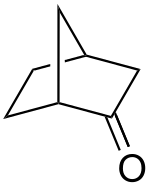
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name Bicycloheptan-2-one | |
| Other names 2-Norbornanone | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.134 |
| PubChem CID | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C7H10O |
| Molar mass | 110.156 g·mol |
| Appearance | Colorless solid |
| Melting point | 93 to 96 °C (199 to 205 °F; 366 to 369 K) |
| Boiling point | 168 to 172 °C (334 to 342 °F; 441 to 445 K) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa). Infobox references | |
Norcamphor is an organic compound, classified as a bicyclic ketone. It is an analog of camphor, but without the three methyl groups. A colorless solid, it is used as a building block in organic synthesis. Norcamphor is prepared from norbornene via the 2-formate ester, which is oxidized. It is a useful precursor to norborneols.
See also
References
- ^ "Norcamphor". Sigma-Aldrich. Retrieved March 11, 2013.
- Kleinfelter, Donald C.; Schleyer, Paul von R. (1962). "2-Norbornanone". Org. Synth. 42: 79. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.042.0079.
This article about a ketone is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |