| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Butene" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (March 2024) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
Butene, also known as butylene, is an alkene with the formula C4H8. The word butene may refer to any of the individual compounds. They are colourless gases that are present in crude oil as a minor constituent in quantities that are too small for viable extraction. Butene is therefore obtained by catalytic cracking of long-chain hydrocarbons left during refining of crude oil. Cracking produces a mixture of products, and the butene is extracted from this by fractional distillation.
Butene can be used as the monomer for polybutene, but this polymer is more expensive than alternatives with shorter carbon chains such as polypropylene. Polybutene is therefore used in more specialized applications. Butenes are more commonly used to make copolymer (mixed with another monomer such as ethylene).
Butenes are major constituents of raffinates, the C4 fractions in oil processing. The raffinates containing butadiene are considered carcinogenic and mutagenic. They can be used as feedstocks for further processing (e. g., on alkylation units), or used as industrial fuel. Their mixing into LPG for nonindustrial uses sometimes occurs but is generally prohibited.
Isomers
Among the molecules which have the chemical formula C4H8 four isomers are alkenes. All four of these hydrocarbons have four carbon atoms and one double bond in their molecules, but have different chemical structures. The IUPAC and common names, respectively, of these chemical compounds are:
| Common name(s) | IUPAC name | Structure | Skeletal formula | 3D model |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-butene, α-butylene | But-1-ene | 
|

| |
| cis-2-butene, cis-β-butylene | (2Z)-but-2-ene | 
|

|

|
| trans-2-butene, trans-β-butylene | (2E)-but-2-ene | 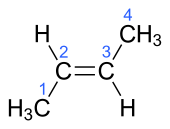
|

|
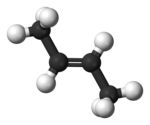
|
| isobutene, isobutylene | 2-methylprop-1-ene | 
|
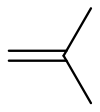
|

|
In the chemical structures above, the small blue numbers in the structure images are the numbering of the atoms in the main backbone chain of the molecules. Other organic compounds have the formula C4H8, namely cyclobutane and methylcyclopropane, but are not alkenes and do not fall under the name butene. There are also cyclic alkenes with four carbon atoms overall such as cyclobutene and two isomers of methylcyclopropene, but they do not have the formula C4H8 and are not discussed here.
See also
References
- Geilen, Frank M.A.; Stochniol, Guido; Peitz, Stephan; Schulte-Koerne, Ekkehard (2014). "Butenes". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a04_483.pub3. ISBN 978-3-527-30673-2.
- Safety Data Sheet pcs.com.sg April 2017
- "Karcinogenní plyn na českém trhu není, sdělila asociace. Inspekce zmírnila své zjištění | Náš REGION".
External links