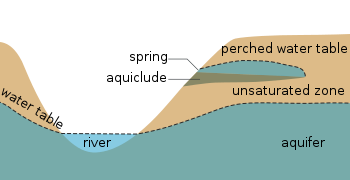
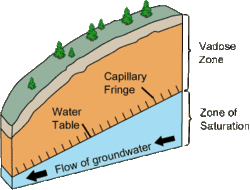
In a cave system, the epiphreatic zone or floodwater zone is the zone between the vadose (unsaturated) zone above and phreatic (saturated) zone below. It is regularly flooded and has a significant porosity. It has a great potential for cave formation.
See also
- Capillary fringe – Subsurface layer in which groundwater seeps up from a water table by capillary action.
- Infiltration (hydrology) – Process by which water on the ground surface enters the soil.
- Phreatic – Term used in several scientific disciplines
- Phreatic zone – Zone in an aquifer below the water table.
- Vadose zone – Unsaturated aquifer above the water table.
References
- Prelovšek, Mitja (2009). Present-Day Speleogenetic Processes, Factors and Features in the Epiphreatic Zone: Dissertation (PDF). University of Nova Gorica. p. 5.
- "Aquifer Anatomy | EARTH 111: Water: Science and Society". www.e-education.psu.edu. Retrieved 2024-06-08.
- "Infiltration | hydrologic cycle | Britannica". www.britannica.com. Retrieved 2024-06-08.
- "saturated zone". Oxford Reference. Retrieved 2024-06-08.
- "USGS Unsaturated Zone Flow Project". wwwrcamnl.wr.usgs.gov. Retrieved 2024-06-08.
This geology article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |