| Native name: جزيرة المحرق (Arabic) | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Geography | |
| Location | Persian Gulf |
| Coordinates | 26°15′N 50°39′E / 26.25°N 50.65°E / 26.25; 50.65 |
| Archipelago | Bahrain |
| Adjacent to | Persian Gulf |
| Total islands | 1 |
| Major islands |
|
| Area | 72.05 km (27.82 sq mi) |
| Length | 18 km (11.2 mi) |
| Width | 5.5 km (3.42 mi) |
| Coastline | 50 km (31 mi) |
| Highest elevation | 10 m (30 ft) |
| Highest point | Al Muharraq |
| Administration | |
| Bahrain | |
| Governorate | Muharraq Governorate |
| Largest settlement | Al Muharraq (pop. 100,000) |
| Demographics | |
| Demonym | Bahraini |
| Population | 200,000 (2014) |
| Pop. density | 4,057/km (10508/sq mi) |
| Ethnic groups | Bahraini 62.4%, non-Bahraini 37.6% |
| Additional information | |
| Time zone | |
| ISO code | BH-14 |
| Official website | www |
Muharraq Island (Arabic: جزيرة المحرق), formerly known as Moharek, is the second largest island in the archipelago of Bahrain after Bahrain Island. It lies 4 km (2.5 mi) east of the capital, Manama, on Bahrain Island.
History
The island is named after Muharraq City, the former capital of Bahrain. The Al Khalifa dynasty settled there in the nineteenth century and resided there until 1923. The island dominated the trade, fishing and especially pearls industries in Bahrain. The pearl center was made a UNESCO world heritage site in 2012. In recent years, major reclamation of artificial islands like Amwaj Islands has taken place north of Muharraq Island. In the south of the island, at Hidd district, the new Bahrain International Investment Park (BIIP) of the free zone was built. In the far south, new Khalifa bin Salman harbor opened in 2009.
Demography
There are several towns and villages located on the Island, including:
- Al Muharraq
- Al Dair
- Arad, formerly a separate island of its own
- Busaiteen
- Hidd
- Galali
- Halat Bu Maher
- Samaheej
Administration
The island belongs to Muharraq Governorate.
Transportation

The island has the 4,000 metres (13,000 ft) Bahrain International Airport (IATA: BAH, ICAO: OBBI) that follows the long east–west axis. The island has the 900 metres (3,000 ft) Muharraq Airfield (ICAO code:none) adjacent to Bahrain International Airport. There are three causeways connecting Muharraq Island with Manama on Bahrain Island:
- Shaikh Hamad Bridge: From Muharraq City to Diplomatic Area
- Shaikh Isa bin Salman Causeway: From Muharraq City/Busaiteen to Diplomatic Area
- Shaikh Khalifa Bridge: From Hidd to Juffair
Image gallery
-
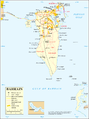 Map 1
Map 1
-
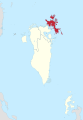 District Map
District Map
-
 Muharraq in the foreground; Manama on Bahrain Island in the background
Muharraq in the foreground; Manama on Bahrain Island in the background
-
Shaikh Isa bin Salman Causeway
See also
Citations
- World Gazetter Archived 2013-02-09 at archive.today
- ^ EB (1911).
- UNESCO
- "Home". biip.com.bh.
Bibliography
- Baynes, T. S., ed. (1878), "Bahrein" , Encyclopædia Britannica, vol. 3 (9th ed.), New York: Charles Scribner's Sons, p. 240.
- Holdich, Thomas Hungerford (1911), "Bahrein Islands" , in Chisholm, Hugh (ed.), Encyclopædia Britannica, vol. 3 (11th ed.), Cambridge University Press, p. 212.
| Islands of Bahrain | |
|---|---|
| Natural | |
| Artificial | |
| Settlements in the Muharraq Governorate of Bahrain | |
|---|---|
This Bahrain location article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |