

In mathematics, a hyperbola is a type of smooth curve lying in a plane, defined by its geometric properties or by equations for which it is the solution set. A hyperbola has two pieces, called connected components or branches, that are mirror images of each other and resemble two infinite bows. The hyperbola is one of the three kinds of conic section, formed by the intersection of a plane and a double cone. (The other conic sections are the parabola and the ellipse. A circle is a special case of an ellipse.) If the plane intersects both halves of the double cone but does not pass through the apex of the cones, then the conic is a hyperbola.
Besides being a conic section, a hyperbola can arise as the locus of points whose difference of distances to two fixed foci is constant, as a curve for each point of which the rays to two fixed foci are reflections across the tangent line at that point, or as the solution of certain bivariate quadratic equations such as the reciprocal relationship In practical applications, a hyperbola can arise as the path followed by the shadow of the tip of a sundial's gnomon, the shape of an open orbit such as that of a celestial object exceeding the escape velocity of the nearest gravitational body, or the scattering trajectory of a subatomic particle, among others.
Each branch of the hyperbola has two arms which become straighter (lower curvature) further out from the center of the hyperbola. Diagonally opposite arms, one from each branch, tend in the limit to a common line, called the asymptote of those two arms. So there are two asymptotes, whose intersection is at the center of symmetry of the hyperbola, which can be thought of as the mirror point about which each branch reflects to form the other branch. In the case of the curve the asymptotes are the two coordinate axes.
Hyperbolas share many of the ellipses' analytical properties such as eccentricity, focus, and directrix. Typically the correspondence can be made with nothing more than a change of sign in some term. Many other mathematical objects have their origin in the hyperbola, such as hyperbolic paraboloids (saddle surfaces), hyperboloids ("wastebaskets"), hyperbolic geometry (Lobachevsky's celebrated non-Euclidean geometry), hyperbolic functions (sinh, cosh, tanh, etc.), and gyrovector spaces (a geometry proposed for use in both relativity and quantum mechanics which is not Euclidean).
Etymology and history
The word "hyperbola" derives from the Greek ὑπερβολή, meaning "over-thrown" or "excessive", from which the English term hyperbole also derives. Hyperbolae were discovered by Menaechmus in his investigations of the problem of doubling the cube, but were then called sections of obtuse cones. The term hyperbola is believed to have been coined by Apollonius of Perga (c. 262 – c. 190 BC) in his definitive work on the conic sections, the Conics. The names of the other two general conic sections, the ellipse and the parabola, derive from the corresponding Greek words for "deficient" and "applied"; all three names are borrowed from earlier Pythagorean terminology which referred to a comparison of the side of rectangles of fixed area with a given line segment. The rectangle could be "applied" to the segment (meaning, have an equal length), be shorter than the segment or exceed the segment.
Definitions
As locus of points


A hyperbola can be defined geometrically as a set of points (locus of points) in the Euclidean plane:
A hyperbola is a set of points, such that for any point of the set, the absolute difference of the distances to two fixed points (the foci) is constant, usually denoted by :The midpoint of the line segment joining the foci is called the center of the hyperbola. The line through the foci is called the major axis. It contains the vertices , which have distance to the center. The distance of the foci to the center is called the focal distance or linear eccentricity. The quotient is the eccentricity .
The equation can be viewed in a different way (see diagram):
If is the circle with midpoint and radius , then the distance of a point of the right branch to the circle equals the distance to the focus :
is called the circular directrix (related to focus ) of the hyperbola. In order to get the left branch of the hyperbola, one has to use the circular directrix related to . This property should not be confused with the definition of a hyperbola with help of a directrix (line) below.
Hyperbola with equation y = A/x


red: A = 1; magenta: A = 4; blue: A = 9
If the xy-coordinate system is rotated about the origin by the angle and new coordinates are assigned, then .
The rectangular hyperbola (whose semi-axes are equal) has the new equation .
Solving for yields
Thus, in an xy-coordinate system the graph of a function with equation is a rectangular hyperbola entirely in the first and third quadrants with
- the coordinate axes as asymptotes,
- the line as major axis ,
- the center and the semi-axis
- the vertices
- the semi-latus rectum and radius of curvature at the vertices
- the linear eccentricity and the eccentricity
- the tangent at point
A rotation of the original hyperbola by results in a rectangular hyperbola entirely in the second and fourth quadrants, with the same asymptotes, center, semi-latus rectum, radius of curvature at the vertices, linear eccentricity, and eccentricity as for the case of rotation, with equation
- the semi-axes
- the line as major axis,
- the vertices
Shifting the hyperbola with equation so that the new center is , yields the new equation and the new asymptotes are and . The shape parameters remain unchanged.
By the directrix property


The two lines at distance from the center and parallel to the minor axis are called directrices of the hyperbola (see diagram).
For an arbitrary point of the hyperbola the quotient of the distance to one focus and to the corresponding directrix (see diagram) is equal to the eccentricity: The proof for the pair follows from the fact that and satisfy the equation The second case is proven analogously.

The inverse statement is also true and can be used to define a hyperbola (in a manner similar to the definition of a parabola):
For any point (focus), any line (directrix) not through and any real number with the set of points (locus of points), for which the quotient of the distances to the point and to the line is is a hyperbola.
(The choice yields a parabola and if an ellipse.)
Proof
Let and assume is a point on the curve. The directrix has equation . With , the relation produces the equations
- and
The substitution yields This is the equation of an ellipse () or a parabola () or a hyperbola (). All of these non-degenerate conics have, in common, the origin as a vertex (see diagram).
If , introduce new parameters so that , and then the equation above becomes which is the equation of a hyperbola with center , the x-axis as major axis and the major/minor semi axis .
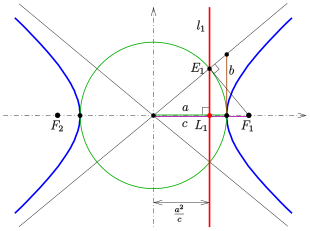
Construction of a directrix
Because of point of directrix (see diagram) and focus are inverse with respect to the circle inversion at circle (in diagram green). Hence point can be constructed using the theorem of Thales (not shown in the diagram). The directrix is the perpendicular to line through point .
Alternative construction of : Calculation shows, that point is the intersection of the asymptote with its perpendicular through (see diagram).
As plane section of a cone

The intersection of an upright double cone by a plane not through the vertex with slope greater than the slope of the lines on the cone is a hyperbola (see diagram: red curve). In order to prove the defining property of a hyperbola (see above) one uses two Dandelin spheres , which are spheres that touch the cone along circles , and the intersecting (hyperbola) plane at points and . It turns out: are the foci of the hyperbola.
- Let be an arbitrary point of the intersection curve.
- The generatrix of the cone containing intersects circle at point and circle at a point .
- The line segments and are tangential to the sphere and, hence, are of equal length.
- The line segments and are tangential to the sphere and, hence, are of equal length.
- The result is: is independent of the hyperbola point , because no matter where point is, have to be on circles , , and line segment has to cross the apex. Therefore, as point moves along the red curve (hyperbola), line segment simply rotates about apex without changing its length.
Pin and string construction

The definition of a hyperbola by its foci and its circular directrices (see above) can be used for drawing an arc of it with help of pins, a string and a ruler:
- Choose the foci and one of the circular directrices, for example (circle with radius )
- A ruler is fixed at point free to rotate around . Point is marked at distance .
- A string gets its one end pinned at point on the ruler and its length is made .
- The free end of the string is pinned to point .
- Take a pen and hold the string tight to the edge of the ruler.
- Rotating the ruler around prompts the pen to draw an arc of the right branch of the hyperbola, because of (see the definition of a hyperbola by circular directrices).
Steiner generation of a hyperbola


The following method to construct single points of a hyperbola relies on the Steiner generation of a non degenerate conic section:
Given two pencils of lines at two points (all lines containing and , respectively) and a projective but not perspective mapping of onto , then the intersection points of corresponding lines form a non-degenerate projective conic section.For the generation of points of the hyperbola one uses the pencils at the vertices . Let be a point of the hyperbola and . The line segment is divided into n equally-spaced segments and this division is projected parallel with the diagonal as direction onto the line segment (see diagram). The parallel projection is part of the projective mapping between the pencils at and needed. The intersection points of any two related lines and are points of the uniquely defined hyperbola.
Remarks:
- The subdivision could be extended beyond the points and in order to get more points, but the determination of the intersection points would become more inaccurate. A better idea is extending the points already constructed by symmetry (see animation).
- The Steiner generation exists for ellipses and parabolas, too.
- The Steiner generation is sometimes called a parallelogram method because one can use other points rather than the vertices, which starts with a parallelogram instead of a rectangle.
Inscribed angles for hyperbolas y = a/(x − b) + c and the 3-point-form

A hyperbola with equation is uniquely determined by three points with different x- and y-coordinates. A simple way to determine the shape parameters uses the inscribed angle theorem for hyperbolas:
In order to measure an angle between two lines with equations in this context one uses the quotientAnalogous to the inscribed angle theorem for circles one gets the
Inscribed angle theorem for hyperbolas — For four points (see diagram) the following statement is true:
The four points are on a hyperbola with equation if and only if the angles at and are equal in the sense of the measurement above. That means if
The proof can be derived by straightforward calculation. If the points are on a hyperbola, one can assume the hyperbola's equation is .
A consequence of the inscribed angle theorem for hyperbolas is the
3-point-form of a hyperbola's equation — The equation of the hyperbola determined by 3 points is the solution of the equation for .
As an affine image of the unit hyperbola x − y = 1

Another definition of a hyperbola uses affine transformations:
Any hyperbola is the affine image of the unit hyperbola with equation .Parametric representation
An affine transformation of the Euclidean plane has the form , where is a regular matrix (its determinant is not 0) and is an arbitrary vector. If are the column vectors of the matrix , the unit hyperbola is mapped onto the hyperbola
is the center, a point of the hyperbola and a tangent vector at this point.
Vertices
In general the vectors are not perpendicular. That means, in general are not the vertices of the hyperbola. But point into the directions of the asymptotes. The tangent vector at point is Because at a vertex the tangent is perpendicular to the major axis of the hyperbola one gets the parameter of a vertex from the equation and hence from which yields
The formulae , , and were used.
The two vertices of the hyperbola are
Implicit representation
Solving the parametric representation for by Cramer's rule and using , one gets the implicit representation
Hyperbola in space
The definition of a hyperbola in this section gives a parametric representation of an arbitrary hyperbola, even in space, if one allows to be vectors in space.
As an affine image of the hyperbola y = 1/x

Because the unit hyperbola is affinely equivalent to the hyperbola , an arbitrary hyperbola can be considered as the affine image (see previous section) of the hyperbola :
is the center of the hyperbola, the vectors have the directions of the asymptotes and is a point of the hyperbola. The tangent vector is At a vertex the tangent is perpendicular to the major axis. Hence and the parameter of a vertex is
is equivalent to and are the vertices of the hyperbola.
The following properties of a hyperbola are easily proven using the representation of a hyperbola introduced in this section.
Tangent construction

The tangent vector can be rewritten by factorization: This means that
the diagonal of the parallelogram is parallel to the tangent at the hyperbola point (see diagram).This property provides a way to construct the tangent at a point on the hyperbola.
This property of a hyperbola is an affine version of the 3-point-degeneration of Pascal's theorem.
- Area of the grey parallelogram
The area of the grey parallelogram in the above diagram is and hence independent of point . The last equation follows from a calculation for the case, where is a vertex and the hyperbola in its canonical form
Point construction

For a hyperbola with parametric representation (for simplicity the center is the origin) the following is true:
For any two points the pointsare collinear with the center of the hyperbola (see diagram).
The simple proof is a consequence of the equation .
This property provides a possibility to construct points of a hyperbola if the asymptotes and one point are given.
This property of a hyperbola is an affine version of the 4-point-degeneration of Pascal's theorem.
Tangent–asymptotes triangle

For simplicity the center of the hyperbola may be the origin and the vectors have equal length. If the last assumption is not fulfilled one can first apply a parameter transformation (see above) in order to make the assumption true. Hence are the vertices, span the minor axis and one gets and .
For the intersection points of the tangent at point with the asymptotes one gets the points The area of the triangle can be calculated by a 2 × 2 determinant: (see rules for determinants). is the area of the rhombus generated by . The area of a rhombus is equal to one half of the product of its diagonals. The diagonals are the semi-axes of the hyperbola. Hence:
The area of the triangle is independent of the point of the hyperbola:Reciprocation of a circle
The reciprocation of a circle B in a circle C always yields a conic section such as a hyperbola. The process of "reciprocation in a circle C" consists of replacing every line and point in a geometrical figure with their corresponding pole and polar, respectively. The pole of a line is the inversion of its closest point to the circle C, whereas the polar of a point is the converse, namely, a line whose closest point to C is the inversion of the point.
The eccentricity of the conic section obtained by reciprocation is the ratio of the distances between the two circles' centers to the radius r of reciprocation circle C. If B and C represent the points at the centers of the corresponding circles, then
Since the eccentricity of a hyperbola is always greater than one, the center B must lie outside of the reciprocating circle C.
This definition implies that the hyperbola is both the locus of the poles of the tangent lines to the circle B, as well as the envelope of the polar lines of the points on B. Conversely, the circle B is the envelope of polars of points on the hyperbola, and the locus of poles of tangent lines to the hyperbola. Two tangent lines to B have no (finite) poles because they pass through the center C of the reciprocation circle C; the polars of the corresponding tangent points on B are the asymptotes of the hyperbola. The two branches of the hyperbola correspond to the two parts of the circle B that are separated by these tangent points.
Quadratic equation
A hyperbola can also be defined as a second-degree equation in the Cartesian coordinates in the plane,
provided that the constants and satisfy the determinant condition
This determinant is conventionally called the discriminant of the conic section.
A special case of a hyperbola—the degenerate hyperbola consisting of two intersecting lines—occurs when another determinant is zero:
This determinant is sometimes called the discriminant of the conic section.
The general equation's coefficients can be obtained from known semi-major axis semi-minor axis center coordinates , and rotation angle (the angle from the positive horizontal axis to the hyperbola's major axis) using the formulae:
These expressions can be derived from the canonical equation
by a translation and rotation of the coordinates :
Given the above general parametrization of the hyperbola in Cartesian coordinates, the eccentricity can be found using the formula in Conic section#Eccentricity in terms of coefficients.
The center of the hyperbola may be determined from the formulae
In terms of new coordinates, and the defining equation of the hyperbola can be written
The principal axes of the hyperbola make an angle with the positive -axis that is given by
Rotating the coordinate axes so that the -axis is aligned with the transverse axis brings the equation into its canonical form
The major and minor semiaxes and are defined by the equations
where and are the roots of the quadratic equation
For comparison, the corresponding equation for a degenerate hyperbola (consisting of two intersecting lines) is
The tangent line to a given point on the hyperbola is defined by the equation
where and are defined by
The normal line to the hyperbola at the same point is given by the equation
The normal line is perpendicular to the tangent line, and both pass through the same point
From the equation
the left focus is and the right focus is where is the eccentricity. Denote the distances from a point to the left and right foci as and For a point on the right branch,
and for a point on the left branch,
This can be proved as follows:
If is a point on the hyperbola the distance to the left focal point is
To the right focal point the distance is
If is a point on the right branch of the hyperbola then and
Subtracting these equations one gets
If is a point on the left branch of the hyperbola then and
Subtracting these equations one gets
In Cartesian coordinates
Equation
If Cartesian coordinates are introduced such that the origin is the center of the hyperbola and the x-axis is the major axis, then the hyperbola is called east-west-opening and
- the foci are the points ,
- the vertices are .
For an arbitrary point the distance to the focus is and to the second focus . Hence the point is on the hyperbola if the following condition is fulfilled Remove the square roots by suitable squarings and use the relation to obtain the equation of the hyperbola:
This equation is called the canonical form of a hyperbola, because any hyperbola, regardless of its orientation relative to the Cartesian axes and regardless of the location of its center, can be transformed to this form by a change of variables, giving a hyperbola that is congruent to the original (see below).
The axes of symmetry or principal axes are the transverse axis (containing the segment of length 2a with endpoints at the vertices) and the conjugate axis (containing the segment of length 2b perpendicular to the transverse axis and with midpoint at the hyperbola's center). As opposed to an ellipse, a hyperbola has only two vertices: . The two points on the conjugate axes are not on the hyperbola.
It follows from the equation that the hyperbola is symmetric with respect to both of the coordinate axes and hence symmetric with respect to the origin.
Eccentricity
For a hyperbola in the above canonical form, the eccentricity is given by
Two hyperbolas are geometrically similar to each other – meaning that they have the same shape, so that one can be transformed into the other by rigid left and right movements, rotation, taking a mirror image, and scaling (magnification) – if and only if they have the same eccentricity.
Asymptotes


Solving the equation (above) of the hyperbola for yields It follows from this that the hyperbola approaches the two lines for large values of . These two lines intersect at the center (origin) and are called asymptotes of the hyperbola
With the help of the second figure one can see that
- The perpendicular distance from a focus to either asymptote is (the semi-minor axis).
From the Hesse normal form of the asymptotes and the equation of the hyperbola one gets:
- The product of the distances from a point on the hyperbola to both the asymptotes is the constant which can also be written in terms of the eccentricity e as
From the equation of the hyperbola (above) one can derive:
- The product of the slopes of lines from a point P to the two vertices is the constant
In addition, from (2) above it can be shown that
- The product of the distances from a point on the hyperbola to the asymptotes along lines parallel to the asymptotes is the constant
Semi-latus rectum
The length of the chord through one of the foci, perpendicular to the major axis of the hyperbola, is called the latus rectum. One half of it is the semi-latus rectum . A calculation shows The semi-latus rectum may also be viewed as the radius of curvature at the vertices.
Tangent
The simplest way to determine the equation of the tangent at a point is to implicitly differentiate the equation of the hyperbola. Denoting dy/dx as y′, this produces With respect to , the equation of the tangent at point is
A particular tangent line distinguishes the hyperbola from the other conic sections. Let f be the distance from the vertex V (on both the hyperbola and its axis through the two foci) to the nearer focus. Then the distance, along a line perpendicular to that axis, from that focus to a point P on the hyperbola is greater than 2f. The tangent to the hyperbola at P intersects that axis at point Q at an angle ∠PQV of greater than 45°.
Rectangular hyperbola
In the case the hyperbola is called rectangular (or equilateral), because its asymptotes intersect at right angles. For this case, the linear eccentricity is , the eccentricity and the semi-latus rectum . The graph of the equation is a rectangular hyperbola.
Parametric representation with hyperbolic sine/cosine
Using the hyperbolic sine and cosine functions , a parametric representation of the hyperbola can be obtained, which is similar to the parametric representation of an ellipse: which satisfies the Cartesian equation because
Further parametric representations are given in the section Parametric equations below.

Conjugate hyperbola
Main article: Conjugate hyperbolaFor the hyperbola , change the sign on the right to obtain the equation of the conjugate hyperbola:
- (which can also be written as ).
A hyperbola and its conjugate may have diameters which are conjugate. In the theory of special relativity, such diameters may represent axes of time and space, where one hyperbola represents events at a given spatial distance from the center, and the other represents events at a corresponding temporal distance from the center.
- and also specify conjugate hyperbolas.
In polar coordinates



Origin at the focus
The polar coordinates used most commonly for the hyperbola are defined relative to the Cartesian coordinate system that has its origin in a focus and its x-axis pointing toward the origin of the "canonical coordinate system" as illustrated in the first diagram.
In this case the angle is called true anomaly.
Relative to this coordinate system one has that
and
Origin at the center
With polar coordinates relative to the "canonical coordinate system" (see second diagram) one has that
For the right branch of the hyperbola the range of is
Eccentricity
When using polar coordinates, the eccentricity of the hyperbola can be expressed as where is the limit of the angular coordinate. As approaches this limit, r approaches infinity and the denominator in either of the equations noted above approaches zero, hence:
Parametric equations
A hyperbola with equation can be described by several parametric equations:
- Through hyperbolic trigonometric functions
- As a rational representation
- Through circular trigonometric functions
- With the tangent slope as parameter: A parametric representation, which uses the slope of the tangent at a point of the hyperbola can be obtained analogously to the ellipse case: Replace in the ellipse case by and use formulae for the hyperbolic functions. One gets Here, is the upper, and the lower half of the hyperbola. The points with vertical tangents (vertices ) are not covered by the representation. The equation of the tangent at point is This description of the tangents of a hyperbola is an essential tool for the determination of the orthoptic of a hyperbola.
Hyperbolic functions
Main article: Hyperbolic functions
Just as the trigonometric functions are defined in terms of the unit circle, so also the hyperbolic functions are defined in terms of the unit hyperbola, as shown in this diagram. In a unit circle, the angle (in radians) is equal to twice the area of the circular sector which that angle subtends. The analogous hyperbolic angle is likewise defined as twice the area of a hyperbolic sector.
Let be twice the area between the axis and a ray through the origin intersecting the unit hyperbola, and define as the coordinates of the intersection point. Then the area of the hyperbolic sector is the area of the triangle minus the curved region past the vertex at : which simplifies to the area hyperbolic cosine Solving for yields the exponential form of the hyperbolic cosine: From one gets and its inverse the area hyperbolic sine: Other hyperbolic functions are defined according to the hyperbolic cosine and hyperbolic sine, so for example
Properties
Reflection property

The tangent at a point bisects the angle between the lines This is called the optical property or reflection property of a hyperbola.
- Proof
Let be the point on the line with the distance to the focus (see diagram, is the semi major axis of the hyperbola). Line is the bisector of the angle between the lines . In order to prove that is the tangent line at point , one checks that any point on line which is different from cannot be on the hyperbola. Hence has only point in common with the hyperbola and is, therefore, the tangent at point .
From the diagram and the triangle inequality one recognizes that holds, which means: . But if is a point of the hyperbola, the difference should be .
Midpoints of parallel chords


The midpoints of parallel chords of a hyperbola lie on a line through the center (see diagram).
The points of any chord may lie on different branches of the hyperbola.
The proof of the property on midpoints is best done for the hyperbola . Because any hyperbola is an affine image of the hyperbola (see section below) and an affine transformation preserves parallelism and midpoints of line segments, the property is true for all hyperbolas:
For two points of the hyperbola
- the midpoint of the chord is
- the slope of the chord is
For parallel chords the slope is constant and the midpoints of the parallel chords lie on the line
Consequence: for any pair of points of a chord there exists a skew reflection with an axis (set of fixed points) passing through the center of the hyperbola, which exchanges the points and leaves the hyperbola (as a whole) fixed. A skew reflection is a generalization of an ordinary reflection across a line , where all point-image pairs are on a line perpendicular to .
Because a skew reflection leaves the hyperbola fixed, the pair of asymptotes is fixed, too. Hence the midpoint of a chord divides the related line segment between the asymptotes into halves, too. This means that . This property can be used for the construction of further points of the hyperbola if a point and the asymptotes are given.
If the chord degenerates into a tangent, then the touching point divides the line segment between the asymptotes in two halves.
Orthogonal tangents – orthoptic

For a hyperbola the intersection points of orthogonal tangents lie on the circle .
This circle is called the orthoptic of the given hyperbola.
The tangents may belong to points on different branches of the hyperbola.
In case of there are no pairs of orthogonal tangents.
Pole-polar relation for a hyperbola

Any hyperbola can be described in a suitable coordinate system by an equation . The equation of the tangent at a point of the hyperbola is If one allows point to be an arbitrary point different from the origin, then
- point is mapped onto the line , not through the center of the hyperbola.
This relation between points and lines is a bijection.
The inverse function maps
- line onto the point and
- line onto the point
Such a relation between points and lines generated by a conic is called pole-polar relation or just polarity. The pole is the point, the polar the line. See Pole and polar.
By calculation one checks the following properties of the pole-polar relation of the hyperbola:
- For a point (pole) on the hyperbola the polar is the tangent at this point (see diagram: ).
- For a pole outside the hyperbola the intersection points of its polar with the hyperbola are the tangency points of the two tangents passing (see diagram: ).
- For a point within the hyperbola the polar has no point with the hyperbola in common. (see diagram: ).
Remarks:
- The intersection point of two polars (for example: ) is the pole of the line through their poles (here: ).
- The foci and respectively and the directrices and respectively belong to pairs of pole and polar.
Pole-polar relations exist for ellipses and parabolas, too.
Other properties
- The following are concurrent: (1) a circle passing through the hyperbola's foci and centered at the hyperbola's center; (2) either of the lines that are tangent to the hyperbola at the vertices; and (3) either of the asymptotes of the hyperbola.
- The following are also concurrent: (1) the circle that is centered at the hyperbola's center and that passes through the hyperbola's vertices; (2) either directrix; and (3) either of the asymptotes.
- Since both the transverse axis and the conjugate axis are axes of symmetry, the symmetry group of a hyperbola is the Klein four-group.
- The rectangular hyperbolas xy = constant admit group actions by squeeze mappings which have the hyperbolas as invariant sets.
Arc length
The arc length of a hyperbola does not have an elementary expression. The upper half of a hyperbola can be parameterized as
Then the integral giving the arc length from to can be computed as:
After using the substitution , this can also be represented using the incomplete elliptic integral of the second kind with parameter :
Using only real numbers, this becomes
where is the incomplete elliptic integral of the first kind with parameter and is the Gudermannian function.
Derived curves

Several other curves can be derived from the hyperbola by inversion, the so-called inverse curves of the hyperbola. If the center of inversion is chosen as the hyperbola's own center, the inverse curve is the lemniscate of Bernoulli; the lemniscate is also the envelope of circles centered on a rectangular hyperbola and passing through the origin. If the center of inversion is chosen at a focus or a vertex of the hyperbola, the resulting inverse curves are a limaçon or a strophoid, respectively.
Elliptic coordinates
A family of confocal hyperbolas is the basis of the system of elliptic coordinates in two dimensions. These hyperbolas are described by the equation
where the foci are located at a distance c from the origin on the x-axis, and where θ is the angle of the asymptotes with the x-axis. Every hyperbola in this family is orthogonal to every ellipse that shares the same foci. This orthogonality may be shown by a conformal map of the Cartesian coordinate system w = z + 1/z, where z= x + iy are the original Cartesian coordinates, and w=u + iv are those after the transformation.
Other orthogonal two-dimensional coordinate systems involving hyperbolas may be obtained by other conformal mappings. For example, the mapping w = z transforms the Cartesian coordinate system into two families of orthogonal hyperbolas.
Conic section analysis of the hyperbolic appearance of circles

As images of the circles one gets a circle (magenta), ellipses, hyperbolas and lines. The special case of a parabola does not appear in this example.
(If center O were on the sphere, all images of the circles would be circles or lines; see stereographic projection).
Besides providing a uniform description of circles, ellipses, parabolas, and hyperbolas, conic sections can also be understood as a natural model of the geometry of perspective in the case where the scene being viewed consists of circles, or more generally an ellipse. The viewer is typically a camera or the human eye and the image of the scene a central projection onto an image plane, that is, all projection rays pass a fixed point O, the center. The lens plane is a plane parallel to the image plane at the lens O.
The image of a circle c is
- a circle, if circle c is in a special position, for example parallel to the image plane and others (see stereographic projection),
- an ellipse, if c has no point with the lens plane in common,
- a parabola, if c has one point with the lens plane in common and
- a hyperbola, if c has two points with the lens plane in common.
(Special positions where the circle plane contains point O are omitted.)
These results can be understood if one recognizes that the projection process can be seen in two steps: 1) circle c and point O generate a cone which is 2) cut by the image plane, in order to generate the image.
One sees a hyperbola whenever catching sight of a portion of a circle cut by one's lens plane. The inability to see very much of the arms of the visible branch, combined with the complete absence of the second branch, makes it virtually impossible for the human visual system to recognize the connection with hyperbolas.
Applications


Sundials
Hyperbolas may be seen in many sundials. On any given day, the sun revolves in a circle on the celestial sphere, and its rays striking the point on a sundial traces out a cone of light. The intersection of this cone with the horizontal plane of the ground forms a conic section. At most populated latitudes and at most times of the year, this conic section is a hyperbola. In practical terms, the shadow of the tip of a pole traces out a hyperbola on the ground over the course of a day (this path is called the declination line). The shape of this hyperbola varies with the geographical latitude and with the time of the year, since those factors affect the cone of the sun's rays relative to the horizon. The collection of such hyperbolas for a whole year at a given location was called a pelekinon by the Greeks, since it resembles a double-bladed axe.
Multilateration
A hyperbola is the basis for solving multilateration problems, the task of locating a point from the differences in its distances to given points — or, equivalently, the difference in arrival times of synchronized signals between the point and the given points. Such problems are important in navigation, particularly on water; a ship can locate its position from the difference in arrival times of signals from a LORAN or GPS transmitters. Conversely, a homing beacon or any transmitter can be located by comparing the arrival times of its signals at two separate receiving stations; such techniques may be used to track objects and people. In particular, the set of possible positions of a point that has a distance difference of 2a from two given points is a hyperbola of vertex separation 2a whose foci are the two given points.
Path followed by a particle
The path followed by any particle in the classical Kepler problem is a conic section. In particular, if the total energy E of the particle is greater than zero (that is, if the particle is unbound), the path of such a particle is a hyperbola. This property is useful in studying atomic and sub-atomic forces by scattering high-energy particles; for example, the Rutherford experiment demonstrated the existence of an atomic nucleus by examining the scattering of alpha particles from gold atoms. If the short-range nuclear interactions are ignored, the atomic nucleus and the alpha particle interact only by a repulsive Coulomb force, which satisfies the inverse square law requirement for a Kepler problem.
Korteweg–de Vries equation
The hyperbolic trig function appears as one solution to the Korteweg–de Vries equation which describes the motion of a soliton wave in a canal.
Angle trisection

As shown first by Apollonius of Perga, a hyperbola can be used to trisect any angle, a well studied problem of geometry. Given an angle, first draw a circle centered at its vertex O, which intersects the sides of the angle at points A and B. Next draw the line segment with endpoints A and B and its perpendicular bisector . Construct a hyperbola of eccentricity e=2 with as directrix and B as a focus. Let P be the intersection (upper) of the hyperbola with the circle. Angle POB trisects angle AOB.
To prove this, reflect the line segment OP about the line obtaining the point P' as the image of P. Segment AP' has the same length as segment BP due to the reflection, while segment PP' has the same length as segment BP due to the eccentricity of the hyperbola. As OA, OP', OP and OB are all radii of the same circle (and so, have the same length), the triangles OAP', OPP' and OPB are all congruent. Therefore, the angle has been trisected, since 3×POB = AOB.
Efficient portfolio frontier
In portfolio theory, the locus of mean-variance efficient portfolios (called the efficient frontier) is the upper half of the east-opening branch of a hyperbola drawn with the portfolio return's standard deviation plotted horizontally and its expected value plotted vertically; according to this theory, all rational investors would choose a portfolio characterized by some point on this locus.
Biochemistry
In biochemistry and pharmacology, the Hill equation and Hill-Langmuir equation respectively describe biological responses and the formation of protein–ligand complexes as functions of ligand concentration. They are both rectangular hyperbolae.
Hyperbolas as plane sections of quadrics
Hyperbolas appear as plane sections of the following quadrics:
- Elliptic cone
- Hyperbolic cylinder
- Hyperbolic paraboloid
- Hyperboloid of one sheet
- Hyperboloid of two sheets
-
 Elliptic cone
Elliptic cone
-
 Hyperbolic cylinder
Hyperbolic cylinder
-
 Hyperbolic paraboloid
Hyperbolic paraboloid
-
 Hyperboloid of one sheet
Hyperboloid of one sheet
-
 Hyperboloid of two sheets
Hyperboloid of two sheets
See also
Other conic sections
Other related topics
- Elliptic coordinates, an orthogonal coordinate system based on families of ellipses and hyperbolas.
- Hyperbolic growth
- Hyperbolic partial differential equation
- Hyperbolic sector
- Hyperboloid structure
- Hyperbolic trajectory
- Hyperboloid
- Multilateration
- Rotation of axes
- Translation of axes
- Unit hyperbola
Notes
- ^ Oakley 1944, p. 17.
- Heath, Sir Thomas Little (1896), "Chapter I. The discovery of conic sections. Menaechmus", Apollonius of Perga: Treatise on Conic Sections with Introductions Including an Essay on Earlier History on the Subject, Cambridge University Press, pp. xvii–xxx.
- Boyer, Carl B.; Merzbach, Uta C. (2011), A History of Mathematics, Wiley, p. 73, ISBN 9780470630563,
It was Apollonius (possibly following up a suggestion of Archimedes) who introduced the names "ellipse" and "hyperbola" in connection with these curves.
- Eves, Howard (1963), A Survey of Geometry (Vol. One), Allyn and Bacon, pp. 30–31
- Protter & Morrey 1970, pp. 308–310.
- ^ Protter & Morrey 1970, p. 310.
- Apostol, Tom M.; Mnatsakanian, Mamikon A. (2012), New Horizons in Geometry, The Dolciani Mathematical Expositions #47, The Mathematical Association of America, p. 251, ISBN 978-0-88385-354-2
- The German term for this circle is Leitkreis which can be translated as "Director circle", but that term has a different meaning in the English literature (see Director circle).
- Frans van Schooten: Mathematische Oeffeningen, Leyden, 1659, p. 327
- E. Hartmann: Lecture Note Planar Circle Geometries, an Introduction to Möbius-, Laguerre- and Minkowski Planes, p. 93
- W. Benz: Vorlesungen über Geomerie der Algebren, Springer (1973)
- Lecture Note Planar Circle Geometries, an Introduction to Moebius-, Laguerre- and Minkowski Planes, S. 33, (PDF; 757 kB)
- Lecture Note Planar Circle Geometries, an Introduction to Moebius-, Laguerre- and Minkowski Planes, S. 32, (PDF; 757 kB)
- Fanchi, John R. (2006). Math refresher for scientists and engineers. John Wiley and Sons. Section 3.2, pages 44–45. ISBN 0-471-75715-2.
- Korn, Granino A; Korn, Theresa M. (2000). Mathematical Handbook for Scientists and Engineers: Definitions, Theorems, and Formulas for Reference and Review (second ed.). Dover Publ. p. 40.
- Protter & Morrey 1970, pp. APP-29–APP-30.
- ^ Mitchell, Douglas W., "A property of hyperbolas and their asymptotes", Mathematical Gazette 96, July 2012, 299–301.
- J. W. Downs, Practical Conic Sections, Dover Publ., 2003 (orig. 1993): p. 26.
- Casey, John, (1885) "A treatise on the analytical geometry of the point, line, circle, and conic sections, containing an account of its most recent extensions, with numerous examples"
- Coffman, R. T.; Ogilvy, C. S. (1963), "The 'Reflection Property' of the Conics", Mathematics Magazine, 36 (1): 11–12, doi:10.1080/0025570X.1963.11975375, JSTOR 2688124 Flanders, Harley (1968), "The Optical Property of the Conics", American Mathematical Monthly, 75 (4): 399, doi:10.1080/00029890.1968.11970997, JSTOR 2313439
Brozinsky, Michael K. (1984), "Reflection Property of the Ellipse and the Hyperbola", College Mathematics Journal, 15 (2): 140–42, doi:10.1080/00494925.1984.11972763 (inactive 2024-12-16), JSTOR 2686519
{{citation}}: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of December 2024 (link) - "Hyperbola". Mathafou.free.fr. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 26 August 2018.
- ^ "Properties of a Hyperbola". Archived from the original on 2017-02-02. Retrieved 2011-06-22.
- Carlson, B. C. (2010), "Elliptic Integrals", in Olver, Frank W. J.; Lozier, Daniel M.; Boisvert, Ronald F.; Clark, Charles W. (eds.), NIST Handbook of Mathematical Functions, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-19225-5, MR 2723248.
- Heilbron, John L. (1968). "The Scattering of α and β Particles and Rutherford's Atom". Archive for History of Exact Sciences. 4 (4): 247–307. doi:10.1007/BF00411591. JSTOR 41133273.
- Since 2 times the distance of P to is PP' which is equal to BP by directrix-focus property
- This construction is due to Pappus of Alexandria (circa 300 A.D.) and the proof comes from Kazarinoff 1970, p. 62.
References
- Kazarinoff, Nicholas D. (1970), Ruler and the Round, Boston: Prindle, Weber & Schmidt, ISBN 0-87150-113-9
- Oakley, C. O. (1944), An Outline of the Calculus, New York: Barnes & Noble
- Protter, Murray H.; Morrey, Charles B. Jr. (1970), College Calculus with Analytic Geometry (2nd ed.), Reading: Addison-Wesley, LCCN 76087042
External links
- "Hyperbola", Encyclopedia of Mathematics, EMS Press, 2001
- Apollonius' Derivation of the Hyperbola at Convergence
- Mathematische Oeffeningen, Frans van Schooten, 1659
- Weisstein, Eric W. "Hyperbola". MathWorld.
 In practical applications, a hyperbola can arise as the path followed by the shadow of the tip of a
In practical applications, a hyperbola can arise as the path followed by the shadow of the tip of a  the asymptotes are the two
the asymptotes are the two  of the set, the absolute difference of the distances
of the set, the absolute difference of the distances  to two fixed points
to two fixed points  (the foci) is constant, usually denoted by
(the foci) is constant, usually denoted by  :
:

 of the line segment joining the foci is called the center of the hyperbola. The line through the foci is called the major axis. It contains the vertices
of the line segment joining the foci is called the center of the hyperbola. The line through the foci is called the major axis. It contains the vertices  , which have distance
, which have distance  to the center. The distance
to the center. The distance  of the foci to the center is called the focal distance or linear eccentricity. The quotient
of the foci to the center is called the focal distance or linear eccentricity. The quotient  is the eccentricity
is the eccentricity  .
.
 can be viewed in a different way (see diagram):
can be viewed in a different way (see diagram): is the circle with midpoint
is the circle with midpoint  and radius
and radius  , then the distance of a point
, then the distance of a point  :
:

 with the coordinate axes as asymptotes
with the coordinate axes as asymptotes and new coordinates
and new coordinates  are assigned, then
are assigned, then  .
. (whose
(whose  .
Solving for
.
Solving for  yields
yields 
 with equation
with equation
 is a rectangular hyperbola entirely in the first and third
is a rectangular hyperbola entirely in the first and third  as major axis ,
as major axis , and the semi-axis
and the semi-axis 


 and the eccentricity
and the eccentricity 
 at point
at point 
 results in a rectangular hyperbola entirely in the second and fourth quadrants, with the same asymptotes, center, semi-latus rectum, radius of curvature at the vertices, linear eccentricity, and eccentricity as for the case of
results in a rectangular hyperbola entirely in the second and fourth quadrants, with the same asymptotes, center, semi-latus rectum, radius of curvature at the vertices, linear eccentricity, and eccentricity as for the case of 
 as major axis,
as major axis,
 so that the new center is
so that the new center is  , yields the new equation
, yields the new equation
 and the new asymptotes are
and the new asymptotes are  and
and  . The shape parameters
. The shape parameters  remain unchanged.
remain unchanged.
 from the center and parallel to the minor axis are called directrices of the hyperbola (see diagram).
from the center and parallel to the minor axis are called directrices of the hyperbola (see diagram).
 The proof for the pair
The proof for the pair  follows from the fact that
follows from the fact that  and
and  satisfy the equation
satisfy the equation
 The second case is proven analogously.
The second case is proven analogously.
 (focus), any line
(focus), any line  (directrix) not through
(directrix) not through  the set of points (locus of points), for which the quotient of the distances to the point and to the line is
the set of points (locus of points), for which the quotient of the distances to the point and to the line is  is a hyperbola.
is a hyperbola.
 yields a
yields a  an
an  and assume
and assume  . With
. With  , the relation
, the relation  produces the equations
produces the equations
 and
and 
 yields
yields
 This is the equation of an ellipse (
This is the equation of an ellipse ( so that
so that  , and then the equation above becomes
, and then the equation above becomes
 which is the equation of a hyperbola with center
which is the equation of a hyperbola with center  , the x-axis as major axis and the major/minor semi axis
, the x-axis as major axis and the major/minor semi axis  point
point  of directrix
of directrix  (see diagram) and focus
(see diagram) and focus  (in diagram green). Hence point
(in diagram green). Hence point  can be constructed using the
can be constructed using the  through point
through point  , which are spheres that touch the cone along circles
, which are spheres that touch the cone along circles  ,
,  and circle
and circle  .
. and
and  are tangential to the sphere
are tangential to the sphere  and, hence, are of equal length.
and, hence, are of equal length. and
and  are tangential to the sphere
are tangential to the sphere  and, hence, are of equal length.
and, hence, are of equal length. is independent of the hyperbola point
is independent of the hyperbola point  have to be on circles
have to be on circles  has to cross the apex. Therefore, as point
has to cross the apex. Therefore, as point  simply rotates about apex without changing its length.
simply rotates about apex without changing its length. .
. (see the definition of a hyperbola by circular directrices).
(see the definition of a hyperbola by circular directrices). of lines at two points
of lines at two points  (all lines containing
(all lines containing  and
and  , respectively) and a projective but not perspective mapping
, respectively) and a projective but not perspective mapping  of
of  onto
onto  , then the intersection points of corresponding lines form a non-degenerate projective conic section.
, then the intersection points of corresponding lines form a non-degenerate projective conic section.
 one uses the pencils at the vertices
one uses the pencils at the vertices  be a point of the hyperbola and
be a point of the hyperbola and  . The line segment
. The line segment  is divided into n equally-spaced segments and this division is projected parallel with the diagonal
is divided into n equally-spaced segments and this division is projected parallel with the diagonal  (see diagram). The parallel projection is part of the projective mapping between the pencils at
(see diagram). The parallel projection is part of the projective mapping between the pencils at  and
and  needed. The intersection points of any two related lines
needed. The intersection points of any two related lines  and
and  are points of the uniquely defined hyperbola.
are points of the uniquely defined hyperbola.
 is uniquely determined by three points
is uniquely determined by three points  with different x- and y-coordinates. A simple way to determine the shape parameters
with different x- and y-coordinates. A simple way to determine the shape parameters  uses the inscribed angle theorem for hyperbolas:
uses the inscribed angle theorem for hyperbolas:
 in this context one uses the quotient
in this context one uses the quotient

 (see diagram) the following statement is true:
(see diagram) the following statement is true:
 if and only if the angles at
if and only if the angles at  and
and  are equal in the sense of the measurement above. That means if
are equal in the sense of the measurement above. That means if 
 .
.
 is the solution of the equation
is the solution of the equation  for
for  .
.
 .
.
 , where
, where  is an arbitrary vector. If
is an arbitrary vector. If  are the column vectors of the matrix
are the column vectors of the matrix  is mapped onto the hyperbola
is mapped onto the hyperbola

 a point of the hyperbola and
a point of the hyperbola and  a tangent vector at this point.
a tangent vector at this point.
 are not the vertices of the hyperbola. But
are not the vertices of the hyperbola. But  point into the directions of the asymptotes. The tangent vector at point
point into the directions of the asymptotes. The tangent vector at point  is
is
 Because at a vertex the tangent is perpendicular to the major axis of the hyperbola one gets the parameter
Because at a vertex the tangent is perpendicular to the major axis of the hyperbola one gets the parameter  of a vertex from the equation
of a vertex from the equation
 and hence from
and hence from
 which yields
which yields

 ,
,  , and
, and  were used.
were used.

 by
by  , one gets the implicit representation
, one gets the implicit representation

 to be vectors in space.
to be vectors in space.
 , an arbitrary hyperbola can be considered as the affine image (see previous section) of the hyperbola
, an arbitrary hyperbola can be considered as the affine image (see previous section) of the hyperbola  :
:

 is the center of the hyperbola, the vectors
is the center of the hyperbola, the vectors  is a point of the hyperbola. The tangent vector is
is a point of the hyperbola. The tangent vector is
 At a vertex the tangent is perpendicular to the major axis. Hence
At a vertex the tangent is perpendicular to the major axis. Hence
 and the parameter of a vertex is
and the parameter of a vertex is

 is equivalent to
is equivalent to  and
and  are the vertices of the hyperbola.
are the vertices of the hyperbola.
 This means that
This means that
 is parallel to the tangent at the hyperbola point
is parallel to the tangent at the hyperbola point  in the above diagram is
in the above diagram is
 and hence independent of point
and hence independent of point 
 (for simplicity the center is the origin) the following is true:
(for simplicity the center is the origin) the following is true:
 the points
the points

