
Low-energy electron diffraction (LEED) is a technique for the determination of the surface structure of single-crystalline materials by bombardment with a collimated beam of low-energy electrons (30–200 eV) and observation of diffracted electrons as spots on a fluorescent screen.
LEED may be used in one of two ways:
- Qualitatively, where the diffraction pattern is recorded and analysis of the spot positions gives information on the symmetry of the surface structure. In the presence of an adsorbate the qualitative analysis may reveal information about the size and rotational alignment of the adsorbate unit cell with respect to the substrate unit cell.
- Quantitatively, where the intensities of diffracted beams are recorded as a function of incident electron beam energy to generate the so-called I–V curves. By comparison with theoretical curves, these may provide accurate information on atomic positions on the surface at hand.
Historical perspective
An electron-diffraction experiment similar to modern LEED was the first to observe the wavelike properties of electrons, but LEED was established as an ubiquitous tool in surface science only with the advances in vacuum generation and electron detection techniques.
Davisson and Germer's discovery of electron diffraction
The theoretical possibility of the occurrence of electron diffraction first emerged in 1924, when Louis de Broglie introduced wave mechanics and proposed the wavelike nature of all particles. In his Nobel-laureated work de Broglie postulated that the wavelength of a particle with linear momentum p is given by h/p, where h is the Planck constant. The de Broglie hypothesis was confirmed experimentally at Bell Labs in 1927, when Clinton Davisson and Lester Germer fired low-energy electrons at a crystalline nickel target and observed that the angular dependence of the intensity of backscattered electrons showed diffraction patterns. These observations were consistent with the diffraction theory for X-rays developed by Bragg and Laue earlier. Before the acceptance of the de Broglie hypothesis, diffraction was believed to be an exclusive property of waves.
Davisson and Germer published notes of their electron-diffraction experiment result in Nature and in Physical Review in 1927. One month after Davisson and Germer's work appeared, Thompson and Reid published their electron-diffraction work with higher kinetic energy (thousand times higher than the energy used by Davisson and Germer) in the same journal. Those experiments revealed the wave property of electrons and opened up an era of electron-diffraction study.
Development of LEED as a tool in surface science
Though discovered in 1927, low-energy electron diffraction did not become a popular tool for surface analysis until the early 1960s. The main reasons were that monitoring directions and intensities of diffracted beams was a difficult experimental process due to inadequate vacuum techniques and slow detection methods such as a Faraday cup. Also, since LEED is a surface-sensitive method, it required well-ordered surface structures. Techniques for the preparation of clean metal surfaces first became available much later.
Nonetheless, H. E. Farnsworth and coworkers at Brown University pioneered the use of LEED as a method for characterizing the absorption of gases onto clean metal surfaces and the associated regular adsorption phases, starting shortly after the Davisson and Germer discovery into the 1970s.
In the early 1960s LEED experienced a renaissance, as ultra-high vacuum became widely available, and the post acceleration detection method was introduced by Germer and his coworkers at Bell Labs using a flat phosphor screen. Using this technique, diffracted electrons were accelerated to high energies to produce clear and visible diffraction patterns on the screen. Ironically the post-acceleration method had already been proposed by Ehrenberg in 1934. In 1962 Lander and colleagues introduced the modern hemispherical screen with associated hemispherical grids. In the mid-1960s, modern LEED systems became commercially available as part of the ultra-high-vacuum instrumentation suite by Varian Associates and triggered an enormous boost of activities in surface science. Notably, future Nobel prize winner Gerhard Ertl started his studies of surface chemistry and catalysis on such a Varian system.
It soon became clear that the kinematic (single-scattering) theory, which had been successfully used to explain X-ray diffraction experiments, was inadequate for the quantitative interpretation of experimental data obtained from LEED. At this stage a detailed determination of surface structures, including adsorption sites, bond angles and bond lengths was not possible. A dynamical electron-diffraction theory, which took into account the possibility of multiple scattering, was established in the late 1960s. With this theory, it later became possible to reproduce experimental data with high precision.
Experimental setup
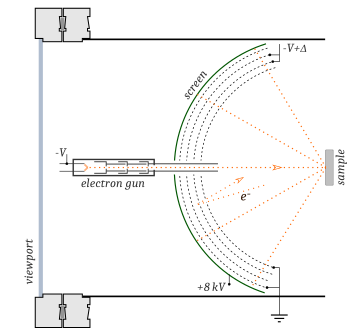
In order to keep the studied sample clean and free from unwanted adsorbates, LEED experiments are performed in an ultra-high vacuum environment (residual gas pressure <10 Pa).
LEED optics
The main components of a LEED instrument are:
- An electron gun from which monochromatic electrons are emitted by a cathode filament that is at a negative potential, typically 10–600 V, with respect to the sample. The electrons are accelerated and focused into a beam, typically about 0.1 to 0.5 mm wide, by a series of electrodes serving as electron lenses. Some of the electrons incident on the sample surface are backscattered elastically, and diffraction can be detected if sufficient order exists on the surface. This typically requires a region of single crystal surface as wide as the electron beam, although sometimes polycrystalline surfaces such as highly oriented pyrolytic graphite (HOPG) are sufficient.
- A high-pass filter for scattered electrons in the form of a retarding field analyzer, which blocks all but elastically scattered electrons. It usually contains three or four hemispherical concentric grids. Because only radial fields around the sampled point would be allowed and the geometry of the sample and the surrounding area is not spherical, the space between the sample and the analyzer has to be field-free. The first grid, therefore, separates the space above the sample from the retarding field. The next grid is at a negative potential to block low energy electrons, and is called the suppressor or the gate. To make the retarding field homogeneous and mechanically more stable another grid at the same potential is added behind the second grid. The fourth grid is only necessary when the LEED is used like a tetrode and the current at the screen is measured, when it serves as screen between the gate and the anode.
- A hemispherical positively-biased fluorescent screen on which the diffraction pattern can be directly observed, or a position-sensitive electron detector. Most new LEED systems use a reverse view scheme, which has a minimized electron gun, and the pattern is viewed from behind through a transmission screen and a viewport. Recently, a new digitized position sensitive detector called a delay-line detector with better dynamic range and resolution has been developed.
Sample
The sample of the desired surface crystallographic orientation is initially cut and prepared outside the vacuum chamber. The correct alignment of the crystal can be achieved with the help of X-ray diffraction methods such as Laue diffraction. After being mounted in the UHV chamber the sample is cleaned and flattened. Unwanted surface contaminants are removed by ion sputtering or by chemical processes such as oxidation and reduction cycles. The surface is flattened by annealing at high temperatures. Once a clean and well-defined surface is prepared, monolayers can be adsorbed on the surface by exposing it to a gas consisting of the desired adsorbate atoms or molecules.
Often the annealing process will let bulk impurities diffuse to the surface and therefore give rise to a re-contamination after each cleaning cycle. The problem is that impurities that adsorb without changing the basic symmetry of the surface, cannot easily be identified in the diffraction pattern. Therefore, in many LEED experiments Auger electron spectroscopy is used to accurately determine the purity of the sample.
Using the detector for Auger electron spectroscopy
LEED optics is in some instruments also used for Auger electron spectroscopy. To improve the measured signal, the gate voltage is scanned in a linear ramp. An RC circuit serves to derive the second derivative, which is then amplified and digitized. To reduce the noise, multiple passes are summed up. The first derivative is very large due to the residual capacitive coupling between gate and the anode and may degrade the performance of the circuit. By applying a negative ramp to the screen this can be compensated. It is also possible to add a small sine to the gate. A high-Q RLC circuit is tuned to the second harmonic to detect the second derivative.
Data acquisition
A modern data acquisition system usually contains a CCD/CMOS camera pointed to the screen for diffraction pattern visualization and a computer for data recording and further analysis. More expensive instruments have in-vacuum position sensitive electron detectors that measure the current directly, which helps in the quantitative I–V analysis of the diffraction spots.
Theory
Surface sensitivity
The basic reason for the high surface sensitivity of LEED is that for low-energy electrons the interaction between the solid and electrons is especially strong. Upon penetrating the crystal, primary electrons will lose kinetic energy due to inelastic scattering processes such as plasmon and phonon excitations, as well as electron–electron interactions.
In cases where the detailed nature of the inelastic processes is unimportant, they are commonly treated by assuming an exponential decay of the primary electron-beam intensity I0 in the direction of propagation:
Here d is the penetration depth, and denotes the inelastic mean free path, defined as the distance an electron can travel before its intensity has decreased by the factor 1/e. While the inelastic scattering processes and consequently the electronic mean free path depend on the energy, it is relatively independent of the material. The mean free path turns out to be minimal (5–10 Å) in the energy range of low-energy electrons (20–200 eV). This effective attenuation means that only a few atomic layers are sampled by the electron beam, and, as a consequence, the contribution of deeper atoms to the diffraction progressively decreases.
Kinematic theory: single scattering

Kinematic diffraction is defined as the situation where electrons impinging on a well-ordered crystal surface are elastically scattered only once by that surface. In the theory the electron beam is represented by a plane wave with a wavelength given by the de Broglie hypothesis:
The interaction between the scatterers present in the surface and the incident electrons is most conveniently described in reciprocal space. In three dimensions the primitive reciprocal lattice vectors are related to the real space lattice {a, b, c} in the following way:

For an incident electron with wave vector and scattered wave vector , the condition for constructive interference and hence diffraction of scattered electron waves is given by the Laue condition:
where (h, k, l) is a set of integers, and
is a vector of the reciprocal lattice. Note that these vectors specify the Fourier components of charge density in the reciprocal (momentum) space, and that the incoming electrons scatter at these density modulations within the crystal lattice. The magnitudes of the wave vectors are unchanged, i.e. , because only elastic scattering is considered. Since the mean free path of low-energy electrons in a crystal is only a few angstroms, only the first few atomic layers contribute to the diffraction. This means that there are no diffraction conditions in the direction perpendicular to the sample surface. As a consequence, the reciprocal lattice of a surface is a 2D lattice with rods extending perpendicular from each lattice point. The rods can be pictured as regions where the reciprocal lattice points are infinitely dense. Therefore, in the case of diffraction from a surface the Laue condition reduces to the 2D form:
where and are the primitive translation vectors of the 2D reciprocal lattice of the surface and , denote the component of respectively the reflected and incident wave vector parallel to the sample surface. and are related to the real space surface lattice, with as the surface normal, in the following way:
The Laue-condition equation can readily be visualized using the Ewald's sphere construction. Figures 3 and 4 show a simple illustration of this principle: The wave vector of the incident electron beam is drawn such that it terminates at a reciprocal lattice point. The Ewald's sphere is then the sphere with radius and origin at the center of the incident wave vector. By construction, every wave vector centered at the origin and terminating at an intersection between a rod and the sphere will then satisfy the 2D Laue condition and thus represent an allowed diffracted beam.

Interpretation of LEED patterns
Figure 4 shows the Ewald's sphere for the case of normal incidence of the primary electron beam, as would be the case in an actual LEED setup. It is apparent that the pattern observed on the fluorescent screen is a direct picture of the reciprocal lattice of the surface. The spots are indexed according to the values of h and k. The size of the Ewald's sphere and hence the number of diffraction spots on the screen is controlled by the incident electron energy. From the knowledge of the reciprocal lattice models for the real space lattice can be constructed and the surface can be characterized at least qualitatively in terms of the surface periodicity and the point group. Figure 7 shows a model of an unreconstructed (100) face of a simple cubic crystal and the expected LEED pattern. Since these patterns can be inferred from the crystal structure of the bulk crystal, known from other more quantitative diffraction techniques, LEED is more interesting in the cases where the surface layers of a material reconstruct, or where surface adsorbates form their own superstructures.
Superstructures
Main article: Superstructure (condensed matter)
Overlaying superstructures on a substrate surface may introduce additional spots in the known (1×1) arrangement. These are known as extra spots or super spots. Figure 6 shows many such spots appearing after a simple hexagonal surface of a metal has been covered with a layer of graphene. Figure 7 shows a schematic of real and reciprocal space lattices for a simple (1×2) superstructure on a square lattice.

For a commensurate superstructure the symmetry and the rotational alignment with respect to adsorbent surface can be determined from the LEED pattern. This is easiest shown by using a matrix notation, where the primitive translation vectors of the superlattice {as, bs} are linked to the primitive translation vectors of the underlying (1×1) lattice {a, b} in the following way
The matrix for the superstructure then is
Similarly, the primitive translation vectors of the lattice describing the extra spots {a
s, b
s} are linked to the primitive translation vectors of the reciprocal lattice {a, b}
G is related to G in the following way
Domains

An essential problem when considering LEED patterns is the existence of symmetrically equivalent domains. Domains may lead to diffraction patterns that have higher symmetry than the actual surface at hand. The reason is that usually the cross sectional area of the primary electron beam (~1 mm) is large compared to the average domain size on the surface and hence the LEED pattern might be a superposition of diffraction beams from domains oriented along different axes of the substrate lattice.
However, since the average domain size is generally larger than the coherence length of the probing electrons, interference between electrons scattered from different domains can be neglected. Therefore, the total LEED pattern emerges as the incoherent sum of the diffraction patterns associated with the individual domains.
Figure 8 shows the superposition of the diffraction patterns for the two orthogonal domains (2×1) and (1×2) on a square lattice, i.e. for the case where one structure is just rotated by 90° with respect to the other. The (1×2) structure and the respective LEED pattern are shown in Figure 7. It is apparent that the local symmetry of the surface structure is twofold while the LEED pattern exhibits a fourfold symmetry.
Figure 1 shows a real diffraction pattern of the same situation for the case of a Si(100) surface. However, here the (2×1) structure is formed due to surface reconstruction.
Dynamical theory: multiple scattering
The inspection of the LEED pattern gives a qualitative picture of the surface periodicity i.e. the size of the surface unit cell and to a certain degree of surface symmetries. However it will give no information about the atomic arrangement within a surface unit cell or the sites of adsorbed atoms. For instance, when the whole superstructure in Figure 7 is shifted such that the atoms adsorb in bridge sites instead of on-top sites the LEED pattern stays the same, although the individual spot intensities may somewhat differ.
A more quantitative analysis of LEED experimental data can be achieved by analysis of so-called I–V curves, which are measurements of the intensity versus incident electron energy. The I–V curves can be recorded by using a camera connected to computer controlled data handling or by direct measurement with a movable Faraday cup. The experimental curves are then compared to computer calculations based on the assumption of a particular model system. The model is changed in an iterative process until a satisfactory agreement between experimental and theoretical curves is achieved. A quantitative measure for this agreement is the so-called reliability- or R-factor. A commonly used reliability factor is the one proposed by Pendry. It is expressed in terms of the logarithmic derivative of the intensity:
The R-factor is then given by:
where and is the imaginary part of the electron self-energy. In general, is considered as a good agreement, is considered mediocre and is considered a bad agreement. Figure 9 shows examples of the comparison between experimental I–V spectra and theoretical calculations.

