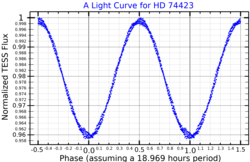
 A light curve for HD 74423 plotted from TESS data | |
| Observation data Epoch J2000.0 Equinox J2000.0 (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Volans |
| Right ascension | 08 40 17.985 |
| Declination | −64° 50′ 16.84″ |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 8.58–8.66 |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | A7VkA0mA0 λ Boo |
| Apparent magnitude (B) | 8.81±0.02 |
| Apparent magnitude (J) | 8.065±0.020 |
| Apparent magnitude (H) | 8.021±0.067 |
| Apparent magnitude (K) | 7.944±0.040 |
| Variable type | α CVn or Ellipsoidal and δ Sct |
| Astrometry | |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −9.719 mas/yr Dec.: 11.732 mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 2.1018 ± 0.0150 mas |
| Distance | 1,550 ± 10 ly (476 ± 3 pc) |
| Details | |
| primary | |
| Mass | 2.1 M☉ |
| Radius | 3.3 R☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 3.6 cgs |
| Temperature | 7,900 K |
| Metallicity | −1.0 dex |
| secondary | |
| Mass | 2.0 M☉ |
| Radius | 3.2 R☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 3.6 cgs |
| Temperature | 7,600 K |
| Metallicity | −1.0 dex |
| Age | 800 Myr |
| Other designations | |
| HD 74423, CD−64°342, SAO 250298, TYC 8934-1662-1, TIC 355151781 | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
HD 74423 is a heartbeat binary star and one component pulsates on only one hemisphere. This is caused by tidal interaction with its partner. The star is located in the Volans constellation.
HD 74423 is slightly variable in brightness. It fluctuates between magnitudes 8.58 and 8.66 every 19 hours. The exact variability type is unclear. It was initially found in a search for α Canum Venaticorum variables and assumed to be one, but has since been considered to be a δ Scuti variable. The spectrum shows unusually strong absorption lines of some iron peak elements, a characteristic of λ Boötis stars. Both components are thought to show the chemical peculiarity.
References
- "MAST: Barbara A. Mikulski Archive for Space Telescopes". Space Telescope Science Institute. Retrieved 8 December 2021.
- Staff (2 August 2008). "Finding the constellation which contains given sky coordinates". DJM.cc. Retrieved 31 July 2020.
- ^ Brown, A. G. A.; et al. (Gaia collaboration) (2021). "Gaia Early Data Release 3: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 649: A1. arXiv:2012.01533. Bibcode:2021A&A...649A...1G. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202039657. S2CID 227254300. (Erratum: doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202039657e). Gaia EDR3 record for this source at VizieR.
- ^ Bernhard, K.; Hümmerich, S.; Otero, S.; Paunzen, E. (2015). "A search for photometric variability in magnetic chemically peculiar stars using ASAS-3 data". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 581: A138. arXiv:1507.01112. Bibcode:2015A&A...581A.138B. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201526424. S2CID 54062866.
- ^ Gray, R. O.; Riggs, Q. S.; Koen, C.; Murphy, S. J.; Newsome, I. M.; Corbally, C. J.; Cheng, K. -P.; Neff, J. E. (2017). "The Discovery of λ Bootis Stars: The Southern Survey I". The Astronomical Journal. 154 (1): 31. Bibcode:2017AJ....154...31G. doi:10.3847/1538-3881/aa6d5e.
- ^ "HD 74423 -- Star". SIMBAD. Centre de Données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Retrieved 31 July 2020.
- ^ Handler, G.; Kurtz, D. W.; Rappaport, S. A.; Saio, H.; Fuller, J.; Jones, D.; Guo, Z.; Chowdhury, S.; Sowicka, P.; Aliçavuş, F. Kahraman; Streamer, M. (9 March 2020). "Tidally trapped pulsations in a close binary star system discovered by TESS". Nature Astronomy. 4 (7): 684–689. arXiv:2003.04071. Bibcode:2020NatAs...4..684H. doi:10.1038/s41550-020-1035-1. ISSN 2397-3366. S2CID 212634328.
- ^ Fuller, J.; Kurtz, D. W.; Handler, G.; Rappaport, S. (2020). "Tidally trapped pulsations in binary stars". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 498 (4): 5730. arXiv:2008.02836. Bibcode:2020MNRAS.498.5730F. doi:10.1093/mnras/staa2376.
External links
| Constellation of Volans | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stars |
| ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Galaxies |
| ||||||||||
| |||||||||||