

In modern usage, a sloop is a sailboat with a single mast generally having only one headsail in front of the mast and one mainsail abaft (behind) the mast. It is a type of fore-and-aft rig. The mainsail may be of any type, most often Bermuda rig, but also others, such as gaff or gunter.
In naval terminology, "sloop-of-war" refers to the purpose of the craft, rather than to the specific size or sail-plan, and thus a sloop should not be confused with a sloop-of-war. As with many rig definitions, it was some time before the term sloop referred to the type of rig.
Regionally, the definition also takes into account the position of the mast. A forward mast placement and a fixed (as opposed to running) bowsprit, but with two headsails may give categorisation as a sloop. An example is the Friendship Sloop.
Origins
The name originates from the Dutch sloep, which is related to the Old English slūpan, to glide. The original Dutch term applied to an open rowing boat. A sloop is usually regarded as a single-masted rig with a single headsail and a fore-and-aft mainsail. In this form, the sloop is the commonest of all sailing rigs – with the Bermuda sloop being the default rig for leisure craft, being used on types that range from simple cruising dinghies to large racing yachts with high-tech sail fabrics and large powerful winches.If the vessel has two or more headsails, the term cutter is usually applied, though there are regional and historic variations on this. A boat with a forward mast placement and a fixed bowsprit, but more than one headsail, may be called a sloop. The Friendship sloop is an example of this. Particularly with historic craft, categorisation as a cutter may rely on having a running bowsprit.
Variations

Before the Bermuda rig became popular outside of Bermuda in the early 20th century, a (non-Bermudian) sloop might carry one or more square-rigged topsails which will be hung from a topsail yard and be supported from below by a crossjack.
A sloop's headsail may be masthead-rigged or fractional-rigged. On a masthead-rigged sloop, the forestay (on which the headsail is carried) attaches at the top of the mast. On a fractional-rigged sloop, the forestay attaches to the mast at a point below the top. A sloop may use a bowsprit, a spar that projects forward from the bow.
Gallery
-
 Bermuda-rigged sloop. The jib is a headsail. See cutter rig for other examples of headsails.
Bermuda-rigged sloop. The jib is a headsail. See cutter rig for other examples of headsails.
-
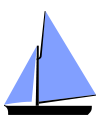 Gunter-rigged sloop
Gunter-rigged sloop
-
 Gaff-rigged sloop with a headsail and a gaff topsail
Gaff-rigged sloop with a headsail and a gaff topsail
-
 Spritsail sloop
Spritsail sloop
-
 Sloop sail with multiple foresails and topsail
Sloop sail with multiple foresails and topsail
See also
- Mast aft rig, a single mast rig with a mast further back than a sloop or cutter
- Chialoup, an historical type of sloop produced in the East Indies
- Bermuda sloop, originally used for a type of sea-going, sloop-rigged vessel. Today used for any Bermuda-rigged sloop
- Bermuda Fitted Dinghy: a scaled-down sloop used for racing in Bermuda
Notes
References
- ^ Bennett, Jenny (2005). Sailing Rigs, an Illustrated Guide. London: Chatham Publishing. ISBN 1-86176-243-7.
- "SLOOP | meaning in the Cambridge English Dictionary". dictionary.cambridge.org. Retrieved 2019-05-12.
- "Sloop". dictionary.com. Retrieved 12 May 2019.
- Fallows, Samuel (1885). Progressive Dictionary of the English Language. Progressive. p. 148.
External links
| Types of sailing vessels and rigs | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overviews | |||||||||||||||||
| Sailing rigs | |||||||||||||||||
| By sailing rigs | |||||||||||||||||
| Multihull vessels | |||||||||||||||||
| Naval and merchant sailing ships and other vessels (by origin date) |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Fishing vessels | |||||||||||||||||
| Recreational vessels | |||||||||||||||||
| Special terms | |||||||||||||||||
| Other types | |||||||||||||||||
| Related | |||||||||||||||||
| Sails, spars and rigging | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| including limited use, outdated | |||||||
| Rigs |
| ||||||
| Sails (sailing rigs) |
| ||||||
| Spars |
| ||||||
| Rigging |
| ||||||