| This article's factual accuracy may be compromised due to out-of-date information. Please help update this article to reflect recent events or newly available information. (March 2017) |
| Flynn's taxonomy |
|---|
| Single data stream |
| Multiple data streams |
| SIMD subcategories |
| See also |

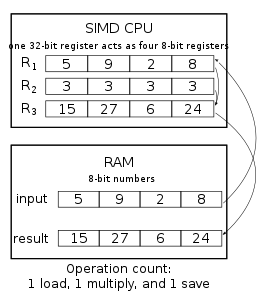
Single instruction, multiple data (SIMD) is a type of parallel processing in Flynn's taxonomy. SIMD can be internal (part of the hardware design) and it can be directly accessible through an instruction set architecture (ISA), but it should not be confused with an ISA. SIMD describes computers with multiple processing elements that perform the same operation on multiple data points simultaneously.
Such machines exploit data level parallelism, but not concurrency: there are simultaneous (parallel) computations, but each unit performs the exact same instruction at any given moment (just with different data). SIMD is particularly applicable to common tasks such as adjusting the contrast in a digital image or adjusting the volume of digital audio. Most modern CPU designs include SIMD instructions to improve the performance of multimedia use. SIMD has three different subcategories in Flynn's 1972 Taxonomy, one of which is SIMT. SIMT should not be confused with software threads or hardware threads, both of which are task time-sharing (time-slicing). SIMT is true simultaneous parallel hardware-level execution.
Each hardware element(PU) working on individual data item sometimes also referred as SIMD lane or channel. Modern graphics processing units (GPUs) are often wide SIMD(typically >16 data lanes or channel) implementations.
History
The first use of SIMD instructions was in the ILLIAC IV, which was completed in 1966.
SIMD was the basis for vector supercomputers of the early 1970s such as the CDC Star-100 and the Texas Instruments ASC, which could operate on a "vector" of data with a single instruction. Vector processing was especially popularized by Cray in the 1970s and 1980s. Vector processing architectures are now considered separate from SIMD computers: Duncan's Taxonomy includes them whereas Flynn's Taxonomy does not, due to Flynn's work (1966, 1972) pre-dating the Cray-1 (1977).
The first era of modern SIMD computers was characterized by massively parallel processing-style supercomputers such as the Thinking Machines CM-1 and CM-2. These computers had many limited-functionality processors that would work in parallel. For example, each of 65,536 single-bit processors in a Thinking Machines CM-2 would execute the same instruction at the same time, allowing, for instance, to logically combine 65,536 pairs of bits at a time, using a hypercube-connected network or processor-dedicated RAM to find its operands. Supercomputing moved away from the SIMD approach when inexpensive scalar MIMD approaches based on commodity processors such as the Intel i860 XP became more powerful, and interest in SIMD waned.
The current era of SIMD processors grew out of the desktop-computer market rather than the supercomputer market. As desktop processors became powerful enough to support real-time gaming and audio/video processing during the 1990s, demand grew for this particular type of computing power, and microprocessor vendors turned to SIMD to meet the demand. Hewlett-Packard introduced MAX instructions into PA-RISC 1.1 desktops in 1994 to accelerate MPEG decoding. Sun Microsystems introduced SIMD integer instructions in its "VIS" instruction set extensions in 1995, in its UltraSPARC I microprocessor. MIPS followed suit with their similar MDMX system.
The first widely deployed desktop SIMD was with Intel's MMX extensions to the x86 architecture in 1996. This sparked the introduction of the much more powerful AltiVec system in the Motorola PowerPC and IBM's POWER systems. Intel responded in 1999 by introducing the all-new SSE system. Since then, there have been several extensions to the SIMD instruction sets for both architectures. Advanced vector extensions AVX, AVX2 and AVX-512 are developed by Intel. AMD supports AVX, AVX2, and AVX-512 in their current products.
All of these developments have been oriented toward support for real-time graphics, and are therefore oriented toward processing in two, three, or four dimensions, usually with vector lengths of between two and sixteen words, depending on data type and architecture. When new SIMD architectures need to be distinguished from older ones, the newer architectures are then considered "short-vector" architectures, as earlier SIMD and vector supercomputers had vector lengths from 64 to 64,000. A modern supercomputer is almost always a cluster of MIMD computers, each of which implements (short-vector) SIMD instructions.
Advantages
An application that may take advantage of SIMD is one where the same value is being added to (or subtracted from) a large number of data points, a common operation in many multimedia applications. One example would be changing the brightness of an image. Each pixel of an image consists of three values for the brightness of the red (R), green (G) and blue (B) portions of the color. To change the brightness, the R, G and B values are read from memory, a value is added to (or subtracted from) them, and the resulting values are written back out to memory. Audio DSPs would likewise, for volume control, multiply both Left and Right channels simultaneously.
With a SIMD processor there are two improvements to this process. For one the data is understood to be in blocks, and a number of values can be loaded all at once. Instead of a series of instructions saying "retrieve this pixel, now retrieve the next pixel", a SIMD processor will have a single instruction that effectively says "retrieve n pixels" (where n is a number that varies from design to design). For a variety of reasons, this can take much less time than retrieving each pixel individually, as with a traditional CPU design.
Another advantage is that the instruction operates on all loaded data in a single operation. In other words, if the SIMD system works by loading up eight data points at once, the add operation being applied to the data will happen to all eight values at the same time. This parallelism is separate from the parallelism provided by a superscalar processor; the eight values are processed in parallel even on a non-superscalar processor, and a superscalar processor may be able to perform multiple SIMD operations in parallel.
Disadvantages
- Not all algorithms can be vectorized easily. For example, a flow-control-heavy task like code parsing may not easily benefit from SIMD; however, it is theoretically possible to vectorize comparisons and "batch flow" to target maximal cache optimality, though this technique will require more intermediate state. Note: Batch-pipeline systems (example: GPUs or software rasterization pipelines) are most advantageous for cache control when implemented with SIMD intrinsics, but they are not exclusive to SIMD features. Further complexity may be apparent to avoid dependence within series such as code strings; while independence is required for vectorization.
- Large register files which increases power consumption and required chip area.
- Currently, implementing an algorithm with SIMD instructions usually requires human labor; most compilers do not generate SIMD instructions from a typical C program, for instance. Automatic vectorization in compilers is an active area of computer science research. (Compare vector processing.)
- Programming with particular SIMD instruction sets can involve numerous low-level challenges.
- SIMD may have restrictions on data alignment; programmers familiar with one particular architecture may not expect this. Worse: the alignment may change from one revision or "compatible" processor to another.
- Gathering data into SIMD registers and scattering it to the correct destination locations is tricky (sometimes requiring permute operations) and can be inefficient.
- Specific instructions like rotations or three-operand addition are not available in some SIMD instruction sets.
- Instruction sets are architecture-specific: some processors lack SIMD instructions entirely, so programmers must provide non-vectorized implementations (or different vectorized implementations) for them.
- Different architectures provide different register sizes (e.g. 64, 128, 256 and 512 bits) and instruction sets, meaning that programmers must provide multiple implementations of vectorized code to operate optimally on any given CPU. In addition, the possible set of SIMD instructions grows with each new register size. Unfortunately, for legacy support reasons, the older versions cannot be retired.
- The early MMX instruction set shared a register file with the floating-point stack, which caused inefficiencies when mixing floating-point and MMX code. However, SSE2 corrects this.
To remedy problems 1 and 5, RISC-V's vector extension uses an alternative approach: instead of exposing the sub-register-level details to the programmer, the instruction set abstracts them out as a few "vector registers" that use the same interfaces across all CPUs with this instruction set. The hardware handles all alignment issues and "strip-mining" of loops. Machines with different vector sizes would be able to run the same code. LLVM calls this vector type "vscale".
An order of magnitude increase in code size is not uncommon, when compared to equivalent scalar or equivalent vector code, and an order of magnitude or greater effectiveness (work done per instruction) is achievable with Vector ISAs.
ARM's Scalable Vector Extension takes another approach, known in Flynn's Taxonomy as "Associative Processing", more commonly known today as "Predicated" (masked) SIMD. This approach is not as compact as Vector processing but is still far better than non-predicated SIMD. Detailed comparative examples are given in the Vector processing page.
Chronology
| Year | Example |
|---|---|
| 1974 | ILLIAC IV |
| 1974 | ICL Distributed Array Processor (DAP) |
| 1976 | Burroughs Scientific Processor |
| 1981 | Geometric-Arithmetic Parallel Processor from Martin Marietta (continued at Lockheed Martin, then at Teranex and Silicon Optix) |
| 1983-1991 | Massively Parallel Processor (MPP), from NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center |
| 1985 | Connection Machine, models 1 and 2 (CM-1 and CM-2), from Thinking Machines Corporation |
| 1987-1996 | MasPar MP-1 and MP-2 |
| 1991 | Zephyr DC from Wavetracer |
| 2001 | Xplor from Pyxsys, Inc. |
Hardware
Small-scale (64 or 128 bits) SIMD became popular on general-purpose CPUs in the early 1990s and continued through 1997 and later with Motion Video Instructions (MVI) for Alpha. SIMD instructions can be found, to one degree or another, on most CPUs, including IBM's AltiVec and SPE for PowerPC, HP's PA-RISC Multimedia Acceleration eXtensions (MAX), Intel's MMX and iwMMXt, SSE, SSE2, SSE3 SSSE3 and SSE4.x, AMD's 3DNow!, ARC's ARC Video subsystem, SPARC's VIS and VIS2, Sun's MAJC, ARM's Neon technology, MIPS' MDMX (MaDMaX) and MIPS-3D. The IBM, Sony, Toshiba co-developed Cell Processor's SPU's instruction set is heavily SIMD based. Philips, now NXP, developed several SIMD processors named Xetal. The Xetal has 320 16-bit processor elements especially designed for vision tasks.
Intel's AVX-512 SIMD instructions process 512 bits of data at once.
Software

SIMD instructions are widely used to process 3D graphics, although modern graphics cards with embedded SIMD have largely taken over this task from the CPU. Some systems also include permute functions that re-pack elements inside vectors, making them particularly useful for data processing and compression. They are also used in cryptography. The trend of general-purpose computing on GPUs (GPGPU) may lead to wider use of SIMD in the future.
Adoption of SIMD systems in personal computer software was at first slow, due to a number of problems. One was that many of the early SIMD instruction sets tended to slow overall performance of the system due to the re-use of existing floating point registers. Other systems, like MMX and 3DNow!, offered support for data types that were not interesting to a wide audience and had expensive context switching instructions to switch between using the FPU and MMX registers. Compilers also often lacked support, requiring programmers to resort to assembly language coding.
SIMD on x86 had a slow start. The introduction of 3DNow! by AMD and SSE by Intel confused matters somewhat, but today the system seems to have settled down (after AMD adopted SSE) and newer compilers should result in more SIMD-enabled software. Intel and AMD now both provide optimized math libraries that use SIMD instructions, and open source alternatives like libSIMD, SIMDx86 and SLEEF have started to appear (see also libm).
Apple Computer had somewhat more success, even though they entered the SIMD market later than the rest. AltiVec offered a rich system and can be programmed using increasingly sophisticated compilers from Motorola, IBM and GNU, therefore assembly language programming is rarely needed. Additionally, many of the systems that would benefit from SIMD were supplied by Apple itself, for example iTunes and QuickTime. However, in 2006, Apple computers moved to Intel x86 processors. Apple's APIs and development tools (XCode) were modified to support SSE2 and SSE3 as well as AltiVec. Apple was the dominant purchaser of PowerPC chips from IBM and Freescale Semiconductor. Even though Apple has stopped using PowerPC processors in their products, further development of AltiVec is continued in several PowerPC and Power ISA designs from Freescale and IBM.
SIMD within a register, or SWAR, is a range of techniques and tricks used for performing SIMD in general-purpose registers on hardware that does not provide any direct support for SIMD instructions. This can be used to exploit parallelism in certain algorithms even on hardware that does not support SIMD directly.
Programmer interface
It is common for publishers of the SIMD instruction sets to make their own C/C++ language extensions with intrinsic functions or special datatypes (with operator overloading) guaranteeing the generation of vector code. Intel, AltiVec, and ARM NEON provide extensions widely adopted by the compilers targeting their CPUs. (More complex operations are the task of vector math libraries.)
The GNU C Compiler takes the extensions a step further by abstracting them into a universal interface that can be used on any platform by providing a way of defining SIMD datatypes. The LLVM Clang compiler also implements the feature, with an analogous interface defined in the IR. Rust's packed_simd crate (and the experimental std::simd) uses this interface, and so does Swift 2.0+.
C++ has an experimental interface std::experimental::simd that works similarly to the GCC extension. LLVM's libcxx seems to implement it. For GCC and libstdc++, a wrapper library that builds on top of the GCC extension is available.
Microsoft added SIMD to .NET in RyuJIT. The System.Numerics.Vector package, available on NuGet, implements SIMD datatypes. Java also has a new proposed API for SIMD instructions available in OpenJDK 17 in an incubator module. It also has a safe fallback mechanism on unsupported CPUs to simple loops.
Instead of providing an SIMD datatype, compilers can also be hinted to auto-vectorize some loops, potentially taking some assertions about the lack of data dependency. This is not as flexible as manipulating SIMD variables directly, but is easier to use. OpenMP 4.0+ has a #pragma omp simd hint. This OpenMP interface has replaced a wide set of nonstandard extensions, including Cilk's #pragma simd, GCC's #pragma GCC ivdep, and many more.
