 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name Phosphirane | |
| Systematic IUPAC name Phosphacyclopropane | |
| Other names Phosphiran | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| PubChem CID | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C2H5P |
| Molar mass | 60.036 g·mol |
| Appearance | colorless gas |
| Melting point | −121 °C (−186 °F; 152 K) |
| Boiling point | 36.5 °C (97.7 °F; 309.6 K) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa). Infobox references | |
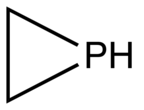
Phosphirane is the organophosphorus compound with the formula C2H4PH. It is a colorless gas of no commercial value. As the simplest cyclic, saturated organophosphorus compound, phosphirane is the prototype of a family of related compounds that have attracted attention from the research community. Phosphirane was first prepared by reaction of 1,2-dichloroethane with the conjugate base of phosphine. Phosphiranes, that is substituted phosphirene compounds where one or more of the H's are replaced organic substituents, are far more commonly discussed than the parent phosphirane.
References
- Wagner, Ross I.; Freeman, LeVern D.; Goldwhite, H.; Rowsell, D. G. (March 1967). "Phosphiran". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 89 (5): 1102–1104. doi:10.1021/ja00981a013.
- François Mathey; Manfred Regitz (1996). "Phosphiranes, Phosphirenes, and Heavier Analogues". Comprehensive Heterocyclic Chemistry II. Vol. 1A. pp. 277–304. doi:10.1016/B978-008096518-5.00008-3. ISBN 978-0-08-096518-5.
- Quin, L. D. (2000). A Guide to Organophosphorus Chemistry. Wiley-Interscience. ISBN 0-471-31824-8.