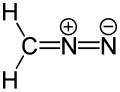
In organic chemistry, a dipolar compound or simply dipole is an electrically neutral molecule carrying a positive and a negative charge in at least one canonical description. In most dipolar compounds the charges are delocalized. Unlike salts, dipolar compounds have charges on separate atoms, not on positive and negative ions that make up the compound. Dipolar compounds exhibit a dipole moment.
Dipolar compounds can be represented by a resonance structure. Contributing structures containing charged atoms are denoted as zwitterions. Some dipolar compounds can have an uncharged canonical form.
Types of dipolar compounds
- 1,2-dipolar compounds have the opposite charges on adjacent atoms.
- 1,3-dipolar compounds have the charges separated over three atoms. They are reactants in 1,3-dipolar cycloadditions.
- Also 1,4-dipolars, 1,5-dipolars, and so on exist.
Examples
See also
References
- ^ IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "dipolar compounds". doi:10.1351/goldbook.D01753
- Braida et al.: A clear correlation between the diradical character of 1,3-dipoles and their reactivity toward ethylene or acetylene.; J. Am. Chem. Soc.; 2010 Jun 9;132(22):7631-7
- Hartmann and Heuschmann: Isolation of a Zwitterion in a Diels–Alder Reaction with Inverse Electron Demand; Angewandte Chemie; september 1989; Volume 28, Issue 9, pages 1267–1268
- ^ MacHiguchi, Takahisa; Okamoto, Junko; Takachi, Junpei; Hasegawa, Toshio; Yamabe, Shinichi; Minato, Tsutomu (2003). "Exclusive Formation of α-Methyleneoxetanes in Ketene−Alkene Cycloadditions. Evidence for Intervention of Both an α-Methyleneoxetane and the Subsequent 1,4-Zwitterion". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 125 (47): 14446–8. doi:10.1021/ja030191g. PMID 14624592.
- Preferred IUPAC Names: "CHAPTER 7: RADICALS, IONS, AND RELATED SPECIES", September 2004, pp. 56-70
- Rolf Huisgen (IUPAC): Cycloaddition mechanism and the solvent dependence of rate; Pure Appl. Chem.; 1980, Vol.52, pp.2283—2302.
 Example of a dipolar compound, represented by a
Example of a dipolar compound, represented by a