United States historic place
| Tiller Ranger Station | |
| U.S. National Register of Historic Places | |
| U.S. Historic district | |
 Tiller Ranger Station, 1941 Tiller Ranger Station, 1941 | |
  | |
| Location | Umpqua National Forest |
|---|---|
| Nearest city | Canyonville, Oregon, USA |
| Coordinates | 42°55′37″N 122°56′59″W / 42.92707°N 122.94978°W / 42.92707; -122.94978 |
| Built | 1935-1942 |
| Architect | U.S. Forest Service, Pacific Northwest Regional Architecture Group |
| Architectural style | Cascadian rustic |
| NRHP reference No. | 91000162 |
| Added to NRHP | 1991 |
The Tiller Ranger Station is a United States Forest Service compound consisting of twenty-seven buildings in Oregon’s Umpqua National Forest. Over the years, it has been the administrative headquarters for five ranger districts. It is located in the small unincorporated community of Tiller, Oregon, United States. The historic structures were built in the rustic style by the Civilian Conservation Corps between 1935 and 1942. Today, the ranger station is the headquarters for the Tiller Ranger District, and is listed on the National Register of Historic Places.
History
In the early 20th century, the forest road networks were not well developed. To facilitate work in National Forests, the Forest Service built district ranger stations at strategic locations within the forest to house full-time employees and provide logistics support to fire patrols and project crews working in remote areas of the forest. After World War II, the Forest Service greatly expanded its road network, allowing employees to get to most forest areas within a few hours. As a result, many of the more isolated ranger stations were closed or converted to summer guard stations. However, the Tiller Ranger Station has continuously served as a district headquarters since it was established. Over the years, five ranger districts have used the Tiller Ranger Station as their administrative headquarters.
In 1908, the Umpqua National Forest was created in southern Oregon. The Summit Ranger District was established in 1913 as an administrative subdivision of the Umpqua National Forest. However, the district was not staffed with a ranger until 1918. The Summit district was responsible for the south bank of the South Umpqua River extending east to the Rogue-Umpqua divide in the Rattlesnake Mountain area. The Deadman Ranger District was also created in 1913 and staffed in 1918. It covered the north side of the South Umpqua River drainage. Both districts had their administrative headquarters at the Tiller Ranger Station.
The South Umpqua Ranger District was established in 1916. Its district headquarters was also located at Tiller Ranger Station. In 1920, the Summit and Deadman ranger districts were merged into the South Umpqua district.

In 1935, the Civilian Conservation Corps began doing construction work at the ranger station. Between 1935 and 1942, Civilian Conservation Corps crews built a number of ranger station buildings. The Civilian Conservation Corps personnel worked under the supervision of Forest Service rangers. All of the buildings constructed during that period were designed by the Forest Service's Pacific Northwest Regional Architecture Group, and were built in the Cascadian rustic style.
The Cow Creek Ranger District was created in 1946 from a division of the large South Umpqua Ranger District. Two years later, the two ranger districts were recombined into a single South Umpqua district. In 1954, the South Umpqua district was again divided into a new Cow Creek district and a smaller South Umpqua district; however, the two districts had different boundaries than the earlier division. The South Umpqua district retained authority over the upper South Umpqua River drainage while the Cow Creek district administered the Cow Creek, Elk Creek, and Beaver Creek watersheds. Both districts maintained district offices at Tiller Ranger Station.
In 1956, the Cow Creek Ranger District was reduced in size when a large portion of the Oregon and California Railroad lands were administratively transferred to the Bureau of Land Management. The Cow Creek district was renamed the Tiller Ranger District in 1964. In 1968, the South Umpqua Ranger District was consolidated with the Tiller Ranger District. The new district kept the Tiller name because the administrative headquarters was still located at the Tiller Ranger Station.
Today, the Tiller Ranger District covers 325,106 acres (1,315.66 km) on the western slopes of the Cascade Mountains in southern Oregon. The Tiller Ranger Station still serves as the administrative headquarters for the district. 27 buildings make up the ranger station complex, nine of which are historically important. All the historic buildings except the barn are located in close proximity to one another, with the non-historic structures on the periphery of the compound. The historic buildings are all in excellent condition and are still used by Forest Service employees. Because the Tiller Ranger Station is of unique historic value as an early Forest Service ranger station, the compound was listed on the National Register of Historic Places on 6 March 1991. The historic district covers approximately 12 acres (49,000 m).
Structures
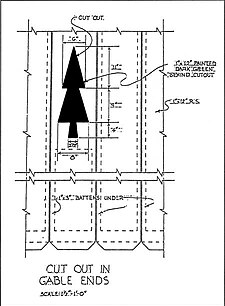
With nine historic buildings, the Tiller Ranger Station is a classic Forest Service ranger station. All of the historic buildings were built by the Civilian Conservation Corps between 1935 and 1942. Their work included four ranger residences, an equipment warehouse, a vehicle repair shop, a barn (now used for storage), and two garages. The buildings were constructed in the Cascadian rustic architectural style using weatherboard, wood shingles, native lava stone, and concrete as the principal building materials. Many of the gables and shutters have the open pine tree logo common to Forest Service structures built during the 1930s.
The four ranger residences are all of unique design. All of the residences were built in the late 1930s. The largest (Residence #1058) was built in 1936. It is a T-shaped, one-and-one-half-story wood-frame building on a concrete foundation. It has a high gabled roof with intersecting cross-gabled hip extensions above the main entry. Three stone steps lead to a flagstone porch in front of the main entrance. The front porch is supported by square posts. There is a stone masonry chimney on the east side of the building. The building's exterior is covered with wood shingles except the gable ends and gablets which have vertical board siding. Like the other three residences, the building has six-over-six double-hung sash windows flanked by decorative shutters with pine tree logo cut-outs. Adjacent to the residence is a hip roof garage with the shingle siding. There is a pine tree cut-out on the main vehicle entry door.
The other three residences are all one-story structures. One is a T-shaped design while the remaining two have rectangular footprints. All three are wood-frame structures on concrete foundations. They all have shingles exteriors, flagstone porches, stone masonry chimneys, and gabled roofs. However, each has a different floor plan and exterior look. There is a second garage located next to the T-shaped residence.
The Civilian Conservation Corps also built three non-residential structures at the Tiller Ranger Station. The warehouse is a one-and-one-half-story rectangular building with a large drive-in storage area at one end and an interior storage area at the other end. It is a wood-frame structure with horizontal wood siding. The automotive shop is also a one-and-one-half-story rectangular building. It is a wood-frame structure on a concrete foundation with vertical board siding. The shop has three large vehicle bays with pull-down doors and an adjoining storage and work area.

The barn is a two-story rectangular structure built in 1940. It is a wood-frame building on a concrete foundation with a gambrel roof. The barn has a wood shingle exterior with simple four-panel wood-casement windows. There are two ground-floor entry doors on the south gable end of the building. There is also a hayloft entry on the second floor above the ground-floor entrances. The loft entrance is covered with large side-hung double-doors. On the east side of the building, there is another doorway near the center of the structure along with two large drive-in entry doors for loading and unloading. There is a large shed attached to the north end of the barn. The shed-annex has a drive-in entrance on the east side of the building next to the barn's two drive-in loading doors. The Forest Service now uses the barn for general-purpose storage.
Location
The Tiller Ranger Station is in southeastern Douglas County, Oregon surrounded by the Umpqua National Forest. The elevation at the site is 1,043 feet (318 m) above sea level. The forest around the ranger station is made up of Douglas fir, hemlock, and Western red cedar.
The Tiller Ranger Station is 17 miles (27 km) east of Canyonville, Oregon in the small unincorporated community of Tiller, Oregon. The ranger station is on the south bank of the South Umpqua River, just off Oregon Route 227. The Forest Service district office and all of the historic buildings are on the north side of the highway.
References
- "A Bit of History", Recreation Rentals of the Pacific Northwest, Pacific Northwest Region, United States Forest Service, United States Department of Agriculture, Portland, Oregon, 8 February 2010.
- ^ "Ranger Districts and District Ranger 1916-2008", Umpqua National Forest, United States Forest Service, Department of Agriculture, Roseburg, Oregon, 3 September 2008.
- ^ "Tiller Ranger Station", National Register of Historic Places Registration Form, National Park Service, United States Department of Interior, Washington, D.C., 9 October 1987.
- ^ "History", Umpqua National Forest, United States Forest Service, Department of Agriculture, Roseburg, Oregon, 5 August 2008.
- "Tiller Ranger Station", National Register of Historic Places, www.nationalregisterofhistoricalplaces.com, 8 February 2010.
- ^ "Tiller Ranger Station", Historical Places Database, www.hpdb.org, Oakland, California, 8 February 2010.
- "Tiller Ranger Station", Archiplanet, www.archiplanet.org, 5 December 2006.
- Tiller, Oregon topographic map, United States Geological Survey, United States Department of Interior, Reston, Virginia; displayed via ACME mapper, www.acme.com, 8 February 2010.
External links
| U.S. National Register of Historic Places in Oregon | ||
|---|---|---|
| Lists by county | [REDACTED]  | |
| Portland lists | ||
| Other lists | ||
- Park buildings and structures on the National Register of Historic Places in Oregon
- Historic districts on the National Register of Historic Places in Oregon
- Buildings and structures in Douglas County, Oregon
- Civilian Conservation Corps in Oregon
- Rustic architecture in Oregon
- Government buildings completed in 1936
- United States Forest Service ranger stations
- National Register of Historic Places in Douglas County, Oregon
- 1936 establishments in Oregon



