics | |||||||
| Parasympathomimetics |
| ||||||
| Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors/ (sulfonamides) | |||||||
| Beta blocking agents | |||||||
| Prostaglandin analogues (F2α) | |||||||
| Other agents | |||||||