 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name Cobalt(II) iodide | |
| Other names cobaltous iodide, cobalt diiodide | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number |
|
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.035.697 |
| EC Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | CoI2 |
| Molar mass | 312.7421 g/mol (anhydrous) 420.83 g/mol (hexahydrate) |
| Appearance | α-form: black hexagonal crystal β-form: yellow powder |
| Density | α-form: 5.584 g/cm β-form: 5.45 g/cm hexahydrate: 2.79 g/cm |
| Melting point | α-form: 515-520 °C under vacuum β-form: converts to α-form at 400 °C |
| Boiling point | 570 °C (1,058 °F; 843 K) |
| Solubility in water | 67.0 g/100 mL |
| Magnetic susceptibility (χ) | +10,760·10 cm/mol |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
| Pictograms |  
|
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statements | H302, H312, H315, H319, H332, H335 |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) |
 |
| Related compounds | |
| Other anions | Cobalt(II) fluoride Cobalt(II) chloride Cobalt(II) bromide |
| Other cations | Nickel(II) iodide Copper(I) iodide |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Cobalt(II) iodide or cobaltous iodide are the inorganic compounds with the formula CoI2 and the hexahydrate CoI2(H2O)6. These salts are the principal iodides of cobalt.
Synthesis
Cobalt(II) iodide is prepared by treating cobalt powder with gaseous hydrogen iodide. The hydrated form CoI2.6H2O can be prepared by the reaction of cobalt(II) oxide (or related cobalt compounds) with hydroiodic acid.
Cobalt(II) iodide crystallizes in two polymorphs, the α- and β-forms. The α-polymorph consists of black hexagonal crystals, which turn dark green when exposed to air. Under a vacuum at 500 °C, samples of α-CoI2 sublime, yielding the β-polymorph as a yellow crystals. β-CoI2 also readily absorbs moisture from the air, converting into green hydrate. At 400 °C, β-CoI2 reverts to the α-form.
Structures
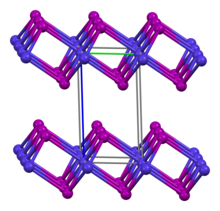
The anhydrous salts adopt the cadmium halide structures.
The hexaaquo salt consists of separated and iodide ions as verified crystallographically.
Reactions and applications
Anhydrous cobalt(II) iodide is sometimes used to test for the presence of water in various solvents.
Cobalt(II) iodide is used as a catalyst, e.g. in carbonylations. It catalyzes the reaction of diketene with Grignard reagents, useful for the synthesis of terpenoids
References
- Perry, Dale L.; Phillips, Sidney L. (1995), Handbook of Inorganic Compounds, San Diego: CRC Press, pp. 127–8, ISBN 0-8493-8671-3, retrieved 2008-06-03
- ^ O. Glemser "Cobalt, Nickel" in Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry, 2nd Ed. Edited by G. Brauer, Academic Press, 1963, NY. Vol. 1. p. 1518.
- “Structure Cristalline et Expansion Thermique de L’Iodure de Nickel Hexahydrate“ (Crystal structure and thermal expansion of nickel(II) iodide hexahydrate) Louër, Michele; Grandjean, Daniel; Weigel, Dominique Journal of Solid State Chemistry (1973), 7(2), 222-8. doi:10.1016/0022-4596(73)90157-6
- "The crystal structure of the crystalline hydrates of transition metal salts. The structure of CoI2·6H2O" Shchukarev, S. A.; Stroganov, E. V.; Andreev, S. N.; Purvinskii, O. F. Zhurnal Strukturnoi Khimii 1963, vol. 4, pp. 63-6.<!no doi in CAS-->
- Armarego, Wilfred L. F.; Chai, Christina L. L. (2003), Purification of Laboratory Chemicals, Butterworth-Heinemann, p. 26, ISBN 0-7506-7571-3, retrieved 2008-06-03
- Agreda, V. H.; Zoeller, Joseph R. (1992), Acetic Acid and Its Derivatives, CRC Press, p. 74, ISBN 0-8247-8792-7, retrieved 2008-06-03
| Cobalt compounds | |
|---|---|
| Cobalt(I) | |
| Cobalt(II) | |
| Cobalt(0,III) | |
| Cobalt(II,III) | |
| Cobalt(III) | |
| Cobalt(III,IV) | |
| Cobalt(IV) | |
| Cobalt(V) | |
| Salts and covalent derivatives of the iodide ion | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||