 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Butoxamine |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C15H25NO3 |
| Molar mass | 267.369 g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
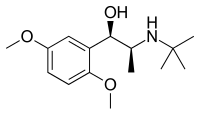
Butaxamine (INN; also known as butoxamine) is a β2-selective beta blocker. Its primary use is in experimental situations in which blockade of β2 receptors is necessary to determine the activity of the drug (i.e. if the β2 receptor is completely blocked, but the given effect is still present, the given effect is not a characteristic of the β2 receptor). It has no clinical use. An alternative name is α-(1-ethyl)-2,5-dimethoxybenzyl alcohol.
See also
References
- "Definition: butoxamine from Online Medical Dictionary".
- Hillman KL, Doze VA, Porter JE (August 2005). "Functional characterization of the beta-adrenergic receptor subtypes expressed by CA1 pyramidal cells in the rat hippocampus". J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 314 (2): 561–7. doi:10.1124/jpet.105.084947. PMID 15908513. S2CID 12446381.
| Beta blockers (C07) | |
|---|---|
| β, non-selective | |
| β1-selective | |
| β2-selective | |
| α1- + β-selective | |
| |
This pharmacology-related article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |