| Revision as of 23:59, 13 September 2006 editMarco a1981 (talk | contribs)7 editsmNo edit summary← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 17:40, 2 January 2025 edit undoCitation bot (talk | contribs)Bots5,436,102 edits Altered title. | Use this bot. Report bugs. | Suggested by Dominic3203 | Category:Articles contradicting other articles | #UCB_Category 39/267 | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Sociocultural region in West and Central Asia}} | |||
| ]'''Greater Iran''' (in ]: ایران بزرگ pron: ''Iran-e Bozorg'', also ایرانزمین pron: ''Iran-zameen'') is a term for the entire region where ] were once or are today spoken, as well as areas that were part of various empires based in '''Iran''' (]). The ] uses the term '''Iranian Cultural Continent''' , and other names such as '''Greater Persia''' or '''Persian cultural continent''' have also been used, especially in Afghanistan and Tajikistan. | |||
| {{Seealso|Indo-Persian culture|Turco-Persian tradition}} | |||
| {{pp-move-indef}} | |||
| {{Multiple issues|section=| | |||
| {{Synthesis |date=August 2023}} | |||
| {{Over-quotation|date=August 2023}} | |||
| }}{{Contains special characters|Perso-Arabic}} | |||
| ] at its greatest extent {{Circa|620}}, under ]]]{{History of Greater Iran sidebar}} | |||
| '''Greater Iran''' or '''Greater Persia''' ({{langx|fa|ایران بزرگ}} {{Transliteration|fa|Irān-e Bozorg}}), also called the '''Iranosphere''' or the '''Persosphere''', is an expression that denotes a wide socio-cultural region comprising parts of ], the ], ], ], and ] (specifically the ])—all of which have been affected, to some degree, by the ] and the ].<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Frye |first1=Richard Nelson |year=1962 |title=Reitzenstein and Qumrân Revisited by an Iranian, Richard Nelson Frye, The Harvard Theological Review, Vol. 55, No. 4 (Oct. 1962), pp. 261–268 |url=https://www.jstor.org/pss/1508723 |journal=The Harvard Theological Review |volume=55 |issue=4 |pages=261–268 |doi=10.1017/S0017816000007926 |jstor=1508723 |s2cid=162213219}}</ref><ref>. (2007), 39: pp 307–309 Copyright © 2007 Cambridge University Press.</ref> | |||
| It is defined by having long been ruled by the dynasties of various ],{{NoteTag|These include the ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ] and ].}}<ref name="Marcinkowski">{{cite book|last=Marcinkowski|first=Christoph|title=Shi'ite Identities: Community and Culture in Changing Social Contexts|year=2010|publisher=LIT Verlag Münster|isbn=978-3-643-80049-7|page=83}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url = http://azadegan.info/files/Dr.Frye-discusses-greater-Iran-on-CNN.mp4 |title = Interview with Richard N. Frye (CNN) <!-- |access-date = 2007 --> |archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20160423185051/http://azadegan.info/files/Dr.Frye-discusses-greater-Iran-on-CNN.mp4 |archive-date = 2016-04-23 |url-status = dead }}</ref><ref> I use the term Iran in an historical contextPersia would be used for the modern state, more or less equivalent to "western Iran". I use the term "Greater Iran" to mean what I suspect most Classicists and ancient historians really mean by their use of Persia—that which was within the political boundaries of States ruled by Iranians.</ref> under whom the local populaces gradually incorporated some degree of Iranian influence into their cultural and/or linguistic traditions;{{notetag|For example, those regions and peoples in the ] that were not under direct Iranian rule.}} or alternatively as where a considerable number of Iranians settled to still maintain communities who patronize their respective cultures,{{notetag|Such as in the western parts of ], ] and ].}} geographically corresponding to the areas surrounding the ].<ref name="IRAN i. LANDS OF IRAN">{{cite web|title=IRAN i. LANDS OF IRAN|publisher=]|url=http://www.iranicaonline.org/articles/iran-i-lands-of-iran}}</ref><ref>. Clive Holes. 2001. Page XXX. {{ISBN|978-90-04-10763-2}}.</ref> It is referred to as the "Iranian Cultural Continent" by '']''.<ref>{{Unbulleted list citebundle | {{cite web |url=https://www.iranicaonline.org/uploads/pdfs/2008-eif-annual-report.pdf |title= 2008 Annual Report |year=2009 |website=Encyclopædia Iranica |publisher=Center for Iranian Studies, Columbia University |location=New York |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230812060239/https://www.iranicaonline.org/uploads/pdfs/2008-eif-annual-report.pdf |archive-date=2023-08-12 |quote=Covering a multi-lingual and multi-ethnic cultural continent, the Encyclopædia Iranica’s scope encompasses all aspects of the life, history, and civilization of all the peoples who speak or once spoke an Iranian language |quote-page=5}}. | {{cite magazine |last1=Boss |first1=Shira J. |date=November 2003 |title=Encyclopaedia Iranica: Comprehensive research project about the "Iranian Cultural Continent" thrives on Riverside Drive |url=https://www.college.columbia.edu/cct_archive/nov03/features5.html |url-status=live |magazine=Columbia College Today |location=New York |publisher=] Office of Alumni Affairs and Development |volume=30 |issue=2 |pages=32–33 |issn=0572-7820 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210215041808/https://www.college.columbia.edu/cct_archive/nov03/features5.html |archive-date=2021-02-15}} Scan of print version available at {{Internet Archive|id=ldpd_12981092_045|name=''Columbia College Today'', v. 30 (2003–04)|page=126}}. | {{cite web |url=https://www.pbs.org/wgbh/pages/frontline/tehranbureau/2008/12/encyclopaedia-iranica-an-iranian-love-story.html |title=Encyclopaedia Iranica: an Iranian love story |last1=Niknejad |first1=Kelly Golnoush |date=2008-12-07 |orig-date=first published March 2005 |department=] |website=] |publisher=] |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100426140933/https://www.pbs.org/wgbh/pages/frontline/tehranbureau/2008/12/encyclopaedia-iranica-an-iranian-love-story.html |archive-date=2010-04-26}} }}</ref> | |||
| Traditionally, and until recent times, ethnicity has never been a defining separating criteria in these regions. In the words of ]: | |||
| Throughout the 16th–19th centuries, Iran lost many of the territories that had been conquered under the ] and ]. | |||
| :"Many times I have emphasized that the present peoples of Central Asia, whether Iranian or Turkic speaking, have one culture, one religion, one set of social values and traditions with only language separating them." | |||
| The ] resulted in the loss of present-day ] to the ], as outlined in the ] in 1555 and the ] in 1639. | |||
| Only in modern times did western colonial intervention and ethnicity tend to become a dividing force between the provinces of Greater Iran. As ] states, "ethnic nationalism is largely a nineteenth century phenomenon, even if it is fashionable to retroactively extend it."<ref>]. ''Eternal Iran''. Palgrave Macmillan. 2005 ISBN 1-4039-6276-6 p.23</ref> "Greater Iran" however has been more of a cultural super-state, rather than a political one to begin with. | |||
| Simultaneously, the ] resulted in the loss of the Caucasus to the ]: the ] in 1813 saw Iran cede present-day ], ], and most of ];<ref>{{cite book |author=India. Foreign and Political Dept. |url=https://archive.org/details/acollectiontrea14deptgoog |title=A Collection of Treaties, Engagements, and Sunnuds, Relating to India and Neighbouring Countries: Persia and the Persian Gulf |publisher=G. A. Savielle and P. M. Cranenburgh, Bengal Print. Co |year=1892 |pages=x (10) |quote=treaty of gulistan.}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last1=Mikaberidze |first1=Alexander |title=Historical Dictionary of Georgia |date=2015 |publisher=Rowman & Littlefield |isbn=978-1-4422-4146-6 |pages=348–349 |quote=Persia lost all its territories to the north of the Aras River, which included all of Georgia, and parts of Armenia and Azerbaijan.}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last1=Olsen |first1=James Stuart |title=Historical Dictionary of European Imperialism |last2=Shadle |first2=Robert |date=1991 |publisher=Greenwood Publishing Group |isbn=978-0-313-26257-9 |page=314 |quote=In 1813 Iran signed the Treaty of Gulistan, ceding Georgia to Russia.}}</ref> the ] in 1828 saw Iran cede present-day ], the remainder of Azerbaijan, and ], setting the northern boundary along the ].<ref>{{cite book |author=Roxane Farmanfarmaian |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Q_CPdClFR2cC&q=Qajar+loss+of+Afghanistan&pg=PA4 |title=War and peace in Qajar Persia: implications past and present |publisher=Psychology Press |year=2008 |isbn=978-0-203-93830-0 |page=4}}</ref>{{sfn|Fisher|Avery|Hambly|Melville|1991|p=329}} | |||
| Obviously, "Greater Iran" has had no fixed boundaries, nor even a fixed definition. While some sources specifically define Greater Iran to include the current republics of ], ], ], and ]n Republics , other sources such as ] give a more broader definition and define it to have included "much of the Caucasus, Afghanistan, and Central Asia, with cultural influences extending to China, India, and the Semitic speaking world." According to Frye, "Iran means all lands and peoples where Iranian languages were and are spoken, and where in the past, multi-faceted Iranian cultures existed." <ref>], ''Greater Iran'', ISBN 1-56859-177-2 p.''xi''</ref> | |||
| Parts of ] were lost to the ] through the ] in 1857 and the ] in 1905.<ref>{{cite book |author=Erik Goldstein |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=_sZpuJhvK_4C&q=treaty+of+paris+Afghanistan&pg=PA72 |title=Wars and peace treaties, 1816-1991 |publisher=Psychology Press |year=1992 |isbn=978-0-203-97682-1 |pages=72–73}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|title=A history of Persia, Volume 2|author=Sir Percy Molesworth Sykes|publisher=Macmillan and co.|year=1915|page=|url=https://archive.org/details/cu31924088418466|quote=Macmahon arbitration persia.}}</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| In the work ''Nuzhat al-Qolub'' (نزهه القلوب), the medieval geographer ] writes: | |||
| ==Etymology== | |||
| چند شهر است اندر ایران مرتفع تر از همه<br> | |||
| The name "Iran", meaning "land of the ]s", is the ] continuation of the old ] plural ''aryānām'' (proto-Iranian, meaning "of the Aryans"), first attested in the ] as ''airyānąm'' (the text of which is composed in ], an old ] spoken in northeastern Greater Iran, or in what are now ], ], ] and ]).<ref name="Encyclopaedia Iranica1">{{cite web | url=http://www.iranicaonline.org/articles/zoroastrianism-i-historical-review | title=ZOROASTRIANISM i. HISTORICAL REVIEW | access-date=2011-01-14 | author=William W. Malandra | date=2005-07-20}}</ref><ref name="Encyclopaedia Iranica">{{cite web | url=http://www.iranicaonline.org/articles/eastern-iranian-languages | title=EASTERN IRANIAN LANGUAGES | access-date=2011-01-14 | author=Nicholas Sims-Williams}}</ref><ref>{{cite web | url=http://www.iranicaonline.org/articles/iran | title=IRAN | access-date=2011-01-14}}</ref><ref>{{cite web | url=http://www.iranicaonline.org/articles/avestan-language | title=AVESTAN LANGUAGE I-III | access-date=2011-01-14 | author=K. Hoffmann}}</ref> | |||
| ''Some cities of Iran are better than the rest,''<br> | |||
| بهتر و سازنده تر از خوشی آب و هوا<br> | |||
| ''these have pleasant and compromising weather,''<br> | |||
| گنجه پر گنج در اران صفاهان در عراق<br> | |||
| ''The wealthy ] of ], and ] as well,''<br> | |||
| در خراسان مرو و طوس در روم باشد اقسرا<br> | |||
| ''] and ] in ], and ] (Aqsara) too.'' | |||
| The proto-Iranian term ''aryānām'' is present in the term '']'', the homeland of ] and ], near the provinces of ], ], ], etc., listed in the first chapter of the ].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.iranicaonline.org/articles/eran-wez|title=ĒRĀN-WĒZ|work=iranicaonline.org|access-date=9 December 2015}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.iranicaonline.org/articles/zoroaster-ii-general-survey|title=ZOROASTER ii. GENERAL SURVEY|work=iranicaonline.org|access-date=9 December 2015}}</ref> The Avestan evidence is confirmed by ] sources: ] is spoken of as being between ] and the ].<ref name="Encyclopaedia Iranica2">{{cite web | url=http://www.iranicaonline.org/articles/iranian-identity-ii-pre-islamic-period | title=IRANIAN IDENTITY ii. PRE-ISLAMIC PERIOD | access-date=2011-01-14 | author=Ahmad Ashraf}}</ref> | |||
| A detailed list of these provinces follows in this article. | |||
| However, this is a ] pronunciation of the name Haroyum/Haraiva (]), which the Greeks called 'Aria'<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.heritageinstitute.com/zoroastrianism/aria/index.htm|title=Haroyu|author=Ed Eduljee|work=heritageinstitute.com|access-date=9 December 2015}}</ref> (a land listed separately from the homeland of the Aryans).<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.heritageinstitute.com/zoroastrianism/aryans/location.htm|title=Aryan Homeland, Airyana Vaeja, Location. Aryans and Zoroastrianism.|author=Ed Eduljee|work=heritageinstitute.com|access-date=9 December 2015}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.heritageinstitute.com/zoroastrianism/aryans/airyanavaeja.htm|title=Aryan Homeland, Airyana Vaeja, in the Avesta. Aryan lands and Zoroastrianism.|author=Ed Eduljee|work=heritageinstitute.com|access-date=9 December 2015}}</ref> | |||
| ==Background== | |||
| While up until the end of the ] in the 3rd century CE, the idea of "Irān" had an ethnic, linguistic, and religious value, it did not yet have a political import. The idea of an "Iranian" empire or kingdom in a political sense is a purely ] one. It was the result of a convergence of interests between the new dynasty and the ] ], as we can deduce from the available evidence. | |||
| ] of the ] writes: | |||
| This convergence gave rise to the idea of an Ērān-šahr "Kingdom of the Iranians", which was "ēr" (] equivalent of ] "ariya" and Avestan "airya").<ref name="Encyclopaedia Iranica2" /> | |||
| :''"Many Iranians consider their natural sphere of influence to extend beyond Iran's present borders. After all, Iran was once much larger. Portuguese forces seized islands and ports in the 16th and 17th centuries. In the 19th century, the ] wrested from ]'s control what is today ], ], and part of ]. Iranian elementary school texts teach about the Iranian roots not only of cities like ], but also cities further north like ] in southern ]. The ] lost much of his claim to western ] following the Anglo-Iranian war of 1856-1857. Only in 1970 did a ] sponsored consultation end Iranian claims to suzerainty over the ] island nation of ]. In centuries past, Iranian rule once stretched westward into modern ] and beyond. When the western world complains of Iranian interference beyond its borders, the Iranian government often convincesd itself that it is merely exerting its influence in lands that were once its own. Simultaneously, Iran's losses at the hands of outside powers have contributed to a sense of grievance that continues to the present day."''<ref>]. ''Eternal Iran''. Palgrave. 2005. Coauthored with ]. ISBN 1-4039-6276-6 p.9,10</ref> | |||
| ==Definition== | |||
| In ], Greater Iran is called ''Iranzamin'' (ایرانزمین) which means "The Land of Iran". ''Iranzamin'' was in the mythical times opposed to the ''Turanzamin'' the Land of ], which was located in the upper part of ]. <ref>], ], see under entry "Turan"</ref> | |||
| ] defines Greater Iran as including "''much of the Caucasus, Iraq, Afghanistan, Pakistan and Central Asia, with cultural influences extending to China and western India''." | |||
| According to him, "''Iran means all lands and peoples where Iranian languages were and are spoken, and where in the past, multi-faceted Iranian cultures existe''d."<ref>], ''Greater Iran'', {{ISBN|978-1-56859-177-3}} p.''xi''</ref> | |||
| In the pre-Islamic period, Iranians distinguished two main regions in the territory they ruled, one Iran and the other ''Aniran''. By Iran they meant all the regions inhabited by ]. That region was much vaster than it is today. This notion of ''Iran'' as a territory (opposed to ''Aniran'') can be seen as the core of early Greater Iran. Later many changes occurred in the boundaries and areas where Iranians lived but the languages and culture remained the dominant medium in many parts of the Greater Iran. | |||
| ] notes that while "''A general assumption is often made that the various Iranian peoples of 'greater Iran'—a cultural area that stretched from Mesopotamia and the Caucasus into ], ], Bactria, and the ] and included Persians, ], Parthians and ] among others—were all 'Zoroastrians' in pre-Islamic times... This view, even though common among serious scholars, is almost certainly overstated''." He argues that "''While the various Iranian peoples did indeed share a common ] and pool of religious myths and ], in actuality a variety of ] were worshipped—particularly ], the god of covenants, and ], the goddess of the waters, but also many others—depending on the time, place, and particular group concerned''".<ref>], "Religions of the Silk Road: Premodern Patterns of globalization", Palgrave Macmillan, rev. 2nd edition, 2010. pg 27</ref> | |||
| As an example, the Persian language was the main literary language and the language of correspondence in ] and Caucasus prior to the Russian occupation, Central Asia being the birthplace of modern Persian language. Furthermore, according to the ] government, Persian language was also used in Iraqi Kurdistan, prior to the British Occupation and Mandate in 1918-1932 . | |||
| To the ], Greater Iran ended at the ] located in ].<ref>J.M. Cook, "The Rise of the Achaemenids and Establishment of Their Empire" in | |||
| With ] continuously advancing south in the course of two wars against Persia, and the treaties of ] and ] in the western frontiers, plus the unexpected death of ] in 1823, and the murdering of Persia's Grand ] (Mirza AbolQasem Qa'im Maqām), many Central Asian khanates began losing hope for any support from Persia against the ]ist armies. <ref>], ''Kharazm: What do I know about Iran?''. 2004. ISBN 964-379-023-1, p.78</ref> The Russian armies occupied the ] coast in 1849, ] in 1864, ] in 1867, ] in 1868, and ] and ] in 1873. | |||
| Ilya Gershevitch, William Bayne Fisher, J. A. Boyle "Cambridge History of Iran", Vol 2. pg 250. Excerpt: "To the Greeks, Greater Iran ended at the Indus".</ref> | |||
| According to ] and ] most of Western ''greater Iran'' spoke Southwestern Iranian languages in the Achaemenid era while the Eastern territory spoke Eastern Iranian languages related to Avestan.<ref>Mallory, J. P.; Adams, D. Q. (1997), Encyclopedia of Indo-European culture, London and Chicago: Fitzroy-Dearborn, {{ISBN|978-1-884964-98-5}}. pg 307: "Dialectically, Old Persian is regarded as a southwestern Iranian language in contrast to the east Iranian Avestan which covered most of the rest of Greater Iran. However, it is important to note that during the Achaemeid era, the official language of the empire was ], which was the mother tongue of the ancient , since it was the language of literature, religion, and science at that time. language had a great impact on Persian and survived as the dominant language in the middle east until the .</ref> | |||
| Again ]: | |||
| ] also states that after the dissolution of the ], the ] became rulers of greater Iran<ref>George Lane, "Daily Life in the Mongol Empire", Greenwood Publishing Group, 2006. pg 10" The year following 1260 saw the empire irrevocably split but also signaled the emergence of the two greatest achievements of the house of Chinggis, namely the Yuan dynasty of greater China and the Il-Khanid dynasty of greater Iran.</ref> and ], according to Judith G. Kolbas, was the ruler of this expanse between 1304 and 1317 A.D.<ref>Judith G. Kolbas, "The Mongols in Iran", Excerpt from 399: "Uljaytu, Ruler of Greater Iran from 1304 to 1317 A.D."</ref> | |||
| :''"Iran today is just a rump of what it once was. At its height, Iranian rulers controlled ], ], much of ], and the ]. Many Iranians today consider these areas part of a greater Iranian sphere of influence."''<ref>]. ''Eternal Iran''. Palgrave. 2005. Coauthored with ]. ISBN 1-4039-6276-6 p.30</ref> | |||
| ], including Timurid historian ], define Iranshahr (Greater Iran) as extending from the ] to the ]<ref>Mīr Khvānd, Muḥammad ibn Khāvandshāh, Tārīkh-i rawz̤at al-ṣafā. Taṣnīf Mīr Muḥammad ibn Sayyid Burhān al-Dīn Khāvand Shāh al-shahīr bi-Mīr Khvānd. Az rū-yi nusakh-i mutaʻaddadah-i muqābilah gardīdah va fihrist-i asāmī va aʻlām va qabāyil va kutub bā chāphā-yi digar mutamāyiz mībāshad. Markazī-i Khayyām Pīrūz . {{lang|fa|{{nastaliq|ایرانشهر از کنار فرات تا جیهون است و وسط آبادانی عالم است|fa}}}}. Iranshahr stretches from the Euphrates to the Oxus, and it is the center of the prosperity of the World.</ref> | |||
| :''"Since the days of the ], the Iranians had the protection of geography. But high mountains and vast emptiness of the ] were no longer enough to shield Iran from the Russian army or British navy. Both literally, and figuratively, Iran shrank. At the beginning of the nineteenth century, Azerbaijan, Armenia, much of Georgia, and Afghanistan were Iranian, but by the end of the century, all this territory had been lost as a result of European military action."''<ref>]. ''Eternal Iran''. Palgrave. 2005. Coauthored with ]. ISBN 1-4039-6276-6 p.31-32</ref> | |||
| The '']'' takes a geographical approach in referring to the "historical and cultural" entity of "Greater Iran" as "areas of Iran, parts of Afghanistan, Chinese and ]".<ref>''The Cambridge History of Iran, Vol. III: The Seleucid, Parthian and Sasanian Periods'', ], Review author: ], ], </ref> | |||
| ==Treaties== | |||
| *]: Persia loses ] and modern Iraq to the ]. | |||
| *]: Iran loses control over large areas of the Caucasus. | |||
| *]: Signed by ]. ] gains sovereingty over the Caucasus. | |||
| *]: Signed by ]. Iran loses ] and parts of Afghanistan in exchange for the evacuation of Iran's southern ports by ]. | |||
| *]: Signed by ]. Iran loses ] and parts of ] in exchange for security guarantees from ]. | |||
| *1893: Iran further loses regions near the ] river that were entitled to it from the Akhal Treaty. This treaty was signed by General Boutsoff and ''Mirza Ali Asghar Amin al-Sultan'' on May 27, 1893. | |||
| *1907: Persia was to be carved up into three regions, according to the ]. | |||
| *1970: Iran abandons sovereignty rights over ] to ] in exchange for ] and ] islands in the ]. | |||
| == |
==Background== | ||
| ] Coin of ]|An ] Coin of ] (r. 1736–1747), reverse: "Coined on gold the word of kingdom in the world, Nader of '''Greater Iran''' and the world-conqueror king."<ref>Numista: .</ref>]] | |||
| Greater Iran is called ''Iranzamin'' ({{lang|fa|{{nastaliq|ایرانزمین|fa}}}}) which means "Iranland" or "The Land of Iran". ''Iranzamin'' was in the mythical times as opposed to the ''Turanzamin'', "The Land of ]", which was located in the upper part of Central Asia.<ref>], ], see under entry "Turan"</ref>{{verify source |date=September 2023}} | |||
| <center> | |||
| <gallery> | |||
| Image:1753vaugondy.jpg|A 1753 map by Robert De Vaugondy titled ''ESTATS DU GRAND-SEIGNEUR EN ASIE'' where the color yellow marks the Greater Persian territores. | |||
| |1650 map by Johannes Blaeu. | |||
| Image:Achaemenid Empire.jpg|Map depiction from 500BC. | |||
| Image:Iran e Bozorg.jpg|19th century British map depicting Greater Persia. | |||
| Image:Persia1808.JPG|An 1808 British map of Persia. | |||
| Image:Iran e Bozorg2.jpg|Map depiction of 1719 of Central Asia. | |||
| Image:Matthaus 1598.JPG|1598 ] map of the region. | |||
| Image:Moll 1720.JPG|Herman Moll's map of 1720. Note the provincial markings. | |||
| Image:Hondius 1610.JPG|1610 Map by Dutch map maker Jodocus Hondius showing Bactria and Georgia among the territories. | |||
| </gallery> | |||
| </center> | |||
| With ] continuously advancing south in the course of two wars against Persia, and the treaties of Turkmenchay and Gulistan in the western frontiers, plus the unexpected death of ] in 1833, and the murdering of Persia's Grand ] (]), many Central Asian khanates began losing hope for any support from Persia against the ]ist armies.<ref>], ''Kharazm: What do I know about Iran?''. 2004. {{ISBN|978-964-379-023-3}}, p.78</ref> The Russian armies occupied the ] coast in 1849, ] in 1864, ] in 1867, ] in 1868, and ] and ] in 1873. | |||
| ==]s and Provinces of Greater Iran (Persia)== | |||
| ===]=== | |||
| ]"Khwarazm is one of the regions of ''Iran-zameen'', and is the home of the ancient Iranians, ], according to the ancient book of the ]." <ref>], ''Kharazm: What do I know about Iran?''. 2004. ISBN 964-379-023-1, p.111</ref> Modern scholars believe Khwarazm to be what ancient ] texts refer to as ]. <ref>Farahvoshi, Bahram. ''Iranovich'', ] Press. 1991, p.8</ref> These sources claim that ], which was the capital of ancient Khwarazm for many years, was actually "Ourva": the eighth land of ] mentioned in the ] text of ].<ref>Javan, Musa. ''Tarikh-i Ijtima'i Iran-i Bastan (The social history of ancient Iran)'', 1961, p24</ref> Michael Witzel, a researcher in early Indo-European history, believes that ] was located in what is now ] , the northern areas of which were a part of Ancient Khwarezm and ]. Others such as ] historian ] believe Khwarazm to be the "most likely locale" corresponding to the original home of the ]n people <ref>], ''The History of Iran''. 2001. ISBN 0-313-30731-8, p.28</ref>, while ] calls Khwarazm "the cradle of the ] tribe" (مهد قوم آریا). Today Khwarazm is split between several central Asian republics. | |||
| :''"Many Iranians consider their natural sphere of influence to extend beyond Iran's present borders. After all, Iran was once much larger. Portuguese forces seized islands and ports in the 16th and 17th centuries. In the 19th century, the Russian Empire wrested from ]'s control what is today Armenia, ], and part of Georgia. Iranian elementary school texts teach about the Iranian roots not only of cities like ], but also cities further north like ] in southern Russia. The ] lost much of his claim to western Afghanistan following the Anglo-Iranian war of 1856-1857. Only in 1970 did a ] sponsored consultation end Iranian claims to ] over the ] island nation of ]. In centuries past, Iranian rule once stretched westward into modern Iraq and beyond. When the western world complains of Iranian interference beyond its borders, the Iranian government often convinced itself that it is merely exerting its influence in lands that were once its own. Simultaneously, Iran's losses at the hands of outside powers have contributed to a sense of grievance that continues to the present day."'' -] of the ]<ref>]. ''Eternal Iran''. Palgrave. 2005. Coauthored with ]. {{ISBN|978-1-4039-6276-8}} p.9,10</ref> | |||
| Superimposed on and overlapping with ] was ] which roughly covered nearly the same geographical areas in Central Asia (starting from ] eastward through northern Afghanistan roughly until the foothills of ]). Current day provinces such as ] in ], ], ], and ] in ] are all remnants of the old ]. Until the 13th century and the devastating Mongol invasion of the region, Khorasan was considered the cultural capital of ].<ref> | |||
| Lorentz, J. ''Historical Dictionary of Iran''. 1995. ISBN 0-8108-2994-0</ref> | |||
| :''"Iran today is just a rump of what it once was. At its height, Iranian rulers controlled Iraq, Afghanistan, Western Pakistan, much of Central Asia, and the Caucasus. Many Iranians today consider these areas part of a greater Iranian sphere of influence."'' - ]<ref>]. ''Eternal Iran''. Palgrave. 2005. Coauthored with ]. {{ISBN|978-1-4039-6276-8}} p.30</ref> | |||
| <center> | |||
| <gallery> | |||
| Image:Bukhara07.jpg|''Madresh-i Chahor Minor'' ("School of four minarets" in Persian), ], ]. | |||
| Image:Bukhara14.jpg|] the great ]. | |||
| Image:Gure Amir.JPG|The magnificent '']'' ("tomb of the Amir" in Persian) | |||
| Image:Tajikestan.JPG|''Masjed-i Bibi-khanum'' ("Mosque of The Lady" in Persian), ] | |||
| Image:Prokudin-Gorskii-17.jpg|''Masjed-i Shah-i Zendeh'' ("Mosque of the immortal King" in Persian), ] | |||
| Image:Bukhara16.jpg|''Taq-i Zargaran'' ("Arch of the goldsmiths" in Persian), Bukhara | |||
| Image:Bukhara ark.jpg|''Arg-i Bukhara'' ("Citadel of Bukhara" in Persian), is not unsimilar to ] or ] in ] | |||
| Image:Herat citadel.jpg|''Arg-i Herat'', ], from the ] era. | |||
| Image:Humayuns Tomb Delhi 31-05-2005 pic3.jpg|], ]. | |||
| Image:Turk23.jpg|], ]. | |||
| <!-- Unsourced image removed: Image:Derbent sassanid.jpg|], ], ]. --> | |||
| Image:Itimad-Agra.jpg|], ]. | |||
| </gallery> | |||
| </center> | |||
| :''"Since the days of the ], the Iranians had the protection of geography. But high mountains and the vast emptiness of the Iranian plateau were no longer enough to shield Iran from the Russian army or British navy. Both literally, and figuratively, Iran shrank. At the beginning of the nineteenth century, Azerbaijan, Armenia, and Afghanistan were Iranian, but by the end of the century, all this territory had been lost as a result of European military action."''<ref>]. ''Eternal Iran''. Palgrave. 2005. Coauthored with ]. {{ISBN|978-1-4039-6276-8}} p.31-32</ref> | |||
| ====]==== | |||
| The national anthem in Tajikistan, "]", attests to the Perso-Tajik identity, which has seen a large revival, after the breakup of the ]. ] is almost identical to that spoken in Afghanistan and Iran, and their cities have Persian names, e.g. ], ] (Esfarayen), ], ], ], ], ], ], and ] (). | |||
| ==Regions== | |||
| Some experts even argue that ] are culturally closer to the Persian original root, as the Iranians to the west have mingled and mixed with various empires over the years. | |||
| In the 8th century, Iran was conquered by the ] ] who ruled from ]. The territory of Iran at that time was composed of two portions: '']'' (western portion) and ''Khorasan'' (eastern portion). The dividing region was mostly the cities of ] and ]. The ], ] and ] divided their empires into Iraqi and Khorasani regions. This point can be observed in many books such as ]'s ''"Tārīkhi Baïhaqī"'', ]'s ''Faza'ilul al-anam min rasa'ili hujjat al-Islam'' and other books. Transoxiana and ] were mostly included in the Khorasanian region. | |||
| ===Caucasus=== | |||
| Afghans take pride in being close descendants of the ]s(]), or to be more precise: ''']''' - the Greek pronunciation of the ancient ]n ] or the ] "Aryavarta", Land of the Aryans. Today this Old-Persian, and Avestan expression is preserved in the name of the Afghan national airline, ]. The term 'Ariana Afghanistan' is still popular amongst many people in the country. | |||
| ====North Caucasus==== | |||
| {{See also|History of Dagestan|History of Kabardino-Balkaria|Russo-Persian Wars|Treaty of Gulistan|Treaty of Turkmenchay|Tat people (Caucasus)}} | |||
| ] fortress in ], Dagestan. Now inscribed on Russia's ] world heritage list since 2003.]] | |||
| ] was part of ], and hence was recognized with the name Khorasan (along with regions centered around Merv and Neishabur), which in Pahlavi means "The Eastern Land" (خاور زمین in Persian). <ref>], '']'', Tehran University Press, p.8457</ref> | |||
| Dagestan remains the bastion of ] in the ] with fine examples of Iranian architecture like the Sassanid citadel in ], the strong influence of ], and common Persian names amongst the ethnic peoples of Dagestan. The ethnic Persian population of the North Caucasus, the ], remain, despite strong assimilation over the years, still visible in several North Caucasian cities. Even today, after decades of partition, some of these regions retain Iranian influences, as seen in their old beliefs, traditions and customs (e.g. ]).<ref>'']'': "Caucasus Iran" article, p.84-96.</ref> | |||
| ] is where ] is located, home of ], ], and where many other notables in ] came from. The ] language of ], is a nearly identical dialect of the Persian language. It is widely spoken in ]. | |||
| ====South Caucasus==== | |||
| At the latest, ] lost control of ] to the British in 1857. In 1856 Britain prevented Iran from reasserting control over ], which had been part of ] during the ages, but had been ruled by native Afghans since the mid-18th century. Britain supported the eastern part of ] incorporation into Afghanistan; therefore the current borders of ] would not be determined until the coming of the British. | |||
| {{See also|Azerbaijani people|History of Azerbaijan|Tat people (Iran)|Tat people (Caucasus)|Safavid conversion of Iran to Shia Islam|Old Azeri language|Shirvan|Arran (Caucasus)|Shirvanshah|Iranian Azerbaijanis}} | |||
| According to ], the territories of ] and the republic of ] usually shared the same history from the time of ancient Media (ninth to seventh centuries b.c.) and the Persian Empire (sixth to fourth centuries b.c.).<ref>Historical Background Vol. 3, Colliers Encyclopedia CD-ROM, 02-28-1996</ref>{{page needed |date=September 2023}} | |||
| But still even today, Persian names are far abound across the towns and districts of the country: ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], and ] among others. | |||
| Intimately and inseparably intertwined histories for millennia, Iran irrevocably lost the territory that is nowadays Azerbaijan in the course of the 19th century. With the ] of 1813 following the ] Iran had to cede eastern ], its possessions in the ] and many of those in what is today the ], which included the khanates of ], ], ], ], ], ], ], and parts of ]. These Khanates comprise most of what is today the Republic of Azerbaijan and Dagestan in Southern Russia. In the ] of 1828 following the ], the result was even more disastrous, and resulted in Iran being forced to cede the remainder of the ], the khanates of ] and ], and the Mughan region to Russia. All these territories together, lost in 1813 and 1828 combined, constitute all of the modern-day Republic of Azerbaijan, ], and southern ]. The area to the North of the river ], among which the territory of the contemporary republic of Azerbaijan were Iranian territory until they were occupied by Russia in the course of the 19th century.<ref name="Swietochowski Borderland">{{cite book |last=Swietochowski|first=Tadeusz |author-link= Tadeusz Swietochowski |year=1995|title=Russia and Azerbaijan: A Borderland in Transition|pages= 69, 133 |publisher=] |url= https://books.google.com/books?id=FfRYRwAACAAJ&q=Russia+and+Iran+in+the+great+game:+travelogues+and+orientalism|isbn=978-0-231-07068-3}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last=L. Batalden|first=Sandra |year=1997|title=The newly independent states of Eurasia: handbook of former Soviet republics|page= 98|publisher=Greenwood Publishing Group |url= https://books.google.com/books?id=WFjPAxhBEaEC&q=The+newly+independent+states+of+Eurasia:+handbook+of+former+Soviet+republics|isbn=978-0-89774-940-4}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |first1=Robert E. |last1=Ebel |first2=Rajan |last2=Menon |year=2000|title=Energy and conflict in Central Asia and the Caucasus|page= 181 |publisher=Rowman & Littlefield |url= https://books.google.com/books?id=-sCpf26vBZ0C&q=Energy+and+conflict+in+Central+Asia+and+the+Caucasus|isbn=978-0-7425-0063-1}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last=Andreeva|first=Elena |year=2010|title=Russia and Iran in the great game: travelogues and orientalism|page= 6 |edition= reprint |publisher=Taylor & Francis | url= https://books.google.com/books?id=FfRYRwAACAAJ&q=%3DRussia+and+Iran+in+the+great+game:+travelogues+and+orientalism|isbn=978-0-415-78153-4}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last=Çiçek, Kemal|first=Kuran, Ercüment |year=2000|title=The Great Ottoman-Turkish Civilisation|publisher=University of Michigan |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=c5VpAAAAMAAJ&q=The+Great+Ottoman-Turkish+Civilisation|isbn=978-975-6782-18-7}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|last=Ernest Meyer, Karl|first=Blair Brysac, Shareen|year=2006|title=Tournament of Shadows: The Great Game and the Race for Empire in Central Asia|page=66|publisher=Basic Books|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Ssv-GONnxTsC&q=Tournament+of+Shadows:+The+Great+Game+and+the+Race+for+Empire+in+Central+Asia|isbn=978-0-465-04576-1}}{{Dead link|date=May 2023 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }}</ref> | |||
| ززابل به کابل رسید آن زمان<br> | |||
| From ] he arrived to ]<br> | |||
| گرازان و خندان و دل شادمان<br> | |||
| Strutting, happy, and mirthful<br> | |||
| ''---] in ]'' | |||
| Many localities in this region bear Persian names or names derived from Iranian languages and Azerbaijan remains by far Iran's closest cultural, religious, ethnic, and historical neighbor. ] are by far the second-largest ethnicity in Iran, and comprise the largest community of ethnic Azerbaijanis in the world, vastly outnumbering the number in the Republic of Azerbaijan. Both nations are the only officially Shia majority in the world, with adherents of the religion comprising an absolute majority in both nations. The people of nowadays Iran and Azerbaijan were ] during exactly the same time in history. Furthermore, the name of "Azerbaijan" is derived through the name of the Persian ] which ruled the contemporary region of ] and minor parts of the Republic of Azerbaijan in ancient times.<ref>{{cite book |last=Houtsma|first=M. Th. |author-link=Martijn Theodoor Houtsma |year= 1993|title= First Encyclopaedia of Islam 1913–1936 |edition= reprint |publisher= BRILL |isbn=978-90-04-09796-4}}</ref><ref name="Schippmann">{{cite book |last=Schippmann|first=Klaus |year=1989 |title=Azerbaijan: Pre-Islamic History|pages= 221–224|publisher=Encyclopædia Iranica |isbn=978-0-933273-95-5}}</ref> | |||
| ====]==== | |||
| Home of the ] (]). ] is also where the half-Persian caliph ] moved his capital to, inorder to move the center of the caliphate away from Arab speaking lands. The city of ] is yet another Persian word meaning "city of love", and like Iran, Afghanistan, and Uzbekistan, it was once part of ]. | |||
| === |
===Central Asia=== | ||
| ] head of a ] wearing a distinctive ]n-style headdress, ], ], ], 3rd-2nd century BCE.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Litvinskij |first1=B. A. |last2=Pichikian |first2=I. R. |year=1994 |title=The Hellenistic Architecture and Art of the Temple of the Oxus |journal=Bulletin of the Asia Institute |publisher=] |volume=8 |pages=47–66 |jstor=24048765 |issn=0890-4464}}</ref>]] | |||
| The famous cities of ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], and ] are located here. Many experts point to these cities as the birthplace of modern Persian language. The ]s, who claimed inheritance to the ]s, had their capital built here. | |||
| ] is one of the regions of ''Iran-zameen'', and is the home of the ancient Iranians, ], according to the ancient book of the ]. Modern scholars believe Khwarazm to be what ancient Avestic texts refer to as "Ariyaneh Waeje" or Iran vij. ''Iranovich'' These sources claim that ], which was the capital of ancient Khwarazm for many years, was actually "Ourva": the eighth land of ] mentioned in the ] text of Vendidad. Others such as ] historian ] believe Khwarazm to be the "most likely locale" corresponding to the original home of the Avestan people,<ref>], ''The History of Iran''. 2001. {{ISBN|978-0-313-30731-7}}, p.28</ref>{{Verify source|date=September 2023}} while Dehkhoda calls Khwarazm "the cradle of the ]n people" (مهد قوم آریا). Today Khwarazm is split between several central Asian republics. | |||
| ای بخارا شاد باش و دیر زی<br> | |||
| Oh ]! Joy to you and live long!<br> | |||
| شاه زی تو میهمان آید همی<br> | |||
| Your King comes to you in ceremony.<br> | |||
| ''---]'' | |||
| Superimposed on and overlapping with Chorasmia was Khorasan which roughly covered nearly the same geographical areas in Central Asia (starting from ] eastward through northern Afghanistan roughly until the foothills of ], ancient ]). Current day provinces such as ] in ], ], ], and ] in Iran are all remnants of the old Khorasan. Until the 13th century and the devastating Mongol invasion of the region, Khorasan was considered the cultural capital of Greater Iran.<ref> | |||
| ====Western China==== | |||
| Lorentz, J. ''Historical Dictionary of Iran''. 1995. {{ISBN|978-0-8108-2994-7}}</ref>{{page needed |date=September 2023}} | |||
| The ] regions of ] harbored a Persian population and culture. <ref>See: | |||
| *], p.443 for ''Persian settlements in southwestern China'' | |||
| *'']'' for more links on the historical ties.</ref> | |||
| ===China=== | |||
| === ] regions=== | |||
| ====Xinjiang==== | |||
| ] relief is located near ], in the Kurdish region of Iran, and is believed to depict either ] or ].]] | |||
| {{See also|China–Iran relations|Tajiks of Xinjiang}} | |||
| The Kurdish regions together including those in ], ] and ], in addition to Iran, constitute what is commonly referred to as the greater ]. The Kurdish regions in ], ] and ] are entwined with the culture and history of that of the rest of Greater Iran. The Kurds and Lurs of Iran are spread out through many provinces, and are thought to also be closely descended from the Aryan tribes of antiquity. ] was born from a Kurdish mother of the Shabankareh tribe of ]. Kurdish ancestors are believed to have consisted of the ancient tribes descending from the Caucauses, such as ] tribes, as well as the later Indo-Iranian speaking ]. The ] established the ] in 728 BCE, before forming a union with the Persian tribes and creating the Iranian Empire. | |||
| {{Synthesis|date=December 2015}} | |||
| The ] regions of China harbored a Tajik population and culture.<ref>See '']'', p. 443, for Persian settlements in southwestern China; '']'' for more on the historical ties. | |||
| ===]=== | |||
| </ref> Chinese Tashkurgan Tajik Autonomous County was always counted as a part of the Iranian cultural & linguistic continent with ], ], and ] bound to the Iranian history.<ref>"Persian language in ]" (زبان فارسی در سین کیانگ). Zamir Sa'dollah Zadeh (دکتر ضمیر سعدالله زاده). ''Nameh-i Iran'' (نامه ایران) V.1. Editor: Hamid Yazdan Parast (حمید یزدان پرست). {{ISBN|978-964-423-572-6}} ] collection under DS 266 N336 2005.</ref> | |||
| The western provinces of Pakistan, which comprise the ] and ], are predominantly Iranian-speaking regions where ] and ] comprise the vast majority of the local populations and remain an extension of Iranian civilization in the east. In addition, many remains of Persian architecture still remain in these areas (e.g. ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], and ]), and up to 1 million Persian speakers still exist. | |||
| ===West Asia=== | |||
| Parts of Pakistan east of the Indus river are traditionally thought of as ] rather than being part of greater Iran. | |||
| ====Bahrain==== | |||
| Pakistan's national language, ] borrows heavily from ], while the nation's national poet, Muhammad Iqbal wrote the majority of poems in Persian. Pakistan's national anthem is also in Persian, and many educated Pakistanis are fluent in the language. In addition Persian influence resonates in arts and architecture. | |||
| {{See also|Ajam of Bahrain|Huwala people}} | |||
| ]]] | |||
| ===Parts of the ''']''' region=== | |||
| ] remains can be seen up far north as "''']'''", now in southern Russia (the words ] and darband are both Persian). These parts were mostly annexed by ] over the course of the 18th and 19th centuries. yet even today, most of these regions continue to retain their ''Greater Persian'' identity, as can be seen in their traditions and customs (e.g. ]). ''For a discussion see <ref>]: "Caucasus Iran" article, p.84-96.</ref>'' | |||
| From the 6th century BC to the 3rd century BC, Bahrain was a prominent part of the Persian Empire under the ] dynasty. It was referred to by the Greeks as "]", the centre of ] trading, when ] discovered it while serving under ].<ref name="Larsen">''Life and Land Use on the Bahrain Islands: The Geoarchaeology of an Ancient ...'' by Curtis E. Larsen p. 13</ref> From the 3rd century BC to the arrival of Islam in the 7th century AD, the island was controlled by two other Iranian dynasties, the ] and the ]. | |||
| ====]==== | |||
| Separated from Iran in the mid-1800s, by virtue of the ] and ]. The city of ] (Bād-kubeh) is another city with an originally Persian name. The word Azerbaijan itself is from the Persian "Azar-Padegan" (Atropatan). | |||
| In the 3rd century AD, the Sassanids succeeded the Parthians and controlled the area for four centuries until the Arab conquest.<ref name="Federal Research Division page 7"/> ], the first ruler of the Iranian Sassanid dynasty marched to Oman and Bahrain and defeated Sanatruq<ref>Robert G. Hoyland, ''Arabia and the Arabs: From the Bronze Age to the Coming of Islam'', Routledge 2001p28</ref> (or Satiran<ref name="Mojtahed-Zadeh">''Security and Territoriality in the Persian Gulf: A Maritime Political Geography'' by Pirouz Mojtahed-Zadeh, page 119</ref>), probably the Parthian governor of Bahrain.<ref name = "Jamsheed"/> He appointed his son ] as governor. Shapur constructed a new city there and named it Batan Ardashir after his father.<ref name="Mojtahed-Zadeh"/> At this time, it incorporated the southern Sassanid province covering the Persian Gulf's southern shore plus the archipelago of Bahrain.<ref name="Jamsheed">Conflict and Cooperation: Zoroastrian Subalterns and Muslim Elites in ... By Jamsheed K. Choksy, 1997, page 75</ref> The southern province of the Sassanids was subdivided into three districts; Haggar (now al-Hafuf province, Saudi Arabia), Batan Ardashir (now ] province, Saudi Arabia), and ] (now Bahrain Island)<ref name="Mojtahed-Zadeh"/> (In ]/Pahlavi it means "ewe-fish").<ref>Yoma 77a and Rosh Hashbanah, 23a</ref> | |||
| Despite the annexation of this area by ], the main part of Azerbaijan remians inside the modern day ]. | |||
| ] at their greatest extent]] | |||
| By about 130 BC, the Parthian dynasty brought the Persian Gulf under their control and extended their influence as far as ]. Because they needed to control the Persian Gulf trade route, the Parthians established garrisons along the southern coast of the Persian Gulf.<ref name="Federal Research Division page 7">''Bahrain'' by Federal Research Division, page 7</ref> | |||
| through warfare and economic distress, been reduced to only 60.<ref>Juan Cole, ''Sacred Space and Holy War'', IB Tauris, 2007 p52</ref> | |||
| The influence of Iran was further undermined at the end of the 18th century when the ideological power struggle between the Akhbari-Usuli strands culminated in victory for the Usulis in Bahrain.<ref> Maximilian Terhalle, ''Middle East Policy'', Volume 14 Issue 2 Page 73, June 2007</ref> | |||
| An Afghan uprising led by Hotakis of Kandahar at the beginning of the 18th century resulted in the near-collapse of the Safavid state.{{CN|date=May 2023}} In the resultant power vacuum, ], ending over one hundred years of Persian hegemony in Bahrain. The Omani invasion began a period of political instability and a quick succession of outside rulers took power with consequent destruction. According to a contemporary account by theologian, Sheikh Yusuf Al Bahrani, in an unsuccessful attempt by the Persians and their Bedouin allies to take back Bahrain from the ] Omanis, much of the country was burnt to the ground.<ref> published in ''Interpreting the Self, Autobiography in the Arabic Literary Tradition'', Edited by Dwight F. Reynolds, University of California Press Berkeley 2001</ref> Bahrain was eventually sold back to the Persians by the Omanis, but the weakness of the Safavid empire saw ] tribes seize control.<ref>The Autobiography of Yūsuf al-Bahrānī (1696–1772) from Lu'lu'at al-Baḥrayn, from the final chapter featured in ''Interpreting the Self, Autobiography in the Arabic Literary Tradition'', Edited by Dwight F. Reynolds, University of California Press Berkeley 2001 p221</ref> | |||
| گزیده هر چه در ایران بزرگان<br> | |||
| ] under ]]] | |||
| زآذربایگان و ری و گرگان | |||
| In 1730, the new Shah of ], ], sought to re-assert Persian sovereignty in Bahrain. He ordered Latif Khan, the admiral of the Persian navy in the Persian Gulf, to prepare an invasion fleet in ].{{CN|date=May 2023}} The Persians invaded in March or early April 1736 when the ruler of Bahrain, Shaikh Jubayr, was away on ].{{CN|date=May 2023}} The invasion brought the island back under central rule and to challenge Oman in the Persian Gulf. He sought help from the British and Dutch, and he eventually recaptured Bahrain in 1736.<ref>Charles Belgrave, The Pirate Coast, G. Bell & Sons, 1966 p19</ref> During the ] era, Persian control over Bahrain waned{{CN|date=May 2023}} and in 1753, Bahrain was occupied by the Sunni Persians of the ]-based Al Madhkur family,<ref>Ahmad Mustafa Abu Hakim, ''History of Eastern Arabia 1750–1800'', Khayat, 1960, p78</ref><!--unreliable source--> who ruled Bahrain in the name of Persia and paid allegiance to ]. | |||
| ]]] | |||
| During most of the second half of the eighteenth century, Bahrain was ruled by ], the ruler of ]. The Bani Utibah tribe from Zubarah exceeded in taking over Bahrain after war broke out in 1782. Persian attempts to reconquer the island in 1783 and in 1785 failed; the 1783 expedition was a joint Persian-] invasion force that never left Bushehr. The 1785 invasion fleet, composed of forces from Bushehr, Rig, and ] was called off after the death of the ruler of Shiraz, ]. Due to internal difficulties, the Persians could not attempt another invasion.{{CN|date=May 2023}} In 1799, Bahrain came under threat from the ] policies of ], the ], when he invaded the island under the pretext that Bahrain did not pay taxes owed.{{CN|date=May 2023}} The Bani Utbah solicited the aid of Bushire to expel the Omanis on the condition that Bahrain would become a ] of Persia. In 1800, Sayyid Sultan invaded Bahrain again in retaliation and deployed a garrison at ], in ] island and had appointed his twelve-year-old son Salim, as Governor of the island.<ref>James Onley, The Politics of Protection in the Gulf: The Arab Rulers and the British Resident in the Nineteenth Century, Exeter University, 2004 p44</ref> | |||
| ] at its greatest extent]] | |||
| Many names of villages in Bahrain are derived from the ] language.<ref name=Tajer>{{cite book|last=Al-Tajer|first=Mahdi Abdulla|title=Language & Linguistic Origins In Bahrain|year=1982|publisher=Taylor & Francis|isbn=978-0-7103-0024-9|pages=134, 135|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=BNs9AAAAIAAJ&q=bahrain%20village%20persian%20name&pg=PA134}}</ref> These names were thought to have been as a result influences during the ] rule of Bahrain (1501–1722) and previous Persian rule. Village names such as ], ], ], ], ] were originally derived from the Persian language, suggesting that Persians had a substantial effect on the island's history.<ref name=Tajer/> The local ] dialect has also borrowed many words from the Persian language.<ref name=Tajer/> Bahrain's capital city, ] is derived from two Persian words meaning 'I' and 'speech'.<ref name=Tajer/>{{contradict-inline|article=Manama|section=Etymology|date=March 2018}} | |||
| In 1910, the Persian community funded and opened a ], Al-Ittihad school, that taught ] amongst other subjects.<ref>{{cite book|last=Shirawi|first=May Al-Arrayed|title=Education in Bahrain - 1919-1986, An Analytical Study of Problems and Progress|url=http://etheses.dur.ac.uk/6662/1/6662_3966.PDF?UkUDh:CyT|year=1987|publisher=Durham University|page=60}}</ref> | |||
| All the nobles and greats of Iran,<br> | |||
| According to the 1905 census, there were 1650 Bahraini citizens of Persian origin.<ref name=pol/> | |||
| Choose from Azarbaijan, ], and ].<br> | |||
| --'']'' | |||
| Historian Nasser Hussain says that many Iranians fled their native country in the early 20th century due to a law king ] issued which banned women from wearing the ], or because they feared for their lives after fighting the English or to find jobs. They were coming to Bahrain from Bushehr and the ] between 1920 and 1940. In the 1920s, local Persian merchants were prominently involved in the consolidation of Bahrain's first powerful lobby with connections to the municipality in an effort to contest the municipal legislation of British control.<ref name=pol>{{cite book|last=Fuccaro|first=Nelida|title=Histories of City and State in the Persian Gulf: Manama Since 1800|page=114|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=wKU6jvKGicUC|isbn=978-0-521-51435-4|date=2009-09-03|publisher=Cambridge University Press }}</ref> | |||
| ====Armenia ("Armanestan")==== | |||
| ] was a province of various ]s since the ] period and was heavily influenced by ]. Armenia however, has historically been largely populated by a distinct ]-speaking people who merged with local ] peoples, rather than being directly associated with the Iranian peoples. Ancient Armenian society was a combination of local cultures, Iranian social and political structures, and ]/] traditions. <ref>See: | |||
| *Link: | |||
| *] p.417-483 for a lengthy discussion on this topic. Link: </ref> Due to centuries of independent indigenous development, conquests by western powers including the ] and ], and its diverse diasporic population that has absorbed many cultural traits, especially those of ] and ], Armenia can be termed a ] state. | |||
| Bahrain's local Persian community has heavily influenced the country's local food dishes. One of the most notable local delicacies of the people in Bahrain is '']'', which is consumed in Southern Iran as well. It is a watery, earth-brick-coloured sauce made from sardines, and consumed with bread or other food. Bahrain's Persians are also famous in Bahrain for bread-making. Another local delicacy is ''pishoo'' made from ] (''golab'') and ]. Other food items consumed are similar to ]. | |||
| Iran continues to have a ] that links ] to Iranian culture. Many Armenians such as ] were directly involved and remembered in the ]. | |||
| ==== |
====Iraq==== | ||
| {{See also|Iran–Iraq relations|Iran–Iraq War|Persians in Iraq|Asuristan}} | |||
| Early in antiquity, ] is known to have had fortifications built here. In later times, some of Persia's literary and intellectual figures from the ] period have hailed from this region. Also separated from Greater-Iran/Persia in the mid-1800s, by virtue of the ] and ]. | |||
| Throughout history, Iran always had strong cultural ties with the region of present-day ]. ] is considered the cradle of civilization and the place where the first empires in history were established. These empires, namely the ]ian, ], ]n, and ]n, dominated the ancient middle east for millennia, which explains the great influence of Mesopotamia on the Iranian culture and history, and it is also the reason why the later Iranian and Greek dynasties chose Mesopotamia to be the political center of their rule. For a period of around 500 years, what is now Iraq formed the core of Iran, with the Iranian ] and ] empire having their capital in what is modern-day Iraq for the same centuries-long time span. (]) | |||
| که تا جایگه یافتی نخچوان<br> | |||
| Oh Nakhchivan, respect youve attained,<br> | |||
| بدین شاه شد بخت پیرت جوان<br> | |||
| With this King in luck youll remain.<br> | |||
| ''---]'' | |||
| {{cquote|Of the four residences of the ] named by ]—], ] or ], ] and ]—the last was maintained as their most important capital, the fixed winter quarters, the central office of bureaucracy, exchanged only in the heat of summer for some cool spot in the highlands.<ref name=EY>{{cite book|last=Yarshater|first=Ehsan|author-link=Ehsan Yarshater|title=The Cambridge History of Iran, Volume 3|year=1993|publisher=]|isbn=978-0-521-20092-9|page=482|quote=Of the four residences of the Achaemenids named by ]—], ] or ], ] and ]—the last was maintained as their most important capital, the fixed winter quarters, the central office of bureaucracy, exchanged only in the heat of summer for some cool spot in the highlands. Under the ] and the ] the site of the Mesopotamian capital moved a little to the north on the ]—to ] and ]. It is indeed symbolic that these new foundations were built from the bricks of ancient ], just as later ], a little further upstream, was built out of the ruins of the ] double city of ].}}</ref> | |||
| ====] and ]==== | |||
| ], 1620. Artist is ]. Painting is located at Berlin's Museum Für Islamische Kunst.]] | |||
| ], or "Gorjestan" was a Persian Province during ] times (particularly starting with Hormozd IV). During the ] era, Georgia became so culturally intertwined with Iran that they almost repalced the ] in the Safavid courts. ] was even the official administrative language of Georgia in the time of Shah Tahmasb, and Allah-verdi Khan, whom the famous landmark of ] in ] is named after, was among the Georgian elite that were involved in the Safavid government. And ], ], was the son of a Georgian father.<ref>Patrick Clawson. Eternal Iran. Palgrave. 2005. Coauthored with Michael Rubin. ISBN 1-4039-6276-6 p.168</ref> Georgia was again a direct province of Persia from 1629 until 1762 when the Russian influence arrived. | |||
| Under the ] and the ] the site of the Mesopotamian capital moved a little to the north on the ]—to ] and ]. It is indeed symbolic that these new foundations were built from the bricks of ancient ], just as later ], a little further upstream, was built out of the ruins of the ] double city of ].<ref name=EY />|||Iranologist ]|The Cambridge History of Iran,<ref name=EY />}} | |||
| The aforementioned is especially true of "Eastern Georgia". Eastern Georgia historically was attached to the south for support, as opposed to Western Georgia, which looked for help to the North. The city of "Teflis" (now ]) was Persianized for quite some time. The ]id heir to the throne prince ] spent much time there. | |||
| ], written in ] ] in the name of the ] king, ], describes the Persian takeover of ] (An ancient city in modern-day Iraq).]] | |||
| In the end, Persia was unable to challenge Russia in Georgia, and officially gave up claim to Georgia according to the text of the ] and ]. Today, Georgia continues to be Europeanized. | |||
| ] at time of ]]] | |||
| For a lengthy discussion, see <ref>]'s reference on Gorjestan: </ref> | |||
| According to ] ]:<ref>{{cite book|last=Frye|first=Richard N.|author-link=Richard N. Frye|title=The Golden Age of Persia: The Arabs in the East|year=1975|publisher=Weidenfeld and Nicolson|isbn=978-0-7538-0944-0|page=184|quote= throughout Iran's history the western part of the land has been frequently more closely connected with the lowlands of Mesopotamia than with the rest of the plateau to the east of the central deserts.}}</ref><ref name=NY>{{cite book|last=Yavari|first=Neguin|title=Iranian Perspectives on the Iran-Iraq War; Part II. Conceptual Dimensions; 7. National, Ethnic, and Sectarian Issues in the Iran–Iraq War|year=1997|publisher=]|isbn=978-0-8130-1476-0|page=80|quote=Between the coming of the 'Abbasids and the Mongol onslaught, Iraq and western Iran shared a closer history than did eastern Iran and its western counterpart.}}</ref> | |||
| {{quote|Throughout Iran's history the western part of the land has been frequently more closely connected with the ]s of Mesopotamia (Iraq) than with the rest of the ] to the east of the central deserts ] and ]]. | Richard N. Frye | ''The Golden Age of Persia: The Arabs in the East''}} | |||
| ===Modern-Day ]=== | |||
| This is what used to be the western part of Greater Iran. At times, it also included what is today eastern ], as it is where the ] capital was located (]). There are still cities and provinces in contemporary Iraq where the Persian names of the city are still retained. e.g. ] or ]. Other cities of Iraq with originally Persian names include ''Nokard'' --> ], ''Budh-Aadashir'' --> ], ''Suristan'' --> ], ''Shahrban'' --> ], ''Anbar'' --> ], ] --> ''Shatt al-Arab'', and ''Asheb'' --> ]. <ref>See: محمدی ملایری، محمد: فرهنگ ایران در دوران انتقال از عصر ساسانی به عصر اسلامی، جلد دوم: دل ایرانشهر، تهران، انتشارات توس 1375.: Mohammadi Malayeri, M.: Del-e Iranshahr, vol. II, Tehran 1375 Hs.</ref> | |||
| {{Rquote|right|Between the coming of the Abbasids and the Mongol onslaught , Iraq and western Iran shared a closer history than did eastern Iran and its western counterpart. | Neguin Yavari | ''Iranian Perspectives on the Iran–Iraq War''<ref name=NY />}} | |||
| ] verifies this: | |||
| Testimony to the close relationship shared by Iraq and western Iran during the ] and later centuries, is the fact that the two regions came to share the same name. The western region of ] (ancient Media) was called ] ("Persian Iraq"), while central-southern ] (Babylonia) was called 'Irāq al-'Arabī ("Arabic Iraq") or Bābil ("Babylon"). | |||
| :"Arab nationalists may seek retroactively to extend the present into the past, but this skews reality. Iranian domains once extended well into what is now Iraq. The first Sassanian capital was at Ctesiphon, 21 miles southeast of Baghdad."<ref>]. ''Eternal Iran''. Palgrave Macmillan. 2005. ISBN 1-4039-6276-6,</ref> | |||
| For centuries the two neighbouring regions were known as "]" ("al-'Iraqain"). The 12th century Persian poet ] wrote a famous poem ''Tohfat-ul Iraqein'' ("The Gift of the Two Iraqs"). The city of ] in western Iran still bears the region's old name, and Iranians still traditionally call the region between ], ] and ] "ʿErāq". | |||
| Even after Iraq was Arabized during the Islamic conquests of the 7th century, the Persian presence was still quite recognizeable and dominant at times, as many famous Persian ] clerics are buried in ] and ]. At the latest, the ]s lost control of these areas to the Ottoman Empire | |||
| During the medieval ages, Mesopotamian and Iranian peoples knew each other's languages because of trade, and because Arabic was the language of religion and science at that time. The ] historian ] (d. 1430) wrote of Iraq:<ref>{{cite web|last=Morony|first=Michael G|author-link=Michael G. Morony|title=IRAQ AND ITS RELATIONS WITH IRAN|url=http://www.iranicaonline.org/articles/iraq-i-late-sasanid-early-islamic|work=IRAQ i. IN THE LATE SASANID AND EARLY ISLAMIC ERAS|publisher=]|access-date=11 February 2012|quote=Persian remained the language of most of the sedentary people as well as that of the chancery until the 15th century and thereafter, as attested by Ḥāfeẓ-e Abru (d. 1430) who said, "The majority of inhabitants of Iraq know Persian and Arabic, and from the time of the domination of Turkic people the Turkish language has also found currency: as the city people and those engaged in trade and crafts are Persophone, the Bedouins are Arabophone, and the governing classes are Turkophone. But, all three peoples (qawms) know each other's languages due to the mixture and amalgamation."}}</ref> | |||
| ==References== | |||
| {{quote|The majority of inhabitants of Iraq know ] and ], and from the time of the domination of ] the ] has also found currency. | Ḥāfeẓ-e Abru}} | |||
| <references/> | |||
| ] share religious and certain cultural ties with ]. The majority of Iranians are Twelver ] (an Islamic sect). | |||
| ==Further reading== | |||
| Iraqi culture has commonalities with the ]. The ] also has similarities to the ], including common dishes and cooking techniques. The ] has absorbed many words from the ].<ref>{{cite book|last1=Csató|first1=Éva Ágnes|last2=Isaksson|first2=Bo|last3=Jahani|first3=Carina |title=Linguistic Convergence and Areal Diffusion: Case Studies from Iranian, Semitic and Turkic|year=2005|publisher=]|isbn=978-0-415-30804-5|page=177}}</ref> | |||
| *"Ethnic Identity in Iran" by ], JSAI 26, 2002, see p.82 | |||
| * | |||
| == |
===Kurdistan=== | ||
| ] speak a Northwestern Iranian language known as ]. Some historians and linguists, such as ], have suggested that the ], an Iranian people who inhabited much of western Iran, including Azerbaijan and Kurdistan, might have been forefathers of modern Kurds.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Gershevitch |first1=Ilya |year=1967 |title=Professor Vladimir Minorsky |journal=Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society of Great Britain and Ireland |volume=99 |issue=1/2 |pages=53–57 |doi=10.1017/S0035869X00125638 |jstor=25202975 |doi-access=free}}</ref> | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| ==See also== | |||
| *] | |||
| {{Portal|Iran|Religion}} | |||
| {{Divcol}} | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | |||
| *] cultures | |||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| {{Divcolend}} | |||
| ==Notes and references== | |||
| == Other cultural continents == | |||
| ===Explanatory footnotes=== | |||
| * ] | |||
| {{notefoot}} | |||
| * ] | |||
| == |
===Citation footnotes=== | ||
| {{Reflist|2}} | |||
| ===In English=== | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| === |
===General references=== | ||
| * {{cite book | last1 = Fisher | first1 = William Bayne | last2 = Avery | first2= P. | last3 = Hambly | first3 = G. R. G | last4 = Melville | first4 = C. | title = The Cambridge History of Iran | volume = 7 | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=H20Xt157iYUC&q=agha+muhammad+khan+invade+georgia | publisher = ] | location = Cambridge | year = 1991 | isbn = 978-0-521-20095-0 }} | |||
| * | |||
| *{{cite book |first=Richard |last=Foltz |author-link=Richard Foltz |title=Iran in World History |publisher=Oxford University Press |location=New York |year=2015 |isbn=978-0-19-933549-7}} | |||
| * | |||
| * Marcinkowski, Christoph (2010). ''Shi'ite Identities: Community and Culture in Changing Social Contexts''. Berlin: Lit Verlag 2010. {{ISBN|978-3-643-80049-7}}. | |||
| * | |||
| {{Iran topics}} | |||
| ] | |||
| {{Irredentism}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 17:40, 2 January 2025
Sociocultural region in West and Central Asia See also: Indo-Persian culture and Turco-Persian traditionThis article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
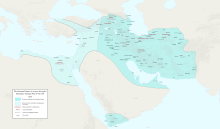
Greater Iran or Greater Persia (Persian: ایران بزرگ Irān-e Bozorg), also called the Iranosphere or the Persosphere, is an expression that denotes a wide socio-cultural region comprising parts of West Asia, the Caucasus, Central Asia, South Asia, and East Asia (specifically the Tarim Basin)—all of which have been affected, to some degree, by the Iranian peoples and the Iranian languages.
It is defined by having long been ruled by the dynasties of various Iranian empires, under whom the local populaces gradually incorporated some degree of Iranian influence into their cultural and/or linguistic traditions; or alternatively as where a considerable number of Iranians settled to still maintain communities who patronize their respective cultures, geographically corresponding to the areas surrounding the Iranian plateau. It is referred to as the "Iranian Cultural Continent" by Encyclopædia Iranica.
Throughout the 16th–19th centuries, Iran lost many of the territories that had been conquered under the Safavids and Qajars.
The Ottoman–Iranian Wars resulted in the loss of present-day Iraq to the Ottoman Empire, as outlined in the Treaty of Amasya in 1555 and the Treaty of Zuhab in 1639.
Simultaneously, the Russo-Iranian Wars resulted in the loss of the Caucasus to the Russian Empire: the Treaty of Gulistan in 1813 saw Iran cede present-day Dagestan, Georgia, and most of Azerbaijan; the Treaty of Turkmenchay in 1828 saw Iran cede present-day Armenia, the remainder of Azerbaijan, and Iğdır, setting the northern boundary along the Aras River.
Parts of Afghanistan were lost to the British Empire through the Treaty of Paris in 1857 and the McMahon Arbitration in 1905.
Etymology
The name "Iran", meaning "land of the Aryans", is the New Persian continuation of the old genitive plural aryānām (proto-Iranian, meaning "of the Aryans"), first attested in the Avesta as airyānąm (the text of which is composed in Avestan, an old Iranian language spoken in northeastern Greater Iran, or in what are now Afghanistan, Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan and Tajikistan).
The proto-Iranian term aryānām is present in the term Airyana Vaēǰah, the homeland of Zoroaster and Zoroastrianism, near the provinces of Sogdiana, Margiana, Bactria, etc., listed in the first chapter of the Vidēvdād. The Avestan evidence is confirmed by Greek sources: Arianē is spoken of as being between Persia and the Indian subcontinent.
However, this is a Greek pronunciation of the name Haroyum/Haraiva (Herat), which the Greeks called 'Aria' (a land listed separately from the homeland of the Aryans).
While up until the end of the Parthian period in the 3rd century CE, the idea of "Irān" had an ethnic, linguistic, and religious value, it did not yet have a political import. The idea of an "Iranian" empire or kingdom in a political sense is a purely Sasanian one. It was the result of a convergence of interests between the new dynasty and the Zoroastrian clergy, as we can deduce from the available evidence.
This convergence gave rise to the idea of an Ērān-šahr "Kingdom of the Iranians", which was "ēr" (Middle Persian equivalent of Old Persian "ariya" and Avestan "airya").
Definition
Richard Nelson Frye defines Greater Iran as including "much of the Caucasus, Iraq, Afghanistan, Pakistan and Central Asia, with cultural influences extending to China and western India."
According to him, "Iran means all lands and peoples where Iranian languages were and are spoken, and where in the past, multi-faceted Iranian cultures existed."
Richard Foltz notes that while "A general assumption is often made that the various Iranian peoples of 'greater Iran'—a cultural area that stretched from Mesopotamia and the Caucasus into Khwarizm, Transoxiana, Bactria, and the Pamirs and included Persians, Medes, Parthians and Sogdians among others—were all 'Zoroastrians' in pre-Islamic times... This view, even though common among serious scholars, is almost certainly overstated." He argues that "While the various Iranian peoples did indeed share a common pantheon and pool of religious myths and symbols, in actuality a variety of deities were worshipped—particularly Mitra, the god of covenants, and Anahita, the goddess of the waters, but also many others—depending on the time, place, and particular group concerned".
To the Ancient Greeks, Greater Iran ended at the Indus River located in Pakistan.
According to J. P. Mallory and Douglas Q. Adams most of Western greater Iran spoke Southwestern Iranian languages in the Achaemenid era while the Eastern territory spoke Eastern Iranian languages related to Avestan.
George Lane also states that after the dissolution of the Mongol Empire, the Ilkhanids became rulers of greater Iran and Uljaytu, according to Judith G. Kolbas, was the ruler of this expanse between 1304 and 1317 A.D.
Primary sources, including Timurid historian Mir Khwand, define Iranshahr (Greater Iran) as extending from the Euphrates to the Oxus
The Cambridge History of Iran takes a geographical approach in referring to the "historical and cultural" entity of "Greater Iran" as "areas of Iran, parts of Afghanistan, Chinese and Soviet Central Asia".
Background

Greater Iran is called Iranzamin (ایرانزمین) which means "Iranland" or "The Land of Iran". Iranzamin was in the mythical times as opposed to the Turanzamin, "The Land of Turan", which was located in the upper part of Central Asia.
With Imperial Russia continuously advancing south in the course of two wars against Persia, and the treaties of Turkmenchay and Gulistan in the western frontiers, plus the unexpected death of Abbas Mirza in 1833, and the murdering of Persia's Grand Vizier (Mirza AbolQasem Qa'im Maqām), many Central Asian khanates began losing hope for any support from Persia against the Tsarist armies. The Russian armies occupied the Aral coast in 1849, Tashkent in 1864, Bukhara in 1867, Samarkand in 1868, and Khiva and Amudarya in 1873.
- "Many Iranians consider their natural sphere of influence to extend beyond Iran's present borders. After all, Iran was once much larger. Portuguese forces seized islands and ports in the 16th and 17th centuries. In the 19th century, the Russian Empire wrested from Tehran's control what is today Armenia, Republic of Azerbaijan, and part of Georgia. Iranian elementary school texts teach about the Iranian roots not only of cities like Baku, but also cities further north like Derbent in southern Russia. The Shah lost much of his claim to western Afghanistan following the Anglo-Iranian war of 1856-1857. Only in 1970 did a UN sponsored consultation end Iranian claims to suzerainty over the Persian Gulf island nation of Bahrain. In centuries past, Iranian rule once stretched westward into modern Iraq and beyond. When the western world complains of Iranian interference beyond its borders, the Iranian government often convinced itself that it is merely exerting its influence in lands that were once its own. Simultaneously, Iran's losses at the hands of outside powers have contributed to a sense of grievance that continues to the present day." -Patrick Clawson of the Washington Institute for Near East Policy
- "Iran today is just a rump of what it once was. At its height, Iranian rulers controlled Iraq, Afghanistan, Western Pakistan, much of Central Asia, and the Caucasus. Many Iranians today consider these areas part of a greater Iranian sphere of influence." - Patrick Clawson
- "Since the days of the Achaemenids, the Iranians had the protection of geography. But high mountains and the vast emptiness of the Iranian plateau were no longer enough to shield Iran from the Russian army or British navy. Both literally, and figuratively, Iran shrank. At the beginning of the nineteenth century, Azerbaijan, Armenia, and Afghanistan were Iranian, but by the end of the century, all this territory had been lost as a result of European military action."
Regions
In the 8th century, Iran was conquered by the Arab Abbassids who ruled from Baghdad. The territory of Iran at that time was composed of two portions: Persian Iraq (western portion) and Khorasan (eastern portion). The dividing region was mostly the cities of Gurgan and Damaghan. The Ghaznavids, Seljuqs and Timurids divided their empires into Iraqi and Khorasani regions. This point can be observed in many books such as Abul Fazl Bayhqi's "Tārīkhi Baïhaqī", Al-Ghazali's Faza'ilul al-anam min rasa'ili hujjat al-Islam and other books. Transoxiana and Chorasmia were mostly included in the Khorasanian region.
Caucasus
North Caucasus
See also: History of Dagestan, History of Kabardino-Balkaria, Russo-Persian Wars, Treaty of Gulistan, Treaty of Turkmenchay, and Tat people (Caucasus)
Dagestan remains the bastion of Persian culture in the North Caucasus with fine examples of Iranian architecture like the Sassanid citadel in Derbent, the strong influence of Persian cuisine, and common Persian names amongst the ethnic peoples of Dagestan. The ethnic Persian population of the North Caucasus, the Tats, remain, despite strong assimilation over the years, still visible in several North Caucasian cities. Even today, after decades of partition, some of these regions retain Iranian influences, as seen in their old beliefs, traditions and customs (e.g. Norouz).
South Caucasus
See also: Azerbaijani people, History of Azerbaijan, Tat people (Iran), Tat people (Caucasus), Safavid conversion of Iran to Shia Islam, Old Azeri language, Shirvan, Arran (Caucasus), Shirvanshah, and Iranian AzerbaijanisAccording to Tadeusz Swietochowski, the territories of Iran and the republic of Azerbaijan usually shared the same history from the time of ancient Media (ninth to seventh centuries b.c.) and the Persian Empire (sixth to fourth centuries b.c.).
Intimately and inseparably intertwined histories for millennia, Iran irrevocably lost the territory that is nowadays Azerbaijan in the course of the 19th century. With the Treaty of Gulistan of 1813 following the Russo-Persian War (1804–1813) Iran had to cede eastern Georgia, its possessions in the North Caucasus and many of those in what is today the Azerbaijan Republic, which included the khanates of Baku, Shirvan, Karabakh, Ganja, Shaki, Quba, Derbent, and parts of Talysh. These Khanates comprise most of what is today the Republic of Azerbaijan and Dagestan in Southern Russia. In the Treaty of Turkmenchay of 1828 following the Russo-Persian War (1826–1828), the result was even more disastrous, and resulted in Iran being forced to cede the remainder of the Talysh Khanate, the khanates of Nakhichevan and Erivan, and the Mughan region to Russia. All these territories together, lost in 1813 and 1828 combined, constitute all of the modern-day Republic of Azerbaijan, Armenia, and southern Dagestan. The area to the North of the river Aras, among which the territory of the contemporary republic of Azerbaijan were Iranian territory until they were occupied by Russia in the course of the 19th century.
Many localities in this region bear Persian names or names derived from Iranian languages and Azerbaijan remains by far Iran's closest cultural, religious, ethnic, and historical neighbor. Azerbaijanis are by far the second-largest ethnicity in Iran, and comprise the largest community of ethnic Azerbaijanis in the world, vastly outnumbering the number in the Republic of Azerbaijan. Both nations are the only officially Shia majority in the world, with adherents of the religion comprising an absolute majority in both nations. The people of nowadays Iran and Azerbaijan were converted to Shiism during exactly the same time in history. Furthermore, the name of "Azerbaijan" is derived through the name of the Persian satrap which ruled the contemporary region of Iranian Azerbaijan and minor parts of the Republic of Azerbaijan in ancient times.
Central Asia

Khwarazm is one of the regions of Iran-zameen, and is the home of the ancient Iranians, Airyanem Vaejah, according to the ancient book of the Avesta. Modern scholars believe Khwarazm to be what ancient Avestic texts refer to as "Ariyaneh Waeje" or Iran vij. Iranovich These sources claim that Urgandj, which was the capital of ancient Khwarazm for many years, was actually "Ourva": the eighth land of Ahura Mazda mentioned in the Pahlavi text of Vendidad. Others such as University of Hawaii historian Elton L. Daniel believe Khwarazm to be the "most likely locale" corresponding to the original home of the Avestan people, while Dehkhoda calls Khwarazm "the cradle of the Aryan people" (مهد قوم آریا). Today Khwarazm is split between several central Asian republics.
Superimposed on and overlapping with Chorasmia was Khorasan which roughly covered nearly the same geographical areas in Central Asia (starting from Semnan eastward through northern Afghanistan roughly until the foothills of Pamir, ancient Mount Imeon). Current day provinces such as Sanjan in Turkmenia, Razavi Khorasan Province, North Khorasan Province, and Southern Khorasan Province in Iran are all remnants of the old Khorasan. Until the 13th century and the devastating Mongol invasion of the region, Khorasan was considered the cultural capital of Greater Iran.
China
Xinjiang
See also: China–Iran relations and Tajiks of Xinjiang| This article or section possibly contains synthesis of material that does not verifiably mention or relate to the main topic. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. (December 2015) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
The Tashkurgan Tajik Autonomous County regions of China harbored a Tajik population and culture. Chinese Tashkurgan Tajik Autonomous County was always counted as a part of the Iranian cultural & linguistic continent with Kashgar, Yarkand, and Hotan bound to the Iranian history.
West Asia
Bahrain
See also: Ajam of Bahrain and Huwala people
From the 6th century BC to the 3rd century BC, Bahrain was a prominent part of the Persian Empire under the Achaemenid dynasty. It was referred to by the Greeks as "Tylos", the centre of pearl trading, when Nearchus discovered it while serving under Alexander the Great. From the 3rd century BC to the arrival of Islam in the 7th century AD, the island was controlled by two other Iranian dynasties, the Parthians and the Sassanids.
In the 3rd century AD, the Sassanids succeeded the Parthians and controlled the area for four centuries until the Arab conquest. Ardashir, the first ruler of the Iranian Sassanid dynasty marched to Oman and Bahrain and defeated Sanatruq (or Satiran), probably the Parthian governor of Bahrain. He appointed his son Shapur I as governor. Shapur constructed a new city there and named it Batan Ardashir after his father. At this time, it incorporated the southern Sassanid province covering the Persian Gulf's southern shore plus the archipelago of Bahrain. The southern province of the Sassanids was subdivided into three districts; Haggar (now al-Hafuf province, Saudi Arabia), Batan Ardashir (now al-Qatif province, Saudi Arabia), and Mishmahig (now Bahrain Island) (In Middle-Persian/Pahlavi it means "ewe-fish").
By about 130 BC, the Parthian dynasty brought the Persian Gulf under their control and extended their influence as far as Oman. Because they needed to control the Persian Gulf trade route, the Parthians established garrisons along the southern coast of the Persian Gulf. through warfare and economic distress, been reduced to only 60. The influence of Iran was further undermined at the end of the 18th century when the ideological power struggle between the Akhbari-Usuli strands culminated in victory for the Usulis in Bahrain.
An Afghan uprising led by Hotakis of Kandahar at the beginning of the 18th century resulted in the near-collapse of the Safavid state. In the resultant power vacuum, Oman invaded Bahrain in 1717, ending over one hundred years of Persian hegemony in Bahrain. The Omani invasion began a period of political instability and a quick succession of outside rulers took power with consequent destruction. According to a contemporary account by theologian, Sheikh Yusuf Al Bahrani, in an unsuccessful attempt by the Persians and their Bedouin allies to take back Bahrain from the Kharijite Omanis, much of the country was burnt to the ground. Bahrain was eventually sold back to the Persians by the Omanis, but the weakness of the Safavid empire saw Huwala tribes seize control.

In 1730, the new Shah of Persia, Nadir Shah, sought to re-assert Persian sovereignty in Bahrain. He ordered Latif Khan, the admiral of the Persian navy in the Persian Gulf, to prepare an invasion fleet in Bushehr. The Persians invaded in March or early April 1736 when the ruler of Bahrain, Shaikh Jubayr, was away on hajj. The invasion brought the island back under central rule and to challenge Oman in the Persian Gulf. He sought help from the British and Dutch, and he eventually recaptured Bahrain in 1736. During the Qajar era, Persian control over Bahrain waned and in 1753, Bahrain was occupied by the Sunni Persians of the Bushire-based Al Madhkur family, who ruled Bahrain in the name of Persia and paid allegiance to Karim Khan Zand.
During most of the second half of the eighteenth century, Bahrain was ruled by Nasr Al-Madhkur, the ruler of Bushehr. The Bani Utibah tribe from Zubarah exceeded in taking over Bahrain after war broke out in 1782. Persian attempts to reconquer the island in 1783 and in 1785 failed; the 1783 expedition was a joint Persian-Qawasim invasion force that never left Bushehr. The 1785 invasion fleet, composed of forces from Bushehr, Rig, and Shiraz was called off after the death of the ruler of Shiraz, Ali Murad Khan. Due to internal difficulties, the Persians could not attempt another invasion. In 1799, Bahrain came under threat from the expansionist policies of Sayyid Sultan, the Sultan of Oman, when he invaded the island under the pretext that Bahrain did not pay taxes owed. The Bani Utbah solicited the aid of Bushire to expel the Omanis on the condition that Bahrain would become a tributary state of Persia. In 1800, Sayyid Sultan invaded Bahrain again in retaliation and deployed a garrison at Arad Fort, in Muharraq island and had appointed his twelve-year-old son Salim, as Governor of the island.
Many names of villages in Bahrain are derived from the Persian language. These names were thought to have been as a result influences during the Safavid rule of Bahrain (1501–1722) and previous Persian rule. Village names such as Karbabad, Salmabad, Karzakan, Duraz, Barbar were originally derived from the Persian language, suggesting that Persians had a substantial effect on the island's history. The local Bahrani Arabic dialect has also borrowed many words from the Persian language. Bahrain's capital city, Manama is derived from two Persian words meaning 'I' and 'speech'.
In 1910, the Persian community funded and opened a private school, Al-Ittihad school, that taught Farsi amongst other subjects. According to the 1905 census, there were 1650 Bahraini citizens of Persian origin.
Historian Nasser Hussain says that many Iranians fled their native country in the early 20th century due to a law king Reza Shah issued which banned women from wearing the hijab, or because they feared for their lives after fighting the English or to find jobs. They were coming to Bahrain from Bushehr and the Fars province between 1920 and 1940. In the 1920s, local Persian merchants were prominently involved in the consolidation of Bahrain's first powerful lobby with connections to the municipality in an effort to contest the municipal legislation of British control.
Bahrain's local Persian community has heavily influenced the country's local food dishes. One of the most notable local delicacies of the people in Bahrain is mahyawa, which is consumed in Southern Iran as well. It is a watery, earth-brick-coloured sauce made from sardines, and consumed with bread or other food. Bahrain's Persians are also famous in Bahrain for bread-making. Another local delicacy is pishoo made from rose water (golab) and agar agar. Other food items consumed are similar to Persian cuisine.
Iraq
See also: Iran–Iraq relations, Iran–Iraq War, Persians in Iraq, and AsuristanThroughout history, Iran always had strong cultural ties with the region of present-day Iraq. Mesopotamia is considered the cradle of civilization and the place where the first empires in history were established. These empires, namely the Sumerian, Akkadian, Babylonian, and Assyrian, dominated the ancient middle east for millennia, which explains the great influence of Mesopotamia on the Iranian culture and history, and it is also the reason why the later Iranian and Greek dynasties chose Mesopotamia to be the political center of their rule. For a period of around 500 years, what is now Iraq formed the core of Iran, with the Iranian Parthian and Sasanian empire having their capital in what is modern-day Iraq for the same centuries-long time span. (Ctesiphon)
Of the four residences of the Achaemenids named by Herodotus—Ecbatana, Pasargadae or Persepolis, Susa and Babylon—the last was maintained as their most important capital, the fixed winter quarters, the central office of bureaucracy, exchanged only in the heat of summer for some cool spot in the highlands. Under the Seleucids and the Parthians the site of the Mesopotamian capital moved a little to the north on the Tigris—to Seleucia and Ctesiphon. It is indeed symbolic that these new foundations were built from the bricks of ancient Babylon, just as later Baghdad, a little further upstream, was built out of the ruins of the Sassanian double city of Seleucia-Ctesiphon.
— Iranologist Ehsan Yarshater, The Cambridge History of Iran,


According to Iranologist Richard N. Frye:
Throughout Iran's history the western part of the land has been frequently more closely connected with the lowlands of Mesopotamia (Iraq) than with the rest of the plateau to the east of the central deserts .
— Richard N. Frye, The Golden Age of Persia: The Arabs in the East
Between the coming of the Abbasids and the Mongol onslaught , Iraq and western Iran shared a closer history than did eastern Iran and its western counterpart.
— Neguin Yavari, Iranian Perspectives on the Iran–Iraq War
Testimony to the close relationship shared by Iraq and western Iran during the Abbasid era and later centuries, is the fact that the two regions came to share the same name. The western region of Iran (ancient Media) was called 'Irāq-e 'Ajamī ("Persian Iraq"), while central-southern Iraq (Babylonia) was called 'Irāq al-'Arabī ("Arabic Iraq") or Bābil ("Babylon").
For centuries the two neighbouring regions were known as "The Two Iraqs" ("al-'Iraqain"). The 12th century Persian poet Khāqāni wrote a famous poem Tohfat-ul Iraqein ("The Gift of the Two Iraqs"). The city of Arāk in western Iran still bears the region's old name, and Iranians still traditionally call the region between Tehran, Isfahan and Īlām "ʿErāq".
During the medieval ages, Mesopotamian and Iranian peoples knew each other's languages because of trade, and because Arabic was the language of religion and science at that time. The Timurid historian Ḥāfeẓ-e Abru (d. 1430) wrote of Iraq:
The majority of inhabitants of Iraq know Persian and Arabic, and from the time of the domination of Turkic people the Turkish language has also found currency.
— Ḥāfeẓ-e Abru
Iraqis share religious and certain cultural ties with Iranians. The majority of Iranians are Twelver Shia (an Islamic sect).
Iraqi culture has commonalities with the culture of Iran. The Mesopotamian cuisine also has similarities to the Persian cuisine, including common dishes and cooking techniques. The Iraqi dialect has absorbed many words from the Persian language.
Kurdistan
Kurds speak a Northwestern Iranian language known as Kurdish. Some historians and linguists, such as Vladimir Minorsky, have suggested that the Medes, an Iranian people who inhabited much of western Iran, including Azerbaijan and Kurdistan, might have been forefathers of modern Kurds.
See also
- Persianization
- Culture of Iran
- Greater Armenia
- Greater Central Asia
- Greater Khorasan
- Iranian peoples
- Iranian studies
- Culture of Azerbaijan
- Azerbaijani language
- Old Azeri language
- History of the Kurdish people
- Kurdish culture
- Kurdish language
- Persianate society
- List of Persia-related topics
- -stan
- Pan-Iranism
Notes and references
Explanatory footnotes
- These include the Medes, Achaemenids, Parthians, Sasanians, Samanids, Saffarids, Safavids, Afsharids and Qajars.
- For example, those regions and peoples in the North Caucasus that were not under direct Iranian rule.
- Such as in the western parts of South Asia, Bahrain and Tajikistan.
Citation footnotes
- Frye, Richard Nelson (1962). "Reitzenstein and Qumrân Revisited by an Iranian, Richard Nelson Frye, The Harvard Theological Review, Vol. 55, No. 4 (Oct. 1962), pp. 261–268". The Harvard Theological Review. 55 (4): 261–268. doi:10.1017/S0017816000007926. JSTOR 1508723. S2CID 162213219.
- International Journal of Middle East Studies. (2007), 39: pp 307–309 Copyright © 2007 Cambridge University Press.
- Marcinkowski, Christoph (2010). Shi'ite Identities: Community and Culture in Changing Social Contexts. LIT Verlag Münster. p. 83. ISBN 978-3-643-80049-7.
- "Interview with Richard N. Frye (CNN)". Archived from the original on 2016-04-23.
- Richard Nelson Frye, The Harvard Theological Review, Vol. 55, No. 4 (Oct. 1962), pp. 261–268 I use the term Iran in an historical contextPersia would be used for the modern state, more or less equivalent to "western Iran". I use the term "Greater Iran" to mean what I suspect most Classicists and ancient historians really mean by their use of Persia—that which was within the political boundaries of States ruled by Iranians.
- "IRAN i. LANDS OF IRAN". Encyclopædia Iranica.
- Dialect, Culture, and Society in Eastern Arabia: Glossary. Clive Holes. 2001. Page XXX. ISBN 978-90-04-10763-2.
-
- "2008 Annual Report" (PDF). Encyclopædia Iranica. New York: Center for Iranian Studies, Columbia University. 2009. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2023-08-12. p. 5:
Covering a multi-lingual and multi-ethnic cultural continent, the Encyclopædia Iranica's scope encompasses all aspects of the life, history, and civilization of all the peoples who speak or once spoke an Iranian language
. - Boss, Shira J. (November 2003). "Encyclopaedia Iranica: Comprehensive research project about the "Iranian Cultural Continent" thrives on Riverside Drive". Columbia College Today. Vol. 30, no. 2. New York: Columbia College Office of Alumni Affairs and Development. pp. 32–33. ISSN 0572-7820. Archived from the original on 2021-02-15. Scan of print version available at Columbia College Today, v. 30 (2003–04) at the Internet Archive.
- Niknejad, Kelly Golnoush (2008-12-07) . "Encyclopaedia Iranica: an Iranian love story". Tehran Bureau. Frontline. PBS. Archived from the original on 2010-04-26.
- "2008 Annual Report" (PDF). Encyclopædia Iranica. New York: Center for Iranian Studies, Columbia University. 2009. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2023-08-12. p. 5:
- India. Foreign and Political Dept. (1892). A Collection of Treaties, Engagements, and Sunnuds, Relating to India and Neighbouring Countries: Persia and the Persian Gulf. G. A. Savielle and P. M. Cranenburgh, Bengal Print. Co. pp. x (10).
treaty of gulistan.
- Mikaberidze, Alexander (2015). Historical Dictionary of Georgia. Rowman & Littlefield. pp. 348–349. ISBN 978-1-4422-4146-6.
Persia lost all its territories to the north of the Aras River, which included all of Georgia, and parts of Armenia and Azerbaijan.
- Olsen, James Stuart; Shadle, Robert (1991). Historical Dictionary of European Imperialism. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 314. ISBN 978-0-313-26257-9.
In 1813 Iran signed the Treaty of Gulistan, ceding Georgia to Russia.
- Roxane Farmanfarmaian (2008). War and peace in Qajar Persia: implications past and present. Psychology Press. p. 4. ISBN 978-0-203-93830-0.
- Fisher et al. 1991, p. 329.
- Erik Goldstein (1992). Wars and peace treaties, 1816-1991. Psychology Press. pp. 72–73. ISBN 978-0-203-97682-1.
- Sir Percy Molesworth Sykes (1915). A history of Persia, Volume 2. Macmillan and co. p. 469.
Macmahon arbitration persia.
- William W. Malandra (2005-07-20). "ZOROASTRIANISM i. HISTORICAL REVIEW". Retrieved 2011-01-14.
- Nicholas Sims-Williams. "EASTERN IRANIAN LANGUAGES". Retrieved 2011-01-14.
- "IRAN". Retrieved 2011-01-14.
- K. Hoffmann. "AVESTAN LANGUAGE I-III". Retrieved 2011-01-14.
- "ĒRĀN-WĒZ". iranicaonline.org. Retrieved 9 December 2015.
- "ZOROASTER ii. GENERAL SURVEY". iranicaonline.org. Retrieved 9 December 2015.
- ^ Ahmad Ashraf. "IRANIAN IDENTITY ii. PRE-ISLAMIC PERIOD". Retrieved 2011-01-14.
- Ed Eduljee. "Haroyu". heritageinstitute.com. Retrieved 9 December 2015.
- Ed Eduljee. "Aryan Homeland, Airyana Vaeja, Location. Aryans and Zoroastrianism". heritageinstitute.com. Retrieved 9 December 2015.
- Ed Eduljee. "Aryan Homeland, Airyana Vaeja, in the Avesta. Aryan lands and Zoroastrianism". heritageinstitute.com. Retrieved 9 December 2015.
- Frye, Richard Nelson, Greater Iran, ISBN 978-1-56859-177-3 p.xi
- Richard Foltz, "Religions of the Silk Road: Premodern Patterns of globalization", Palgrave Macmillan, rev. 2nd edition, 2010. pg 27
- J.M. Cook, "The Rise of the Achaemenids and Establishment of Their Empire" in Ilya Gershevitch, William Bayne Fisher, J. A. Boyle "Cambridge History of Iran", Vol 2. pg 250. Excerpt: "To the Greeks, Greater Iran ended at the Indus".
- Mallory, J. P.; Adams, D. Q. (1997), Encyclopedia of Indo-European culture, London and Chicago: Fitzroy-Dearborn, ISBN 978-1-884964-98-5. pg 307: "Dialectically, Old Persian is regarded as a southwestern Iranian language in contrast to the east Iranian Avestan which covered most of the rest of Greater Iran. However, it is important to note that during the Achaemeid era, the official language of the empire was Aramaic, which was the mother tongue of the ancient , since it was the language of literature, religion, and science at that time. language had a great impact on Persian and survived as the dominant language in the middle east until the .
- George Lane, "Daily Life in the Mongol Empire", Greenwood Publishing Group, 2006. pg 10" The year following 1260 saw the empire irrevocably split but also signaled the emergence of the two greatest achievements of the house of Chinggis, namely the Yuan dynasty of greater China and the Il-Khanid dynasty of greater Iran.
- Judith G. Kolbas, "The Mongols in Iran", Excerpt from 399: "Uljaytu, Ruler of Greater Iran from 1304 to 1317 A.D."
- Mīr Khvānd, Muḥammad ibn Khāvandshāh, Tārīkh-i rawz̤at al-ṣafā. Taṣnīf Mīr Muḥammad ibn Sayyid Burhān al-Dīn Khāvand Shāh al-shahīr bi-Mīr Khvānd. Az rū-yi nusakh-i mutaʻaddadah-i muqābilah gardīdah va fihrist-i asāmī va aʻlām va qabāyil va kutub bā chāphā-yi digar mutamāyiz mībāshad. Markazī-i Khayyām Pīrūz . ایرانشهر از کنار فرات تا جیهون است و وسط آبادانی عالم است. Iranshahr stretches from the Euphrates to the Oxus, and it is the center of the prosperity of the World.
- The Cambridge History of Iran, Vol. III: The Seleucid, Parthian and Sasanian Periods, Ehsan Yarshater, Review author: Richard N. Frye, International Journal of Middle East Studies, Vol. 21, No. 3. (Aug. 1989), pp.415.
- Numista: Ashrafi - Nader Afshar Type A2; Širâz mint.
- Dehkhoda Dictionary, Dehkhoda, see under entry "Turan"
- Homayoun, N. T., Kharazm: What do I know about Iran?. 2004. ISBN 978-964-379-023-3, p.78
- Patrick Clawson. Eternal Iran. Palgrave. 2005. Coauthored with Michael Rubin. ISBN 978-1-4039-6276-8 p.9,10
- Patrick Clawson. Eternal Iran. Palgrave. 2005. Coauthored with Michael Rubin. ISBN 978-1-4039-6276-8 p.30
- Patrick Clawson. Eternal Iran. Palgrave. 2005. Coauthored with Michael Rubin. ISBN 978-1-4039-6276-8 p.31-32
- Encyclopædia Iranica: "Caucasus Iran" article, p.84-96.
- Historical Background Vol. 3, Colliers Encyclopedia CD-ROM, 02-28-1996
- Swietochowski, Tadeusz (1995). Russia and Azerbaijan: A Borderland in Transition. Columbia University Press. pp. 69, 133. ISBN 978-0-231-07068-3.
- L. Batalden, Sandra (1997). The newly independent states of Eurasia: handbook of former Soviet republics. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 98. ISBN 978-0-89774-940-4.
- Ebel, Robert E.; Menon, Rajan (2000). Energy and conflict in Central Asia and the Caucasus. Rowman & Littlefield. p. 181. ISBN 978-0-7425-0063-1.
- Andreeva, Elena (2010). Russia and Iran in the great game: travelogues and orientalism (reprint ed.). Taylor & Francis. p. 6. ISBN 978-0-415-78153-4.
- Çiçek, Kemal, Kuran, Ercüment (2000). The Great Ottoman-Turkish Civilisation. University of Michigan. ISBN 978-975-6782-18-7.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Ernest Meyer, Karl, Blair Brysac, Shareen (2006). Tournament of Shadows: The Great Game and the Race for Empire in Central Asia. Basic Books. p. 66. ISBN 978-0-465-04576-1.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Houtsma, M. Th. (1993). First Encyclopaedia of Islam 1913–1936 (reprint ed.). BRILL. ISBN 978-90-04-09796-4.
- Schippmann, Klaus (1989). Azerbaijan: Pre-Islamic History. Encyclopædia Iranica. pp. 221–224. ISBN 978-0-933273-95-5.
- Litvinskij, B. A.; Pichikian, I. R. (1994). "The Hellenistic Architecture and Art of the Temple of the Oxus". Bulletin of the Asia Institute. 8. Asia Institute: 47–66. ISSN 0890-4464. JSTOR 24048765.
- Daniel, E., The History of Iran. 2001. ISBN 978-0-313-30731-7, p.28
- Lorentz, J. Historical Dictionary of Iran. 1995. ISBN 978-0-8108-2994-7
- See Encyclopædia Iranica, p. 443, for Persian settlements in southwestern China; Iran-China Relations for more on the historical ties.
- "Persian language in Xinjiang" (زبان فارسی در سین کیانگ). Zamir Sa'dollah Zadeh (دکتر ضمیر سعدالله زاده). Nameh-i Iran (نامه ایران) V.1. Editor: Hamid Yazdan Parast (حمید یزدان پرست). ISBN 978-964-423-572-6 Perry–Castañeda Library collection under DS 266 N336 2005.
- Life and Land Use on the Bahrain Islands: The Geoarchaeology of an Ancient ... by Curtis E. Larsen p. 13
- ^ Bahrain by Federal Research Division, page 7
- Robert G. Hoyland, Arabia and the Arabs: From the Bronze Age to the Coming of Islam, Routledge 2001p28
- ^ Security and Territoriality in the Persian Gulf: A Maritime Political Geography by Pirouz Mojtahed-Zadeh, page 119
- ^ Conflict and Cooperation: Zoroastrian Subalterns and Muslim Elites in ... By Jamsheed K. Choksy, 1997, page 75
- Yoma 77a and Rosh Hashbanah, 23a
- Juan Cole, Sacred Space and Holy War, IB Tauris, 2007 p52
- Are the Shia Rising? Maximilian Terhalle, Middle East Policy, Volume 14 Issue 2 Page 73, June 2007
- Autobiography of Sheikh Yusuf Al Bahrani published in Interpreting the Self, Autobiography in the Arabic Literary Tradition, Edited by Dwight F. Reynolds, University of California Press Berkeley 2001
- The Autobiography of Yūsuf al-Bahrānī (1696–1772) from Lu'lu'at al-Baḥrayn, from the final chapter An Account of the Life of the Author and the Events That Have Befallen Him featured in Interpreting the Self, Autobiography in the Arabic Literary Tradition, Edited by Dwight F. Reynolds, University of California Press Berkeley 2001 p221
- Charles Belgrave, The Pirate Coast, G. Bell & Sons, 1966 p19
- Ahmad Mustafa Abu Hakim, History of Eastern Arabia 1750–1800, Khayat, 1960, p78
- James Onley, The Politics of Protection in the Gulf: The Arab Rulers and the British Resident in the Nineteenth Century, Exeter University, 2004 p44
- ^ Al-Tajer, Mahdi Abdulla (1982). Language & Linguistic Origins In Bahrain. Taylor & Francis. pp. 134, 135. ISBN 978-0-7103-0024-9.
- Shirawi, May Al-Arrayed (1987). Education in Bahrain - 1919-1986, An Analytical Study of Problems and Progress (PDF). Durham University. p. 60.
- ^ Fuccaro, Nelida (2009-09-03). Histories of City and State in the Persian Gulf: Manama Since 1800. Cambridge University Press. p. 114. ISBN 978-0-521-51435-4.
- ^ Yarshater, Ehsan (1993). The Cambridge History of Iran, Volume 3. Cambridge University Press. p. 482. ISBN 978-0-521-20092-9.
Of the four residences of the Achaemenids named by Herodotus—Ecbatana, Pasargadae or Persepolis, Susa and Babylon—the last was maintained as their most important capital, the fixed winter quarters, the central office of bureaucracy, exchanged only in the heat of summer for some cool spot in the highlands. Under the Seleucids and the Parthians the site of the Mesopotamian capital moved a little to the north on the Tigris—to Seleucia and Ctesiphon. It is indeed symbolic that these new foundations were built from the bricks of ancient Babylon, just as later Baghdad, a little further upstream, was built out of the ruins of the Sassanian double city of Seleucia-Ctesiphon.
- Frye, Richard N. (1975). The Golden Age of Persia: The Arabs in the East. Weidenfeld and Nicolson. p. 184. ISBN 978-0-7538-0944-0.
throughout Iran's history the western part of the land has been frequently more closely connected with the lowlands of Mesopotamia than with the rest of the plateau to the east of the central deserts.
- ^ Yavari, Neguin (1997). Iranian Perspectives on the Iran-Iraq War; Part II. Conceptual Dimensions; 7. National, Ethnic, and Sectarian Issues in the Iran–Iraq War. University Press of Florida. p. 80. ISBN 978-0-8130-1476-0.
Between the coming of the 'Abbasids and the Mongol onslaught, Iraq and western Iran shared a closer history than did eastern Iran and its western counterpart.
- Morony, Michael G. "IRAQ AND ITS RELATIONS WITH IRAN". IRAQ i. IN THE LATE SASANID AND EARLY ISLAMIC ERAS. Encyclopædia Iranica. Retrieved 11 February 2012.
Persian remained the language of most of the sedentary people as well as that of the chancery until the 15th century and thereafter, as attested by Ḥāfeẓ-e Abru (d. 1430) who said, "The majority of inhabitants of Iraq know Persian and Arabic, and from the time of the domination of Turkic people the Turkish language has also found currency: as the city people and those engaged in trade and crafts are Persophone, the Bedouins are Arabophone, and the governing classes are Turkophone. But, all three peoples (qawms) know each other's languages due to the mixture and amalgamation."
- Csató, Éva Ágnes; Isaksson, Bo; Jahani, Carina (2005). Linguistic Convergence and Areal Diffusion: Case Studies from Iranian, Semitic and Turkic. Routledge. p. 177. ISBN 978-0-415-30804-5.
- Gershevitch, Ilya (1967). "Professor Vladimir Minorsky". Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society of Great Britain and Ireland. 99 (1/2): 53–57. doi:10.1017/S0035869X00125638. JSTOR 25202975.
General references
- Fisher, William Bayne; Avery, P.; Hambly, G. R. G; Melville, C. (1991). The Cambridge History of Iran. Vol. 7. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-20095-0.
- Foltz, Richard (2015). Iran in World History. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-933549-7.
- Marcinkowski, Christoph (2010). Shi'ite Identities: Community and Culture in Changing Social Contexts. Berlin: Lit Verlag 2010. ISBN 978-3-643-80049-7.
| Iran topics | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Irredentism | |
|---|---|
| Africa | |
| North America | |
| South America | |
| Western Asia | |
| Southern Asia | |
| Eastern and Southeastern Asia | |
| Central and Eastern Europe | |
| Southern Europe | |
| Italy | |
| Northern Europe | |
| Western Europe | |
| Oceania | |
| Related concepts: Border changes since 1914 · Partitionism · Reunification · Revanchism · Revisionism · Rump state | |
- Cultural regions
- Geography of Iran
- History of Iran
- Culture of Iran
- Georgia (country)–Iran relations
- Azerbaijan–Iran relations
- Iran–Pakistan relations
- Iran–Iraq relations
- Armenia–Iran relations
- Afghanistan–Iran relations
- Central Asia
- Country classifications
- Middle East
- West Asia
- Historical geography of Iran
- Historical regions of Iran
- Historical regions
