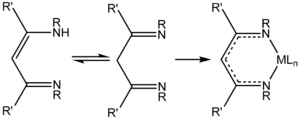
NacNac is a class of anionic bidentate ligands. 1,3-Diketimines are often referred to as "HNacNac", a modification of the abbreviation Hacac used for 1,3-diketones. These species can exist as a mixture of tautomers.
Preparation of ligands and complexes
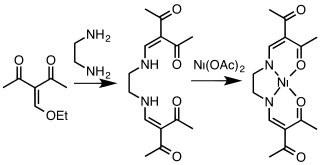
Acetylacetone and related 1,3-diketones condense with primary alkyl- or arylamines resulting in replacement of the carbonyl oxygen atoms with NR groups, where R = aryl, alkyl. To prepare 1,3-diketimines from bulky amines, e.g. 2,4,6-trimethylanilines, prolonged reaction times are required. 2,6-Diisopropylaniline is a common bulky building block.
Deprotonation of HNacNac compounds affords anionic bidentate ligands that form a variety of coordination complexes. Some derivatives with large R groups can be used to stabilize low valent main group and transition metal complexes. Unlike the situation for the acetylacetonates, the steric properties of the coordinating atoms in NacNac ligands is adjustable by changes in the R substituent. Attachment to a metal center is usually carried out by initial deprotonation of HNacNac with n-butyllithium; the lithium derivative is then treated with a metal chloride to eliminate lithium chloride. In some cases, HNacNacs also serve as charge-neutral 1,3-diimine ligands.
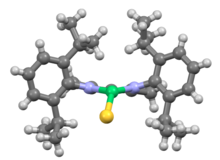
Related NacNac ligands
NacNac ligands are diimine analogues of acetylacetonate ligands. An intermediate class of ligands are derived from monoimino-ketones. The first Dipp-NacNac ligand was synthesized by Dr. Francis S. Mair in 1998.
See also
References
- Mindiola, D. J.; Holland, P. L.; Warren, T. H. (2010). "Complexes of Bulky β-Diketiminate Ligands". Inorganic Syntheses. 35: 1–55. doi:10.1002/9780470651568.ch1.
- Bourget-Merle, L.; Lappert, M. F.; Severn, J. R. (2002). "The Chemistry of Diketiminatometal Complexes". Chemical Reviews. 102: 3031–3066. doi:10.1021/cr010424r.
- Qian, B.; Ward, D. L.; Smith, M.R. (1998). "Synthesis, Structure, and Reactivity of β-Diketiminato Aluminum Complexes". Organometallics. 17: 3070–3076. doi:10.1021/om970886o.
- Hartmann, N.J.; Wu, G.; Hayton, T. W. (2015). "Synthesis of a "Masked" Terminal Nickel(II) Sulfide by Reductive Deprotection and its Reaction with Nitrous Oxide". Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 54: 14956–9. doi:10.1002/anie.201508232. PMC 4715500. PMID 26457792.
- ^ Weber, Birgit; Jäger, Ernst-G. (2009). "Structure and Magnetic Properties of Iron(II/III) Complexes with N
2O
2-Coordinating Schiff Base-Like Ligands". Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2009: 455. doi:10.1002/ejic.200990003. - Riley, Dennis P.; Busch, Daryle H. (1978). "Macrocyclic Tetraazatetraenato Ligands and their Metal Complexes". Inorg. Synth. 18: 36. doi:10.1002/9780470132494.ch7.
- Mair, Frank S.; Cope, Elaine K.; Clegg, William; Edwards, Andrew J. (1998). "Structural Characterization of ∞: A Heavy Alkali Metal Diazapentadienyl Complex". Inorg. Chem. 37. doi:10.1021/ic970956j.