This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|

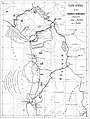
━━━ Routes with passenger traffic
━━━ Routes in usable state
·········· Unusable or dismantled routes
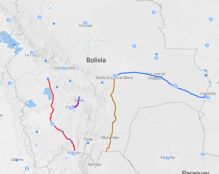
The Bolivian rail network has had a peculiar development throughout its history.
History
Main article: History of rail transport in Bolivia
Gauges
| This section does not cite any sources. Please help improve this section by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (May 2023) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
All railways in Bolivia are now 1,000 mm (3 ft 3+3⁄8 in) Metre gauge. The Antofagasta to Uyuni line was originally 2 ft 6 in (762 mm) gauge.
Maps
FCAB Line from Antofagasta

Rail link to Peru
| This section does not cite any sources. Please help improve this section by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (May 2023) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
Bolivia built a line to the shores of Lake Titicaca.
Lines in the south, east
| This section does not cite any sources. Please help improve this section by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (May 2023) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |

A line from São Paulo, Brazil, enters Bolivia at Puerto Suarez and connects to this line at Santa Cruz. In the 1950s this last major rail system was completed. A line was intended to run from Santa Cruz to Trinidad (about 500 km (310 mi) in the north center of the country, but never reached there, it ended north of Yapacani (150 km (93 mi)), from where since 2014 an industrial spur is under construction to the ammonia/urea factory near Bulo Bulo (60 km (37 mi)).
Spur lines were run to mining districts and the regional capital of Cochabamba.
Mamore and Madeira Railway
Main article: Madeira-Mamoré RailroadAnother railway was a local line in the Amazonian jungle. The Madeira-Mamoré Railroad runs in a 365 kilometres (227 mi) loop around the unnavigable section to Guajará-Mirim on the Mamoré River.
Steel lines to the Silver at Potosi
| This section does not cite any sources. Please help improve this section by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (May 2023) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
Rio Mulatos-Potosí line is a train line in Bolivia, containing Cóndor station, the world's ninth highest railway station (4,787 m (15,705 ft)).
Future plans
| This section needs to be updated. Please help update this article to reflect recent events or newly available information. (December 2022) |
The government of Evo Morales has proposed a rail line uniting La Paz, Cochabamba, and Santa Cruz, connecting onwards to Brazil and the Pacific coast.
The department of Cochabamba and the national government are contracting design studies in 2011 for regional trains to run on two routes: Cochabamba-Caluyo-Tarata-Cliza-Punata-Arani and Sipe Sipe-Vinto-Cochabamba-Sacaba-Chiñata. A 180-day study on Sipe Sipe-Chiñata line is being carried out between August 2011 and February 2012. This project, known as Mi Tren, is under construction and due for completion in 2020.
International rail links to adjacent countries
- Argentina – yes – 1,000 mm (3 ft 3+3⁄8 in) both countries
- Brazil – yes – 1,000 mm (3 ft 3+3⁄8 in) gauge both countries
- Chile – yes – 1,000 mm (3 ft 3+3⁄8 in) gauge both countries
- Peru – Shipping by car float from 1,000 mm (3 ft 3+3⁄8 in) railhead in Guaqui to 1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in) railhead in Puno across Lake Titicaca
Incidents
In 2007 thieves had stolen 100 meters of Bolivian track overnight, and the morning freight had insufficient distance to stop. Photo of the site shows locomotives 1021 and 951 remained upright, but extensive damage ensued.
See also
References
Notes
- Brazil's Devil's Railway gets new lease of life BBC
- "Buscan apoyo chino para tren eléctrico". La Razón. 2011-01-30. Retrieved 2011-03-11.
- Nava B., Jhenny (2011-03-11). "Gobernador anuncia estudio para reactivar el ferrocarril". Opinión. Cochabamba. Retrieved 2011-03-11.
- Alcócer Caero, Gisela (2011-08-24). "Un consorcio elabora el plan para reactivar tren del valle". Los Tiempos. Cochabamba. Retrieved 2011-08-24.
Bibliography
- Walker, Christopher; Binns, Donald (2005). Railways of Bolivia: Locomotives, Railcars and Rolling Stock. North Yorkshire: Trackside Publications. ISBN 1900095289.
External links
- Historia de los ferrocarriles en Bolivia
- Ferrocarriles Bolivia. Del anhelo a la frustración. Desarrollo, producción, economía y dependencia. Archived 2017-09-10 at the Wayback Machine
- Empresa Ferroviaria Andina (FCA)
- Empresa Ferroviaria Oriental S.A.
- Ferrocarril de Antofagasta a Bolivia Archived 2015-09-24 at the Wayback Machine
- Ferrocarril de Guaqui a La Paz
- Viaje en tren entre Sucre y Potosí Archived 2016-11-08 at the Wayback Machine
[REDACTED] Media related to Rail transport in Bolivia at Wikimedia Commons
| Rail transport in South America | |
|---|---|
| Sovereign states | |
| Dependencies and other territories | |
<Wikibase-sitelinks>
Category: