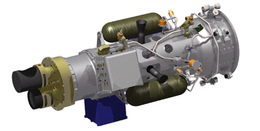
 XSS-10 computer model XSS-10 computer model | |
| Mission type | Technology |
|---|---|
| Operator | AFRL |
| COSPAR ID | 2003-005B |
| SATCAT no. | 27664 |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Manufacturer | Boeing |
| Launch mass | 28 kilograms (62 lb) |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | January 29, 2003, 18:06:00 (2003-01-29UTC18:06Z) UTC |
| Rocket | Delta II 7925-9.5 (Delta 295) |
| Launch site | Cape Canaveral SLC-17B |
| Orbital parameters | |
| Reference system | Geocentric |
| Regime | Low Earth |
| Eccentricity | 0.020384971 |
| Perigee altitude | 518.0 kilometers (321.9 mi) |
| Apogee altitude | 805.0 kilometers (500.2 mi) |
| Inclination | 39.75 degrees |
| Period | 98.0 minutes |
| Epoch | 29 January 2003, 13:06:00 UTC |
XSS-10 (eXperimental Small Satellite 10) was a small, low-cost micro-spacecraft developed by the U.S. Air Force Research Laboratory's Space Vehicles Directorate to test technology for line-of-sight guidance of spacecraft. The project was initiated at AFRL by Program Manager David Barnhart and completed by Georgia Tech Research Institute engineer Thom Davis and team. The project was declared a success shortly after launch.

References
- "NASA - NSSDCA - Spacecraft - Trajectory Details". nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov. Retrieved 2018-05-02.
- Banke, Jim (2003-01-30). "Air Force XSS-10 Micro-Satellite Mission a Success". Space.com. Archived from the original on May 13, 2008. Retrieved 2008-07-28.
- Barnhart, David A.; Hunter, Roger C.; Weston, Alan R.; Chioma, Vincent J.; Steiner, Mark; Larsen, William (October 1998). XSS-10 micro-satellite demonstration. AIAA Defense and Civil Space Programs Conference and Exhibit. Huntsville, AL: American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics. doi:10.2514/6.1998-5298. AIAA 1998-5298.
- "Big plans for small satellites". Historical archive. Georgia Tech Research Institute. Retrieved 2012-10-26.
- Sanders, Jane M (2003-08-11). "The Little Engine That Could". Research Horizons. Georgia Institute of Technology. Retrieved 2012-10-26.
External links
- XSS Micro-Satellite at Boeing.com
| U.S. Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL) spacecraft and air vehicles | |
|---|---|
| Launch/orbital vehicles |
|
| University Nanosat Program | |
| Space weather satellites | |
| Technology demonstrators |
|
| Tactical Satellite Program satellites | |
| USAF and USSF space vehicle designations (since 1962) | |
|---|---|
| SLV series | |
| SB series | |
| Satellites | |
| |
| ← 2002Orbital launches in 20032004 → | |
|---|---|
| January | |
| February | |
| March | |
| April | |
| May | |
| June | |
| July | |
| August | |
| September | |
| October | |
| November | |
| December | |
| Launches are separated by dots ( • ), payloads by commas ( , ), multiple names for the same satellite by slashes ( / ). Crewed flights are underlined. Launch failures are marked with the † sign. Payloads deployed from other spacecraft are (enclosed in parentheses). | |
This article about one or more spacecraft of the United States is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |