| Revision as of 14:09, 12 March 2024 editOntoraul (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users9,048 editsm →Curse of CanaanTag: 2017 wikitext editor← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 20:36, 11 November 2024 edit undoClueBot NG (talk | contribs)Bots, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers6,439,100 editsm Reverting possible vandalism by 92.211.200.177 to version by Monkbot. Report False Positive? Thanks, ClueBot NG. (4357377) (Bot)Tag: Rollback | ||
| (13 intermediate revisions by 9 users not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
| ]"]] | ]"]] | ||
| '''Canaan''' ({{ |
'''Canaan''' ({{Langx|he|כְּנַעַן}} – ''Kənáʿan'', in ] {{Script/Hebrew|כְּנָעַן}} – ''Kənā́ʿan''), according to the ] in the ], was a son of ] and grandson of ], as well as the father of the ]ites. | ||
| == Etymology == | == Etymology == | ||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
| # ]s | # ]s | ||
| # ]s | # ]s | ||
| Other passages in the Bible offer different lists of the exact names of the Canaanite tribes. For example, {{bibleverse|Genesis|15:19-21|}} lists the ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], and ]. While {{bibleverse|Exodus|3:8|}} only lists the Canaanite, the Hittite, the Amorite, the Perizzite, the Hivite, and the | |||
| Jebusite. How those other Biblical lists of Canaanite tribes jibes with the genealogical listing of Canaan's sons has been subject to much discussion. It has further been argued that the Biblical term Canaanite is actually ], which refers to both the broader Canaanite nation and to a specific Canaanite tribe within that nation.<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Klein |first=Reuven Chaim (Rudolph) |date= |title=Nations and Super-Nations of Canaan |url=https://tobias-lib.ub.uni-tuebingen.de/xmlui/bitstream/handle/10900/148214/jbq_462_kleincanaan.pdf |journal=Jewish Bible Quarterly | issn=0792-3910 |volume=46 |issue=2 |pages=73–85}}</ref> | |||
| According to traditional ]n histories, Canaan's son Arwadi (lit. "the Arvadite") and his wife Entela crossed from Asia into Ethiopia in 2101 BC, and the ] tribe were said to be descended from their son, ''Anayer''. There is further an Ethiopian tradition that two other Canaanite tribes, viz. the Sinites and Zemarites, also entered Ethiopia at the time it was ruled by the ], and became the ] and ]s, respectively.<ref>Yohannes Wolde Mariam, ''Yealem Tarik'', 1948 pp. 105–106.</ref> The Qemant relate that they share their Canaanite origin with the other Agaw groups.<ref>{{Cite book|title=The Qemant: A Pagan-Hebraic Peasantry of Ethiopia|last=Gamst|year=1969|first=Frederick C.|pages=37}}</ref> The Omotic speaking ] have a similar tradition of descent from Canaan's son Hamati<ref>{{Cite book|title=Inter-ethnic Relations on a Frontier: Mätakkäl (Ethiopia), 1898–1991|last=Endalew|first=Tsega|pages=23}}</ref> Similarly, the Shinasha extend the Canaanite ancestry to neighboring ethnic groups<ref>{{Cite book|title=An Archaeology of Resistance: Materiality and Time in an African Borderland|last=González-Ruibal|first=Alfredo|page=109}}{{ISBN?}}</ref> | According to traditional ]n histories, Canaan's son Arwadi (lit. "the Arvadite") and his wife Entela crossed from Asia into Ethiopia in 2101 BC, and the ] tribe were said to be descended from their son, ''Anayer''. There is further an Ethiopian tradition that two other Canaanite tribes, viz. the Sinites and Zemarites, also entered Ethiopia at the time it was ruled by the ], and became the ] and ]s, respectively.<ref>Yohannes Wolde Mariam, ''Yealem Tarik'', 1948 pp. 105–106.</ref> The Qemant relate that they share their Canaanite origin with the other Agaw groups.<ref>{{Cite book|title=The Qemant: A Pagan-Hebraic Peasantry of Ethiopia|last=Gamst|year=1969|first=Frederick C.|pages=37}}</ref> The Omotic speaking ] have a similar tradition of descent from Canaan's son Hamati<ref>{{Cite book|title=Inter-ethnic Relations on a Frontier: Mätakkäl (Ethiopia), 1898–1991|last=Endalew|first=Tsega|pages=23}}</ref> Similarly, the Shinasha extend the Canaanite ancestry to neighboring ethnic groups<ref>{{Cite book|title=An Archaeology of Resistance: Materiality and Time in an African Borderland|last=González-Ruibal|first=Alfredo|page=109}}{{ISBN?}}</ref> | ||
| The Persian historian ] (c. 915) recounted a tradition that the wife of Canaan was named Arsal, a daughter of Batawil son of ], and that she bore him the "Blacks, Nubians, ], ], ], and all the peoples of the Sudan."<ref>{{Cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=BQNtV--kD5sC&dq=qarnabil&pg=PA11|title=The History of al-Ṭabarī Vol. 2: Prophets and Patriarchs|first=Abū Jaʿfar Muḥammad ibn Jarīr|last=al-Ṭabarī|date=January 1, 1987|publisher=SUNY Press|isbn=9780873959216 |via=Google Books}}</ref> Likewise, ] tells that "Canaan is the father of the Sudan |
The Persian historian ] (c. 915) recounted a tradition that the wife of Canaan was named Arsal, a daughter of Batawil son of ], and that she bore him the "Blacks, Nubians, ], ], ], and all the peoples of the Sudan."<ref>{{Cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=BQNtV--kD5sC&dq=qarnabil&pg=PA11|title=The History of al-Ṭabarī Vol. 2: Prophets and Patriarchs|first=Abū Jaʿfar Muḥammad ibn Jarīr|last=al-Ṭabarī|date=January 1, 1987|publisher=SUNY Press|isbn=9780873959216 |via=Google Books}}</ref> Likewise, ] tells that "Canaan is the father of the Sudan.<ref>Futuah Misr, p. 8</ref> | ||
| The German historian ] (fl. c. 1525) recorded a legend that Canaan's sons ''the "Arkite"'' and ''the "Hamathite"'' first settled in the area of Greece, and gave their names to the regions of ] and ]. | The German historian ] (fl. c. 1525) recorded a legend that Canaan's sons ''the "Arkite"'' and ''the "Hamathite"'' first settled in the area of Greece, and gave their names to the regions of ] and ]. | ||
| Line 56: | Line 58: | ||
| The usurpation theory is similarly believed by ]. According to Barne's exegesis of Genesis 10:18, the Canaanite clans scattered after the ] incident and settled in the southern Levant, where they named the region after themselves. It is unknown whether they were dispersed violently or not. However, Canaan's cousin, ], had a "grasping tendency", making Barnes believe that Canaan had similar qualities. Thus, Canaan's settlement of the southern Levant was interpreted as a violent conquest, with Canaan "seizing upon the country with a high hand".<ref>{{Cite web |date=2024 |title=Genesis 10 Barnes' Notes |url=https://biblehub.com/commentaries/barnes/genesis/10.htm |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240206091716/https://biblehub.com/commentaries/barnes/genesis/10.htm |archive-date=February 6, 2024 |website=Biblehub.com}}</ref> | The usurpation theory is similarly believed by ]. According to Barne's exegesis of Genesis 10:18, the Canaanite clans scattered after the ] incident and settled in the southern Levant, where they named the region after themselves. It is unknown whether they were dispersed violently or not. However, Canaan's cousin, ], had a "grasping tendency", making Barnes believe that Canaan had similar qualities. Thus, Canaan's settlement of the southern Levant was interpreted as a violent conquest, with Canaan "seizing upon the country with a high hand".<ref>{{Cite web |date=2024 |title=Genesis 10 Barnes' Notes |url=https://biblehub.com/commentaries/barnes/genesis/10.htm |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240206091716/https://biblehub.com/commentaries/barnes/genesis/10.htm |archive-date=February 6, 2024 |website=Biblehub.com}}</ref> | ||
| ==In Islam== | |||
| In the ], Noah has four sons, the youngest of whom refuses to board the ark and subsequently drowns. Although unnamed in the text, tradition sometimes refers to him as ''Kan'an,'' an Arabic version of "Canaan." Alternatively, this figure is sometimes named ''Yam'' instead. However, this has not been supported by any textual revelation nor by any prophetic tradition , and it is mostly traced to influence of the Jewish scholars’ interpretation of the Genesis 9:20-27, which later was without relying on any religious text nor revelation. | |||
| ==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| * ], the location | * ], the location and its historical inhabitants | ||
| * ], its historical inhabitants | |||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| Line 65: | Line 69: | ||
| {{reflist|30em}} | {{reflist|30em}} | ||
| ===Bibliography=== | === Bibliography === | ||
| * {{cite book |last=Goldenberg |first=David M. |editor1-last=Stemberger |editor1-first=Günter |editor2-last=Perani |editor2-first=Mauro |title=The Words of a Wise Man's Mouth Are Gracious |chapter=What did Ham do to Noah? |year=2005 |publisher=Walter de Gruyter |isbn= 9783110188493|chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=4cr-mix9kMgC&pg=PA261}} | * {{cite book |last=Goldenberg |first=David M. |editor1-last=Stemberger |editor1-first=Günter |editor2-last=Perani |editor2-first=Mauro |title=The Words of a Wise Man's Mouth Are Gracious |chapter=What did Ham do to Noah? |year=2005 |publisher=Walter de Gruyter |isbn= 9783110188493|chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=4cr-mix9kMgC&pg=PA261}} | ||
| * {{Cite book |last=Kugel |first=James L. |title=Traditions of the Bible |publisher=Harvard University Press |year=1998 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=QUkaVq_GlJUC&pg=PA222 |isbn=9780674791510}} | * {{Cite book |last=Kugel |first=James L. |title=Traditions of the Bible |publisher=Harvard University Press |year=1998 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=QUkaVq_GlJUC&pg=PA222 |isbn=9780674791510}} | ||
Latest revision as of 20:36, 11 November 2024
Biblical figure| This article's lead section may be too short to adequately summarize the key points. Please consider expanding the lead to provide an accessible overview of all important aspects of the article. (December 2021) |

Canaan (Hebrew: כְּנַעַן – Kənáʿan, in pausa כְּנָעַן – Kənā́ʿan), according to the Book of Genesis in the Hebrew Bible, was a son of Ham and grandson of Noah, as well as the father of the Canaanites.
Etymology
The English term Canaan (pronounced /ˈkeɪnən/ since c. AD 1500, due to the Great Vowel Shift) comes from the Hebrew כנען (knʿn), via Greek Χαναάν Khanaan and Latin Canaan. It appears as ki-na-ah-na in the Amarna letters (14th century BC), and knʿn is found on coins from Phoenicia in the last half of the 1st millennium. It first occurs in Greek in the writings of Hecataeus as Khna(Χνᾶ). Scholars connect the name Canaan with knʿn, Kana'an, the general Northwest Semitic name for this region.
The etymology is uncertain. One explanation is that it has an original meaning of "lowlands", from a Semitic root knʿ "to be low, humble, depressed", in contrast with Aram, "highlands". An alternative suggestion derives the term from Hurrian Kinahhu, purportedly referring to the colour purple, so that Canaan and Phoenicia would be synonyms ("Land of Purple"), but it is just as common to assume that Kinahhu was simply the Hurrian rendition of the Semitic knʿn.
Descendants of Canaan
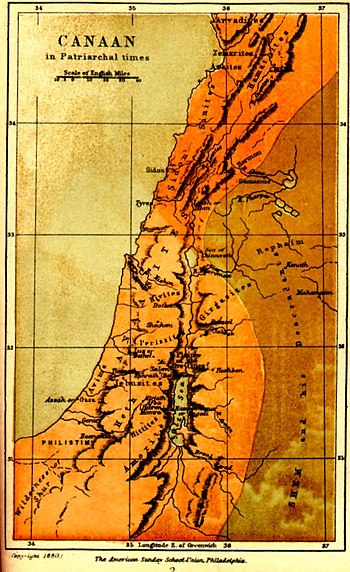
According to the Table of Nations in Genesis 10 (verses 15–19), Canaan was the ancestor of the tribes who originally occupied the ancient Land of Canaan: all the territory from Sidon or Hamath in the north to Gaza in the southwest and Lasha in the southeast. This territory, known as the Levant, is roughly the areas of modern-day Israel, Palestine, Lebanon, western Jordan, and western Syria. Canaan's firstborn son was Sidon, who shares his name with the Phoenician city of Sidon in present-day Lebanon. His second son was Heth. Canaan's descendants, according to the Hebrew Bible, include:
- Sidonians
- Hittites, children of Heth
- Jebusites
- Amorites
- Girgashites
- Hivites
- Arkites
- Sinites
- Arvadites
- Zemarites
- Hamathites
Other passages in the Bible offer different lists of the exact names of the Canaanite tribes. For example, Genesis 15:19–21 lists the Kenites, Kenizzites, Kadmonites, Hittites, Perizzites, Rephaim, Amorites, Canaanites, Girgashites, and Jebusites. While Exodus 3:8 only lists the Canaanite, the Hittite, the Amorite, the Perizzite, the Hivite, and the Jebusite. How those other Biblical lists of Canaanite tribes jibes with the genealogical listing of Canaan's sons has been subject to much discussion. It has further been argued that the Biblical term Canaanite is actually synecdoche, which refers to both the broader Canaanite nation and to a specific Canaanite tribe within that nation.
According to traditional Ethiopian histories, Canaan's son Arwadi (lit. "the Arvadite") and his wife Entela crossed from Asia into Ethiopia in 2101 BC, and the Qemant tribe were said to be descended from their son, Anayer. There is further an Ethiopian tradition that two other Canaanite tribes, viz. the Sinites and Zemarites, also entered Ethiopia at the time it was ruled by the Kingdom of Kush, and became the Shanqella and Weyto peoples, respectively. The Qemant relate that they share their Canaanite origin with the other Agaw groups. The Omotic speaking Shinasha have a similar tradition of descent from Canaan's son Hamati Similarly, the Shinasha extend the Canaanite ancestry to neighboring ethnic groups The Persian historian Muhammad ibn Jarir al-Tabari (c. 915) recounted a tradition that the wife of Canaan was named Arsal, a daughter of Batawil son of Tiras, and that she bore him the "Blacks, Nubians, Fezzan, Zanj, Zaghawah, and all the peoples of the Sudan." Likewise, Abd al Hakam tells that "Canaan is the father of the Sudan.
The German historian Johannes Aventinus (fl. c. 1525) recorded a legend that Canaan's sons the "Arkite" and the "Hamathite" first settled in the area of Greece, and gave their names to the regions of Arcadia and Emathia.
Curse of Canaan
Main article: Curse of HamAccording to Genesis 9:20–27, Noah became drunk and afterward cursed Canaan. This is the Curse of Canaan, called the "Curse of Ham" since Classical antiquity because of the interpretation that Canaan was punished for his father Ham's sins. However, there are interpretations that Canaan was the sole sinner himself. The sin in question is debated, ranging from literal voyeurism, castration or incestuous rape.
Ham's transgression:
And Ham, the father of Canaan, saw the nakedness of his father, and told his two brethren without. (Genesis 9:22)
Genesis 9:24–27
And Noah awoke from his wine, and knew what his younger son had done unto him.
And he said, Cursed Canaan; a servant of servants shall he be unto his brethren.
And he said, Blessed the LORD God of Shem; and Canaan shall be his servant.
God shall enlarge Japheth, and he shall dwell in the tents of Shem; and Canaan shall be his servant.
(—Authorized King James Version)
Some modern scholars view the curse of Canaan in Genesis 9:20–27 as an early Hebrew rationalization for Israel's conquest of Canaan. When Noah cursed Canaan in Genesis 9:25, he used the expression "Cursed be Canaan; A servant of servants He shall be to his brethren." The expression "servant of servants", otherwise translated "slave of slaves", emphasizes the extreme degree of servitude that Canaan will experience in relation to his "brothers". In the subsequent passage, "of Shem... may Canaan be his servant," the narrator is foreshadowing Israel's conquest of the promised land. Biblical scholar Philip R. Davies explains that the author of this narrative used Noah to curse Canaan, in order to provide justification for the later Israelites driving out and enslaving the Canaanites.
Extrabiblical tradition believes that Canaan was cursed with a second curse after "squatting" in Shem's inherited territory. According to the Book of Jubilees:
And Canaan saw the land of Lebanon to the river of Egypt, that it was very good, and he went not into the land of his inheritance to the west (that is to) the sea, and he dwelt in the land of Lebanon, eastward and westward from the border of Jordan and from the border of the sea. And Ham, his father, and Cush and Mizraim his brothers said unto him: 'Thou hast settled in a land which is not thine, and which did not fall to us by lot: do not do so; for if thou dost do so, thou and thy sons will fall in the land and (be) accursed through sedition; for by sedition ye have settled, and by sedition will thy children fall, and thou shalt be rooted out for ever. Dwell not in the dwelling of Shem; for to Shem and to his sons did it come by their lot. Cursed art thou, and cursed shalt thou be beyond all the sons of Noah, by the curse by which we bound ourselves by an oath in the presence of the holy judge, and in the presence of Noah our father.' But he did not hearken unto them, and dwelt in the land of Lebanon from Hamath to the entering of Egypt, he and his sons until this day. And for this reason that land is named Canaan.
— Jubilees 10:29–34.
The usurpation theory is similarly believed by Albert Barnes. According to Barne's exegesis of Genesis 10:18, the Canaanite clans scattered after the Tower of Babel incident and settled in the southern Levant, where they named the region after themselves. It is unknown whether they were dispersed violently or not. However, Canaan's cousin, Nimrod, had a "grasping tendency", making Barnes believe that Canaan had similar qualities. Thus, Canaan's settlement of the southern Levant was interpreted as a violent conquest, with Canaan "seizing upon the country with a high hand".
In Islam
In the Qur'an, Noah has four sons, the youngest of whom refuses to board the ark and subsequently drowns. Although unnamed in the text, tradition sometimes refers to him as Kan'an, an Arabic version of "Canaan." Alternatively, this figure is sometimes named Yam instead. However, this has not been supported by any textual revelation nor by any prophetic tradition , and it is mostly traced to influence of the Jewish scholars’ interpretation of the Genesis 9:20-27, which later was adopted by some Muslim scholars without relying on any religious text nor revelation.
See also
- Canaan, the location and its historical inhabitants
- Generations of Noah
References
- Asheri, David; Lloyd, Alan; Corcella, Aldo (2007). A Commentary on Herodotus, Books 1-4. Oxford University Press. p. 75.
- "Bible places; or, The topography of the Holy Land: a succinct account of all the places, rivers, and mountains of the land of Israel, mentioned in the Bible, ..." HathiTrust.
- Gesenius, Hebrew Lexicon
- Lemche, Niels-Peter (1991). The Canaanites and their Land: The Tradition of the Canaanites. Continuum. pp. 24–32. ISBN 978-0-567-45111-8.
- María E. Aubet. The Phoenicians and the West: politics, colonies and trade, ISBN 978-0-521-79543-2), 2001, p. 66
- Klein, Reuven Chaim (Rudolph). "Nations and Super-Nations of Canaan" (PDF). Jewish Bible Quarterly. 46 (2): 73–85. ISSN 0792-3910.
- Yohannes Wolde Mariam, Yealem Tarik, 1948 pp. 105–106.
- Gamst, Frederick C. (1969). The Qemant: A Pagan-Hebraic Peasantry of Ethiopia. p. 37.
- Endalew, Tsega. Inter-ethnic Relations on a Frontier: Mätakkäl (Ethiopia), 1898–1991. p. 23.
- González-Ruibal, Alfredo. An Archaeology of Resistance: Materiality and Time in an African Borderland. p. 109.
- al-Ṭabarī, Abū Jaʿfar Muḥammad ibn Jarīr (January 1, 1987). The History of al-Ṭabarī Vol. 2: Prophets and Patriarchs. SUNY Press. ISBN 9780873959216 – via Google Books.
- Futuah Misr, p. 8
- Metcalf, Alida C. (2005). Go-betweens and the colonization of Brazil, 1500–1600. University of Texas Press. pp. 163–164. ISBN 978-0-292-71276-8.
- Goldenberg, David M. (2009). The Curse of Ham. Princeton University Press. p. 157. ISBN 978-1-4008-2854-8.
- Kugel 1998, p. 223.
- Goldenberg 2005, pp. 259–60.
- Goldenberg 2005, p. 258.
- Gowan, Donald E. (1988). Genesis 1–11: Eden to Babel. Wm. B. Eerdmans. pp. 110–115. ISBN 0-8028-0337-7.
- Ellens, J. Harold, & Rollins, Wayne G., eds. (2004). Psychology and the Bible: A New Way to Read the Scriptures. v. 1–4. Westport: Praeger Publishers. ISBN 978-0275983475 p. 54
- Haynes, Stephen R. (2002). Noah's curse: the biblical justification of American slavery. p. 184. ISBN 978-0-19-514279-2.
- Philip R. Davies; John Rogerson (2005). The Old Testament World second edition. Louisville: Westminster John Knox Press. pp. 121–122. ISBN 0-664-23025-3.
- "Genesis 10 Barnes' Notes". Biblehub.com. 2024. Archived from the original on February 6, 2024.
Bibliography
- Goldenberg, David M. (2005). "What did Ham do to Noah?". In Stemberger, Günter; Perani, Mauro (eds.). The Words of a Wise Man's Mouth Are Gracious. Walter de Gruyter. ISBN 9783110188493.
- Kugel, James L. (1998). Traditions of the Bible. Harvard University Press. ISBN 9780674791510.
| Descendants of Noah in Genesis 10 | |
|---|---|
| Shem and Semitic | |
| Ham and Hamitic | |
| Japheth and Japhetic | |