Dynamical LEED calculations
The term dynamical stems from the studies of X-ray diffraction and describes the situation where the response of the crystal to an incident wave is included self-consistently and multiple scattering can occur. The aim of any dynamical LEED theory is to calculate the intensities of diffraction of an electron beam impinging on a surface as accurately as possible.
A common method to achieve this is the self-consistent multiple scattering approach. One essential point in this approach is the assumption that the scattering properties of the surface, i.e. of the individual atoms, are known in detail. The main task then reduces to the determination of the effective wave field incident on the individual scatters present in the surface, where the effective field is the sum of the primary field and the field emitted from all the other atoms. This must be done in a self-consistent way, since the emitted field of an atom depends on the incident effective field upon it. Once the effective field incident on each atom is determined, the total field emitted from all atoms can be found and its asymptotic value far from the crystal then gives the desired intensities.
A common approach in LEED calculations is to describe the scattering potential of the crystal by a "muffin tin" model, where the crystal potential can be imagined being divided up by non-overlapping spheres centered at each atom such that the potential has a spherically symmetric form inside the spheres and is constant everywhere else. The choice of this potential reduces the problem to scattering from spherical potentials, which can be dealt with effectively. The task is then to solve the Schrödinger equation for an incident electron wave in that "muffin tin" potential.
Related techniques
Tensor LEED
In LEED the exact atomic configuration of a surface is determined by a trial and error process where measured I–V curves are compared to computer-calculated spectra under the assumption of a model structure. From an initial reference structure a set of trial structures is created by varying the model parameters. The parameters are changed until an optimal agreement between theory and experiment is achieved. However, for each trial structure a full LEED calculation with multiple scattering corrections must be conducted. For systems with a large parameter space the need for computational time might become significant. This is the case for complex surfaces structures or when considering large molecules as adsorbates.
Tensor LEED is an attempt to reduce the computational effort needed by avoiding full LEED calculations for each trial structure. The scheme is as follows: One first defines a reference surface structure for which the I–V spectrum is calculated. Next a trial structure is created by displacing some of the atoms. If the displacements are small the trial structure can be considered as a small perturbation of the reference structure and first-order perturbation theory can be used to determine the I–V curves of a large set of trial structures.
Spot profile analysis low-energy electron diffraction (SPA-LEED)
A real surface is not perfectly periodic but has many imperfections in the form of dislocations, atomic steps, terraces and the presence of unwanted adsorbed atoms. This departure from a perfect surface leads to a broadening of the diffraction spots and adds to the background intensity in the LEED pattern.
SPA-LEED is a technique where the profile and shape of the intensity of diffraction beam spots is measured. The spots are sensitive to the irregularities in the surface structure and their examination therefore permits more-detailed conclusions about some surface characteristics. Using SPA-LEED may for instance permit a quantitative determination of the surface roughness, terrace sizes, dislocation arrays, surface steps and adsorbates.
Although some degree of spot profile analysis can be performed in regular LEED and even LEEM setups, dedicated SPA-LEED setups, which scan the profile of the diffraction spot over a dedicated channeltron detector allow for much higher dynamic range and profile resolution.
Other
- Spin-polarized low energy electron diffraction
- Inelastic low energy electron diffraction
- Very low-energy electron diffraction (VLEED)
- Reflection high-energy electron diffraction (RHEED)
- Ultrafast low-energy electron diffraction (ULEED)
See also
External links
References
- ^ K. Oura; V. G. Lifshifts; A. A. Saranin; A. V. Zotov; M. Katayama (2003). Surface Science. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg New York. pp. 1–45. ISBN 9783540005452.
- ^ M. A. Van Hove; W. H. Weinberg; C. M. Chan (1986). Low-Energy Electron Diffraction. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg New York. pp. 1–27, 46–89, 92–124, 145–172. doi:10.1002/maco.19870380711. ISBN 978-3-540-16262-9.
- Fifty years of electron diffraction : in recognition of fifty years of achievement by the crystallographers and gas diffractionists in the field of electron diffraction. Goodman, P. (Peter), 1928–, International Union of Crystallography. Dordrecht, Holland: Published for the International Union of Crystallography by D. Reidel. 1981. ISBN 90-277-1246-8. OCLC 7276396.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: others (link) - E. J. Scheibner, L. H. Germer, and C. D. Hartman (1960). "Apparatus for Direct Observation of LEED Patterns". Rev. Sci. Instrum. 31 (2): 112–114. Bibcode:1960RScI...31..112S. doi:10.1063/1.1716903.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - L. H. Germer, and C. D. Hartman (1960). "Improved LEED Apparatus". Rev. Sci. Instrum. 31 (7): 784. Bibcode:1960RScI...31..784G. doi:10.1063/1.1717051.
- W. Ehrenberg (1934). "A new method of investigating the diffraction of slow electrons by crystals". Phil. Mag. 18 (122): 878–901. doi:10.1080/14786443409462562.
- J. J. Lander, J. Morrison, and F. Unterwald (1962). "Improved Design and Method of Operation of LEED Equipment". Rev. Sci. Instrum. 33 (7): 782–783. Bibcode:1962RScI...33..782L. doi:10.1063/1.1717975.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Ertl, G. (1967). "Untersuchung von oberflächenreaktionen mittels beugung langsamer elektronen (LEED)". Surface Science. 6 (2): 208–232. doi:10.1016/0039-6028(67)90005-2. ISSN 0039-6028.
- Human, D.; Hu, X. F.; Hirschmugl, C. J.; Ociepa, J.; Hall, G.; Jagutzki, O.; Ullmann-Pfleger, K. (2006-02-01). "Low energy electron diffraction using an electronic delay-line detector". Review of Scientific Instruments. 77 (2): 023302–023302–8. Bibcode:2006RScI...77b3302H. doi:10.1063/1.2170078. ISSN 0034-6748.
- Pendry (1974). Low-Energy Electron Diffraction. Academic Press Inc. (London) LTD. pp. 1–75. ISBN 9780125505505.
- Zangwill, A., "Physics at Surfaces", Cambridge University Press (1988), p.33
- C. Kittel (1996). "2". Introduction to Solid State Physics. John Wiley, US.
- J.B. Pendry (1980). "Reliability Factors for LEED Calculations". J. Phys. C. 13 (5): 937–944. Bibcode:1980JPhC...13..937P. doi:10.1088/0022-3719/13/5/024.
- E.G. McRae (1967). "Self-Consistent Multiple-Scattering Approach to the Interpretation of Low-Energy Electron Diffraction". Surface Science. 8 (1–2): 14–34. Bibcode:1967SurSc...8...14M. doi:10.1016/0039-6028(67)90071-4.
- P.J. Rous J.B. Pendry (1989). "Tensor LEED I: A Technique for high speed surface structure determination by low energy electron diffraction". Comput. Phys. Commun. 54 (1): 137–156. Bibcode:1989CoPhC..54..137R. doi:10.1016/0010-4655(89)90039-8.
- P.J. Rous J.B. Pendry (1989). "The theory of Tensor LEED". Surf. Sci. 219 (3): 355–372. Bibcode:1989SurSc.219..355R. doi:10.1016/0039-6028(89)90513-X.
- ^ M. Henzler (1982). "Studies of Surface Imperfections". Appl. Surf. Sci. 11/12: 450–469. Bibcode:1982ApSS...11..450H. doi:10.1016/0378-5963(82)90092-7.
- Horn-von Hoegen, Michael (1999). "Growth of semiconductor layers studied by spot profile analysing low energy electron diffraction" (PDF). Zeitschrift für Kristallographie. 214: 684–721. doi:10.1524/zkri.1999.214.11.684. Retrieved 25 January 2020.

 denotes the
denotes the 

 and scattered wave vector
and scattered wave vector  , the condition for constructive interference and hence diffraction of scattered electron waves is given by the
, the condition for constructive interference and hence diffraction of scattered electron waves is given by the 

 , because only elastic scattering is considered.
Since the mean free path of low-energy electrons in a crystal is only a few angstroms, only the first few atomic layers contribute to the diffraction. This means that there are no diffraction conditions in the direction perpendicular to the sample surface. As a consequence, the reciprocal lattice of a surface is a 2D lattice with rods extending perpendicular from each lattice point. The rods can be pictured as regions where the reciprocal lattice points are infinitely dense.
Therefore, in the case of diffraction from a surface the Laue condition reduces to the 2D form:
, because only elastic scattering is considered.
Since the mean free path of low-energy electrons in a crystal is only a few angstroms, only the first few atomic layers contribute to the diffraction. This means that there are no diffraction conditions in the direction perpendicular to the sample surface. As a consequence, the reciprocal lattice of a surface is a 2D lattice with rods extending perpendicular from each lattice point. The rods can be pictured as regions where the reciprocal lattice points are infinitely dense.
Therefore, in the case of diffraction from a surface the Laue condition reduces to the 2D form:

 and
and  are the primitive translation vectors of the 2D reciprocal lattice of the surface and
are the primitive translation vectors of the 2D reciprocal lattice of the surface and  ,
,  denote the component of respectively the reflected and incident wave vector parallel to the sample surface.
denote the component of respectively the reflected and incident wave vector parallel to the sample surface.  and
and  are related to the real space surface lattice, with
are related to the real space surface lattice, with  as the surface normal, in the following way:
as the surface normal, in the following way:

 of the incident electron beam is drawn such that it terminates at a reciprocal lattice point. The Ewald's sphere is then the sphere with radius
of the incident electron beam is drawn such that it terminates at a reciprocal lattice point. The Ewald's sphere is then the sphere with radius  and origin at the center of the incident wave vector. By construction, every wave vector centered at the origin and terminating at an intersection between a rod and the sphere will then satisfy the 2D Laue condition and thus represent an allowed diffracted beam.
and origin at the center of the incident wave vector. By construction, every wave vector centered at the origin and terminating at an intersection between a rod and the sphere will then satisfy the 2D Laue condition and thus represent an allowed diffracted beam.






 and
and  is the imaginary part of the electron self-energy. In general,
is the imaginary part of the electron self-energy. In general,  is considered as a good agreement,
is considered as a good agreement,  is considered mediocre and
is considered mediocre and  is considered a bad agreement. Figure 9 shows examples of the comparison between experimental I–V spectra and theoretical calculations.
is considered a bad agreement. Figure 9 shows examples of the comparison between experimental I–V spectra and theoretical calculations.