| A major contributor to this article appears to have a close connection with its subject. It may require cleanup to comply with Misplaced Pages's content policies, particularly neutral point of view. Please discuss further on the talk page. (June 2016) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |

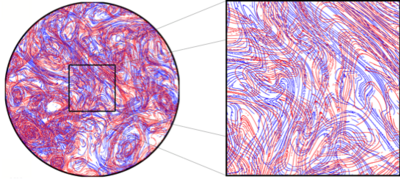
Lagrangian coherent structures (LCSs) are distinguished surfaces of trajectories in a dynamical system that exert a major influence on nearby trajectories over a time interval of interest. The type of this influence may vary, but it invariably creates a coherent trajectory pattern for which the underlying LCS serves as a theoretical centerpiece. In observations of tracer patterns in nature, one readily identifies coherent features, but it is often the underlying structure creating these features that is of interest.
As illustrated on the right, individual tracer trajectories forming coherent patterns are generally sensitive with respect to changes in their initial conditions and the system parameters. In contrast, the LCSs creating these trajectory patterns turn out to be robust and provide a simplified skeleton of the overall dynamics of the system. The robustness of this skeleton makes LCSs ideal tools for model validation, model comparison and benchmarking. LCSs can also be used for now-casting and even short-term forecasting of pattern evolution in complex dynamical systems.
Physical phenomena governed by LCSs include floating debris, oil spills, surface drifters and chlorophyll patterns in the ocean; clouds of volcanic ash and spores in the atmosphere; and coherent crowd patterns formed by humans and animals.
While LCSs generally exist in any dynamical system, their role in creating coherent patterns is perhaps most readily observable in fluid flows.
General definitions
Material surfaces

On a phase space and over a time interval , consider a non-autonomous dynamical system defined through the flow map , mapping initial conditions into their position for any time . If the flow map is a diffeomorphism for any choice of , then for any smooth set of initial conditions in , the set
is an invariant manifold in the extended phase space . Borrowing terminology from fluid dynamics, we refer to the evolving time slice of the manifold as a material surface (see Fig. 1). Since any choice of the initial condition set yields an invariant manifold , invariant manifolds and their associated material surfaces are abundant and generally undistinguished in the extended phase space. Only few of them will act as cores of coherent trajectory patterns.
LCSs as exceptional material surfaces

In order to create a coherent pattern, a material surface should exert a sustained and consistent action on nearby trajectories throughout the time interval . Examples of such action are attraction, repulsion, or shear. In principle, any well-defined mathematical property qualifies that creates coherent patterns out of randomly selected nearby initial conditions.
Most such properties can be expressed by strict inequalities. For instance, we call a material surface attracting over the interval if all small enough initial perturbations to are carried by the flow into even smaller final perturbations to . In classical dynamical systems theory, invariant manifolds satisfying such an attraction property over infinite times are called attractors. They are not only special, but even locally unique in the phase space: no continuous family of attractors may exist.
In contrast, in dynamical systems defined over a finite time interval , strict inequalities do not define exceptional (i.e., locally unique) material surfaces. This follows from the continuity of the flow map over . For instance, if a material surface attracts all nearby trajectories over the time interval , then so will any sufficiently close other material surface.
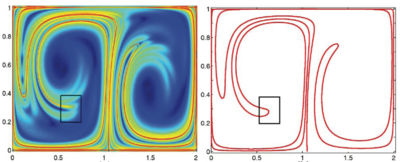
Thus, attracting, repelling and shearing material surfaces are necessarily stacked on each other, i.e., occur in continuous families. This leads to the idea of seeking LCSs in finite-time dynamical systems as exceptional material surfaces that exhibit a coherence-inducing property more strongly than any of the neighboring material surfaces. Such LCSs, defined as extrema (or more generally, stationary surfaces) for a finite-time coherence property, will indeed serve as observed centerpieces of trajectory patterns. Examples of attracting, repelling and shearing LCSs are in a direct numerical simulation of 2D turbulence are shown in Fig.2a.
LCSs vs. classical invariant manifolds
Classical invariant manifolds are invariant sets in the phase space of an autonomous dynamical system. In contrast, LCSs are only required to be invariant in the extended phase space. This means that even if the underlying dynamical system is autonomous, the LCSs of the system over the interval will generally be time-dependent, acting as the evolving skeletons of observed coherent trajectory patterns. Figure 2b shows the difference between an attracting LCS and a classic unstable manifold of a saddle point, for evolving times, in an autonomous dynamical system.

Objectivity of LCSs
Assume that the phase space of the underlying dynamical system is the material configuration space of a continuum, such as a fluid or a deformable body. For instance, for a dynamical system generated by an unsteady velocity field
the open set of possible particle positions is a material configuration space. In this space, LCSs are material surfaces, formed by trajectories. Whether or not a material trajectory is contained in an LCS is a property that is independent of the choice of coordinates, and hence cannot depend of the observer. As a consequence, LCSs are subject to the basic objectivity (material frame-indifference) requirement of continuum mechanics. The objectivity of LCSs requires them to be invariant with respect to all possible observer changes, i.e., linear coordinate changes of the form where is the vector of the transformed coordinates; is an arbitrary proper orthogonal matrix representing time-dependent rotations; and is an arbitrary -dimensional vector representing time-dependent translations. As a consequence, any self-consistent LCS definition or criterion should be expressible in terms of quantities that are frame-invariant. For instance, the strain rate and the spin tensor defined as transform under Euclidean changes of frame into the quantities
A Euclidean frame change is, therefore, equivalent to a similarity transform for , and hence an LCS approach depending only on the eigenvalues and eigenvectors of is automatically frame-invariant. In contrast, an LCS approach depending on the eigenvalues of is generally not frame-invariant.
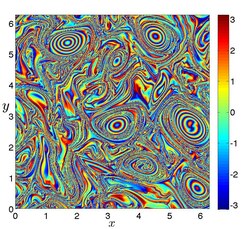
A number of frame-dependent quantities, such as , , , as well as the averages or eigenvalues of these quantities, are routinely used in heuristic LCS detection. While such quantities may effectively mark features of the instantaneous velocity field , the ability of these quantities to capture material mixing, transport, and coherence is limited and a priori unknown in any given frame. As an example, consider the linear unsteady fluid particle motion
which is an exact solution of the two-dimensional Navier–Stokes equations. The (frame-dependent) Okubo-Weiss criterion classifies the whole domain in this flow as elliptic (vortical) because holds, with referring to the Euclidean matrix norm. As seen in Fig. 3, however, trajectories grow exponentially along a rotating line and shrink exponentially along another rotating line. In material terms, therefore, the flow is hyperbolic (saddle-type) in any frame.

Since Newton’s equation for particle motion and the Navier–Stokes equations for fluid motion are well known to be frame-dependent, it might first seem counterintuitive to require frame-invariance for LCSs, which are composed of solutions of these frame-dependent equations. Recall, however, that the Newton and Navier–Stokes equations represent objective physical principles for material particle trajectories. As long as correctly transformed from one frame to the other, these equations generate physically the same material trajectories in the new frame. In fact, we decide how to transform the equations of motion from an -frame to a -frame through a coordinate change precisely by upholding that trajectories are mapped into trajectories, i.e., by requiring to hold for all times. Temporal differentiation of this identity and substitution into the original equation in the -frame then yields the transformed equation in the -frame. While this process adds new terms (inertial forces) to the equations of motion, these inertial terms arise precisely to ensure the invariance of material trajectories. Fully composed of material trajectories, LCSs remain invariant in the transformed equation of motion defined in the -frame of reference. Consequently, any self-consistent LCS definition or detection method must also be frame-invariant.
Hyperbolic LCSs

Motivated by the above discussion, the simplest way to define an attracting LCS is by requiring it to be a locally strongest attracting material surface in the extended phase space (see. Fig. 4) . Similarly, a repelling LCS can be defined as a locally strongest repelling material surface. Attracting and repelling LCSs together are usually referred to as hyperbolic LCSs, as they provide a finite-time generalization of the classic concept of normally hyperbolic invariant manifolds in dynamical systems.
Diagnostic approach: Finite-time Lyapunov exponent (FTLE) ridges
Heuristically, one may seek initial positions of repelling LCSs as set of initial conditions at which infinitesimal perturbations to trajectories starting from grow locally at the highest rate relative to trajectories starting off of . The heuristic element here is that instead of constructing a highly repelling material surface, one simply seeks points of large particle separation. Such a separation may well be due to strong shear along the set of points so identified; this set is not at all guaranteed to exert any normal repulsion on nearby trajectories.
The growth of an infinitesimal perturbation along a trajectory is governed by the flow map gradient . Let be a small perturbation to the initial condition , with , and with denoting an arbitrary unit vector in . This perturbation generally grows along the trajectory into the perturbation vector . Then the maximum relative stretching of infinitesimal perturbations at the point can be computed as
where denotes the right Cauchy–Green strain tensor. One then concludes that the maximum relative stretching experienced along a trajectory starting from is just . As this relative stretching tends to grow rapidly, it is more convenient to work with its growth exponent , which is then precisely the finite-time Lyapunov exponent (FTLE)
Therefore, one expects hyperbolic LCSs to appear as codimension-one local maximizing surfaces (or ridges) of the FTLE field. This expectation turns out to be justified in the majority of cases: time positions of repelling LCSs are marked by ridges of . By applying the same argument in backward time, we obtain that time positions of attracting LCSs are marked by ridges of the backward FTLE field .
The classic way of computing Lyapunov exponents is solving a linear differential equation for the linearized flow map . A more expedient approach is to compute the FTLE field from a simple finite-difference approximation to the deformation gradient. For example, in a three-dimenisonal flow, we launch a trajectory from any element of a grid of initial conditions. Using the coordinate representation for the evolving trajectory , we approximate the gradient of the flow map as

with a small vector pointing in the coordinate direction. For two-dimensional flows, only the first minor matrix of the above matrix is relevant.

Issues with inferring hyperbolic LCSs from FTLE ridges
FTLE ridges have proven to be a simple and efficient tool for the visualize hyperbolic LCSs in a number of physical problems, yielding intriguing images of initial positions of hyperbolic LCSs in different applications (see, e.g., Figs. 5a-b). However, FTLE ridges obtained over sliding time windows do not form material surfaces. Thus, ridges of under varying cannot be used to define Lagrangian objects, such as hyperbolic LCSs. Indeed, a locally strongest repelling material surface over will generally not play the same role over and hence its evolving position at time will not be a ridge for . Nonetheless, evolving second-derivative FTLE ridges computed over sliding intervals of the form have been identified by some authors broadly with LCSs. In support of this identification, it is also often argued that the material flux over such sliding-window FTLE ridges should necessarily be small.
The "FTLE ridge=LCS" identification, however, suffers form the following conceptual and mathematical problems:
- Second-derivative FTLE ridges are necessarily straight lines and hence do not exist in physical problems.
- FTLE ridges computed over sliding time windows with a varying are generally not Lagrangian and the flux through them is generally not small.
- In particular, a broadly referenced material flux formula for FTLE ridges is incorrect, even for straight FTLE ridges
- FTLE ridges mark hyperbolic LCS positions, but also highlight surfaces of high shear. A convoluted mixture of both types of surfaces often arises in applications (see Fig. 6 for an example).
- There are several other types LCSs (elliptic and parabolic) beyond the hyperbolic LCSs highlighted by FTLE ridges
Local variational approach: Shrink and stretch surfaces
The local variational theory of hyperbolic LCSs builds on their original definition as strongest repelling or repelling material surfaces in the flow over the time interval . At an initial point , let denote a unit normal to an initial material surface (cf. Fig. 6). By the invariance of material lines, the tangent space is mapped into the tangent space of by the linearized flow map . At the same time, the image of the normal normal under generally does not remain normal to . Therefore, in addition to a normal component of length , the advected normal also develops a tangential component of length (cf. Fig. 7).

If , then the evolving material surface strictly repels nearby trajectories by the end of the time interval . Similarly, signals that strictly attracts nearby trajectories along its normal directions. A repelling (attracting) LCS over the interval can be defined as a material surface whose net repulsion is pointwise maximal (minimal) with respect to perturbations of the initial normal vector field . As earlier, we refer to repelling and attracting LCSs collectively as hyperbolic LCSs.
Solving these local extremum principles for hyperbolic LCSs in two and three dimensions yields unit normal vector fields to which hyperbolic LCSs should everywhere be tangent. The existence of such normal surfaces also requires a Frobenius-type integrability condition in the three-dimensional case. All these results can be summarized as follows:
| LCS | Normal vector field of for | ODE for for n=2 | Frobenius-type PDE for for n=3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Attracting | (stretch lines) | (stretch surfaces) | |
| Repelling | (shrink lines) | (shrink surfaces) |
Repelling LCSs are obtained as most repelling shrink lines, starting from local maxima of . Attracting LCSs are obtained as most attracting stretch lines, starting from local minima of . These starting points serve are initial positions of exceptional saddle-type trajectories in the flow. An example of the local variational computation of a repelling LCS is shown in FIg. 8. The computational algorithm is available in LCS Tool.
In 3D flows, instead of solving the Frobenius PDE (see table above) for hyperbolic LCSs, an easier approach is to construct intersections of hyperbolic LCSs with select 2D planes, and fit a surface numerically to a large number of such intersection curves. Let us denote the unit normal of a 2D plane by . The intersection curve of a 2D repelling LCS surface with the plane is normal to both and to the unit normal of the LCS. As a consequence, an intersection curve satisfies the ODE
whose trajectories we refer to as reduced shrink lines. (Strictly speaking, this equation is not an ordinary differential equation, given that its right-hand side is not a vector field, but a direction field, which is generally not globally orientable). Intersections of hyperbolic LCSs with are fastest contracting reduced shrink lines. Determining such shrink lines in a smooth family of nearby planes, then fitting a surface to the curve family so obtained yields a numerical approximation of a 2D repelling LCS.
Global variational approach: Shrink- and stretchlines as null-geodesics
A general material surface experiences shear and strain in its deformation, both of which depend continuously on initial conditions by the continuity of the map . The averaged strain and shear within a strip of -close material lines, therefore, typically show variation within such a strip. The two-dimensional geodesic theory of LCSs seeks exceptionally coherent locations where this general trend fails, resulting in an order of magnitude smaller variability in shear or strain than what is normally expected across an strip. Specifically, the geodesic theory searches for LCSs as special material lines around which material strips show no variability either in the material-line averaged shear (Shearless LCSs) or in the material-line averaged strain (Strainless or Elliptic LCSs). Such LCSs turn out to be null-geodesics of appropriate metric tensors defined by the deformation field—hence the name of this theory.
Shearless LCSs are found to be null-geodesics of a Lorentzian metric tensor defined as
Such null-geodesics can be proven to be tensorlines of the Cauchy–Green strain tensor, i.e., are tangent to the direction field formed by the strain eigenvector fields . Specifically, repelling LCSs are trajectories of starting from local maxima of the eigenvalue field. Similarly, attracting LCSs are trajectories of starting from local minims of the eigenvalue field. This agrees with the conclusion of the local variational theory of LCSs. The geodesic approach, however, also sheds more light on the robustness of hyperbolic LCSs: hyperbolic LCSs only prevail as stationary curves of the averaged shear functional under variations that leave their endpoints fixed. This is to be contrasted with parabolic LCSs (see below), which are also shearless LCSs but prevail as stationary curves to the shear functional even under arbitrary variations. As a consequence, individual trajectories are objective, and statements about the coherent structures they form should also be objective.
A sample application is shown in Fig. 9, where the sudden appearance of a hyperbolic core (strongest attracting part of a stretchline) within the oil spill caused the notable Tiger-Tail instability in the shape of the oil spill.
Elliptic LCSs
Elliptc LCSs are closed and nested material surfaces that act as building blocks of the Lagrangian equivalents of vortices, i.e., rotation-dominated regions of trajectories that generally traverse the phase space without substantial stretching or folding. They mimic the behavior of Kolmogorov–Arnold–Moser (KAM) tori that form elliptic regions in Hamiltonian systems. There coherence can be approached either through their homogeneous material rotation or through their homogeneous stretching properties.
Rotational coherence from the polar rotation angle (PRA)
As a simplest approach to rotational coherence, one may define an elliptic LCS as a tubular material surface along which small material volumes complete the same net rotation over the time intervall of interest. A challenge in that in each material volume element, all individual material fibers (tangent vectors to trajectories) perform different rotations.
To obtain a well-defined bulk rotation for each material element, one may employ the unique left and right polar decompositions of the flow gradient in the form
where the proper orthogonal tensor is called the rotation tensor and the symmetric, positive definite tensors are called the left stretch tensor and right stretch tensor, respectively.
Since the Cauchy–Green strain tensor can be written as the local material straining described by the eigenvalues and eigenvectors of are fully captured by the singular values and singular vectors of the stretch tensors. The remaining factor in the deformation gradient is represented by , interpreted as the bulk solid-body rotation component of volume elements. In planar motions, this rotation is defined relative to the normal of the plane. In three dimensions, the rotation is defined relative to the axis defined by the eigenvector of corresponding to its unit eigenvalue. In higher-dimensional flows, the rotation tensor cannot be viewed as a rotation about a single axis.

In two and three dimensions, therefore, there exists a polar rotation angle (PRA) that characterises the material rotation generated by for a volume element centered at the initial condition . This PRA is well-defined up to multiples of . For two-dimensional flows, the PRA can be computed from the invariants of using the formulas
which yield a four-quadrant version of the PRA via the formula
For three-dimensional flows, the PRA can again be computed from the invariants of from the formulas
where is the Levi-Civita symbol, is the eigenvector corresponding to the unit eigenvector of the matrix .
The time positions of elliptic LCSs are visualized as tubular level sets of the PRA distribution . In two-dimensions, therefore, (polar) elliptic LCSs are simply closed level curves of the PRA, which turn out to be objective. In three dimensions, (polar) elliptic LCSs are toroidal or cylindrical level surfaces of the PRA, which are, however, not objective and hence will generally change in rotating frames. Coherent Lagrangian vortex boundaries can be visualized as outermost members of nested families of elliptic LCSs. Two- and three-dimensional examples of elliptic LCS revealed by tubular level surfaces of the PRA are shown in Fig. 10a-b.
Rotational coherence from the Lagrangian-averaged vorticity deviation (LAVD)
The level sets of the PRA are objective in two dimensions but not in three dimensions. An additional shortcoming of the polar rotation tensor is its dynamical inconsistency: polar rotations computed over adjacent sub-intervals of a total deformation do not sum up to the rotation computed for the full-time interval of the same deformation. Therefore, while is the closest rotation tensor to in the norm over a fixed time interval , these piecewise best fits do not form a family of rigid-body rotations as and are varied. For this reason, rotations predicted by the polar rotation tensor over varying time intervals divert from the experimentally observed mean material rotation of fluid elements.

An alternative to the classic polar decomposition provides a resolution to both the non-objectivity and the dynamic inconsistency issue. Specifically, the Dynamic Polar Decomposition (DPD) of the deformation gradient is also of the form
where the proper orthogonal tensor is the dynamic rotation tensor and the non-singular tensors are the left dynamic stretch tensor and right dynamic stretch tensor, respectively. Just as the classic polar decomposition, the DPD is valid in any finite dimension. Unlike the classic polar decomposition, however, the dynamic rotation and stretch tensors are obtained from solving linear differential equations, rather than from matrix manipulations. In particular, is the deformation gradient of the purely rotational flow
and is the deformation gradient of the purely straining flow
.
The dynamic rotation tensor can further be factorized into two deformation gradients: one for a spatially uniform (rigid-body) rotation, and one that deviates from this uniform rotation:
As a spatially independent rigid-body rotation, the proper orthogonal relative rotation tensor is dynamically consistent, serving as the deformation gradient of the relative rotation flow
In contrast, the proper orthogonal mean rotation tensor is the deformation gradient of the mean-rotation flow
The dynamic consistency of implies that the total angle swept by around its own axis of rotation is dynamically consistent. This intrinsic rotation angle is also objective, and turns out to equal to one half of the Lagrangian-averaged vorticity deviation (LAVD). The LAVD is defined as the trajectory-averaged magnitude of the deviation of the vorticity from its spatial mean. With the vorticity and its spatial mean the LAVD over a time interval therefore takes the form
with denoting the (possibly time-varying) domain of definition of the velocity field . This result applies both in two- and three dimensions, and enables the computation of a well-defined, objective and dynamically consistent material rotation angle along any trajectory.

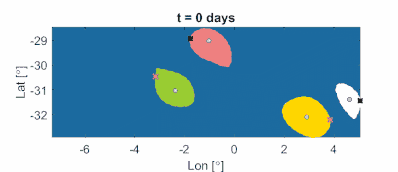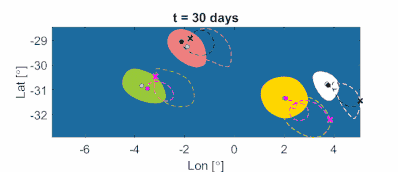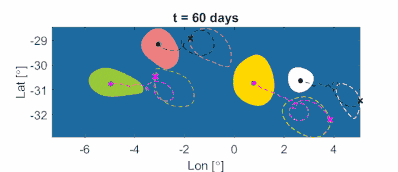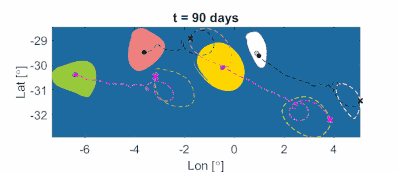
Outermost complex tubular level curves of the LAVD define initial positions of rotationally coherent material vortex boundaries in two-dimensional unsteady flows (see Fig. 11a). By construction, these boundaries may exhibit transverse filamentation, but any developing filament keeps rotating with the boundary, without global transverse departure form the material vortex. (Exceptions are inviscid flows where such a global departure of LAVD level surfaces from a vortex is possible as fluid elements preserve their material rotation rate for all times). Remarkably, centers of rotationally coherent vortices (defined by local maxima of the LAVD field) can be proven to be the observed centers of attraction or repulsion for finite-size (inertial) particle motion in geophysical flows (see Fig. 11b). In three-dimensional flows, tubular level surfaces of the LAVD define initial positions of two-dimensional eddy boundary surfaces (see Fig. 11c) that remain rotationally coherent over a time intcenter|erval (see Fig. 11d).

Stretching-based coherence from a local variational approach: Shear surfaces
The local variational theory of elliptic LCSs targets material surfaces that locally maximize material shear over the finite time interval of interest. This means that at initial point each point of an elliptic LCS , the tangent space is the plane along which the local Lagrangian shear is maximal (cf. Fig 7).
Introducing the two-dimensional shear vector field and the three-dimensional shear normal vector field
the criteria for two- and three-dimensional elliptic LCSs can be summarized as follows:
| LCS | Normal vector field of for n=3 | ODE for for n=2 | Frobenius-type PDE for for n=3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Elliptic | (shear lines) | (shear surfaces) |
For 3D flows, as in the case of hyperbolic LCSs, solving the Frobenius PDE can be avoided. Instead, one can construct intersections of a tubular elliptic LCS with select 2D planes, and fit a surface numerically to a large number of these intersection curves. As for hyperbolic LCSs above, let us denote the unit normal of a 2D plane by . Again, the intersection curves of elliptic LCSs with the plane are normal to both and to the unit normal of the LCS. As a consequence, an intersection curve satisfies the reduced shear ODE whose trajectories we refer to as reduced shear lines. (Strictly speaking, the reduced shear ODE is not an ordinary differential equation, given that its right-hand side is not a vector field, but a direction field, which is generally not globally orientable). Intersections of tubular elliptic LCSs with are limit cycles of the reduced shear ODE. Determining such limit cycles in a smooth family of nearby planes, then fitting a surface to the limit cycle family yields a numerical approximation for 2D shear surface. A three-dimensional example of this local variational computation of an elliptic LCS is shown in Fig. 11.

Stretching-based coherence from a global variational approach: lambda-lines

As noted above under hyperbolic LCSs, a global variational approach has been developed in two dimensions to capture elliptic LCSs as closed stationary curves of the material-line-averaged Lagrangian strain functional. Such curves turn out to be closed null-geodesics of the generalized Green–Lagrange strain tensor family , where is a positive parameter (Lagrange multiplier). The closed null-geodesics can be shown to coincide with limit cycles of the family of direction fields
Note that for , the direction field coincides with the direction field for shearlines obtained above from the local variational theory of LCSs.
Trajectories of are referred to as -lines. Remarkably, they are initial positions of material lines that are infinitesimally uniformly stretching under the flow map . Specifically, any subset of a -line is stretched by a factor of between the times and . As an example, Fig. 13 shows elliptic LCSs identified as closed -lines within the Great Red Spot of Jupiter.
Parabolic LCSs
Parabolic LCSs are shearless material surfaces that delineate cores of jet-type sets of trajectories. Such LCSs are characterized by both low stretching (because they are inside a non-stretching structure), but also by low shearing (because material shearing is minimal in jet cores).
Diagnostic approach: Finite-time Lyapunov exponents (FTLE) trenches
Since both shearing and stretching are as low as possible along a parabolic LCS, one may seek initial positions of such material surfaces as trenches of the FTLE field . A geophysical example of a parabolic LCS (generalized jet core) revealed as a trench of the FTLE field is shown in Fig. 14a.
Global variational approach: Heteroclinic chains of null-geodesics
In two dimensions, parabolic LCSs are also solutions of the global shearless variational principle described above for hyperbolic LCSs. As such, parabolic LCSs are composed of shrink lines and stretch lines that represent geodesics of the Lorentzian metric tensor . In contrast to hyperbolic LCSs, however, parabolic LCSs satisfy more robust boundary conditions: they remain stationary curves of the material-line-averaged shear functional even under variations to their endpoints. This explains the high degree of robustness and observability that jet cores exhibit in mixing. This is to be contrasted with the highly sensitive and fading footprint of hyperbolic LCSs away from strongly hyperbolic regions in diffusive tracer patterns.
Under variable endpoint boundary conditions, initial positions of parabolic LCSs turn out to be alternating chains of shrink lines and stretch lines that connect singularities of these line fields. These singularities occur at points where , and hence no infinitesimal deformation takes place between the two time instances and . Fig. 14b shows an example of parabolic LCSs in Jupiter's atmosphere, located using this variational theory. The chevron-type shapes forming out of circular material blobs positioned along the jet core is characteristic of tracer deformation near parabolic LCSs.

Software packages for LCS computations
Particle advection and Finite-Time Lyapunov Exponent calculation:
- ManGen (source code)
- LCS MATLAB Kit (source code)
- FlowVC (source code)
- cuda_ftle (source code)
- CTRAJ
- Newman (source code)
- FlowTK (source code)
Jupyter notebooks that guide you through methods used to extract advective, diffusive, stochastic and active transport barriers from discrete velocity data.
- TBarrier (source code)
See also
- Turbulence
- Chaos theory
- Dynamical systems theory
- Spectral submanifold
- Eulerian coherent structure
- Coherent turbulent structure
References
- ^ Haller, G. (2023). Transport Barriers and Coherent Structures in Flow Data. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9781009225199.
- ^ Haller, G.; Yuan, G. (2000). "Lagrangian coherent structures and mixing in two-dimensional turbulence". Physica D: Nonlinear Phenomena. 147 (3–4): 352. Bibcode:2000PhyD..147..352H. doi:10.1016/S0167-2789(00)00142-1.
- Peacock, T.; Haller, G. (2013). "Lagrangian coherent structures: The hidden skeleton of fluid flows". Physics Today. 66 (2): 41. Bibcode:2013PhT....66b..41P. doi:10.1063/PT.3.1886.
- ^ Haller, G. (2015). "Lagrangian Coherent Structures". Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics. 47 (1): 137–162. Bibcode:2015AnRFM..47..137H. doi:10.1146/annurev-fluid-010313-141322.
- Bozorgmagham, A. E.; Ross, S. D.; Schmale, D. G. (2013). "Real-time prediction of atmospheric Lagrangian coherent structures based on forecast data: An application and error analysis". Physica D: Nonlinear Phenomena. 258: 47–60. Bibcode:2013PhyD..258...47B. doi:10.1016/j.physd.2013.05.003.
- Bozorgmagham, A. E.; Ross, S. D. (2015). "Atmospheric Lagrangian coherent structures considering unresolved turbulence and forecast uncertainty". Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation. 22 (1–3): 964–979. Bibcode:2015CNSNS..22..964B. doi:10.1016/j.cnsns.2014.07.011.
- Olascoaga, M. J.; Haller, G. (2012). "Forecasting sudden changes in environmental pollution patterns". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 109 (13): 4738–4743. Bibcode:2012PNAS..109.4738O. doi:10.1073/pnas.1118574109. PMC 3323984. PMID 22411824.
- Nencioli, F.; d'Ovidio, F.; Doglioli, A. M.; Petrenko, A. A. (2011). "Surface coastal circulation patterns by in-situ detection of Lagrangian coherent structures". Geophysical Research Letters. 38 (17): n/a. Bibcode:2011GeoRL..3817604N. doi:10.1029/2011GL048815.
- Olascoaga, M. J.; Beron-Vera, F. J.; Haller, G.; Triñanes, J.; Iskandarani, M.; Coelho, E. F.; Haus, B. K.; Huntley, H. S.; Jacobs, G.; Kirwan, A. D.; Lipphardt, B. L.; Özgökmen, T. M.; h. m. Reniers, A. J.; Valle-Levinson, A. (2013). "Drifter motion in the Gulf of Mexico constrained by altimetric Lagrangian coherent structures". Geophysical Research Letters. 40 (23): 6171. Bibcode:2013GeoRL..40.6171O. doi:10.1002/2013GL058624.
- Huhn, F.; von Kameke, A.; Pérez-Muñuzuri, V.; Olascoaga, M. J.; Beron-Vera, F. J. (2012). "The impact of advective transport by the South Indian Ocean Countercurrent on the Madagascar plankton bloom". Geophysical Research Letters. 39 (6): n/a. Bibcode:2012GeoRL..39.6602H. doi:10.1029/2012GL051246.
- Peng, J.; Peterson, R. (2012). "Attracting structures in volcanic ash transport". Atmospheric Environment. 48: 230–239. Bibcode:2012AtmEn..48..230P. doi:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2011.05.053.
- Tallapragada, P.; Ross, S. D.; Schmale, D. G. (2011). "Lagrangian coherent structures are associated with fluctuations in airborne microbial populations". Chaos: An Interdisciplinary Journal of Nonlinear Science. 21 (3): 033122. Bibcode:2011Chaos..21c3122T. doi:10.1063/1.3624930. hdl:10919/24411. PMID 21974657.
- Ali, S.; Shah, M. (2007). "A Lagrangian Particle Dynamics Approach for Crowd Flow Segmentation and Stability Analysis". 2007 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. p. 1. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.63.4342. doi:10.1109/CVPR.2007.382977. ISBN 978-1-4244-1179-5. S2CID 8190391.
- Haller, G. (2001). "Lagrangian structures and the rate of strain in a partition of two-dimensional turbulence". Physics of Fluids. 13 (11): 3365–3385. Bibcode:2001PhFl...13.3365H. doi:10.1063/1.1403336.
- Haller, G. (2005). "An objective definition of a vortex". Journal of Fluid Mechanics. 525: 1–26. Bibcode:2005JFM...525....1H. doi:10.1017/S0022112004002526 (inactive 29 November 2024). S2CID 12867087.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of November 2024 (link) - Haller, G. (2001). "Distinguished material surfaces and coherent structures in three-dimensional fluid flows". Physica D: Nonlinear Phenomena. 149 (4): 248–277. Bibcode:2001PhyD..149..248H. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.331.6383. doi:10.1016/S0167-2789(00)00199-8.
- Mathur, M.; Haller, G.; Peacock, T.; Ruppert-Felsot, J.; Swinney, H. (2007). "Uncovering the Lagrangian Skeleton of Turbulence". Physical Review Letters. 98 (14): 144502. Bibcode:2007PhRvL..98n4502M. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.98.144502. PMID 17501277.
- ^ Haller, G. (2002). "Lagrangian coherent structures from approximate velocity data". Physics of Fluids. 14 (6): 1851–1861. Bibcode:2002PhFl...14.1851H. doi:10.1063/1.1477449.
- Kasten, J.; Petz, C.; Hotz, I.; Hege, H. C.; Noack, B. R.; Tadmor, G. (2010). "Lagrangian feature extraction of the cylinder wake". Physics of Fluids. 22 (9): 091108–091108–1. Bibcode:2010PhFl...22i1108K. doi:10.1063/1.3483220.
- Sanderson, A. R. (2014). "An Alternative Formulation of Lyapunov Exponents for Computing Lagrangian Coherent Structures". 2014 IEEE Pacific Visualization Symposium. pp. 277–280. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.657.3742. doi:10.1109/PacificVis.2014.27. ISBN 978-1-4799-2873-6. S2CID 7716670.
- ^ Shadden, S. C.; Lekien, F.; Marsden, J. E. (2005). "Definition and properties of Lagrangian coherent structures from finite-time Lyapunov exponents in two-dimensional aperiodic flows". Physica D: Nonlinear Phenomena. 212 (3–4): 271–304. Bibcode:2005PhyD..212..271S. doi:10.1016/j.physd.2005.10.007.
- ^ Lekien, F.; Shadden, S. C.; Marsden, J. E. (2007). "Lagrangian coherent structures in n-dimensional systems" (PDF). Journal of Mathematical Physics. 48 (6): 065404. Bibcode:2007JMP....48f5404L. doi:10.1063/1.2740025.
- ^ Shadden, S.C. (2005). "LCS Tutorial". Archived from the original on 2012-07-23.
- Lipinski, D.; Mohseni, K. (2010). "A ridge tracking algorithm and error estimate for efficient computation of Lagrangian coherent structures". Chaos: An Interdisciplinary Journal of Nonlinear Science. 20 (1): 017504. Bibcode:2010Chaos..20a7504L. doi:10.1063/1.3270049. PMID 20370294.
- Norgard, G.; Bremer, P. T. (2012). "Second derivative ridges are straight lines and the implications for computing Lagrangian Coherent Structures". Physica D: Nonlinear Phenomena. 241 (18): 1475. Bibcode:2012PhyD..241.1475N. doi:10.1016/j.physd.2012.05.006.
- Schindler, B.; Peikert, R.; Fuchs, R.; Theisel, H. (2012). "Ridge Concepts for the Visualization of Lagrangian Coherent Structures". Topological Methods in Data Analysis and Visualization II. Mathematics and Visualization. p. 221. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-23175-9_15. ISBN 978-3-642-23174-2.
- ^ Haller, G. (2011). "A variational theory of hyperbolic Lagrangian Coherent Structures". Physica D: Nonlinear Phenomena. 240 (7): 574–598. Bibcode:2011PhyD..240..574H. doi:10.1016/j.physd.2010.11.010.
- ^ Farazmand, M.; Haller, G. (2012). "Erratum and addendum to "A variational theory of hyperbolic Lagrangian coherent structures" [Physica D 240 (2011) 574–598]". Physica D: Nonlinear Phenomena. 241 (4): 439. Bibcode:2012PhyD..241..439F. doi:10.1016/j.physd.2011.09.013.
- Farazmand, M.; Haller, G. (2012). "Computing Lagrangian coherent structures from their variational theory". Chaos: An Interdisciplinary Journal of Nonlinear Science. 22 (1): 013128. Bibcode:2012Chaos..22a3128F. doi:10.1063/1.3690153. PMID 22463004.
- ^ Blazevski, D.; Haller, G. (2014). "Hyperbolic and elliptic transport barriers in three-dimensional unsteady flows". Physica D: Nonlinear Phenomena. 273–274: 46–62. arXiv:1306.6497. Bibcode:2014PhyD..273...46B. doi:10.1016/j.physd.2014.01.007. S2CID 44079483.
- ^ Farazmand, M.; Blazevski, D.; Haller, G. (2014). "Shearless transport barriers in unsteady two-dimensional flows and maps". Physica D: Nonlinear Phenomena. 278–279: 44–57. arXiv:1308.6136. Bibcode:2014PhyD..278...44F. doi:10.1016/j.physd.2014.03.008. S2CID 44141020.
- ^ Farazmand, Mohammad; Haller, George (2016). "Polar rotation angle identifies elliptic islands in unsteady dynamical systems". Physica D: Nonlinear Phenomena. 315: 1–12. arXiv:1503.05970. Bibcode:2016PhyD..315....1F. doi:10.1016/j.physd.2015.09.007. S2CID 44190280.
- ^ Haller, George (2016). "Dynamic rotation and stretch tensors from a dynamic polar decomposition". Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids. 86: 70–93. arXiv:1510.05367. Bibcode:2016JMPSo..86...70H. doi:10.1016/j.jmps.2015.10.002. S2CID 44073994.
- ^ Haller, George; Hadjighasem, Alireza; Farazmand, Mohammad; Huhn, Florian (2016). "Defining Coherent Vortices Objectively from the Vorticity". Journal of Fluid Mechanics. 795: 136–173. arXiv:1506.04061. Bibcode:2016JFM...795..136H. doi:10.1017/jfm.2016.151. S2CID 44191318.
- Haller, G.; Beron-Vera, F. J. (2012). "Geodesic theory of transport barriers in two-dimensional flows". Physica D: Nonlinear Phenomena. 241 (20): 1680. Bibcode:2012PhyD..241.1680H. doi:10.1016/j.physd.2012.06.012.
- ^ Hadjighasem, A.; Haller, G. (2016). "Geodesic Transport Barriers in Jupiter's Atmosphere: A Video-Based Analysis". SIAM Review. 58 (1): 69–89. arXiv:1408.5594. doi:10.1137/140983665. S2CID 31876317.
- Haller, G.; Beron-Vera, F. J. (2013). "Coherent Lagrangian vortices: The black holes of turbulence". Journal of Fluid Mechanics. 731: R4. arXiv:1308.2352. Bibcode:2013JFM...731R...4H. doi:10.1017/jfm.2013.391. S2CID 119570289.
- Beron-Vera, F. J.; Olascoaga, M. A. J.; Brown, M. G.; KoçAk, H.; Rypina, I. I. (2010). "Invariant-tori-like Lagrangian coherent structures in geophysical flows". Chaos: An Interdisciplinary Journal of Nonlinear Science. 20 (1): 017514. Bibcode:2010Chaos..20a7514B. doi:10.1063/1.3271342. PMID 20370304.
- Beron-Vera, F. J.; Olascoaga, M. A. J.; Brown, M. G.; Koçak, H. (2012). "Zonal Jets as Meridional Transport Barriers in the Subtropical and Polar Lower Stratosphere". Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences. 69 (2): 753. Bibcode:2012JAtS...69..753B. doi:10.1175/JAS-D-11-084.1 (inactive 2 December 2024).
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of December 2024 (link) - Lekien, Francois; Coulliette, Chad. "ManGen 1.4.4". Archived from the original on 2009-01-07.
- Dabiri, John O. "LCS MATLAB Kit".
- Shadden, Shawn C. "FlowVC".
- Jimenez, Raymond; Vankerschaver, Joris. "cuda_ftle". Archived from the original on 2011-05-17.
- Mills, Peter. "CTRAJ".
- Du Toit, Philip C. "Newman". Archived from the original on 2010-06-13.
- Ameli, Siavash; Desai, Yogin; Shadden, Shawn C. (2014). "Development of an Efficient and Flexible Pipeline for Lagrangian Coherent Structure Computation" (PDF). In Peer-Timo Bremer; Ingrid Hotz; Valerio Pascucci; Ronald Peikert (eds.). Topological Methods in Data Analysis and Visualization III. Mathematics and Visualization. Springer. pp. 201–215. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-04099-8_13. ISBN 978-3-319-04099-8. ISSN 1612-3786. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-10-06.
- Encinas Bartos, Alex Pablo; Kaszás, Balint; Haller, George. "TBarrier". GitHub.
Further reading
[REDACTED] Scholia has a topic profile for Lagrangian coherent structure.- Salman, H.; Hesthaven, J. S.; Warburton, T.; Haller, G. (2006). "Predicting transport by Lagrangian coherent structures with a high-order method". Theoretical and Computational Fluid Dynamics. 21 (1): 39–58. Bibcode:2007ThCFD..21...39S. doi:10.1007/s00162-006-0031-0. S2CID 11159109.
- Green, M. A.; Rowley, C. W.; Haller, G. (2007). "Detection of Lagrangian coherent structures in three-dimensional turbulence". Journal of Fluid Mechanics. 572: 111–120. Bibcode:2007JFM...572..111G. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.506.7756. doi:10.1017/S0022112006003648. S2CID 1074531.
 and over a time interval
and over a time interval  , consider a non-autonomous dynamical system defined through the flow map
, consider a non-autonomous dynamical system defined through the flow map  , mapping initial conditions
, mapping initial conditions  into their position
into their position  for any time
for any time  . If the flow map
. If the flow map  is a
is a  of initial conditions in
of initial conditions in 
 . Borrowing terminology from
. Borrowing terminology from  of the manifold
of the manifold  as a
as a  , invariant manifolds and their associated material surfaces are abundant and generally undistinguished in the extended phase space. Only few of them will act as cores of coherent trajectory patterns.
, invariant manifolds and their associated material surfaces are abundant and generally undistinguished in the extended phase space. Only few of them will act as cores of coherent trajectory patterns.
 should exert a sustained and consistent action on nearby trajectories throughout the time interval
should exert a sustained and consistent action on nearby trajectories throughout the time interval  . Examples of such action are attraction, repulsion, or shear. In principle, any well-defined mathematical property qualifies that creates coherent patterns out of randomly selected nearby initial conditions.
. Examples of such action are attraction, repulsion, or shear. In principle, any well-defined mathematical property qualifies that creates coherent patterns out of randomly selected nearby initial conditions.
 . In classical
. In classical  will generally be time-dependent, acting as the evolving skeletons of observed coherent trajectory patterns. Figure 2b shows the difference between an attracting LCS and a classic unstable manifold of a saddle point, for evolving times, in an
will generally be time-dependent, acting as the evolving skeletons of observed coherent trajectory patterns. Figure 2b shows the difference between an attracting LCS and a classic unstable manifold of a saddle point, for evolving times, in an 
 of possible particle positions is a material configuration space. In this space, LCSs are material surfaces, formed by trajectories. Whether or not a material trajectory is contained in an LCS is a property that is independent of the choice of coordinates, and hence cannot depend of the observer. As a consequence, LCSs are subject to the basic
of possible particle positions is a material configuration space. In this space, LCSs are material surfaces, formed by trajectories. Whether or not a material trajectory is contained in an LCS is a property that is independent of the choice of coordinates, and hence cannot depend of the observer. As a consequence, LCSs are subject to the basic  where
where  is the vector of the transformed coordinates;
is the vector of the transformed coordinates;  is an arbitrary
is an arbitrary  proper orthogonal matrix representing time-dependent rotations; and
proper orthogonal matrix representing time-dependent rotations; and  is an arbitrary
is an arbitrary  -dimensional vector representing time-dependent translations. As a consequence, any self-consistent LCS definition or criterion should be expressible in terms of quantities that are frame-invariant. For instance, the
-dimensional vector representing time-dependent translations. As a consequence, any self-consistent LCS definition or criterion should be expressible in terms of quantities that are frame-invariant. For instance, the  and the spin tensor
and the spin tensor  defined as
defined as
 transform under Euclidean changes of frame into the quantities
transform under Euclidean changes of frame into the quantities

 ,
,  ,
,  , as well as the averages or eigenvalues of these quantities, are routinely used in heuristic LCS detection. While such quantities may effectively mark features of the instantaneous velocity field
, as well as the averages or eigenvalues of these quantities, are routinely used in heuristic LCS detection. While such quantities may effectively mark features of the instantaneous velocity field  , the ability of these quantities to capture material mixing, transport, and coherence is limited and a priori unknown in any given frame. As an example, consider the linear unsteady fluid particle motion
, the ability of these quantities to capture material mixing, transport, and coherence is limited and a priori unknown in any given frame. As an example, consider the linear unsteady fluid particle motion

 holds, with
holds, with  referring to the Euclidean matrix norm. As seen in Fig. 3, however, trajectories grow exponentially along a rotating line and shrink exponentially along another rotating line. In material terms, therefore, the flow is hyperbolic (saddle-type) in any frame.
referring to the Euclidean matrix norm. As seen in Fig. 3, however, trajectories grow exponentially along a rotating line and shrink exponentially along another rotating line. In material terms, therefore, the flow is hyperbolic (saddle-type) in any frame.
 -frame to a
-frame to a  -frame through a coordinate change
-frame through a coordinate change  precisely by upholding that trajectories are mapped into trajectories, i.e., by requiring
precisely by upholding that trajectories are mapped into trajectories, i.e., by requiring  to hold for all times. Temporal differentiation of this identity and substitution into the original equation in the
to hold for all times. Temporal differentiation of this identity and substitution into the original equation in the  along a trajectory
along a trajectory  is governed by the flow map gradient
is governed by the flow map gradient  be a small perturbation to the initial condition
be a small perturbation to the initial condition  , with
, with  , and with
, and with  denoting an arbitrary unit vector in
denoting an arbitrary unit vector in  . This perturbation generally grows along the trajectory
. This perturbation generally grows along the trajectory  . Then the maximum relative stretching of infinitesimal perturbations at the point
. Then the maximum relative stretching of infinitesimal perturbations at the point 
 denotes the
denotes the  . As this relative stretching tends to grow rapidly, it is more convenient to work with its growth exponent
. As this relative stretching tends to grow rapidly, it is more convenient to work with its growth exponent  , which is then precisely the finite-time
, which is then precisely the finite-time 
 positions of repelling LCSs are marked by ridges of
positions of repelling LCSs are marked by ridges of  . By applying the same argument in backward time,
we obtain that time
. By applying the same argument in backward time,
we obtain that time  positions of attracting LCSs are marked by ridges of the backward FTLE field
positions of attracting LCSs are marked by ridges of the backward FTLE field  .
.
 . A more expedient approach is to compute the FTLE field from a simple finite-difference approximation to the deformation gradient.
For example, in a three-dimenisonal flow, we launch a trajectory
. A more expedient approach is to compute the FTLE field from a simple finite-difference approximation to the deformation gradient.
For example, in a three-dimenisonal flow, we launch a trajectory  from any element
from any element  for the evolving trajectory
for the evolving trajectory 
 pointing in the
pointing in the  coordinate direction. For two-dimensional flows, only the first
coordinate direction. For two-dimensional flows, only the first  minor matrix of the above matrix is relevant.
minor matrix of the above matrix is relevant.
 do not form material surfaces. Thus, ridges of
do not form material surfaces. Thus, ridges of  under varying
under varying  cannot be used to define Lagrangian objects, such as hyperbolic LCSs. Indeed, a locally strongest repelling material surface over
cannot be used to define Lagrangian objects, such as hyperbolic LCSs. Indeed, a locally strongest repelling material surface over  will generally not play the same role over
will generally not play the same role over  will not be a ridge for
will not be a ridge for  . Nonetheless, evolving second-derivative FTLE ridges computed over sliding intervals of the form
. Nonetheless, evolving second-derivative FTLE ridges computed over sliding intervals of the form  denote a unit normal to an initial material surface
denote a unit normal to an initial material surface  is mapped into the
is mapped into the  by the linearized flow map
by the linearized flow map  . At the same time, the image of the normal
. At the same time, the image of the normal  , the advected normal also develops a tangential component of length
, the advected normal also develops a tangential component of length  (cf. Fig. 7).
(cf. Fig. 7).
 , then the evolving material surface
, then the evolving material surface  signals that
signals that  is pointwise maximal (minimal) with respect to perturbations
of the initial normal vector field
is pointwise maximal (minimal) with respect to perturbations
of the initial normal vector field 

 (stretch lines)
(stretch lines) (stretch surfaces)
(stretch surfaces)

 (shrink lines)
(shrink lines)
 (shrink surfaces)
(shrink surfaces)
 . Attracting LCSs are obtained as most attracting stretch lines, starting from local minima of
. Attracting LCSs are obtained as most attracting stretch lines, starting from local minima of  . These starting points serve are initial positions of exceptional saddle-type trajectories in the flow. An example of the local variational computation of a repelling LCS is shown in FIg. 8. The computational algorithm is available in LCS Tool.
. These starting points serve are initial positions of exceptional saddle-type trajectories in the flow. An example of the local variational computation of a repelling LCS is shown in FIg. 8. The computational algorithm is available in LCS Tool.
 by
by  . The intersection curve of a 2D repelling LCS surface with the plane
. The intersection curve of a 2D repelling LCS surface with the plane  of the LCS. As a consequence, an intersection curve
of the LCS. As a consequence, an intersection curve  satisfies the ODE
satisfies the ODE

 -close material lines, therefore, typically show
-close material lines, therefore, typically show  defined as
defined as

 . Specifically, repelling LCSs are trajectories of
. Specifically, repelling LCSs are trajectories of  where the proper orthogonal tensor
where the proper orthogonal tensor  is called the
is called the  are called the
are called the  the local material straining described by the eigenvalues and eigenvectors of
the local material straining described by the eigenvalues and eigenvectors of  are fully captured by the singular values and singular vectors of the stretch tensors. The remaining factor in the deformation gradient is represented by
are fully captured by the singular values and singular vectors of the stretch tensors. The remaining factor in the deformation gradient is represented by  that characterises the material rotation generated by
that characterises the material rotation generated by  . For two-dimensional flows, the PRA can be computed from the invariants of
. For two-dimensional flows, the PRA can be computed from the invariants of 

 where
where  is the
is the  is the eigenvector corresponding to the unit eigenvector of the matrix
is the eigenvector corresponding to the unit eigenvector of the matrix  .
.
 . In two-dimensions, therefore, (polar) elliptic LCSs are simply closed level curves of the PRA, which turn out to be objective. In three dimensions, (polar) elliptic LCSs are toroidal or cylindrical level surfaces of the PRA, which are, however, not objective and hence will generally change in rotating frames. Coherent Lagrangian vortex boundaries can be visualized as outermost members of nested families of elliptic LCSs. Two- and three-dimensional examples of elliptic LCS revealed by tubular level surfaces of the PRA are shown in Fig. 10a-b.
. In two-dimensions, therefore, (polar) elliptic LCSs are simply closed level curves of the PRA, which turn out to be objective. In three dimensions, (polar) elliptic LCSs are toroidal or cylindrical level surfaces of the PRA, which are, however, not objective and hence will generally change in rotating frames. Coherent Lagrangian vortex boundaries can be visualized as outermost members of nested families of elliptic LCSs. Two- and three-dimensional examples of elliptic LCS revealed by tubular level surfaces of the PRA are shown in Fig. 10a-b.
 in the
in the  norm over a fixed time interval
norm over a fixed time interval 
 is the
is the  are the
are the  is the deformation gradient of the purely rotational flow
is the deformation gradient of the purely rotational flow

 is the deformation gradient of the purely straining flow
is the deformation gradient of the purely straining flow
 .
.

 is dynamically consistent, serving as the deformation gradient of the relative rotation flow
is dynamically consistent, serving as the deformation gradient of the relative rotation flow

 is the deformation gradient of the mean-rotation flow
is the deformation gradient of the mean-rotation flow
 The dynamic consistency of
The dynamic consistency of  implies that the total angle swept by
implies that the total angle swept by  is also objective, and turns out to equal to one half of the Lagrangian-averaged vorticity deviation (LAVD). The LAVD is defined as the trajectory-averaged magnitude of the deviation of the vorticity from its spatial mean. With the vorticity
is also objective, and turns out to equal to one half of the Lagrangian-averaged vorticity deviation (LAVD). The LAVD is defined as the trajectory-averaged magnitude of the deviation of the vorticity from its spatial mean. With the vorticity  and its spatial mean
and its spatial mean
 the LAVD over a time interval
the LAVD over a time interval 
 denoting the (possibly time-varying) domain of definition of the velocity field
denoting the (possibly time-varying) domain of definition of the velocity field  of an elliptic LCS
of an elliptic LCS  is maximal (cf. Fig 7).
is maximal (cf. Fig 7).
 and the three-dimensional shear normal vector field
and the three-dimensional shear normal vector field


 (shear lines)
(shear lines) (shear surfaces)
(shear surfaces)
 whose trajectories we refer to as reduced shear lines. (Strictly speaking, the reduced shear ODE is not an ordinary differential equation, given that its right-hand side is not a vector field, but a direction field, which is generally not globally orientable). Intersections of tubular elliptic LCSs with
whose trajectories we refer to as reduced shear lines. (Strictly speaking, the reduced shear ODE is not an ordinary differential equation, given that its right-hand side is not a vector field, but a direction field, which is generally not globally orientable). Intersections of tubular elliptic LCSs with  -lines, forming transport barriers around the
-lines, forming transport barriers around the  -line) bounding the core of the GRS, as well as the outermost elliptic LCS serving as the Lagrangian vortex boundary of the GRS. Image:Alireza Hadjighasem.
-line) bounding the core of the GRS, as well as the outermost elliptic LCS serving as the Lagrangian vortex boundary of the GRS. Image:Alireza Hadjighasem. , where
, where  is a positive parameter (Lagrange multiplier). The closed null-geodesics can be shown to coincide with limit cycles of the family of direction fields
is a positive parameter (Lagrange multiplier). The closed null-geodesics can be shown to coincide with limit cycles of the family of direction fields

 coincides with the direction field
coincides with the direction field  for shearlines obtained above from the local variational theory of LCSs.
for shearlines obtained above from the local variational theory of LCSs.
 are referred to as
are referred to as  . Specifically, any subset of a
. Specifically, any subset of a  . A geophysical example of a parabolic LCS (generalized jet core) revealed as a trench of the FTLE field is shown in Fig. 14a.
. A geophysical example of a parabolic LCS (generalized jet core) revealed as a trench of the FTLE field is shown in Fig. 14a.
 , and hence no infinitesimal deformation takes place between the two time instances
, and hence no infinitesimal deformation takes place between the two time instances