 .
.
 are the vertices,
are the vertices,  span the minor axis and one gets
span the minor axis and one gets  and
and  .
.
 with the asymptotes one gets the points
with the asymptotes one gets the points
 The
The  can be calculated by a 2 × 2 determinant:
can be calculated by a 2 × 2 determinant:
 (see rules for
(see rules for  is the area of the rhombus generated by
is the area of the rhombus generated by  is independent of the point of the hyperbola:
is independent of the point of the hyperbola: 

 in the
in the 




 and
and  satisfy the determinant condition
satisfy the determinant condition


 is sometimes called the discriminant of the conic section.
is sometimes called the discriminant of the conic section.
 semi-minor axis
semi-minor axis  center coordinates
center coordinates  , and rotation angle
, and rotation angle  (the angle from the positive horizontal axis to the hyperbola's major axis) using the formulae:
(the angle from the positive horizontal axis to the hyperbola's major axis) using the formulae:



 of the hyperbola may be determined from the formulae
of the hyperbola may be determined from the formulae

 and
and  the defining equation of the hyperbola can be written
the defining equation of the hyperbola can be written

 with the positive
with the positive  -axis that is given by
-axis that is given by


 are defined by the equations
are defined by the equations

 and
and  are the
are the 

 on the hyperbola is defined by the equation
on the hyperbola is defined by the equation


 and
and  are defined by
are defined by




 and the right focus is
and the right focus is  where
where  and
and  For a point on the right branch,
For a point on the right branch,




 and
and


 and
and

 ,
, .
. is
is  and to the second focus
and to the second focus  . Hence the point
. Hence the point  Remove the square roots by suitable squarings and use the relation
Remove the square roots by suitable squarings and use the relation  to obtain the equation of the hyperbola:
to obtain the equation of the hyperbola:

 . The two points
. The two points  on the conjugate axes are not on the hyperbola.
on the conjugate axes are not on the hyperbola.

 yields
yields
 It follows from this that the hyperbola approaches the two lines
It follows from this that the hyperbola approaches the two lines
 for large values of
for large values of  . These two lines intersect at the center (origin) and are called asymptotes of the hyperbola
. These two lines intersect at the center (origin) and are called asymptotes of the hyperbola 
 The perpendicular distance from a focus to either asymptote is
The perpendicular distance from a focus to either asymptote is  of the asymptotes and the equation of the hyperbola one gets:
of the asymptotes and the equation of the hyperbola one gets:
 The product of the distances from a point on the hyperbola to both the asymptotes is the constant
The product of the distances from a point on the hyperbola to both the asymptotes is the constant  which can also be written in terms of the eccentricity e as
which can also be written in terms of the eccentricity e as 
 of the hyperbola (above) one can derive:
of the hyperbola (above) one can derive:
 The product of the slopes of lines from a point P to the two vertices is the constant
The product of the slopes of lines from a point P to the two vertices is the constant 
 The product of the distances from a point on the hyperbola to the asymptotes along lines parallel to the asymptotes is the constant
The product of the distances from a point on the hyperbola to the asymptotes along lines parallel to the asymptotes is the constant 
 . A calculation shows
. A calculation shows
 The semi-latus rectum
The semi-latus rectum  With respect to
With respect to  , the equation of the tangent at point
, the equation of the tangent at point 
 the hyperbola is called rectangular (or equilateral), because its asymptotes intersect at right angles. For this case, the linear eccentricity is
the hyperbola is called rectangular (or equilateral), because its asymptotes intersect at right angles. For this case, the linear eccentricity is  , the eccentricity
, the eccentricity  and the semi-latus rectum
and the semi-latus rectum  . The graph of the equation
. The graph of the equation  , a parametric representation of the hyperbola
, a parametric representation of the hyperbola  which satisfies the Cartesian equation because
which satisfies the Cartesian equation because 
 , change the sign on the right to obtain the equation of the conjugate hyperbola:
, change the sign on the right to obtain the equation of the conjugate hyperbola:
 (which can also be written as
(which can also be written as  ).
). and
and  also specify conjugate hyperbolas.
also specify conjugate hyperbolas.




 where
where  is the limit of the angular coordinate. As
is the limit of the angular coordinate. As 





 of the tangent at a point of the hyperbola can be obtained analogously to the ellipse case: Replace in the ellipse case
of the tangent at a point of the hyperbola can be obtained analogously to the ellipse case: Replace in the ellipse case  by
by  and use formulae for the
and use formulae for the  Here,
Here,  is the upper, and
is the upper, and  the lower half of the hyperbola. The points with vertical tangents (vertices
the lower half of the hyperbola. The points with vertical tangents (vertices  ) are not covered by the representation. The equation of the tangent at point
) are not covered by the representation. The equation of the tangent at point  is
is  This description of the tangents of a hyperbola is an essential tool for the determination of the
This description of the tangents of a hyperbola is an essential tool for the determination of the  at the point
at the point  , where
, where  as the coordinates of the intersection point.
Then the area of the hyperbolic sector is the area of the triangle minus the curved region past the vertex at
as the coordinates of the intersection point.
Then the area of the hyperbolic sector is the area of the triangle minus the curved region past the vertex at  :
:
 which simplifies to the
which simplifies to the  Solving for
Solving for  From
From  and its inverse the
and its inverse the  Other hyperbolic functions are defined according to the hyperbolic cosine and hyperbolic sine, so for example
Other hyperbolic functions are defined according to the hyperbolic cosine and hyperbolic sine, so for example

 This is called the optical property or reflection property of a hyperbola.
This is called the optical property or reflection property of a hyperbola.
 be the point on the line
be the point on the line  is the bisector of the angle between the lines
is the bisector of the angle between the lines  . In order to prove that
. In order to prove that  on line
on line  holds, which means:
holds, which means:  . But if
. But if  of the hyperbola
of the hyperbola 


 of a chord there exists a skew reflection with an axis (set of fixed points) passing through the center of the hyperbola, which exchanges the points
of a chord there exists a skew reflection with an axis (set of fixed points) passing through the center of the hyperbola, which exchanges the points  divides the related line segment
divides the related line segment  between the asymptotes into halves, too. This means that
between the asymptotes into halves, too. This means that  . This property can be used for the construction of further points
. This property can be used for the construction of further points  the intersection points of orthogonal tangents lie on the circle
the intersection points of orthogonal tangents lie on the circle  .
.  there are no pairs of orthogonal tangents.
there are no pairs of orthogonal tangents.
 of the hyperbola is
of the hyperbola is  If one allows point
If one allows point  is mapped onto the line
is mapped onto the line  , not through the center of the hyperbola.
, not through the center of the hyperbola. onto the point
onto the point  and
and onto the point
onto the point 
 ).
). ).
). ).
). ) is the pole of the line through their poles (here:
) is the pole of the line through their poles (here:  ).
). and
and  respectively and the directrices
respectively and the directrices  and
and  respectively belong to pairs of pole and polar.
respectively belong to pairs of pole and polar.
 from
from  to
to  can be computed as:
can be computed as:

 , this can also be represented using the
, this can also be represented using the  with parameter
with parameter  :
:


 is the
is the 
 appears as one solution to the
appears as one solution to the  . Construct a hyperbola of
. Construct a hyperbola of