 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Cloxapen, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| Routes of administration | By mouth, IM |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 37 to 90% |
| Protein binding | 95% |
| Elimination half-life | 30 minutes to 1 hour |
| Excretion | kidney and biliary |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.468 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
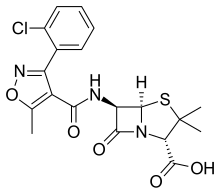
| Formula | C19H18ClN3O5S |
| Molar mass | 435.88 g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
Cloxacillin is an antibiotic useful for the treatment of several bacterial infections. This includes impetigo, cellulitis, pneumonia, septic arthritis, and otitis externa. It is not effective for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). It can be used by mouth and by injection.
Side effects include nausea, diarrhea, and allergic reactions including anaphylaxis. Clostridioides difficile diarrhea may also occur. It is not recommended in people who have previously had a penicillin allergy. Use during pregnancy appears to be relatively safe. Cloxacillin is in the penicillin family of medications.
Cloxacillin was patented in 1960 and approved for medical use in 1965. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It is not commercially available in the United States.
Mechanism of action
It is semisynthetic and in the same class as penicillin. Cloxacillin is used against staphylococci that produce beta-lactamase, due to its large R chain, which does not allow the beta-lactamases to bind. This drug has a weaker antibacterial activity than benzylpenicillin, and is devoid of serious toxicity except for allergic reactions.
Society and culture
Cloxacillin was discovered and developed by Beecham (now GlaxoSmithKline).
It is sold under a number of trade names, including Cloxapen, Cloxacap, Tegopen and Orbenin.
See also
References
- ^ World Health Organization (2009). Stuart MC, Kouimtzi M, Hill SR (eds.). WHO Model Formulary 2008. World Health Organization. pp. 98, 100, 110–111, 586, 602, 614, 623. hdl:10665/44053. ISBN 9789241547659.
- ^ "Cloxacillin (Professional Patient Advice)". www.drugs.com. Archived from the original on 20 December 2016. Retrieved 10 December 2016.
- Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 490. ISBN 9783527607495. Archived from the original on 2016-12-20.
- World Health Organization (2019). World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 21st list 2019. Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/325771. WHO/MVP/EMP/IAU/2019.06. License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
- Greenwood D (2008). Antimicrobial drugs: chronicle of a twentieth century medical triumph. Oxford University Press US. pp. 124–. ISBN 978-0-19-953484-5. Archived from the original on 6 June 2013. Retrieved 18 November 2010.
- Gollakner R (2023-05-09). "Cloxacillin". VCA Animal Hospitals. Retrieved 2023-05-09.
External links
- "Cloxacillin". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
This systemic antibiotic-related article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |