| Revision as of 06:52, 30 January 2022 editDavid Biddulph (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Extended confirmed users, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers88,937 edits →Controversy: {{unsourced section|date=January 2022}}Tag: Reverted← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 19:02, 12 November 2024 edit undo97.102.205.224 (talk) Convert one citation to {{cite web}} template | ||
| (47 intermediate revisions by 28 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Frequency shift keying digital mode}} | |||
| FT8 is a popular ] digital mode. The most widely used FT8 software is ]. It is widely used on the ] (high frequency/HF) bands. The exchange consists of ]s, ]s, and ] grid squares. | |||
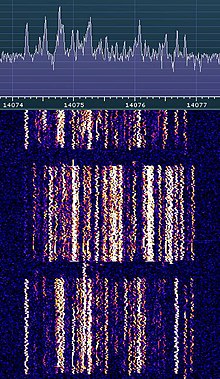
| ⚫ | ] showing FT8 in use on the ].]] | ||
| '''FT8 ''' (short for Franke-Taylor design, 8-FSK modulation) is a ] digital ] used by ] operators worldwide. Following release on June 29, 2017, by its creators ], and Steve Franke, K9AN, along with the software package ],<ref name=":0">{{cite web |last=Burmester |first=Dale |date=March 12, 2019 |title=Amateur Radio Digital Communications Mode FT8 |url=https://site.ieee.org/msn/files/2019/04/FT8-KA9SWE.pdf |access-date=2024-11-11}}</ref> FT8 was adopted rapidly, becoming the most popular digital mode recorded by automatic spotting networks such as ]<ref>{{Cite web |last=Barron |first=Robert |date=2020-02-08 |title=PSK Reporter |url=http://www.ka5wss.com/posts/psk-reporter/ |access-date=2022-10-06 |website=KA5WSS |language=en-US |archive-date=2022-10-06 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20221006195106/http://www.ka5wss.com/posts/psk-reporter/ |url-status=live }}</ref> within 2 years. | |||
| ==Introduction== | |||
| ⚫ | ] |
||
| FT8 is a popular form of digital weak signal communication used primarily by amateur radio operators to communicate on ] with a majority of traffic occurring on the ] amateur bands.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Luscre |first=Anthony |date=2019-10-11 |title=FT8—What Is It and How Can I Get Started? |url=https://www.onallbands.com/ft8-what-is-it-and-how-can-i-get-started/ |access-date=2022-08-17 |website=OnAllBands |language=en-US |archive-date=2022-10-01 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20221001035847/https://www.onallbands.com/ft8-what-is-it-and-how-can-i-get-started/ |url-status=live }}</ref> The mode offers operators the ability to communicate despite unfavorable conditions such as during low ], high RF noise, or with ].<ref>{{Cite web |title=FT8 – Signal Identification Wiki |url=https://www.sigidwiki.com/FT8 |access-date=2022-08-17 |website=www.sigidwiki.com |archive-date=2022-08-17 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220817030846/https://www.sigidwiki.com/FT8 |url-status=live }}</ref> With advances in signal processing technology, software can decode FT8 signals with a signal-to-noise ratio as low as −20 dB in a 2500 Hz bandwidth, which is significantly lower than conventional ] or ] transmissions.<ref>{{Cite web |title=FT8 Mode is Latest Bright Shiny Object in Amateur Radio Digital World |url=http://www.arrl.org/news/ft8-mode-is-latest-bright-shiny-object-in-amateur-radio-digital-world |access-date=2022-08-17 |website=www.arrl.org |language=en |archive-date=2022-05-28 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220528155358/http://www.arrl.org/news/ft8-mode-is-latest-bright-shiny-object-in-amateur-radio-digital-world |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| Joe Taylor, K1JT, announced on June 29, 2017, the availability of FT8 in WSJT-X.<ref>{{cite web | |||
| | title=FT8 Mode is Latest Bright Shiny Object in Amateur Radio Digital World | |||
| | url=http://www.arrl.org/news/ft8-mode-is-latest-bright-shiny-object-in-amateur-radio-digital-world | |||
| | publisher=] (ARRL) | |||
| | date=2017-08-01 | |||
| }}</ref> FT8 stands for "Franke-Taylor design, 8-FSK modulation" and was created by Joe Taylor, K1JT and Steve Franke, K9AN. It is described as being designed for "multi-hop Es where signals may be weak and fading, openings may be short, and you want fast completion of reliable, confirmable ]'s". | |||
| ==Operation== | |||
| According to Taylor, the important characteristics of FT8 are — | |||
| FT8 involves 77-bit message blocks transmitted in regular 15-second periods, consisting of 12.64 seconds of transmission time and 2.36 seconds of decode time, giving a digital data rate of 6.09 bits/sec. Source encoding gives an effective message throughput equivalent to about 5 words per minute. The required signal-to-noise ratio in a 2500 Hz bandwidth is −21 dB, so the corresponding ] is 10 log<sub>10</sub>(2500/6.09) = 26.1 dB greater, or −21 dB + 26.1 = 5.1 dB.<ref name=":0" /> | |||
| * T/R sequence length: 15 s | |||
| * Message length: 75 bits + 12-bit ] | |||
| * FEC code: (174,87) ] | |||
| * Modulation: 8-FSK, keying rate = 6.25 ]; tone spacing = 6.25 ] | |||
| * Waveform: Continuous phase, constant envelope | |||
| * Occupied bandwidth: 50 Hz | |||
| * Synchronization: three 7x7 ]s (start, middle, end of transmission) | |||
| * Transmission duration: 79*1920/12000 = 12.64 s | |||
| * Decoding threshold: -24 dB (with decoding) | |||
| * Operational behavior: similar to HF usage of JT9, JT65 | |||
| * Multi-decoder: finds and decodes all FT8 signals in passband | |||
| * Auto-sequencing after manual start of QSO | |||
| Although FT8 transmissions occur within fixed time windows, the software can cope with discrepancies between sending and receiving systems of up to a second or two. Provided that they are manually set to the correct time every so often (for example, by using ] or other time standard broadcasters), conventional computer Real Time Clocks are usually adequate. However, most FT8 users take advantage of online time servers using ] or time signals from the ] to achieve and maintain better time accuracy, automatically. | |||
| Compared to the so-called "slow modes" (JT9, JT65, QRA64), FT8 is a few decibels less sensitive, but allows completion of QSOs four times faster. Bandwidth is greater than JT9, but about one-quarter of JT65A and less than one-half of QRA64. Compared with the "fast modes" (JT9E-H), FT8 is significantly more sensitive, has much narrower bandwidth, uses the vertical waterfall, and offers multi-decoding over the full displayed passband. <ref>{{cite web|url=http://physics.princeton.edu/pulsar/K1JT/Release_Notes_1.8.0.txt|title=FT8|author=Joe Taylor, K1JT}}</ref> | |||
| ] helps achieve reliable communication despite common RF issues such as fading and interference, and weak/noisy signals due to marginal propagation paths, low power operation and inefficient antennas (e.g. in restricted and overcrowded urban locations). If anticipated messages are missed or not acknowledged, the software can re-send them in the next time-slot. | |||
| == Controversy == | |||
| {{unsourced section|date=January 2022}} | |||
| FT8 is somewhat controversial, with some amateur radio operators having strong opinions either for or against its use. Some common claims in favor of its use are that it reduces the ] of amateur radio by making inefficient antennas (which are more feasible for use in apartments and under many other circumstances) and low-power ] (which are often less expensive than higher-power transceivers), while its opponents often claim that it is "ruining ham radio" or other phrases expressing a belief that use of FT8 is contrary to the purposes of amateur radio. | |||
| The 77 bits are sufficient for free text messages of up to 13 text characters, reminiscent of ] (TXT) messages or ], while a clever data compression scheme reduces the number of digital bits required to pass structured messages containing conventional callsigns, reports and locators. Long or unusual callsigns are problematic for the protocol, however, despite using hashing to pass condensed representations. Decoding errors and hash collisions occasionally generate false 'callsigns' creating puzzlement or excitement if they appear to be rare but genuine calls. | |||
| ⚫ | ==References== | ||
| ==Applications== | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| There are multiple uses for FT8 including contesting,<ref>{{Cite web |title=FT8/FT4 from a contester's perspective – VA7ST.ca |url=https://va7st.ca/2020/10/ft8-ft4-from-a-contesters-perspective/ |access-date=2022-08-17 |language=en-US |archive-date=2022-08-17 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220817030847/https://va7st.ca/2020/10/ft8-ft4-from-a-contesters-perspective/ |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=ARRL Surveying Field Day Participants |url=http://www.arrl.org/news/arrl-surveying-field-day-participants |access-date=2022-08-17 |website=www.arrl.org |language=en |archive-date=2022-08-17 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220817075953/http://www.arrl.org/news/arrl-surveying-field-day-participants |url-status=live }}</ref> testing antennas,<ref>{{Cite web |title=FT8 |url=https://www.rtl-sdr.com/tag/ft8/ |access-date=2022-08-17 |website=www.rtl-sdr.com |archive-date=2022-09-30 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220930170306/https://www.rtl-sdr.com/tag/ft8/ |url-status=live }}</ref> and for scientific research.<ref>{{Cite web |last1=Erickson |first1=P. |last2=Liles |first2=W. |last3=Miller |first3=E. |last4=Miller |first4=E. |date=2020 |title=Amateur digital mode based remote sensing: FT8 use as a radar signal of opportunity for ionospheric characterization |url=https://hamsci.org/publications/amateur-digital-mode-based-remote-sensing-ft8-use-radar-signal-opportunity-ionospheric |access-date=2022-08-17 |website=hamsci.org |archive-date=2022-08-17 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220817030846/https://hamsci.org/publications/amateur-digital-mode-based-remote-sensing-ft8-use-radar-signal-opportunity-ionospheric |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| == Further information == | |||
| is a popular club dedicated to this digital mode. | |||
| The gives pragmatic advice on using FT8 for HF communications. | |||
| ⚫ | == References == | ||
| {{reflist}} | |||
| {{Digital_modes|state=collapsed}} | |||
| {{Two-way_radio|state=collapsed}} | |||
| {{Amateur radio topics|state=collapsed}} | |||
| {{Telecommunications|state=collapsed}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 19:02, 12 November 2024
Frequency shift keying digital mode
FT8 (short for Franke-Taylor design, 8-FSK modulation) is a frequency shift keying digital mode of radio communication used by amateur radio operators worldwide. Following release on June 29, 2017, by its creators Joe Taylor, K1JT, and Steve Franke, K9AN, along with the software package WSJT, FT8 was adopted rapidly, becoming the most popular digital mode recorded by automatic spotting networks such as PSK Reporter within 2 years.
Introduction
FT8 is a popular form of digital weak signal communication used primarily by amateur radio operators to communicate on amateur radio bands with a majority of traffic occurring on the HF amateur bands. The mode offers operators the ability to communicate despite unfavorable conditions such as during low solar activity, high RF noise, or with low transmit power. With advances in signal processing technology, software can decode FT8 signals with a signal-to-noise ratio as low as −20 dB in a 2500 Hz bandwidth, which is significantly lower than conventional CW or SSB transmissions.
Operation
FT8 involves 77-bit message blocks transmitted in regular 15-second periods, consisting of 12.64 seconds of transmission time and 2.36 seconds of decode time, giving a digital data rate of 6.09 bits/sec. Source encoding gives an effective message throughput equivalent to about 5 words per minute. The required signal-to-noise ratio in a 2500 Hz bandwidth is −21 dB, so the corresponding Eb/N0 is 10 log10(2500/6.09) = 26.1 dB greater, or −21 dB + 26.1 = 5.1 dB.
Although FT8 transmissions occur within fixed time windows, the software can cope with discrepancies between sending and receiving systems of up to a second or two. Provided that they are manually set to the correct time every so often (for example, by using WWV or other time standard broadcasters), conventional computer Real Time Clocks are usually adequate. However, most FT8 users take advantage of online time servers using NTP or time signals from the GPS to achieve and maintain better time accuracy, automatically.
Forward error correction helps achieve reliable communication despite common RF issues such as fading and interference, and weak/noisy signals due to marginal propagation paths, low power operation and inefficient antennas (e.g. in restricted and overcrowded urban locations). If anticipated messages are missed or not acknowledged, the software can re-send them in the next time-slot.
The 77 bits are sufficient for free text messages of up to 13 text characters, reminiscent of SMS (TXT) messages or Tweets, while a clever data compression scheme reduces the number of digital bits required to pass structured messages containing conventional callsigns, reports and locators. Long or unusual callsigns are problematic for the protocol, however, despite using hashing to pass condensed representations. Decoding errors and hash collisions occasionally generate false 'callsigns' creating puzzlement or excitement if they appear to be rare but genuine calls.
Applications
There are multiple uses for FT8 including contesting, testing antennas, and for scientific research.
Further information
FT8DMC is a popular club dedicated to this digital mode.
The FT8 Operating Guide gives pragmatic advice on using FT8 for HF communications.
References
- ^ Burmester, Dale (March 12, 2019). "Amateur Radio Digital Communications Mode FT8" (PDF). Retrieved 2024-11-11.
- Barron, Robert (2020-02-08). "PSK Reporter". KA5WSS. Archived from the original on 2022-10-06. Retrieved 2022-10-06.
- Luscre, Anthony (2019-10-11). "FT8—What Is It and How Can I Get Started?". OnAllBands. Archived from the original on 2022-10-01. Retrieved 2022-08-17.
- "FT8 – Signal Identification Wiki". www.sigidwiki.com. Archived from the original on 2022-08-17. Retrieved 2022-08-17.
- "FT8 Mode is Latest Bright Shiny Object in Amateur Radio Digital World". www.arrl.org. Archived from the original on 2022-05-28. Retrieved 2022-08-17.
- "FT8/FT4 from a contester's perspective – VA7ST.ca". Archived from the original on 2022-08-17. Retrieved 2022-08-17.
- "ARRL Surveying Field Day Participants". www.arrl.org. Archived from the original on 2022-08-17. Retrieved 2022-08-17.
- "FT8". www.rtl-sdr.com. Archived from the original on 2022-09-30. Retrieved 2022-08-17.
- Erickson, P.; Liles, W.; Miller, E.; Miller, E. (2020). "Amateur digital mode based remote sensing: FT8 use as a radar signal of opportunity for ionospheric characterization". hamsci.org. Archived from the original on 2022-08-17. Retrieved 2022-08-17.
| Amateur radio digital modes | ||
|---|---|---|
| Frequency-shift keying (FSK) |  | |
| Multiple frequency-shift keying (MFSK) | ||
| Phase-shift keying (PSK) | ||
| COFDM |
| |
| Non-traditional digital modes | ||
| Two-way radio | |
|---|---|
| Amateur and hobbyist | |
| Aviation (aeronautical mobile) | |
| Land-based commercial and government mobile | |
| Marine (shipboard) | |
| Signaling / Selective calling | |
| System elements and principles | |
| Amateur radio | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Activities |  | ||||||
| Culture | |||||||
| Governance | |||||||
| Modes of communication |
| ||||||
| Technologies | |||||||
| Related | |||||||