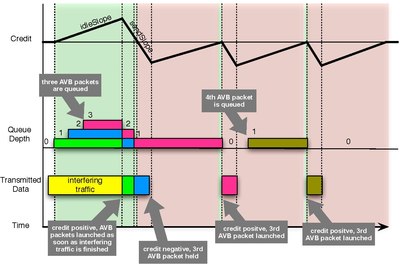
Credit-based fair queuing is a computationally efficient alternative to fair queueing. Credit is accumulated to queues as they wait for service. Credit is spent by queues while they are being serviced. Queues with positive credit are eligible for service. The rate of credit accumulation and release can be adjusted on a queue-by-queue basis to produce a weighted queuing behavior.
Credit-based queuing is used in Resilient Packet Ring networks and in the IEEE 802.1Qav component of Audio Video Bridging and its successor, Time Sensitive Networking. In IEEE 802.1Qav, it is called Credit Based Shaper (CBS).
See also
References
- Bensaou, Brahim; Chan, K. T.; Tsang, Danny H. K. (25–28 May 1997). "Credit-based fair queueing (CBFQ): A simple and feasible scheduling algorithm for packet networks". IEEE ATM '97 Workshop Proceedings (Cat. No.97TH8316). pp. 589–94. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.52.9236. doi:10.1109/ATM.1997.624744. hdl:1783.1/346. ISBN 978-0-7803-4196-8. S2CID 15244826.
- Bensaou, Brahim; Tsang, Danny H. K.; Chan, K.T. "Credit-based fair queueing (CBFQ): a simple service-scheduling algorithm for packet-switched networks", IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking 9(5): 591-604 (2001), doi:10.1109/90.958328
This computer networking article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |