 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name (acetoxy)(triphenyl)stannane | |
| Other names Phentin acetate; Triphenyltin acetate; Triphenylstannyl acetate; Acetic acid tri(phenyl)stannyl ester, Brestan | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.011.804 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII |
|
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C20H18O2Sn |
| Molar mass | 409.07 g/mol |
| Melting point | 122-124 °C |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
| Main hazards | Very toxic Dangerous for the environment |
| GHS labelling: | |
| Pictograms |    
|
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statements | H301, H311, H315, H318, H330, H335, H351, H361d, H372, H410 |
| Precautionary statements | P201, P202, P260, P264, P270, P271, P273, P280, P284, P301+P310, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P308+P313, P310, P320, P330, P332+P313, P361, P363, P391, P403+P233, P405, P501 |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
| LD50 (median dose) | 21 mg/kg (guinea pig, oral) 30 mg/kg (rabbit, oral) 81 mg/kg (mouse, oral) 125 mg/kg (rat, oral) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
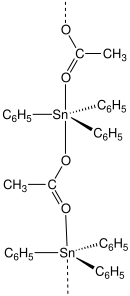
Fentin acetate is an organotin compound with the formula (C6H5)3SnO2CCH3. It is a colourless solid that was previously used as a fungicide.
Structure
Most carboxylates of triphenyltin adopt polymeric structures with five-coordinate Sn centers.
References
- Fentin acetate at Sigma-Aldrich
- "Tin (organic compounds, as Sn)". Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- G. G. Graf "Tin, Tin Alloys, and Tin Compounds" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2005, Wiley-VCH.doi:10.1002/14356007.a27_049
- Fentin Acetate. PubChem. National Library of Medicine. NIH. Accessed 13 July 2023.
- Weng Ng, Seik; Lan Chin, Kwai; Wei, Chen; Kumar Das, V.G.; Butcher, Ray J. (1989). "Variable-temperature tin-119m Mössbauer spectroscopic and x-ray crystallographic study of triphenyltin(IV) chloroacetate, [(C6H5)3SnOC(O)CH2Cl], and a redetermination of d[ln f(T)]/DT for triphenyltin(IV) acetate". Journal of Organometallic Chemistry. 376 (2–3): 277–281. doi:10.1016/0022-328X(89)85138-1.
External links
- Fentin acetate in the Pesticide Properties DataBase (PPDB)