| War of the Third Coalition | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Napoleonic Wars and the Coalition Wars | |||||||
 Click an image to load the appropriate article. Left to right, top to bottom: Battles of Ulm, Trafalgar, Durenstein, Schöngrabern and Austerlitz | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
| |||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
|
Austrian Empire: 20,000 killed or wounded 70,000 captured Russia: 25,000 killed or wounded 25,000 captured Naples: 20,000 killed, wounded or captured Total casualties: 160,000 killed, wounded or captured |
France: 13,500 killed 37,000 wounded 5,000 captured Italy: 350 killed 1,900 wounded Spain: 1,200 killed 1,600 wounded Bavaria: 300 killed 1,200 wounded Total casualties: 62,050 killed, wounded or captured | ||||||
| War of the Third Coalition | |
|---|---|
|
620miles Waterloo9
1 Third Coalition: Germany 1803:...Austerlitz...
2 Fourth Coalition: Prussia 1806:...Jena...
3 Peninsular War: Portugal 1807...Torres Vedras...
4 Peninsular War: Spain 1808...Vitoria...
5 Fifth Coalition: Austria 1809:...Wagram...
6 French invasion of Russia 1812:...Moscow...
7 Sixth Coalition: Germany 1813:...Leipzig...
8 Sixth Coalition: France 1814:...Paris...
9 Hundred Days 1815:...Waterloo...
The War of the Third Coalition (French: Guerre de la Troisième Coalition) was a European conflict lasting from 1805 to 1806 and was the first conflict of the Napoleonic Wars. During the war, France and its client states under Napoleon I and its ally Spain opposed an alliance, the Third Coalition, which was made up of the United Kingdom, the Austrian Empire, the Russian Empire, Naples, Sicily, and Sweden. Prussia remained neutral during the war.
Britain had already been at war with France following the breakdown of the Peace of Amiens and remained the only country still at war with France after the Treaty of Pressburg. From 1803 to 1805, Britain stood under constant threat of a French invasion. The Royal Navy, however, assured its naval dominance at the Battle of Trafalgar in October 1805.
The Third Coalition itself came to full fruition in 1804–05 as Napoleon's actions in Italy and Germany (notably the arrest and execution of the Duc d'Enghien) spurred Austria and Russia into joining Britain against France. The war would be determined on the continent, and the major land operations that sealed the swift French victory involved the Ulm Campaign, a large wheeling manoeuvre by the Grande Armée lasting from late August to mid-October 1805 that captured an entire Austrian army, and the decisive French victory over a combined Austro-Russian force under Alexander I of Russia at the Battle of Austerlitz in early December. Austerlitz effectively brought the Third Coalition to an end, although later there was a small side campaign against Naples, which also resulted in a decisive French victory at the Battle of Campo Tenese.
On 26 December 1805, Austria and France signed the Treaty of Pressburg, which took Austria out of both the war and the Coalition, while it reinforced the earlier treaties of Campo Formio and of Lunéville between the two powers. The treaty confirmed the Austrian cession of lands in Italy to France and in Germany to Napoleon's German allies, imposed an indemnity of 40 million francs on the defeated Habsburgs, and allowed the defeated Russian troops free passage, with their arms and equipment, through hostile territories and back to their home soil. Victory at Austerlitz also prompted Napoleon to create the Confederation of the Rhine, a collection of German client states that pledged themselves to raise an army of 63,000 men. As a direct consequence of those events, the Holy Roman Empire ceased to exist when, in 1806, Francis II abdicated the Imperial throne, becoming Francis I, Emperor of Austria. Those achievements, however, did not establish a lasting peace on the continent. Austerlitz had driven neither Russia nor Britain, whose fleet protected Sicily from a French invasion, to cease fighting. Meanwhile, Prussian worries about the growing French influence in Central Europe sparked the War of the Fourth Coalition in 1806.
Periodisation
Historians differ on when the War of the Third Coalition began and when it ended. From the British perspective, the war started when Britain declared war on France on 18 May 1803, but it was still on its own. It was not until December 1804 when Sweden entered into an alliance with the United Kingdom, not until 11 April 1805 when Russia joined the alliance, not until 16 July when Britain and Russia ratified their treaty of alliance, and only thereafter Austria (9 August) and Naples–Sicily (11 September) completed the fully-fledged coalition.
Meanwhile, Bavaria sided with France on 25 August following the Treaty of Bogenhausen, and Württemberg joined Napoleon on 5 September. No major hostilities between France and any member of the coalition other than Britain (Trafalgar campaign March–November 1805) occurred until the Ulm Campaign (25 September – 20 October 1805). This was in part because Napoleon's planned invasion of the United Kingdom was not called off until 27 August 1805, when he decided to use his invasion force camped at Boulogne against Austria instead.
Likewise, no major battles occurred after the Battle of Austerlitz and the signing of the Peace of Pressburg on 26 December 1805, which forced Austria to leave the Third Coalition and cease hostilities against France. Some historians conclude that Austria's departure "shattered the fragile Third Coalition" and "ended the War of the Third Coalition".
This narrative leaves out the subsequent French invasion of Naples (February–July 1806), which the occupying Anglo-Russian troops hastily evacuated and the remaining Neapolitan forces relatively quickly surrendered. Other scholars argue the southern Italian campaign should be included into the War of the Second Coalition, and criticise ignoring the Mediterranean front by only focusing on land battles in Central Europe and the Trafalgar campaign.
Prelude
From Amiens to the Third Coalition
In March 1802, hostilities between France and the Allies came to an end. However it was clear to the leading European politicians, and especially to Napoleon, that the peace treaties of Lunéville (1801) and Amiens (1802), which ended the Second War of Coalition, were not a lasting solution. Tensions between Napoleon-ruled France and Great Britain had been rising again since the second half of 1802. The fact that Napoleon played an active role in the Caribbean contributed to this. There were also indications that he was once again interested in Egypt and the Middle East. There were reports in French newspapers that 10,000 men would be enough to reconquer Egypt. In Italy, Napoleon increased his influence when he transformed the Cisalpine Republic into the Italian Republic and made himself president. He annexed Piedmont to France. Contrary to the peace treaty of Amiens, the French army was not withdrawn from the Netherlands; instead, the Batavian Republic was given a new constitution based on the French model. The Helvetic Republic was also closely dependent on France. Napoleon had given the country a new federalist constitution with the Act of Mediation. At the same time, the country had had to bind itself politically to France for fifty years.
The peace treaty stipulated that Great Britain was to return all conquered territories except Ceylon and Trinidad to their respective previous owners. Minorca to Spain and Malta to the Order of St. John. In return, France was to leave Egypt and Naples and guarantee the independence of Portugal and the Ionian Islands. In order to prevent Napoleon from advancing further into the Levant, it was necessary for Great Britain to keep Malta and a fleet in the Mediterranean. Russia's interest in Malta offered Napoleon an ideal opportunity for a war in which he hoped to play Britain and Russia off against each other. Napoleon indirectly threatened war on 13 March 1803 when he criticized Britain's violation of the peace treaty to the British ambassador Lord Whitworth. The ambassador returned to London and shortly afterwards, on May 18, Great Britain declared war on France.
Setting up the opposing forces
When Napoleon crowned himself Emperor on December 2, 1804, Austria and Prussia may have been alarmed, but the annexed Italian city-states of Genoa, Parma and Piacenza and his coronation as King of Italy left no doubt as to Napoleon's intentions. On January 21, 1805, Prime Minister William Pitt the Younger presented a treaty of alliance with Russia and Austria. The demands of this treaty were the restoration of the Kingdom of Piedmont-Sardinia, the withdrawal of French troops from Italy, the dissolution of the Batavian Republic and the restoration of Switzerland's independence. In the event of Napoleon's refusal, England would support the coalition forces financially. After all difficulties had been resolved, Great Britain, Austria and Russia signed a treaty on August 9, 1805, forming the third coalition against Napoleon. Prussia remained neutral. On the other side, Napoleon built an alliance of various southern German members of the Holy Roman Empire. These included Württemberg, Bavaria and Baden, which benefited from the Reichsdeputationshauptschluss of February 25, 1803. These enlarged states were in line with Napoleon's calculations. They were to weaken Austria, but were themselves too weak to pose a threat to France.
La Grande Armée at Boulogne
See also: Napoleon's planned invasion of the United Kingdom
Prior to the formation of the Third Coalition, Napoleon had assembled the Army of England, an invasion force meant to strike at England, from around six camps at Boulogne in Northern France. Although they never set foot on British soil, Napoleon's troops received careful and invaluable training for any possible military operation. Boredom among the troops occasionally set in, but Napoleon paid many visits and conducted lavish parades in order to boost the morale of the soldiers.
The men at Boulogne formed the core for what Napoleon would later call La Grande Armée ("The Great Army"). At the start, this French army had about 200,000 men organized into seven corps, each capable of independent action or in concert with other corps. Corps were large combined arms field units typically containing 2–4 infantry divisions, a cavalry division, and about 36 to 40 cannon.
On top of these forces, Napoleon created a cavalry reserve of 22,000 organized into two cuirassier divisions, four mounted dragoon divisions, and two divisions of dismounted dragoons and light cavalry, all supported by 24 artillery pieces. By 1805, the Grande Armée had grown to a force of 350,000, was well equipped, adequately trained, and possessed a skilled officer class.
Russian and Austrian armies
The Imperial Russian Army in 1805 had many characteristics of ancien régime military organization: there was no permanent formation above the regimental level, senior officers were largely recruited from aristocratic circles (including foreigners), and the Russian soldier, in line with 18th-century practice, was regularly beaten and punished to instill discipline. Furthermore, many lower-level officers were poorly trained and had difficulty getting their men to perform the sometimes complex manoeuvres required in a battle. Nevertheless, the Russians did have a fine artillery arm manned by soldiers who regularly fought hard to prevent their pieces from falling into enemy hands.
Archduke Charles, brother of the Austrian Emperor, had started to reform the Austrian army in 1801 by taking away power from the Hofkriegsrat, the military-political council responsible for decision-making in the Austrian armed forces. Charles was Austria's best field commander, but he was unpopular with the imperial court and lost much influence when, against his advice, Austria decided to go to war with France. Karl Mack became the new main commander in Austria's army, instituting reforms on the infantry on the eve of war that called for a regiment to be composed of four battalions of four companies rather than the older three battalions of six companies. The sudden change came with no corresponding officer training, and as a result, these new units were not led as well as they could have been. Austrian cavalry forces were regarded as the best in Europe, but the detachment of many cavalry units to various infantry formations precluded the hitting power of their massed French counterparts.
Ulm campaign
See also: Ulm Campaign
In August 1805, Napoleon, Emperor of the French since May of the previous year, turned his army's sights from the English Channel to the Rhine in order to deal with the new Austrian and Russian threats. The War of the Third Coalition began with the Ulm Campaign, a series of French and Bavarian military manoeuvres and battles designed to outflank an Austrian army under General Mack.
Austrian plans and preparations
General Mack thought that Austrian security relied on sealing off the gaps through the mountainous Black Forest area in Southern Germany that had witnessed much fighting during the campaigns of the French Revolutionary Wars. Mack believed that there would be no action in Central Germany. Mack decided to make the city of Ulm the centrepiece of his defensive strategy, which called for containment of the French until the Russians under Mikhail Kutuzov could arrive and alter the odds against Napoleon. Ulm was protected by the heavily fortified Michelsberg heights, giving Mack the impression that the city was virtually impregnable from outside attack.
Fatally, the Aulic Council decided to make Northern Italy the main theatre of operations for the Austrian army. Archduke Charles was assigned 95,000 troops and directed to cross the Adige river with Mantua, Peschiera, and Milan as the initial objectives.Archduke John was given 23,000 troops and commanded to secure Tyrol while serving as a link between his brother, Charles, and his cousin, Archduke Ferdinand; the latter's force of 72,000, which was to invade Bavaria and hold the defensive line at Ulm, was effectively controlled by Mack.The Austrians also detached individual corps to serve with the Swedish in Pomerania and the British in Naples, though these were designed to obfuscate the French and divert their resources.
French plans and preparations

In both the campaigns of 1796 and 1800, Napoleon had envisaged the Danube theatre as the central focus of French efforts, but in both instances, the Italian theatre became the most important. The Aulic Council thought Napoleon would strike in Italy again. Napoleon had other intentions: 210,000 French troops would be launched eastwards from the camps of Boulogne and would envelop General Mack's exposed Austrian army if it kept marching towards the Black Forest.
Meanwhile, Marshal Murat would conduct cavalry screens across the Black Forest to fool the Austrians into thinking that the French were advancing on a direct west–east axis. The main attack in Germany would be supported by French assaults in other theatres: Marshal Masséna would confront Archduke Charles in Italy with 50,000 men, Marshal St. Cyr would march to Naples with 20,000 men, and Marshal Brune would patrol Boulogne with 30,000 troops against a possible British invasion.
Marshal Joachim Murat and General Bertrand conducted reconnaissance between the area bordering the Tyrol and the Main as General Savary, chief of the planning staff, drew up detailed road surveys of the areas between the Rhine and the Danube. The left-wing of the Grande Armée would move from Hanover and Utrecht to fall on Württemberg; the right and centre, troops from the Channel coast, would concentrate along the Middle Rhine around cities like Mannheim and Strasbourg. While Murat was making demonstrations across the Black Forest, other French forces would then invade the German heartland and swing towards the southeast by capturing Augsburg, a move that was supposed to isolate Mack and interrupt the Austrian lines of communication.
The French invasion

On 22 September, Mack decided to hold the Iller line anchored on Ulm. In the last three days of September, the French began the furious marches that would find them at the Austrian rear. Mack believed that the French would not violate Prussian territory, but when he heard that Bernadotte's I Corps had marched through Prussian Ansbach, he made the critical decision to stay and defend Ulm rather than retreat to the south, which would have offered a reasonable opportunity at saving the bulk of his forces. Napoleon had little accurate information about Mack's intentions or manoeuvres. He knew that Kienmayer's Corps was sent to Ingolstadt east of the French positions, but his agents greatly exaggerated its size.
On 5 October, Napoleon ordered Marshal Ney to join Marshals Lannes, Soult, and Murat in concentrating and crossing the Danube at Donauwörth. The French encirclement was not deep enough to prevent Kienmayer's escape: the French corps did not all arrive at the same place – they instead deployed on a long west–east axis – and the early arrival of Soult and Davout at Donauwörth incited Kienmayer to exercise caution and evasion.Napoleon gradually became more convinced that the Austrians were massed at Ulm and ordered sizeable portions of the French army to concentrate around Donauwörth; on 6 October, three French infantry and cavalry corps headed to Donauwörth to seal off Mack's escape route.
Battle of Wertingen

Realizing the danger of his position, Mack decided to go on the offensive. On 8 October, he commanded the army to concentrate around Günzburg and hoped to strike at Napoleon's lines of communication. Mack instructed Kienmayer to draw Napoleon further east towards Munich and Augsburg. Napoleon did not seriously consider the possibility that Mack would cross the Danube and move away from his central base, but he did realize that seizing the bridges at Günzburg would yield a large strategic advantage. To accomplish this objective, Napoleon sent Ney's Corps to Günzburg, completely unaware that the bulk of the Austrian army was heading to the same destination. On 8 October, however, the campaign witnessed its first serious battle at Wertingen between Auffenburg's troops and those of Murat and Lannes.
For reasons not entirely clear, Mack ordered Auffenburg on 7 October to take his division of 5,000 infantry and 400 cavalry from Günzburg to Wertingen in preparation for the main Austrian advance out of Ulm. Uncertain of what to do and having little hope for reinforcements, Auffenburg was in a dangerous position. The first French forces to arrive were Murat's cavalry divisions – Klein's 1st Dragoons, Beaumont 3rd Dragoons, and Nansouty's cuirassiers. They began to assault the Austrian positions and were soon joined by Oudinot's grenadiers, who were hoping to outflank the Austrians from the north and west. Auffenburg attempted a retreat to the southwest, but he was not quick enough: the Austrians were decimated, losing nearly their entire force, 1,000 to 2,000 of which were prisoners. The Battle of Wertingen had been an easy French victory.
The actions at Wertingen convinced Mack to operate on the left bank of the Danube instead of making a direct eastwards retreat on the right bank. This would require the Austrian army to cross at Günzburg. On 8 October, Ney was operating under Marshal Berthier's directions that called for a direct attack on Ulm the following day. Ney sent in Malher's 3rd Division to capture the Günzburg bridges over the Danube. A column of this division ran into some Tyrolean jägers and captured 200 of them, including their commander General d'Aspré, along with two cannons.
The Austrians noticed these developments and reinforced their positions around Günzburg with three infantry battalions and 20 cannons. Malher's division conducted several heroic attacks against the Austrian positions, but all failed. Mack then sent in Ignác Gyulay with seven infantry battalions and fourteen cavalry squadrons to repair the destroyed bridges, but this force was charged and swept away by the delayed French 59th Infantry Regiment.
Fierce fighting ensued and the French finally managed to establish a foothold on the right bank of the Danube. While the Battle of Günzburg was being fought, Ney sent General Loison's 2nd Division to capture the Danube bridges at Elchingen, which were lightly defended by the Austrians. Having lost most of the Danube bridges, Mack marched his army back to Ulm. By 10 October, Ney's corps had made significant progress: Malher's division had crossed to the right bank, Loison's division held Elchingen, and Dupont's division was heading towards Ulm.
Haslach-Jungingen and Elchingen
Main articles: Battle of Haslach-Jungingen and Battle of Elchingen
The demoralized Austrian army arrived at Ulm in the early hours of 10 October. Mack was deliberating about a course of action to pursue and the Austrian army remained inactive at Ulm until the 11th. Meanwhile, Napoleon was operating under flawed assumptions: he believed the Austrians were moving to the east or southeast and that Ulm was lightly guarded. Ney sensed this misapprehension and wrote to Berthier that Ulm was, in fact, more heavily defended than the French originally thought. During this time, the Russian threat to the east began to preoccupy Napoleon so much that Murat was given command of the right wing of the army, consisting of Ney's and Lannes's corps. The French were separated in two massive rings at this point: the forces of Ney, Lannes and Murat to the west were containing Mack, while those of Soult, Davout, Bernadotte and Marmont to the east were charged with guarding against any possible Russian and Austrian incursions. On 11 October, Ney made a renewed push on Ulm; the 2nd and 3rd divisions were to march to the city along the right bank of the Danube while Dupont's division, supported by one dragoons division, was to march directly for Ulm and seize the entire city. The orders were hopeless because Ney still did not know that the entire Austrian army was stationed at Ulm.
The 32nd Infantry Regiment in Dupont's division marched from Haslach towards Ulm and ran into four Austrian regiments holding Bolfingen. The 32nd carried out several ferocious attacks, but the Austrians held firm and repulsed every single one of them. The Austrians flooded the battle with more cavalry and infantry regiments to Jungingen hoping to score a knockout blow against Ney's corps by enveloping Dupont's force. Dupont sensed what was happening and preempted the Austrians by launching a surprise attack on Jungingen that captured at least 1,000 prisoners. Renewed Austrian attacks drove these forces back to Haslach, which the French managed to hold. Dupont was eventually forced to fall back on Albeck, where he joined d'Hilliers's troops. The effects of the Battle of Haslach-Jungingen on Napoleon's plans are not fully clear, but the Emperor may have finally ascertained that the majority of the Austrian army was concentrated at Ulm. Accordingly, Napoleon sent the corps of Soult and Marmont towards the Iller, meaning he now had four infantry and one cavalry corps to deal with Mack; Davout, Bernadotte, and the Bavarians were still guarding the region around Munich. Napoleon did not intend to fight a battle across rivers and ordered his marshals to capture the important bridges around Ulm. He also began shifting his forces to the north of Ulm because he expected a battle in that region rather than an encirclement of the city itself. These dispositions and actions would lead to a confrontation at Elchingen on the 14th as Ney's forces advanced on Albeck.

At this point in the campaign, the Austrian command staff was in full confusion. Ferdinand began to openly oppose Mack's command style and decisions, charging that the latter spent his days writing contradictory orders that left the Austrian army marching back and forth. On 13 October, Mack sent two columns out of Ulm in preparation for a breakout to the north: one under General Johann Sigismund Riesch headed towards Elchingen to secure the bridge there and the other under Franz von Werneck went north with most of the heavy artillery. Ney hurried his corps forward to reestablish contact with Dupont. Ney led his troops to the south of Elchingen on the right bank of the Danube and began the attack. The field to the side was a partially wooded flood plain, rising steeply to the hill town of Elchingen, which had a wide field of view. The French cleared the Austrian pickets and a regiment boldly attacked and captured the abbey at the top of the hill at bayonet point. The Austrian cavalry was also defeated and Riesch's infantry fled; Ney was given the title "Duke of Elchingen" for his impressive victory.
Battle of Ulm
Main article: Battle of Ulm
Other actions took place on the 14th. Murat's forces joined Dupont at Albeck just in time to drive off an Austrian attack from Werneck; together Murat and Dupont beat the Austrians to the north in the direction of Heidenheim. By night on the 14th, two French corps were stationed in the vicinity of the Austrian encampments at Michelsberg, right outside of Ulm. Mack was now in a dangerous situation: there was no longer any hope of escaping along the north bank, Marmont and the Imperial Guard were hovering at the outskirts of Ulm to the south of the river, and Soult was moving from Memmingen to prevent the Austrians escaping south to the Tyrol. Troubles continued with the Austrian command as Ferdinand overrode the objections of Mack and ordered the evacuation of all cavalry from Ulm, a total of 6,000 troopers. Murat's pursuit was so effective, however, that only eleven squadrons joined Werneck at Heidenheim. Murat continued his harassment of Werneck and forced him to surrender with 8,000 men at Trochtelfingten on 19 October; Murat also took an entire Austrian field park of 500 vehicles, then swept on towards Neustadt and captured 12,000 Austrians.
Events at Ulm were now reaching a conclusion. On 15 October, Ney's troops successfully charged the Michelsberg encampments and on the 16th the French began to bombard Ulm itself. Austrian morale was at a low point and Mack began to realize that there was little hope of rescue. On 17 October, Napoleon's emissary, Ségur, signed a convention with Mack in which the Austrians agreed to surrender on 25 October if no aid came by that date. Gradually, however, Mack heard of the capitulations at Heidenheim and Neresheim and agreed to surrender five days before schedule on 20 October. 10,000 troops from the Austrian garrison managed to escape, but the vast majority of the Austrian force marched out on the 21st and laid down their arms without incident, all with the Grande Armée drawn up in a vast semicircle observing the capitulation.
Battle of Trafalgar
See also: Trafalgar Campaign This section is an excerpt from Battle of Trafalgar.
The Battle of Trafalgar was a naval engagement that took place on 21 October 1805 between the British Royal Navy and the combined fleets of the French and Spanish Navies during the War of the Third Coalition (August–December 1805) of the Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815).
As part of Napoleon's plans to invade the United Kingdom, the French and Spanish fleets combined to take control of the English Channel and provide the Grande Armée safe passage. The allied fleet, under the command of the French admiral, Pierre-Charles Villeneuve, sailed from the port of Cádiz in the south of Spain on 18 October 1805. They encountered the British fleet under Lord Nelson, recently assembled to meet this threat, in the Atlantic Ocean along the southwest coast of Spain, off Cape Trafalgar.
Nelson was outnumbered, with 27 British ships of the line to 33 Franco-Spanish ships, including the largest warship in either fleet, the Spanish Santísima Trinidad. To address this imbalance, Nelson sailed his fleet directly at the allied battle line's flank, hoping to break the line into pieces. Villeneuve had worried that Nelson might attempt this tactic, but for various reasons, failed to prepare for it. The plan worked almost perfectly; Nelson's columns split the Franco-Spanish fleet in three, isolating the rear half from Villeneuve's flag aboard Bucentaure. The allied vanguard sailed off while it attempted to turn around, giving the British temporary superiority over the remainder of their fleet. In the ensuing fierce battle 20 allied ships were lost, while the British lost none.
The offensive exposed the leading British ships to intense crossfire as they approached the Franco-Spanish lines. Nelson's own HMS Victory led the front column and was almost knocked out of action. Nelson was shot by a French musketeer during the battle, and died shortly before it ended. Villeneuve was captured along with his flagship Bucentaure. He attended Nelson's funeral while a captive on parole in Britain. The senior Spanish fleet officer, Admiral Federico Gravina, escaped with the surviving third of the Franco-Spanish fleet; he died six months later of wounds sustained during the battle.
The victory confirmed British naval supremacy, and was achieved in part through Nelson's departure from prevailing naval tactical orthodoxy.Battle of Austerlitz

Preliminaries
The main body of the Grande Armée followed the remains of the Austrian army towards Vienna. Following the failure of the Austrian army at Ulm, a Russian army under General Mikhail Kutuzov was also withdrawing east, and reached the Ill river on 22 October, where it joined with Kienmayer's retreating corps. On 5 November, they held a successful rearguard action in Amstetten. On 7 November, the Russians arrived in St. Pölten, and then moved across the Danube river the next day. Late on 9 November, they destroyed the bridges across the Danube, holding the last one, at Stein, near Krems, until the late afternoon.

The following day, Marshal Mortier ordered General Gazan to attack what they believed to be a Russian rear guard, at the village of Stein. This was a trap on the part of Kutuzov, laid for the sole purpose of convincing Mortier that he had retreated further toward Vienna, when he had actually crossed the Danube in force, and lay concealed behind the ridges above the village. In the ensuing Battle of Dürenstein, three Russian columns circled around the First Division of the Corps Mortier, and attacked Gazan from both the front and the rear. Not until Dupont's division arrived, after dark, was Gazan able to start to evacuate his soldiers to the other side of the Danube. Gazan lost close to 40 percent of his division. In addition, 47 officers and 895 men were captured, and he lost five guns, as well as the eagles of the 4th Infantry Regiment, and the eagle and guidon of the 4th Dragoons. The Russians also lost around 4,000, about 16 percent of their force, and two regimental colors. The Austrian Lt. Field Marshal Johann Heinrich von Schmitt was killed as the battle concluded, probably by Russian musketry in the confused melee.
At the Battle of Schöngrabern (also known as the Battle of Hollabrunn) occurred a week after the battle at Dürenstein. On 16 November 1805. near Hollabrunn in Lower Austria. The Russian army of Kutuzov was retiring north of the Danube before the French army of Napoleon.
On 13 November 1805 Marshals Murat and Lannes, commanding the French advance guard, had captured a bridge over the Danube at Vienna by falsely claiming that an armistice had been signed, and then rushing the bridge while the guards were distracted. Kutuzov needed to gain time in order to make contact near Brünn with reinforcements led by Buxhowden. He ordered his rearguard under Major-General Prince Pyotr Bagration to delay the French.
After Hollabrun, the armies gathered on the plains to the east of Brünn. Napoleon could muster some 75,000 men and 157 guns for the impending battle, but about 7,000 troops under Davout were still far to the south in the direction of Vienna. The Allies had about 73,000 soldiers, seventy percent of them Russian, and 318 guns. On 1 December, both sides occupied their main positions.
Battlefield
The northern part of the battlefield was dominated by the 700-foot (210-metre) Santon hill and the 850-foot (260-metre) Zuran hill, both overlooking the vital Olmutz-Brno road that ran across a west–east axis. To the west of these two hills was the village of Bellowitz, and between them the Bosenitz Stream went south to link up with the Goldbach Stream, the latter flowing astride the villages of Kobelnitz, Sokolnitz, and Telnitz. The centerpiece of the entire area were the Pratzen Heights, a gently sloped hill about 35 to 40 feet (11 to 12 m) in height. An aide noted that the Emperor repeatedly told his Marshals, "Gentlemen, examine this ground carefully, it is going to be a battlefield; you will have a part to play upon it".
Allied plans and dispositions
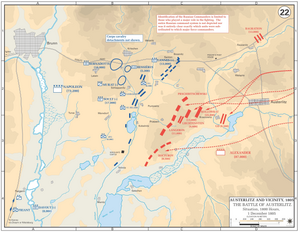
An Allied council met on 1 December to discuss proposals for the battle. Most of the Allied strategists had two fundamental ideas in mind: making contact with the enemy and securing the southern flank that led to Vienna. Although the Tsar and his immediate entourage pushed hard for a battle, Emperor Francis of Austria was in a more cautious mood, and he was seconded by Kutuzov, the main Russian commander. The pressure to fight from the Russian nobles and the Austrian commanders, however, was too strong, and the Allies adopted Austrian Chief of Staff Franz von Weyrother's plan. This called for a main drive against the French right flank, which the Allies noticed was lightly guarded, and diversionary attacks against the French left. The Allies deployed most of their troops into four columns that would attack the French right. The Russian Imperial Guard was held in reserve while Russian troops under Bagration guarded the Allied right.
French plans and dispositions
Days before any actual fighting, Napoleon had given an impression to the Allies that his army was in a weak state and that he desired a negotiated peace. In reality, he was hoping that they would attack, and to encourage them on this mission he deliberately weakened his right flank. On 28 November, Napoleon met with his marshals at Imperial Headquarters and they informed him of their qualms and fears about the upcoming battle, even suggesting a retreat, but he shrugged off their complaints and went to work. Napoleon's plan envisioned that the Allies would throw so many troops to envelop his right flank that their centre would be severely weakened. He then counted on a massive French thrust, to be conducted by 16,000 troops of Soult's IV Corps, through the centre to cripple the Allied army. Meanwhile, to support his weak right flank, Napoleon ordered Davout's III Corps to force march all the way from Vienna and join General Legrand's men, who held the extreme southern flank that would bear the heavy part of the Allied attack. Davout's soldiers had 48 hours to March 110 km (68 mi). Their arrival would be extremely crucial in determining the success or failure of the French plan. The Imperial Guard and Bernadotte's I Corps were held in reserve while the V Corps under Lannes guarded the northern sector of the battle.
Battle is joined
The battle began around 8 a.m. with the first allied column attacking the village of Telnitz, which was defended by the 3rd Line Regiment. This sector of the battlefield witnessed heavy action in the following moments as several ferocious Allied charges evicted the French from the town and forced them on the other side of the Goldbach. The first men of Davout's corps arrived at this time and threw the Allies out of Telnitz before they too were attacked by hussars and re-abandoned the town. Additional Allied attacks out of Telnitz were checked by French artillery. Allied columns started pouring against the French right, but not at the desired speed, so the French were mostly successful in curbing the attacks. In reality, the Allied deployments were mistaken and poorly timed: cavalry detachments under Liechtenstein on the Allied left flank had to be placed in the right flank and in the process they ran into and slowed down part of the second column of infantry that was advancing towards the French right. At the time, the planners thought this was a disaster, but later on it helped the Allies. Meanwhile, the lead elements of the second column were attacking the village of Sokolnitz, which was defended by the 26th Light Regiment and the Tirailleurs, French skirmishers. Initial Allied assaults proved unsuccessful and General Langeron ordered the bombardment of the village. This deadly barrage forced the French out, and around the same time, the third column attacked the castle of Sokolnitz. The French, however, counterattacked and regained the village, only to be thrown out again. Conflict in this area ended momentarily when Friant's division (part of III Corps) retook the village. Sokolnitz was perhaps the most fought over area in the battlefield and would change hands several times as the day progressed.
"One sharp blow and the war is over"

Around 8:45 a.m., finally satisfied at the weakness in the enemy centre, Napoleon asked Soult how long it would take for his men to reach the Pratzen Heights, to which the Marshal replied, "Less than twenty minutes, sire." About 15 minutes later, Napoleon ordered the attack, adding, "One sharp blow and the war is over."
A dense fog helped to cloud the advance of St. Hilaire's division, but as they went up the slope the legendary 'Sun of Austerlitz' ripped the mist apart and encouraged them forward.Russian soldiers and commanders on top of the heights were stunned to see so many French troops coming towards them. Allied commanders were now able to feed some of the delayed detachments of the fourth column into this bitter struggle. Over an hour of horrendous fighting left much of this unit decimated beyond recognition. The other men from the second column, mostly inexperienced Austrians, also participated in the struggle and swung the numbers game against one of the best fighting forces in the French army, finally forcing them to withdraw down the slopes. However, gripped by desperation, St. Hilaire's men struck hard once more and bayoneted the Allies out of the heights. To the north, General Vandamme's division attacked an area called Staré Vinohrady and through talented skirmishing and deadly volleys broke several Allied battalions.
The battle had firmly turned to France's favor, but there was still much fighting ahead. Napoleon ordered Bernadotte's I Corps to support Vandamme's left and moved his own command centre from Zuran Hill to St. Anthony's Chapel on the Pratzen Heights. The difficult position of the Allies was confirmed by the decision to send in the Russian Imperial Guard; Grand Duke Constantine, Tsar Alexander's brother, commanded the Guard and counterattacked in Vandamme's section of the field, forcing a bloody effort and the loss of the only French standard in the battle (the unfortunate victim was a battalion of the 4th Line Regiment). Sensing trouble, Napoleon ordered his own heavy Guard cavalry forward. These men pulverized their Russian counterparts, but with both sides pouring in large masses of cavalry no victor was clear yet. The Russians had a numerical advantage here but fairly soon the tide swung as d'Erlon's Division, the 2nd of Bernadotte's I Corps, deployed on the flank of the action and allowed French cavalry to seek refuge behind their lines. The horse artillery of the Guard also unlimbered a deadly toll on the Russian cavalry and fusiliers. The Russians broke and many died as they were pursued by the reinvigorated French cavalry for about a quarter of a mile.
Endgame

Meanwhile, the northernmost part of the battlefield was also witnessing heavy fighting. Prince Liechtenstein's heavy cavalry began to assault Kellerman's lighter cavalry forces after finally arriving at the correct position in the field. The fighting originally went well for the French, but Kellerman's forces took cover behind General Caffarelli's infantry division once it became clear Russian numbers were too great. Caffarelli's men halted the Russian assaults and permitted Murat to send two cuirassier divisions into the fray to finish off the Russian cavalry for good. The ensuing melee was bitter and long, but the French ultimately prevailed. Lannes then led his V Corps against Bagration's men and after hard fighting managed to drive the skilled Russian commander off the field. He wanted to pursue, but Murat, who was in control of this sector in the battlefield, was against the idea.
Napoleon's focus now shifted towards the southern end of the battlefield where the French and the Allies were still fighting over Sokolnitz and Telnitz. In an effective double-pronged assault, St. Hilaire's division and part of Davout's III Corps smashed through the enemy at Sokolnitz and persuaded the commanders of the first two columns, generals Kienmayer and Langeron, to flee as fast as they could. Buxhowden, the commander of the Allied left and the man responsible for leading the attack, was completely drunk and fled as well. Kienmayer covered his withdrawal with the O'Reilly light cavalry, who gallantly managed to defeat five of six French cavalry regiments before they too had to retreat.
General panic now seized the Allied army and it abandoned the field in any and all possible directions. Russian forces that had been defeated by the French right withdrew south towards Vienna via the Satschan frozen ponds. According to popular myth, the French artillery pounded towards the men, but Napoleon redirected his gunners to fire at the ice. The men drowned in the viciously cold ponds, dozens of artillery pieces going down along with them. Estimates on how many guns were captured differ; there may have been as few as 38 or as many as over 100. Sources also differ on casualties, with figures ranging from as few as 200 to as many as 2,000 dead. Because Napoleon exaggerated this incident in his report of the battle, the low numbers may be more accurate, although doubt remains as to whether they are fully correct. Many regard this incident as one of Napoleon's cruelest acts in war. However, only a few bodies are reported to have been found in the spring of 1806, and it is most likely the incident is a myth.
Italian Campaigns
Venetian front or Italian campaign of 1805
Meanwhile, in Italy, the Austrian Armee von Italien under Archduke Charles fought against the French Armée d'italie under Marshal Masséna. The French managed to gain a bridgehead over the Adige river at Verona on 18 October, and finally, between 29 and 31 October, the outnumbered French defeated the superior Austrian army in the Battle of Caldiero. In November the Austrians retreated, engaging the French vanguard of d'Espagne in several rear-guard actions. Venice was blockaded by French and Italian troops under St.Cyr. Charles' army finally crossed the Isonzo on 14 November, preventing the French from crossing it.

One 4,400-strong Habsburg army that lingered behind, was roundly defeated and captured by Jean Reynier and St. Cyr at the Battle of Castelfranco Veneto on 24 November 1805.
Anglo-Russian occupation of Naples
Main article: Anglo-Russian occupation of NaplesThe French force under St. Cyr then manoeuvred on the frontier of the Kingdom of Naples. The French were being carefully watched by an Anglo-Russian force entrusted with defence of the kingdom. After the Battle of Austerlitz, the Russians withdrew from Italy and the British, unwilling to defend Naples alone, evacuated the mainland altogether and retreated back to Sicily. Meanwhile, the French force, now stationed in Bologna, was reorganised into the Army of Naples and placed under the nominal command of Napoleon's brother Joseph Bonaparte. However, the de facto commander was André Masséna, who commanded the I Corps and was entrusted with the invasion by Joseph.
French invasion of Naples
Main article: Invasion of Naples (1806)On 9 February 1806, Masséna invaded the Kingdom of Naples and two days later, the Bourbon King of Naples, Ferdinand IV also fled to Sicily, protected by the British fleet. Naples soon fell into French hands and by the end of February, only two places in the kingdom still held out. One was the fortress city of Gaeta, north of Naples, and the other was Calabria in the very south of Italy, which was where the remainder of the Royal Neapolitan Army was stationed.
Ferdinand had hoped for a repeat of the events of 1799, when a popular uprising in Calabria eventually caused the downfall of the Parthenopaean Republic, a French client state created after the Neapolitans were defeated the first time during the War of the Second Coalition. However, no such rebellion initially occurred and on 3 March, General Jean Reynier, who commanded the 10,000 strong II Corps of the Army of Naples invaded Calabria. Only a few Calabrians resisted the invading French force and the Royal Neapolitan Army was soundly defeated at the Battle of Campo Tenese on 10 March 1806. Ferdinand now had no choice but to concede the Neapolitan throne to the French. A day after Campo Tenese, Joseph was installed as the new King of Naples. By now, the last regular troops of the Neapolitan army had fled to Sicily and the French controlled the entire Italian mainland except for the fortress of Gaeta, which had been under siege since 26 February. Gaeta surrendered on 18 July, concluding the invasion with a decisive French victory.
Calabrian insurrection
However, all was not going to plan for the French. Supply problems meant that Reynier's II Corps in Calabria was forced to live off the land. For over a month, the peasants of the region had supported the Neapolitan army and were close to starvation. Joseph seemed unaware of the problems and the potential dangers of revolt. Consequently, no extra provisions were sent to the south of Italy. Reynier took the initiative and seized supplies from the local populace, leading predictably to a revolt by the end of March. What started as small bands of partisans eventually expanded into entire villages rising up against the French. With the fortress of Gaeta still holding out, Joseph was unable to send more troops to Calabria, forcing Reynier to reinforce his army with native troops recruited from the larger towns and cities.
By July, Masséna had still failed to take Gaeta due to poor logistical management of the French artillery, slight reinforcements from the British by sea and a series of successful sorties by the Neapolitan garrison against the French sappers. With only Reynier's small force in Calabria still struggling against the revolt, the British organised an expeditionary force under Sir John Stuart to prevent any potential invasion of Sicily and perhaps to trigger a full-scale rebellion against the French across Italy. Although there were early successes for the British, in particular at Maida, the British failed to either reinforce Stuart's expedition or attempt to relieve the Siege of Gaeta. With the French artillery finally able to bombard the walls with their full potential, the Neapolitans eventually surrendered on 18 July, freeing Masséna's I Corps.
Following the surrender, Masséna was ordered south by Joseph to support Reynier's II Corps against the British and the Calabrian insurrection. Now severely outnumbered in mainland Italy, the British retreated back to Sicily. However, the revolt was not suppressed until 1807, by which time Masséna had already requested permission to relinquish command. For the first time in the Napoleonic Wars, the French experienced a brutal guerrilla war carried on by a rebellious population. The French gleaned that the only effective way to deal with such an uprising was to implement terror tactics employed by Reynier. This foreshadowed the same problems the French, and in particular Joseph Bonaparte, would face in Spain during the Peninsular War.
Results

Austerlitz and the preceding campaign profoundly altered the nature of European politics. In three months, the French had occupied Vienna, decimated two armies, and humbled the Austrian Empire. These events sharply contrast with the rigid power structures of the 18th century, when no major European capital was ever held by an enemy army. Austerlitz set the stage for a near-decade of French domination on the European continent, but one of its more immediate impacts was to goad Prussia into war in 1806.
France and Austria signed a truce on 4 December and the Treaty of Pressburg 22 days later took the latter out of the war. Austria agreed to recognize French territory captured by the treaties of Campo Formio (1797) and Lunéville (1801), cede land to Bavaria, Württemberg, and Baden, which were Napoleon's German allies, and pay 40 million francs in war indemnities. Venetia was also given to the Kingdom of Italy. It was a harsh end for Austria, but certainly not a catastrophic peace. The Russian army was allowed to withdraw to home territory and the French encamped themselves in Southern Germany.
In July 1806, Napoleon created the Confederation of the Rhine, a string of German client states which on becoming allies of France pledged themselves to raise an army of 63,000 men. With Napoleon as their "Protector", the confederate states were compelled to leave the Holy Roman Empire, which was dissolved shortly afterward.<Prussia saw these and other moves as an affront to its status as the main power of Central Europe and it went to war with France in 1806.
In Italy, the political situation would remain unchanged until 1815, with the British and Sicilian troops guarding the Bourbon King Ferdinand in Sicily and the Napoleonic King of Naples controlling the mainland. In 1808, Joachim Murat became the King of Naples, after Joseph Bonaparte became King of Spain. Murat made various attempts to cross the Strait of Messina, which all ended in failure, despite once managing to secure a foothold in Sicily.
Casualties and losses
The French lost 12,000 killed, 22,200 wounded and 5,000 captured in 1805, including 5,300 killed and 22,200 wounded in the Austrian Campaign against the Habsburgs and Russians, 2,100 killed and 5,300 wounded in the Italian Campaign, 4,300 killed and 3,700 wounded in the naval war, 200 killed and 400 wounded in the colonies and 100 killed and 400 wounded in coastal defense duties. The 1806 Naples Campaign cost the French 1,500 killed and 5,000 wounded. The Spanish suffered 1,200 killed and 1,600 wounded in the naval war, Bavaria sustained 300 killed and 1,200 wounded in the Austrian Campaign and the Kingdom of Italy lost 100 killed and 400 wounded in the Italian Campaign and 250 killed and 1,500 wounded in the Naples Campaign.
The Austrians lost 20,000 killed and wounded and 70,000 as prisoners. Russian casualties were 25,000 killed and wounded and 25,000 captured. The Neapolitan army of 22,000 was wiped out by the French in 1806, with only 2,000 evacuated to Sicily.
See also
- War of the Fourth Coalition
- List of battles of the War of the Third Coalition
- List of Napoleonic battles
Notes
- This armed conflict has received various names:
- In Russian historiography, it is known as the Russian-Austro-French War (Russian: Русско-австро-французская война)
- it is known as the Austrian campaign of 1805 (French: Campagne d'Autriche de 1805) or the German campaign of 1805 (French: Campagne d'Allemagne de 1805)
Citations
- Rosenberg 2017, p. 168.
- Pagedas 2005, pp. 120–122.
- Chandler 1966, pp. 319–320.
- Rodger 2004, p. 528.
- Schneid 2005, p. 57. sfn error: no target: CITEREFSchneid2005 (help)
- Schneid 2005, pp. 83–87. sfn error: no target: CITEREFSchneid2005 (help)
- Gotthard 2003, p. 160.
- Chandler 1966, p. 323.
- Chandler 1966, pp. 332–333.
- Uffindell 2003, p. 155.
- Fisher & Fremont-Barnes 2004, pp. 31–33.
- Fisher & Fremont-Barnes 2004, p. 36.
- Chandler 1966, p. 382.
- Chandler 1966, p. 385.
- Kagan 2006, pp. 389, 393, 395 397.
- Kagan 2006, pp. 400, 402, 404, 408–409.
- Kagan 2006, pp. 412, 414–417, 420–421.
- Fisher & Fremont-Barnes 2004, pp. 39–41.
- Chandler 1966, pp. 399–400.
- "Napoleonic Wars". Westpoint.edu. U.S. Army. Archived from the original on 28 July 2014. Retrieved 1 July 2017.
- Bennet, Geoffrey (2004). The Battle of Trafalgar. England: Pen & Sword Books Limited, CPI UK, South Yorkshire.
- (in German) Rainer Egger. Das Gefecht bei Dürnstein-Loiben 1805. Wien: Bundesverlag, 1986.
- Smith 1998, p. 213.
- (in German) Jens-Florian Ebert. "Heinrich von Schmitt". Die Österreichischen Generäle 1792–1815. Napoleon Online: Portal zu Epoch Archived 8 April 2000 at the Wayback Machine. Markus Stein, editor. Mannheim, Germany. 14 February 2010 version. Accessed 5 February 2010: (in German) Egger, p. 29.
- Rothenberg, Gunther E. (1999). The Napoleonic Wars. The Cassell history of warfare. London: Cassell. p. 88. ISBN 978-0-304-35267-8.
- Uffindell 2003, p. 19.
- Chandler 1966, pp. 412–413.
- Chandler 1966, p. 416.
- McLynn 1997, p. 342.
- Brooks 2000, p. 109.
- Fisher & Fremont-Barnes 2004, p. 48.
- Fisher & Fremont-Barnes 2004, pp. 48–49.
- Uffindell 2003, p. 21..
- Chandler 1966, p. 425.
- Fisher & Fremont-Barnes 2004, pp. 49–51.
- Fisher & Fremont-Barnes 2004, p. 52.
- Chandler 1966, p. 432.
- ^ Finley 1976, pp. 84–87.
- Masséna & Koch 1848, pp. 194–251..
- Dorne Brose 2013, p. 51.
- ^ Bodart 1916, p. 43.
- ^ Bodart 1916, p. 128.
references
- Black, Jeremy (1999). Britain as a military power, 1688-1815. London: UCL Press. ISBN 185728772X.
- Bodart, G. (1916). Losses of Life in Modern Wars, Austria-Hungary; France. ISBN 978-1-371-46552-0.
- Brooks, Richard, ed. (2000). Atlas of World Military History. London: HarperCollins. ISBN 0-7607-2025-8.
- Chandler, David (1966). The Campaigns of Napoleon. New York: Scribner. ISBN 0-02-523660-1.
- Chandler, David (1979). Dictionary of the Napoleonic Wars. London: Macmillan. OCLC 4932949.
- Dorne Brose, Eric (2013). German History, 1789–1871. From the Holy Roman Empire to the Bismarckian Reich. New York: Berghahn Books. ISBN 9781782380047.
- Dupuy, Trevor N. (1993). Harper Encyclopedia of Military History. New York: HarperCollins. ISBN 0-06-270056-1.
- Finley, Milton C. Jr. (1976). "Prelude to Spain: The Calabrian Insurrection, 1806–1807". Military Affairs. 40 (2). doi:10.2307/1987151. JSTOR 1987151.
- Fisher, Todd; Fremont-Barnes, Gregory (2004). The Napoleonic Wars: The Rise and Fall of an Empire. Oxford: Osprey Publishing. ISBN 1-84176-831-6.
- Gotthard, Axel (2003). Das Alte Reich, 1495-1806. Darmstadt: Wissenschaftliche Buchgesellschaft. ISBN 9783534151189.
- Kagan, Frederick W. (2006). The End of the Old Order. Cambridge: Da Capo Press. ISBN 0-306-81137-5.
- Knight, R. J. B (2013). Britain against Napoleon : the organization of victory, 1793-1815. London: Allen Lane. ISBN 9780141038940.
- Masséna, André; Koch, Jean Baptiste Frédéric (1848). Mémoires de Masséna (in French). Vol. V. Paris: Paulin et Lechevalier.
- McLynn, Frank (1997). Napoleon: A Biography. New York: Arcade Publishing. ISBN 1-55970-631-7.
- Mikaberidze, Alexander (2020). The Napoleonic Wars A Global History. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-995106-2.
- Pagedas, Constantine A. (2005). "Counterpoint to Trafalgar: The Anglo-Russian Invasion of Naples, 1805–1806 (Review)". Mediterranean Quarterly. 16 (1): 120–122. doi:10.1215/10474552-16-1-120. S2CID 154229720.
- Rodger, N.A.M. (2004). The Command of the Ocean. London: Allan Lane. ISBN 0-7139-9411-8.
- Rosenberg, Chaim M. (2017). Losing America, Conquering India: Lord Cornwallis and the Remaking of the British Empire. McFarland. ISBN 978-1-4766-6812-3.
- Smith, Digby (1998). The Greenhill Napoleonic wars data book. London: Greenhill. ISBN 9781853672767.
- Schneid, Frederick C. Napoleon's conquest of Europe: the War of the Third Coalition. Westport: Praeger. ISBN 0275980960.
- Schneid, Frederick C. (2002). Napoleon's Italian Campaigns 1805–1815. Praeger. ISBN 0-275-96875-8.
- Schroeder, Paul W. (1996). The Transformation of European Politics 1763–1848. Oxford U.P. pp. 210–86. ISBN 978-0-19-820654-5.
- Uffindell, Andrew (2003). Great Generals of the Napoleonic Wars. Kent: Spellmount. ISBN 1-86227-177-1.
External links
- Maude, Frederic Natusch (1911). "Napoleonic Campaigns" . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 19 (11th ed.). pp. 212–236.
- War of the Third Coalition
- 19th-century conflicts
- Napoleonic Wars
- Conflicts in 1803
- Conflicts in 1804
- Conflicts in 1805
- Conflicts in 1806
- Napoleon's planned invasion of the United Kingdom
- 1805 in Europe
- Wars involving France
- Wars involving Austria
- Wars involving the United Kingdom
- Wars involving the Russian Empire
- Wars involving Spain
- Wars involving Sweden
- Wars involving Bavaria
- Wars involving the Kingdom of Naples
- Wars involving the Holy Roman Empire
- Wars involving the Kingdom of Sicily
- Wars involving Württemberg