SIMD multi-versioning
Consumer software is typically expected to work on a range of CPUs covering multiple generations, which could limit the programmer's ability to use new SIMD instructions to improve the computational performance of a program. The solution is to include multiple versions of the same code that uses either older or newer SIMD technologies, and pick one that best fits the user's CPU at run-time (dynamic dispatch). There are two main camps of solutions:
- Function multi-versioning (FMV): a subroutine in the program or a library is duplicated and compiled for many instruction set extensions, and the program decides which one to use at run-time.
- Library multi-versioning (LMV): the entire programming library is duplicated for many instruction set extensions, and the operating system or the program decides which one to load at run-time.
FMV, manually coded in assembly language, is quite commonly used in a number of performance-critical libraries such as glibc and libjpeg-turbo. Intel C++ Compiler, GNU Compiler Collection since GCC 6, and Clang since clang 7 allow for a simplified approach, with the compiler taking care of function duplication and selection. GCC and clang requires explicit target_clones labels in the code to "clone" functions, while ICC does so automatically (under the command-line option /Qax). The Rust programming language also supports FMV. The setup is similar to GCC and Clang in that the code defines what instruction sets to compile for, but cloning is manually done via inlining.
As using FMV requires code modification on GCC and Clang, vendors more commonly use library multi-versioning: this is easier to achieve as only compiler switches need to be changed. Glibc supports LMV and this functionality is adopted by the Intel-backed Clear Linux project.
SIMD on the web
In 2013 John McCutchan announced that he had created a high-performance interface to SIMD instruction sets for the Dart programming language, bringing the benefits of SIMD to web programs for the first time. The interface consists of two types:
- Float32x4, 4 single precision floating point values.
- Int32x4, 4 32-bit integer values.
Instances of these types are immutable and in optimized code are mapped directly to SIMD registers. Operations expressed in Dart typically are compiled into a single instruction without any overhead. This is similar to C and C++ intrinsics. Benchmarks for 4×4 matrix multiplication, 3D vertex transformation, and Mandelbrot set visualization show near 400% speedup compared to scalar code written in Dart.
McCutchan's work on Dart, now called SIMD.js, has been adopted by ECMAScript and Intel announced at IDF 2013 that they are implementing McCutchan's specification for both V8 and SpiderMonkey. However, by 2017, SIMD.js has been taken out of the ECMAScript standard queue in favor of pursuing a similar interface in WebAssembly. As of August 2020, the WebAssembly interface remains unfinished, but its portable 128-bit SIMD feature has already seen some use in many engines.
Emscripten, Mozilla's C/C++-to-JavaScript compiler, with extensions can enable compilation of C++ programs that make use of SIMD intrinsics or GCC-style vector code to the SIMD API of JavaScript, resulting in equivalent speedups compared to scalar code. It also supports (and now prefers) the WebAssembly 128-bit SIMD proposal.
Commercial applications
It has generally proven difficult to find sustainable commercial applications for SIMD-only processors.
One that has had some measure of success is the GAPP, which was developed by Lockheed Martin and taken to the commercial sector by their spin-off Teranex. The GAPP's recent incarnations have become a powerful tool in real-time video processing applications like conversion between various video standards and frame rates (NTSC to/from PAL, NTSC to/from HDTV formats, etc.), deinterlacing, image noise reduction, adaptive video compression, and image enhancement.
A more ubiquitous application for SIMD is found in video games: nearly every modern video game console since 1998 has incorporated a SIMD processor somewhere in its architecture. The PlayStation 2 was unusual in that one of its vector-float units could function as an autonomous DSP executing its own instruction stream, or as a coprocessor driven by ordinary CPU instructions. 3D graphics applications tend to lend themselves well to SIMD processing as they rely heavily on operations with 4-dimensional vectors. Microsoft's Direct3D 9.0 now chooses at runtime processor-specific implementations of its own math operations, including the use of SIMD-capable instructions.
A later processor that used vector processing is the Cell Processor used in the Playstation 3, which was developed by IBM in cooperation with Toshiba and Sony. It uses a number of SIMD processors (a NUMA architecture, each with independent local store and controlled by a general purpose CPU) and is geared towards the huge datasets required by 3D and video processing applications. It differs from traditional ISAs by being SIMD from the ground up with no separate scalar registers.
Ziilabs produced an SIMD type processor for use on mobile devices, such as media players and mobile phones.
Larger scale commercial SIMD processors are available from ClearSpeed Technology, Ltd. and Stream Processors, Inc. ClearSpeed's CSX600 (2004) has 96 cores each with two double-precision floating point units while the CSX700 (2008) has 192. Stream Processors is headed by computer architect Bill Dally. Their Storm-1 processor (2007) contains 80 SIMD cores controlled by a MIPS CPU.
See also
- Streaming SIMD Extensions, MMX, SSE2, SSE3, Advanced Vector Extensions, AVX-512
- Instruction set architecture
- Flynn's taxonomy
- SIMD within a register (SWAR)
- Single Program, Multiple Data (SPMD)
- OpenCL
References
- Flynn, Michael J. (September 1972). "Some Computer Organizations and Their Effectiveness" (PDF). IEEE Transactions on Computers. C-21 (9): 948–960. doi:10.1109/TC.1972.5009071.
- "MIMD1 - XP/S, CM-5" (PDF).
- Conte, G.; Tommesani, S.; Zanichelli, F. (2000). "The long and winding road to high-performance image processing with MMX/SSE". Proc. Fifth IEEE Int'l Workshop on Computer Architectures for Machine Perception. doi:10.1109/CAMP.2000.875989. hdl:11381/2297671. S2CID 13180531.
- Lee, R.B. (1995). "Realtime MPEG video via software decompression on a PA-RISC processor". digest of papers Compcon '95. Technologies for the Information Superhighway. pp. 186–192. doi:10.1109/CMPCON.1995.512384. ISBN 0-8186-7029-0. S2CID 2262046.
- "AMD Zen 4 AVX-512 Performance Analysis On The Ryzen 9 7950X Review". www.phoronix.com. Retrieved 2023-07-13.
- Patterson, David; Waterman, Andrew (18 September 2017). "SIMD Instructions Considered Harmful". SIGARCH.
- RE: SSE2 speed, showing how SSE2 is used to implement SHA hash algorithms
- Salsa20 speed; Salsa20 software, showing a stream cipher implemented using SSE2
- Subject: up to 1.4x RSA throughput using SSE2, showing RSA implemented using a non-SIMD SSE2 integer multiply instruction.
- "SIMD library math functions". Stack Overflow. Retrieved 16 January 2020.
- "Vector Extensions". Using the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC). Retrieved 16 January 2020.
- "Clang Language Extensions". Clang 11 documentation. Retrieved 16 January 2020.
- "VcDevel/std-simd". VcDevel. 6 August 2020.
- "RyuJIT: The next-generation JIT compiler for .NET". 30 September 2013.
- "The JIT finally proposed. JIT and SIMD are getting married". 7 April 2014.
- "JEP 338: Vector API".
- "SIMD Directives". www.openmp.org.
- "Tutorial pragma simd". CilkPlus. 18 July 2012. Archived from the original on 4 December 2020. Retrieved 9 August 2020.
- Kruse, Michael. "OMP5.1: Loop Transformations" (PDF).
- "Function multi-versioning in GCC 6". lwn.net.
- "2045-target-feature". The Rust RFC Book.
- "Transparent use of library packages optimized for Intel® architecture". Clear Linux* Project. Retrieved 8 September 2019.
- John McCutchan. "Bringing SIMD to the web via Dart" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-12-03.
- "SIMD in JavaScript". 01.org. 8 May 2014.
- "tc39/ecmascript_simd: SIMD numeric type for EcmaScript". GitHub. Ecma TC39. 22 August 2019. Retrieved 8 September 2019.
- Jensen, Peter; Jibaja, Ivan; Hu, Ningxin; Gohman, Dan; McCutchan, John (2015). "SIMD in JavaScript via C++ and Emscripten" (PDF).
- "Porting SIMD code targeting WebAssembly". Emscripten 1.40.1 documentation.
- "ZiiLABS ZMS-05 ARM 9 Media Processor". ZiiLabs. Archived from the original on 2011-07-18. Retrieved 2010-05-24.
External links
- SIMD architectures (2000)
- Cracking Open The Pentium 3 (1999)
- Short Vector Extensions in Commercial Microprocessor
- Article about Optimizing the Rendering Pipeline of Animated Models Using the Intel Streaming SIMD Extensions
- "Yeppp!": cross-platform, open-source SIMD library from Georgia Tech
- Introduction to Parallel Computing from LLNL Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory Archived 2013-06-10 at the Wayback Machine
- simde on GitHub: A portable implementation of platform-specific intrinsics for other platforms (e.g. SSE intrinsics for ARM NEON), using C/C++ headers
| Parallel computing | |
|---|---|
| General | |
| Levels | |
| Multithreading | |
| Theory | |
| Elements | |
| Coordination | |
| Programming | |
| Hardware | |
| APIs | |
| Problems | |