| Revision as of 16:22, 3 May 2007 editNatasha2006 (talk | contribs)249 editsNo edit summary← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 17:31, 11 October 2024 edit undoFgnievinski (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Extended confirmed users67,080 edits →Discussion | ||
| (207 intermediate revisions by more than 100 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Cardinal direction for steering}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| '''Course''', in ], is the intended flight path of an airplane over the ground; or the direction of a line drawn on a chart representing the intended airplane path, expressed as the angle measured from a specific reference datum clockwise from 0° through 360° to the line. The reference can be ] or ] and called true course or magnetic course respectively. Course is customarily expressed in three digits, using preliminary zeros if needed. | |||
| In ], the '''course''' of a ] or ] is the ] in which the craft is to be ]. The course is to be distinguished from the '']'', which is the direction where the watercraft's ] or the aircraft's ] is pointed.<ref name="Bartlett"> | |||
| In order to be used in a chart <!-- or for ]--Find no reference, and doubt it -->, this reference has to be ]. | |||
| {{Citation|last=Bartlett|first=Tim|title=Adlard Coles Book of Navigations|year=2008|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=RWUQAAAAQBAJ&q=pilotage|page=176|publisher=Adlard Coles|isbn=978-0713689396}}</ref><ref name=Chapman> | |||
| {{cite book | |||
| | last = Husick | |||
| | first = Charles B. | |||
| | title = Chapman Piloting, Seamanship and Small Boat Handling | |||
| | publisher = Sterling Publishing Company, Inc. | |||
| | date = 2009 | |||
| | page = 927 | |||
| | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=S4FwbS8StvEC&q=definition+nautical+course&pg=PA50 | isbn = 9781588167446 }}</ref><ref name=":0">{{Cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=C99DDQAAQBAJ&q=track&pg=PT839|title=Pilot's Handbook of Aeronautical Knowledge: FAA-H-8083-25B|last=Federal Aviation Administration (FAA)|date=2016-09-25|publisher=Ravenio Books|language=en}}</ref> | |||
| The path that a vessel follows is called a '''track''' or, in the case of aircraft, '''ground track''' (also known as ''course made good'' or ''course over the ground'').<ref name="Bartlett" /> The intended track is a '''route'''. | |||
| == Discussion == | |||
| * '''Heading''' (2) is the direction the vessel, aircraft or vehicle is truly "pointing towards" (the heading of the ship shown in the image is 058°). | |||
| {{further|Bearing (angle)#Arcs|Rhumb line#Introduction}} | |||
| {{multiple image | |||
| *Any reading from a magnetic compass refers to ''compass north'' (4), which is supposed to contain a two-part ''compass error:'' <br/>a) The earth's magnetic field's north direction, or ''magnetic north'' (3), almost always differs from true north by ] (6), the local amount of which is given in nautical charts, and <br/>b) ship's own magnetic field may influence the compass by so-called ] (5). <br/>Deviation only depends on the ship's own magnetic field and the heading, and therefore can be checked out and given as a ''deviation table'' or, graphically, as a ]. | |||
| | width1 = 200 | |||
| | footer = True heading (left) and magnetic heading (right) | |||
| | image1 = MISB ST 0601.8 - Platform Heading Angle.png | |||
| | alt1 = | |||
| | width2 = 200 | |||
| | image2 = MISB ST 0601.8 - Platform Magnetic Heading.png | |||
| | alt2 = | |||
| | caption2 = | |||
| }} | |||
| For ships and aircraft, routes are typically ] segments between ]. A navigator determines the ''bearing'' (the compass direction from the craft's current position) of the next waypoint. Because water currents or wind can cause a craft to drift off course, a navigator sets a ''course to steer'' that compensates for drift. The helmsman or pilot points the craft on a ''heading'' that corresponds to the course to steer. If the predicted drift is correct, then the craft's track will correspond to the planned course to the next waypoint.<ref name="Bartlett" /><ref name=":0" /> Course directions are specified in degrees from north, either true or magnetic. In ], north is usually expressed as 360°.<ref name="Nolan2010">{{cite book|author=Michael Nolan|title=Fundamentals of Air Traffic Control|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=6yhTiGC3ulcC&pg=PA201|date=2010|publisher=Cengage Learning|isbn=978-1-4354-8272-2|page=201|quote=For example, a runway heading north would have a magnetic heading of 360°.}}</ref> Navigators used ], instead of compass degrees, e.g. "northeast" instead of 45° until the mid-20th century when the use of degrees became prevalent.<ref>{{Cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=xRqzoX04v5AC&q=cardinal+direction&pg=PA233|title=The Annapolis Book of Seamanship: Third Edition: Completely Revised, Expanded and Updated|last1=Rousmaniere|first1=John|last2=Smith|first2=Mark|date=1999|publisher=Simon and Schuster|isbn=9780684854205|pages=234|language=en}}</ref> | |||
| *The ''compass heading'' or ''compass course'' (7) has to be corrected first for deviation (the "nearer" error), wherefrom results the ''magnetic heading'' (8). Correcting this for variation yields ''true heading'' (2). | |||
| [[Image:Course (navigation).svg|center|upright=3|Heading and track (A to B)<br> | |||
| *In case of a cross ] (9), and/or ] or other current (10), the heading will not meet the desired target, as the vessel will continuously drift sideways; it is necessary to point away from the intended course to counteract these effects. | |||
| 1 – True North <br> | |||
| 2 – Heading, the direction the vessel is "pointing towards" <br> | |||
| 3 – Magnetic north, which differs from true north by the magnetic variation. <br> | |||
| 4 – Compass north, including a two-part error; the magnetic variation (6) and the ship's own magnetic field (5) <br> | |||
| 5 – Magnetic deviation, caused by vessel's magnetic field. <br> | |||
| 6 – Magnetic variation, caused by variations in Earth's magnetic field. <br> | |||
| 7 – Compass heading or compass course, before correction for magnetic deviation or magnetic variation. <br> | |||
| 8 – Magnetic heading, the compass heading corrected for magnetic deviation but not magnetic variation; thus, the heading reliative to magnetic north. <br> | |||
| 9, 10 – Effects of crosswind and tidal current, causing the vessel's track to differ from its heading. <br> | |||
| A, B – Vessel's track.]] | |||
| == |
== See also == | ||
| {{Portal|Geography}} | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| ⚫ | * ] | ||
| ⚫ | * ] | ||
| * ] | |||
| ==References== | |||
| A '''track,''' also ''course over gound,'' is the actual path followed by a moving body, e.g. the vessel's track from A to B in the above given scheme. Some ambiguity exists in the fact that the path a navigator ''intends'' to follow, after evaluating and counteracting possible effects of wind and current, is also called ''track.'' | |||
| {{Reflist}} | |||
| ==External links== | |||
| The track is equivalent to the heading (a ] "right ahead"), if no cross wind and cross current occur (2), but this would hardly ever happen in ]. | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| {{DEFAULTSORT:Course (Navigation)}} | |||
| When wind is present, and is not a directly facing or tail wind, the wind deflects the aircraft (or vessel) from its heading. | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| To correct for the wind, the aircraft (or vessel) points more or less into the wind. The amount depends on the vehicle's speed, the wind's speed, and the angle of the wind in relation to the vehicle. This so-called ] is computed in advance and is frequently checked while "en route". In the above scheme, the track would be (9) for wind from port side. | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] is a format which can store track logs. | |||
| ---- | |||
| ''Notes:'' | |||
| *The above scheme shows a variation of 6° East, as might happen in areas of Pacific ocean, for instance, and | |||
| *a more-than-somewhat exaggerated deviation (taken from a fictitious deviation table for educational purpose) of +12°, for a compass heading of 040°. By conventional ], deviation could usually be kept beyond 10°, and ]es can be degaussed to almost D=0°. | |||
| *The possible influences of wind and current are maximized by presupposing a very slow boat in heavy wind and current. | |||
| *To increase readability of the scheme, all possible influences were given as „positive“, i.e. variation=East, „+“ 12° deviation, wind and current from ]. The principle is the same for the opposite of any of the components. | |||
| ==See also== | |||
| {{nautical portal}} | |||
| ⚫ | *] | ||
| ⚫ | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| == Reference == | |||
| Pilot's Handbook of Aeronautical Knowledge http://www.faa.gov/library/manuals/aviation/pilot_handbook/media/faa-h-8083-25-1of4.pdf | |||
Latest revision as of 17:31, 11 October 2024
Cardinal direction for steering
In navigation, the course of a watercraft or aircraft is the cardinal direction in which the craft is to be steered. The course is to be distinguished from the heading, which is the direction where the watercraft's bow or the aircraft's nose is pointed. The path that a vessel follows is called a track or, in the case of aircraft, ground track (also known as course made good or course over the ground). The intended track is a route.
