| Möbius–Kantor graph | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Named after | August Ferdinand Möbius and S. Kantor |
| Vertices | 16 |
| Edges | 24 |
| Radius | 4 |
| Diameter | 4 |
| Girth | 6 |
| Automorphisms | 96 |
| Chromatic number | 2 |
| Chromatic index | 3 |
| Genus | 1 |
| Book thickness | 3 |
| Queue number | 2 |
| Properties | Symmetric Hamiltonian Bipartite Cubic Unit distance Cayley graph Perfect Orientably simple |
| Table of graphs and parameters | |
In the mathematical field of graph theory, the Möbius–Kantor graph is a symmetric bipartite cubic graph with 16 vertices and 24 edges named after August Ferdinand Möbius and Seligmann Kantor. It can be defined as the generalized Petersen graph G(8,3): that is, it is formed by the vertices of an octagon, connected to the vertices of an eight-point star in which each point of the star is connected to the points three steps away from it (an octagram).
Möbius–Kantor configuration
Main article: Möbius–Kantor configuration
Möbius (1828) asked whether there exists a pair of polygons with p sides each, having the property that the vertices of one polygon lie on the lines through the edges of the other polygon, and vice versa. If so, the vertices and edges of these polygons would form a projective configuration. For p = 4 there is no solution in the Euclidean plane, but Kantor (1882) found pairs of polygons of this type, for a generalization of the problem in which the points and edges belong to the complex projective plane. That is, in Kantor's solution, the coordinates of the polygon vertices are complex numbers. Kantor's solution for p = 4, a pair of mutually-inscribed quadrilaterals in the complex projective plane, is called the Möbius–Kantor configuration. The Möbius–Kantor graph derives its name from being the Levi graph of the Möbius–Kantor configuration. It has one vertex per point and one vertex per triple, with an edge connecting two vertices if they correspond to a point and to a triple that contains that point.
The configuration may also be described algebraically in terms of the abelian group with nine elements. This group has four subgroups of order three (the subsets of elements of the form , , , and ), each of which can be used to partition the nine group elements into three cosets of three elements per coset. These nine elements and twelve cosets form a configuration, the Hesse configuration. Removing the zero element and the four cosets containing zero gives rise to the Möbius–Kantor configuration.
As a subgraph
The Möbius–Kantor graph is a subgraph of the four-dimensional hypercube graph, formed by removing eight edges from the hypercube. Since the hypercube is a unit distance graph, the Möbius–Kantor graph can also be drawn in the plane with all edges unit length, although such a drawing will necessarily have some pairs of crossing edges.
The Möbius–Kantor graph also occurs many times as an induced subgraph of the Hoffman–Singleton graph. Each of these instances is in fact an eigenvector of the Hoffman-Singleton graph, with associated eigenvalue -3. Each vertex not in the induced Möbius–Kantor graph is adjacent to exactly four vertices in the Möbius–Kantor graph, two each in half of a bipartition of the Möbius–Kantor graph.
Topology
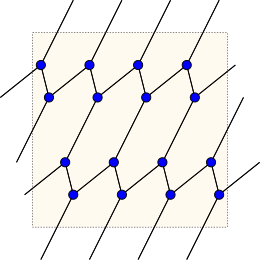
The Möbius–Kantor graph cannot be embedded without crossings in the plane; it has crossing number 4, and is the smallest cubic graph with that crossing number. Additionally, it provides an example of a graph all of whose subgraphs' crossing numbers differ from it by two or more. However, it is a toroidal graph: it has an embedding in the torus in which all faces are hexagons. The dual graph of this embedding is the hyperoctahedral graph K2,2,2,2.
There is an even more symmetric embedding of Möbius–Kantor graph in the double torus which is a regular map, with six octagonal faces, in which all 96 symmetries of the graph can be realized as symmetries of the embedding Its 96-element symmetry group has a Cayley graph that can itself be embedded on the double torus, and was shown by Tucker (1984) to be the unique group with genus two. The Cayley graph on 96 vertices is a flag graph of the genus 2 regular map having Möbius–Kantor graph as a skeleton. This means it can be obtained from the regular map as a skeleton of the dual of its barycentric subdivision. A sculpture by DeWitt Godfrey and Duane Martinez showing the double torus embedding of the symmetries of the Möbius–Kantor graph was unveiled at the Technical Museum of Slovenia as part of the 6th Slovenian International Conference on Graph Theory in 2007. In 2013 a rotating version of the sculpture was unveiled at Colgate University.
The Möbius–Kantor graph admits an embedding into a triple torus (genus 3 torus) that is a regular map having four 12-gonal faces, and is the Petrie dual of the double torus embedding described above.
Lijnen & Ceulemans (2004), motivated by an investigation of potential chemical structures of carbon compounds, studied the family of all embeddings of the Möbius–Kantor graph onto 2-manifolds; they showed that there are 759 inequivalent embeddings. The genus 1 embedding, which is not a regular map, is seen in the diagram above.
Algebraic properties
The automorphism group of the Möbius–Kantor graph is a group of order 96. It acts transitively on the vertices, on the edges and on the arcs of the graph. Therefore, the Möbius–Kantor graph is a symmetric graph. It has automorphisms that take any vertex to any other vertex and any edge to any other edge. According to the Foster census, the Möbius–Kantor graph is the unique cubic symmetric graph with 16 vertices, and the smallest cubic symmetric graph which is not also distance-transitive. The Möbius–Kantor graph is also a Cayley graph.
The generalized Petersen graph G(n,k) is vertex-transitive if and only if n = 10 and k =2 or if k ≡ ±1 (mod n) and is edge-transitive only in the following seven cases: (n,k) = (4,1), (5,2), (8,3), (10,2), (10,3), (12,5), or (24,5). So the Möbius–Kantor graph is one of only seven symmetric Generalized Petersen graphs. Its symmetric double torus embedding is correspondingly one of only seven regular cubic maps in which the total number of vertices is twice the number of vertices per face. Among the seven symmetric generalized Petersen graphs are the cubical graph , the Petersen graph , the dodecahedral graph , the Desargues graph and the Nauru graph .
The characteristic polynomial of the Möbius–Kantor graph is equal to
The Möbius–Kantor graph is a double cover of the graph of the cube.
See also
- Pauli group, whose Cayley graph is the Möbius–Kantor graph
Notes
- ^ Coxeter 1950.
- OEIS sequence A110507
- McQuillan & Richter 1992.
- ^ Marušič & Pisanski 2000.
- Coxeter (1950) credits this embedding to Threlfall (1932).
- Conder & Dobcsányi 2002.
- Frucht, Graver & Watkins 1971.
- McMullen 1992.
- Brouwer, Andrew E. "Möbius-Kantor graph". www.win.tue.nl. Retrieved 2024-07-21.
References
- Conder, Marston; Dobcsányi, Peter (2002), "Trivalent symmetric graphs on up to 768 vertices", Journal of Combinatorial Mathematics and Combinatorial Computing, 40: 41–63, MR 1887966.
- Coxeter, H. S. M. (1950), "Self-dual configurations and regular graphs", Bulletin of the American Mathematical Society, 56 (5): 413–455, doi:10.1090/S0002-9904-1950-09407-5.
- Frucht, Robert; Graver, Jack E.; Watkins, Mark E. (1971), "The groups of the generalized Petersen graphs", Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society, 70 (2): 211–218, Bibcode:1971PCPS...70..211F, doi:10.1017/S0305004100049811, MR 0289365, S2CID 122686848.
- Kantor, Seligmann (1882), "Über die Configurationen (3, 3) mit den Indices 8, 9 und ihren Zusammenhang mit den Curven dritter Ordnung", Sitzungsberichte der Mathematisch-Naturwissenschaftlichen Classe der Kaiserlichen Akademie der Wissenschaften, Wien, 84 (1): 915–932.
- Lijnen, Erwin; Ceulemans, Arnout (2004), "Oriented 2-Cell Embeddings of a Graph and Their Symmetry Classification: Generating Algorithms and Case Study of the Möbius-Kantor Graph", Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling, 44 (5): 1552–1564, doi:10.1021/ci049865c, PMID 15446812.
- Marušič, Dragan; Pisanski, Tomaž (2000), "The remarkable generalized Petersen graph G(8,3)", Mathematica Slovaca, 50: 117–121.
- McMullen, Peter (1992), "The regular polyhedra of type with vertices", Geometriae Dedicata, 43 (3): 285–289, doi:10.1007/BF00151518, S2CID 119591683.
- McQuillan, Dan; Richter, R. Bruce (1992), "On the crossing numbers of certain generalized Petersen graphs", Discrete Mathematics, 104 (3): 311–320, doi:10.1016/0012-365X(92)90453-M, MR 1171327.
- Möbius, August Ferdinand (1828), "Kann von zwei dreiseitigen Pyramiden eine jede in Bezug auf die andere um- und eingeschrieben zugleich heissen?", Journal für die reine und angewandte Mathematik, 3: 273–278; in Gesammelte Werke (1886), vol. 1, pp. 439–446.
- Tucker, Thomas W. (1984), "There is only one group of genus two", Journal of Combinatorial Theory, Series B, 36 (3): 269–275, doi:10.1016/0095-8956(84)90032-7.
- Threlfall, William (1932), "Gruppenbilder", Abhandlungen der Mathematisch-Physischen Klasse der Sächsischen Akademie der Wissenschaften, 41 (6): 1–59.
 with nine elements.
This group has four subgroups of order three (the subsets of elements of the form
with nine elements.
This group has four subgroups of order three (the subsets of elements of the form  ,
,  ,
,  , and
, and  ), each of which can be used to partition the nine group elements into three
), each of which can be used to partition the nine group elements into three 

 , the
, the  , the
, the  , the
, the  and the
and the  .
.

 with
with  vertices",
vertices",