| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Sprut anti-tank gun" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (September 2012) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
Anti-tank gun
| 2A45 Sprut-A | |
|---|---|
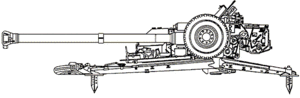 Sprut anti-tank gun Sprut anti-tank gun | |
| Type | Anti-tank gun |
| Place of origin | Soviet Union/Russia |
| Service history | |
| In service | 1989–present |
| Used by | See operators |
| Production history | |
| Designer | Petrov Design Bureau |
| Designed | late 1980s |
| Manufacturer | Artillery Plant Number 9 |
| Produced | 1989–present |
| Variants | See models |
| Specifications | |
| Mass | Transport: 6,500 kg (14,300 lb) Self-propelled: 6,800 kg (15,000 lb) Firing: 6,575 kg (14,495 lb) |
| Length | Transport: 7.12 m (23 ft 4 in) Self-propelled: 6.79 m (22 ft 3 in) |
| Barrel length | Bore: 51 calibres Bore axis: 0.925 m (3 ft 0.4 in) |
| Width | 2.66 m (8 ft 9 in) |
| Height | Transport: 2.09 m (6 ft 10 in) Self-propelled: 2.35 m (7 ft 9 in) |
| Crew | 7 |
| Caliber | 125 mm (4.9 in) |
| Recoil | Hydro-pneumatic |
| Carriage | tripod |
| Elevation | -6° to 25° |
| Traverse | 360° |
| Rate of fire | 6-8 rpm |
| Effective firing range | 2,000 m (2,200 yd) (APFSDS) 5,000 m (5,500 yd) (9M119 Svir ATGM) 12,000 m (13,000 yd) (HE) |
| Operational range | 50 km (55,000 yd) (in APU mode) |
| Maximum speed | 14 km/h (8.7 mph) (in APU mode) |
2A45 and 2A45M are the respective GRAU designations of the Sprut-A and Sprut-B (Russian for octopus or kraken) Soviet smoothbore 125 mm anti-tank guns.
Development
The 2A45M was created in the late 1980s by the Petrov Design Bureau at Artillery Plant Number 9 (OKB-9), which was also responsible for the 122 mm howitzer 2A18 (D-30).
Description (Sprut-B)
A feature of the Sprut-B is its integrated engine, which can propel the gun on relatively flat surfaces (up to 15 degrees of slope) and at 14 km/h on roads. This gives the gun a measure of mobility on the battlefield. Changing gun position from travelling to firing takes 90 seconds; the reverse takes two minutes. Such guns are known in Russian as "self-moving" (самодвижущиеся) in contrast to self-propelled (самоходные), and outside of battle it is towed by an MT-LB.
The gun has a crew of seven. An OP4M-48A direct fire sight is used in daylight, and a 1PN53-1 night-vision sight is used at night. For indirect fire, 2Ts33 iron sights are used, with a PG-1m panoramic sight. The gun can reliably engage targets two metres high at a distance of 2,000 metres.
The barrel features a thermal sleeve to prevent temperature changes affecting the accuracy. The gun uses the same semi-fixed ammunition as the T-64, T-72, T-80, and T-90 tanks.
With the addition of the 9S53 laser fire-control system, the gun can fire laser guided projectiles such as the 9M119 Svir or 9K120 Refleks.
Ammunition
Main article: 125 mm smoothbore ammunitionThe gun uses the same ammunition as the D-81 series of guns used on the T-64, T-72, T-80 and T-90 tanks.
Models
- 2A45 Sprut-A
Stationary towed gun variant.
- 2A45M Sprut-B
Self-propelled towed gun variant that can move under its own power with the addition of wheels and a power unit.
Operators

Current operators
Former operators
 Soviet Union passed construction license to successor states
Soviet Union passed construction license to successor states Belarus
Belarus
See also
- 125 mm smoothbore ammunition
- 2A46 125 mm gun - Soviet–Russian tank-mounted
- List of Soviet tanks
References
- Hull, A.W., Markov, D.R., Zaloga, S.J. (1999). Soviet/Russian Armor and Artillery Design Practices 1945 to Present. Darlington Productions. ISBN 1-892848-01-5.
- Military Parade
- Enemy Forces
- 2A45M on manufacturer site
- Jane's Armour and Artillery 2002-2003