| X-linked myopathy with excessive autophagy | |
|---|---|
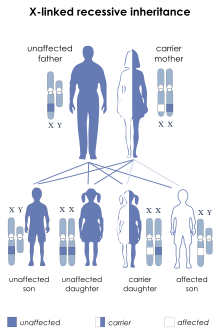 | |
| This condition is inherited in an X-linked recessive manner. | |
| Specialty | Neurology |
X-linked myopathy with excessive autophagy (XMEA) is a rare childhood onset disease characterized by slow progressive vacuolation and atrophy of skeletal muscle. There is no known cardiac or intellectual involvement.
Presentation
The incidence of this disease is not precisely known but it is considered to be rare (< 1/10 population). It has been reported in 15 families to date mostly from Canada, Finland and France.
This disease usually presents between the ages of 5 and 10 years old. The usual picture is with weakness involving the upper legs and affects activities such as running and climbing stairs. As the condition progresses, patients tend to experience weakness in their lower legs and arms. Some remain able to walk in advanced age, while others require assistance in adulthood.
Genetics
This disorder is inherited in a recessive X linked fashion. As a result, males are much more commonly affected than females. It is due to a mutation in VMA21 gene - the human homolog of the yeast Vma21p protein. This gene is located on the long arm of chromosome X (Xq28). It is an essential assembly chaperone of the vacuolar ATPase - the principal mammalian proton pump complex. Mutations in this gene increase lysosomal pH. This in turn reduces lysosomal degradative ability and blocks autophagy.
Pathology
The muscle fibers are rarely necrotic but have evidence of excessive autophagic activity and exocytosis of the phagocytosed material. They have increased variation in size and are predominantly composed of round small and hypertrophic fibers. The vacuoles are strongly reactive for dystrophin and lysosome associated membrane protein 2 (LAMP2). Membrane bound vacuoles and balls of dense material under the basal lamina are present. Deposition of the C5b-9 complement attack complex, subsarcolemmal deposition of calcium and expression of MHC1 complex also occur.
On electron microscopy characteristic balls of dense material are commonly seen. The vacuoles may contain remains of mitochondria, membrane whorls and calcium apatite crystals.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis can be established by muscle biopsy.
Investigations
The serum creatinine is raised.
Differential diagnosis
Treatment
| This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (December 2017) |
History
This disorder was described in 1988 by Kalimo et al in Finland in three brothers. The same condition affected their maternal grandfather and great-uncle.
References
- Kalimo H, Savontaus ML, Lang H, Paljärvi L, Sonninen V, Dean PB, Katevuo K, Salminen A (1988) X-linked myopathy with excessive autophagy: a new hereditary muscle disease. Ann Neurol 23(3):258-265
External links
| Classification | D |
|---|
| Diseases of muscle, neuromuscular junction, and neuromuscular disease | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neuromuscular- junction disease | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Myopathy |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||