| Ki-57 | |
|---|---|
 MC-20-I, with a nickname Asagumo (morning cloud), used by Asahi Shimbun MC-20-I, with a nickname Asagumo (morning cloud), used by Asahi Shimbun | |
| General information | |
| Type | Transport aircraft Paratroop transport Passenger aircraft |
| Manufacturer | Mitsubishi Heavy Industries |
| Primary users | Imperial Japanese Army Air Force Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service Imperial Japanese Airways |
| Number built | 406 |
| History | |
| Manufactured | 1940–1945 |
| Introduction date | 1942 |
| First flight | August 1940 |
| Developed from | Mitsubishi Ki-21 |
The Mitsubishi Ki-57 was a Japanese passenger transport aircraft, developed from the Ki-21 bomber, during the early 1940s.
Development
In 1938, when the Ki-21 heavy bomber began to enter service with the Imperial Japanese Army, its capability attracted the attention of the Imperial Japanese Airways. In consequence, a civil version was developed, and this, generally similar to the Ki-21-I and retaining its powerplant of two 708 kW (950 hp) Nakajima Ha-5 KAI radial engines, differed primarily by having the same wings transferred from a mid- to low-wing configuration and the incorporation of a new fuselage to provide accommodation for up to eleven passengers. This transport version appealed also to the navy, and, following the flight of a prototype in August 1940 and subsequent testing, the type was ordered into production for both civil and military use.
This initial production Ki-57-I had the civil and military designations of MC-20-I and Army Type 100 Transport Model 1, respectively. A total of one-hundred production Ki-57-Is had been built by early 1942, and small numbers of them were transferred for use by the Japanese Navy in a transport role, then becoming redesignated L4M1. After the last of the Ki-57s had been delivered, production was switched to an improved Ki-57-II, which introduced more powerful 805 kW (1,080 hp) Mitsubishi Ha-102 14-cylinder radial engines installed in redesigned nacelles and, at the same time, incorporated a number of detail refinements and minor equipment changes. Civil and military designations of this version were the MC-20-II and Army Type 100 Transport Model 2, respectively. Only 406 were built before production ended in January 1945. Both versions were covered by the Allied reporting name Topsy.
Variants

- Ki-57-I Army Type 100 Transport Model 1: Powered by two 708 kW (950 hp) Nakajima Ha-5 KAI radial engines and a redesigned fuselage to accommodate 11 passengers. About 100 aircraft of this type were built including the civil version.
- MC-20-I: Same as above but built for civil use with Imperial Japanese Airways (Dai Nippon Koku KK).
- Ki-57-II Army Type 100 Transport Model 2:Powered by two 805 kW (1,080 hp) Mitsubishi Ha-102 Zuisei 14-cylinder radial engines installed in redesigned nacelles. Minor equipment and detail refinements were also incorporated. 306 aircraft of this type were produced before the end of production in January 1945.
- MC-20-II: Same as above but built for civil use with Imperial Japanese Airways (Dai Nippon Koku KK).
- L4M1: A small number of Ki-57-Is were transferred for test by the Japanese navy as transports and were redesignated L4M1.
Operators

Wartime
Military operators
Civil operators
- Imperial Japanese Airways (Dai Nippon Koku KK)
- Asahi Shimbun
- Osaka Mainichi Shimbun
- Tyuka Koku Kaisya (in China)
- Manchukuo National Airways (in Manchuria)
- One MC-20 used as presidential transport
- One MC-20 used as presidential transport
Post-war
- The last Ki-57 was used as a trainer and retired in 1952.
- Imperial Japanese Airways (till October 1945)
- Captured aircraft, used by the KNIL.
Accidents and incidents
- On 20 December 1940, an Imperial Japanese Airways MC-20-I (J-BGON, Myuko) crashed into Tokyo Bay off Chiba during CAB's test flight, killing all 13 on board including 8 CAB inspectors.
- On 21 June 1941, a Manchurian Air Transport MC-20 (M-604) crashed into the Sea of Japan, killing all 18 on board.
Specifications (Ki-57-II)
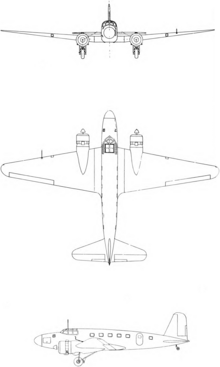
Data from Japanese Aircraft of the Pacific War
General characteristics
- Crew: 4 (pilot, co-pilot, navigator and radio operator)
- Capacity: 11 passengers
- Length: 16.1 m (52 ft 10 in)
- Wingspan: 22.6 m (74 ft 2 in)
- Height: 4.86 m (15 ft 11 in)
- Wing area: 70.08 m (754.3 sq ft)
- Empty weight: 5,585 kg (12,313 lb)
- Gross weight: 8,173 kg (18,018 lb)
- Max takeoff weight: 9,120 kg (20,106 lb)
- Powerplant: 2 × Mitsubishi Ha-102 Zuisei 14-cylinder air-cooled radial engine, 805 kW (1,080 hp) each for take-off
- Propellers: 3-bladed variable-pitch propellers
Performance
- Maximum speed: 470 km/h (290 mph, 250 kn) at 5,800 m (19,000 ft)
- Range: 3,000 km (1,900 mi, 1,600 nmi)
- Service ceiling: 8,000 m (26,000 ft)
- Time to altitude: 5,000 m (16,000 ft) 15 minutes 45 seconds
- Wing loading: 116.6 kg/m (23.9 lb/sq ft)
See also
Related development
Related lists
- List of aircraft of Japan during World War II
- List of aircraft of the Japanese Navy
- List of aircraft of World War II
- List of military aircraft of Japan
References
- Francillon 1979, pp. 182–183
- Francillon 1979, pp. 183–184
- Francillon 1979, p. 184.
- Francillon 1979, pp. 184–185.
- Bibliography
- Francillon, Ph.D., René J. The Mitsubishi Ki-21 (Aircraft in Profile number 172). Leatherhead, Surrey, UK: Profile Publications Ltd., 1967.
- Francillon, René J. (1979). Japanese aircraft of the Pacific War. London: Putnam. ISBN 0-370-30251-6. OCLC 6124909. (new edition 1987 by Putnam Aeronautical Books, ISBN 0-85177-801-1); 3rd edition 1987 by Putnam Aeronautical Books, 1987. ISBN 0-85177-801-1).
External links
- Classic Airplane Museum MC-20 Japanese
- JCAL MC-20 Archived 2015-02-14 at the Wayback Machine Japanese
| Mitsubishi aircraft | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Company designations | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Imperial Japanese Army early designations | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Imperial Japanese Army short designations | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Imperial Japanese Navy short designations |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| World War II Allied reporting names | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Japanese Self-Defense Force designations | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Company divisions |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Imperial Japanese Army Air Service aircraft designations | |
|---|---|
| 1-50 | |
| 51-100 | |
| 100- | |
| Imperial Japanese Navy aircraft designations (short system) | |
|---|---|
| Fighters (A) | |
| Torpedo bombers (B) | |
| Shipboard reconnaissance (C) | |
| Dive bombers (D) | |
| Reconnaissance seaplanes (E) | |
| Observation seaplanes (F) | |
| Land-based bombers (G) | |
| Flying Boats (H) | |
| Land-based Fighters (J) | |
| Trainers (K) | |
| Transports (L) | |
| Special-purpose (M) | |
| Floatplane fighters (N) | |
| Land-based bombers (P) | |
| Patrol (Q) | |
| Land-based reconnaissance (R) | |
| Night fighters (S) | |
| X as second letter is for experimental aircraft or imported technology demonstrators not intended for service, Hyphenated trailing letter (-J, -K, -L, -N or -S) denotes design modified for secondary role, Possibly incorrect designation, but used in many sources | |
| World War II Allied reporting names for Japanese aircraft | |
|---|---|
| Aircraft in Japanese service |
|
| Foreign aircraft thought to be in Japanese service | |