| |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.040.708 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C18H28N4O |
| Molar mass | 316.449 g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
Butalamine is a vasodilator.
Synthesis
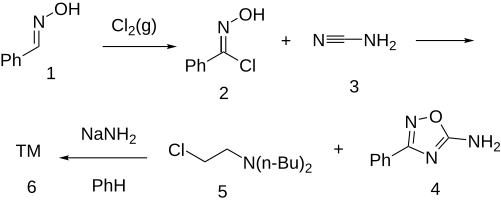
The reaction of benzamidoxime (1) with chlorine and subsequent reaction with cyanamide (3) gives 5-amino-3-phenyl-1,2,4-oxadiazole (4). Base catalyzed alkylation with dibutylaminoethyl chloride (5) completes the synthesis of butalamine (6).
References
- Sterne J (April 1976). "". Fortschritte Der Medizin (in German). 94 (11): 657–9. PMID 823083.
- Aron-samuel Jan Marcel Didier, FR3334M (1965 to Jan Marcel).
- Japan. Pat., 76 108 068, (1976); CA, 87, 5981b
- Aron-Samuel Jan Marcel Didier, Sterne Jean Jacques, U.S. patent 3,338,899 (1967 to).
| Peripheral vasodilators (C04) | |
|---|---|
| Phenylethanolamine derivatives | |
| Alpha blockers |
|
| Nicotinic acid and derivatives | |
| Purine derivatives | |
| Ergot alkaloids | |
| Other peripheral vasodilators | |
This drug article relating to the cardiovascular system is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |