| Part of a series on |
| Purinergic signalling |
|---|
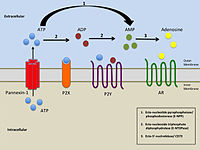 Simplified illustration of extracellular purinergic signalling Simplified illustration of extracellular purinergic signalling |
| Concepts |
| Membrane transporters |
Nucleoside transporters (NTs) are a group of membrane transport proteins which transport nucleoside substrates like adenosine across the membranes of cells and/or vesicles. There are two known types of nucleoside transporters, concentrative nucleoside transporters (CNTs; SLC28) and equilibrative nucleoside transporters (ENTs; SLC29), as well as possibly a yet-unidentified vesicular transporter.
References
- ^ Molina-Arcas M, Casado FJ, Pastor-Anglada M (October 2009). "Nucleoside transporter proteins". Current Vascular Pharmacology. 7 (4): 426–34. PMID 19485885. Archived from the original on 2013-01-13.
Further reading
- Molina-Arcas M, Casado FJ, Pastor-Anglada M (October 2009). "Nucleoside Transporter Proteins". Current Vascular Pharmacology. 7 (4): 426–34. PMID 19485885. Archived from the original on 2013-01-13.
- Molina-Arcas M, Trigueros-Motos L, Casado FJ, Pastor-Anglada M (June 2008). "Physiological and pharmacological roles of nucleoside transporter proteins". Nucleosides, Nucleotides & Nucleic Acids. 27 (6): 769–78. doi:10.1080/15257770802145819. PMID 18600539.
- Gray JH, Owen RP, Giacomini KM (February 2004). "The concentrative nucleoside transporter family, SLC28". Pflügers Archiv: European Journal of Physiology. 447 (5): 728–34. doi:10.1007/s00424-003-1107-y. PMID 12856181.
- Baldwin SA, Beal PR, Yao SY, King AE, Cass CE, Young JD (February 2004). "The equilibrative nucleoside transporter family, SLC29". Pflügers Archiv: European Journal of Physiology. 447 (5): 735–43. doi:10.1007/s00424-003-1103-2. PMID 12838422.
| Membrane transport protein: neurotransmitter transporters (TC 2.A.1.2) | |
|---|---|
| Vesicular | |
| Other | |
| Purine receptor modulators | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Receptor (ligands) |
| ||||||||||
| Transporter (blockers) |
| ||||||||||
| Enzyme (inhibitors) |
| ||||||||||
| Others |
| ||||||||||
| See also: Receptor/signaling modulators | |||||||||||
This membrane protein–related article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |