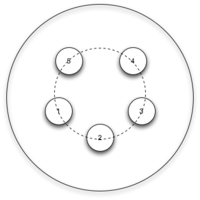
 Drawing of 5-hole (left) and 4-hole (right) pitch circles
Drawing of 5-hole (left) and 4-hole (right) pitch circles
A bolt circle diameter or pitch circle diameter (PCD), sometimes simply called bolt circle or pitch circle, is a common term for when a number of screw holes for bolts are evenly distributed with their centers along an imaginary circle with a given diameter.
An example of use is mounting of car rims, where the bolt circle is one of several factors that determine whether a set of rims will fit a car. For example, a bolt circle of 5×130 or 5-130 indicates that a rim is to be attached to the car via 5 screws evenly spaced along a circle with a diameter of 130 millimeters. Other common uses for bolt circles are for indicating mounting for sim racing and real-world car steering wheels, or in the industry for mounting of servomotors or for specifying the bolt pattern of a flange. Attachment of chain rings for bicycle cranksets are also specified by a bolt circle.
Examples
Racing wheels
On steering wheels for cars utilizing bolt circles, this usually measures 6×70 mm. Some racing wheels attach to the car via a quick release hub, and this hub then usually has a corresponding bolt circle of 6×70 mm. Example of other less used patterns include: 3×1.75 in (44.45 mm), 5×2.75 in (69.85 mm), 6×74 mm and 6×2.75 in (69.85 mm).
Servomotors

Servomotors in the industry are often mounted via a flange-like coupling to give the shortest possible leverage for high-torque uses. Industrial servomotors often use standardised mounting patterns, of which one example is a bolt circle of 4×130 mm diameter (approximately corresponds to a square pattern of 91.9 mm × 91.9 mm).
Car rims

The mounting pattern of most car rims are described using bolt patterns, and this pattern is one of many factors which determine whether a rim will fit a given car. Here, the bolt circle indicates the number of wheel nuts and associated hub bolts (or alternatively just wheel bolts).
An example of a bolt circle is 5×100 which indicates 5 nuts placed on a circle with a diameter of 100 mm. Some of the most common bolt circle diameters on modern cars are 100 mm, 112 mm and 114.3 mm. The bolt circle of a car is one of several parameters that must be checked before buying new rims to make sure they will fit the car (along with wheel offset, hub diameter, and finally the diameter and width of the rim and tire). Over the years, over 30 different bolt circles patterns have been used by car manufacturers, most of which are not compatible with each other.
See also
- Pitch diameter, a dimension of a screw thread
References
- "Wheel Tech: Bolt Pattern".
- Wolf Tooth Tech Help - Measure Bike Chainring BCD Bolt Circle Diameter – Wolf Tooth Components
- ^ Steering Wheel Bolt Patterns Explained
- Quick release hub steering wheel | Raptor Steering Wheels
- "Bolt Circle Diameter (B.C.D.)". Retrieved 3 December 2010.
- "P.C.D." Retrieved 4 December 2010.
- Boltsirkel.no
This article about a mechanical engineering topic is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |