| Valdôtain | |
|---|---|
| valdotèn | |
| Native to | Italy |
| Region | Aosta Valley |
| Native speakers | Approximately 68,000 people (2003) |
| Language family | Indo-European |
| Writing system | Latin |
| Official status | |
| Official language in | Protected by statute in the Aosta Valley, Italy |
| Regulated by | Bureau régional pour l'ethnologie et la linguistique (BREL) |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | – |
| Glottolog | vall1249 |
| IETF | frp-u-sd-it23 |
Valdôtain ([valdotɛ̃]; local dialect: Valdotèn, Valdŏtèn, Valdouhtan) is a dialect of Arpitan (Franco-Provençal) spoken in the Aosta Valley in Italy, and the common language of the Aosta Valley. It is commonly known as patois or patoué. It is not an official language, the two regional official languages being French and Italian, though it is officially recognized.
Distribution and classification
The Aosta Valley represents the only region of the Franco-Provençal area where this language is still widely spoken natively among all age ranges of the population, with a 2001 survey reporting almost 58% of the population know Franco-Provençal. A further 2003 study confirmed the status of Franco-Provençal as a main language for a majority of the population, with significant multilingualism.
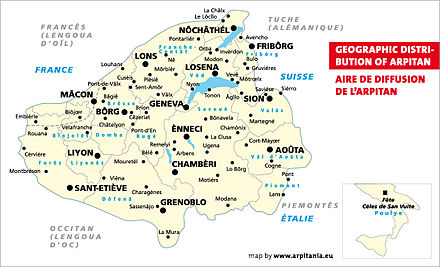
It has been said that in the Aosta Valley there are as many forms of patois as there are bell towers, in reference to the high linguistic diversity in the region within the Valdôtain varieties of Franco-Provençal. However, they can be broadly classified into two main branches: those of the Upper Valley (French: haute Vallée, Italian: alta valle) to the west and of the Lower Valley (French: basse Vallée, Italian: bassa valle) to the east of the city of Aosta. Valdôtain varieties from the Upper Valley tend to be more innovative and have more affinity with from varieties spoken in Savoy and in Valais, across the national borders; meanwhile, those from the Lower Valley tend to be more conservative, with influence from Piedmontese.
The urban variety of Aosta itself (Arpitan: patoué de la Veulla, lit. 'Patois of the City') has often been considered 'neutral', especially for the local-language media.
Vocabulary examples
Several subdialects of Valdôtain exist that exhibit unique features in terms of phonetics and vocabulary.
| Italian | French | West | Central-North | Central-Southeast | East | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| La Thuile | La Salle | Rhêmes-Saint-Georges | Valsavarenche | Cogne | Sarre | Saint-Oyen | Oyace | Quart | Fénis | Champorcher | Valtournenche | Ayas | Emarèse | Arnad | Gaby | ||
| rastrello | râteau | rassi | râhé | rahi | rahi | raté | rati | râti | râti | raté | râti | rati | râté | rahtél | rahté | rahté | rahtél |
| fiore | fleur | flôr | fleu | fleur | fleure | fieur | fleur | flôr | fleu | fleur | fleur | fior | flour | fiour | fiour | fiour | fiour |
| volpe | renard, goupil | rèinâr | rèinâ | rèinar | rèinâr | rèinèar | rèinâr | rèinâ | rèinâr | rèinâr | rèinal | verpeuill | gorpeul | gorpéi | gorpeui | gorpeui | voulp |
| sì | oui, ouais | voué | vouè | vouè | ouè | vouài | ouè | ouè | vouè | vouè | ouè | ouèi | ò | òi | òi | òi | òi |
Linguistic studies

Valdôtain has been the subject of detailed study at the Bureau régional pour l'ethnologie et la linguistique (BREL) in Aosta as well as in the Centre d'études francoprovençales in Saint-Nicolas.
Music
The main modern singers and songwriters in Valdôtain are:
- Louis de Jyaryot, from Ayas;
- Maura Susanna, from Saint-Vincent;
- Magui Bétemps, from Valtournenche.
The traditional Aostan songs in Valdôtain and in French form the core of the activity of the band Trouveur valdotèn.
Poetry
Here is a selection of some of the most important poets in Valdôtain:
Cllier et seren lo ten apré la piôdze
— André Ferré (Saint-Vincent, 1904-1954)
Cé bé soleil que torne égueeyìno la Val
I sorton le feumélle ch'achèté su la lôye
In precassèn de queut tant bien que mal
Esplojon de meuseucca
— Palmyre Arbaney-Farcoz (Doues, 1900 - Aosta, 1980)
Feusette de joèce
Tsarriemèn de note que chorton
Su lé, iou lé clliotse dzalaouse
Le vardon a catson
De nët euna leumiére
— La pastorala, Jean-Baptiste Celogne (Saint-Nicolas, 1826 - Saint-Pierre, 1910)
I berdzè l'at paru
Un andze vin leur dëre:
"Lo Saveur l'est neissu:
un pouro baou l'est son palatse
et sat pei de fen en traver
compouson lo deur matelatse
De ci gran Rei de l'univer;
et din la rigueur de l'iver
de dò trei lindzo l'est qeuveur
Y son vignà de bon matèn<
— Césarine Binel (Champdepraz, 1897 - 1956)
a désèi lo for
Adeline e Dzeusepèn
son lé prumì dou tor.
Pôrton lo bôch de biôla
é eun grou sac pesàn,
lo vouidon su la tôla
pé fare lo bon pan
Dz'é vu su 'na louye, quase se presta a à tsére ba,
— Anaïs Ronc-Désaymonet (Arpuilles, 1890 - Aosta, 1955)
Dé géragnon coleur lilà.
Dz'é vu su 'na viéille fenétra, flourì i soleil
Dé géragnon blan comme la nèi.
Dz'é vu pendre, de la terasse de 'na villà
Dé géragnon coleur fouà.
Fleur di pouro, fleur di reutso, géragnon,
Vo-éte la garniteura de totte le meison.
Vo no portade lo sourire di bon Djeu
Afen de no rendre tcheu moén malereu
See also
References
- Sondage linguistique de la Fondation Émile Chanoux
- Norme in materia di tutela delle minoranze linguistiche storiche, Italian parliament
- Site du Centre d'études francoprovençales : "Au temps de Willien : les ferments de langue" Archived 27 June 2022 at the Wayback Machine.
- Roullet, Stefania (2003). Iannaccaro, Gabriele; Dell’Aquila, Vittorio; Andrione, Etienne (eds.). "Une interprétation sociolinguistique de phénomènes prosodiques: le cas de Cogne (Vallée d'Aoste)" (in French). Une Vallée d’Aoste bilingue dans une Europe plurilingue – Una Valle d’Aosta bilingue in un’Europa plurilingue. Aosta: Fondation Émile Chanoux: 98.
À côté des langues officielles, l'italien (que 97 % de la population valdôtaine dit connaître) et le français (connu par presque 78 % des Valdôtains), qui représentent les modèles de prestige de référence, on y trouve de nombreuses variétés francoprovençales (connues par presque 58 % de la population), ainsi que des variétés alémaniques (walser, connu par 78,4 % de la population de Issime, Gressoney-La-Trinité et Gressoney Saint-Jean, ainsi que par 0,4 % des Valdôtains en dehors de ces communes).
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - Berruto, Gaetano (January 1, 2003). "Una Valle d'Aosta, tante Valli d'Aosta? Considerazioni sulle dimensioni del plurilinguismo in una comunità regionale". Iris.unito.it: 44. Retrieved 4 November 2023.
- ^ "Francoprovençal patois en Vallée d'Aoste". www.patoisvda.org. Retrieved 5 November 2023.
- Bichurina, Natalia (2 September 2016). "Trans-border communities in Europe and the emergence of "new" languages : From "Francoprovençal patois" to "Arpitan" and "Arpitania"". Perpignan. Retrieved 5 November 2023.
Bibliography
- (in French) Jules Brocherel, Le Patois et la langue française en Vallée d'Aoste éd. V. Attinger, Neuchâtel
- (in French) Aimé Chenal, Le franco-provençal valdotain. Morphologie et Syntaxe, Aoste, Musumeci éditeur, 1986, ISBN 8870322327
- (in French) Alexis Bétemps, La langue française en Vallée d'Aoste de 1945 à nos jours, Milan, T.D.L.,
- (in French) Hans-Erich Keller, Études linguistiques sur les parlers valdôtains, éd. A. Francke S.A., Berne, 1958.
- (in French) Ernest Schüle, Histoire linguistique de la Vallée d’Aoste, dans "Bulletin du Centre d’études francoprovençales" n° 22, Imprimerie Valdôtaine, Aoste, 1990.
- (in French) Xavier Favre, Histoire linguistique de la Vallée d’Aoste, dans "Espace, temps et culture en Vallée d’Aoste", Imprimerie Valdôtaine, Aoste, 1996.
- (in French) François-Gabriel Frutaz, Les origines de la langue française en Vallée d’Aoste, Imprimerie Marguerettaz, Aoste, 1913.
- (in French) Édouard Bérard, La langue française dans la Vallée d’Aoste, Aoste, 1861.
- (in French) Alexis Bétemps, Les Valdôtains et leur langue, préface de Henri Armand, Imprimerie Duc, Aoste, 1979.
- (in French) Alexis Bétemps, Le bilinguisme en Vallée d’Aoste : problèmes et perspectives, dans "Les minorités ethniques en Europe", par les soins de A.-L. Sanguin, l’Harmattan, Paris, 1993, pages 131-135.
- (in French) Bétemps, Alexis, Le francoprovençal en Vallée d’Aoste. Problèmes et prospectives, dans Lingua e comunicazione simbolica nella cultura walser, VI. Walsertreffen (6ème rencontre des Walsers), Fondazione Monti, Ausola d’Assola, 1989, p. 355-372
| Languages of Italy | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Historical linguistic minorities: Albanian, Catalan, Croatian, French, Franco-Provençal, Friulian, Germanic, Greek, Ladin, Occitan, Romani, Sardinian, Slovene, Wenzhounese | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gallo-Romance languages and dialects | |
|---|---|
| Areal groups | |
| Langues d'oïl | |
| Francoprovencalic |
|
| |
| Romance languages (classification) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Major branches | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Eastern | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Italo- Dalmatian |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Western |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Others | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reconstructed | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||