Discussion
Further information: Bearing (angle) § Arcs, and Rhumb line § Introduction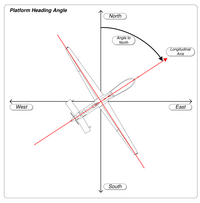
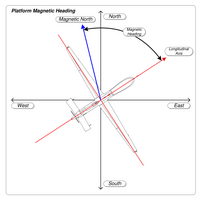 True heading (left) and magnetic heading (right)
True heading (left) and magnetic heading (right)
For ships and aircraft, routes are typically straight-line segments between waypoints. A navigator determines the bearing (the compass direction from the craft's current position) of the next waypoint. Because water currents or wind can cause a craft to drift off course, a navigator sets a course to steer that compensates for drift. The helmsman or pilot points the craft on a heading that corresponds to the course to steer. If the predicted drift is correct, then the craft's track will correspond to the planned course to the next waypoint. Course directions are specified in degrees from north, either true or magnetic. In aviation, north is usually expressed as 360°. Navigators used ordinal directions, instead of compass degrees, e.g. "northeast" instead of 45° until the mid-20th century when the use of degrees became prevalent.
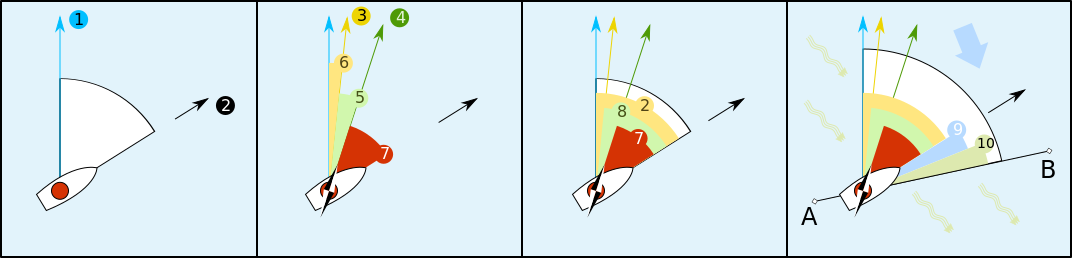
1 – True North
2 – Heading, the direction the vessel is "pointing towards"
3 – Magnetic north, which differs from true north by the magnetic variation.
4 – Compass north, including a two-part error; the magnetic variation (6) and the ship's own magnetic field (5)
5 – Magnetic deviation, caused by vessel's magnetic field.
6 – Magnetic variation, caused by variations in Earth's magnetic field.
7 – Compass heading or compass course, before correction for magnetic deviation or magnetic variation.
8 – Magnetic heading, the compass heading corrected for magnetic deviation but not magnetic variation; thus, the heading reliative to magnetic north.
9, 10 – Effects of crosswind and tidal current, causing the vessel's track to differ from its heading.
A, B – Vessel's track.
See also
- Acronyms and abbreviations in avionics
- Glossary of navigation terms
- Bearing (navigation)
- Breton plotter
- E6B
- Great circle
- Ground track
- Navigation
- Navigation room
- Rhumb line
References
- ^ Bartlett, Tim (2008), Adlard Coles Book of Navigations, Adlard Coles, p. 176, ISBN 978-0713689396
- Husick, Charles B. (2009). Chapman Piloting, Seamanship and Small Boat Handling. Sterling Publishing Company, Inc. p. 927. ISBN 9781588167446.
- ^ Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) (2016-09-25). Pilot's Handbook of Aeronautical Knowledge: FAA-H-8083-25B. Ravenio Books.
- Michael Nolan (2010). Fundamentals of Air Traffic Control. Cengage Learning. p. 201. ISBN 978-1-4354-8272-2.
For example, a runway heading north would have a magnetic heading of 360°.
- Rousmaniere, John; Smith, Mark (1999). The Annapolis Book of Seamanship: Third Edition: Completely Revised, Expanded and Updated. Simon and Schuster. p. 234. ISBN 9780684854205.