| Revision as of 23:58, 14 January 2008 view source71.209.64.173 (talk) →In popular culture← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 19:41, 5 January 2025 view source Haddad Maia fan (talk | contribs)323 editsNo edit summaryTags: Mobile edit Mobile app edit iOS app edit App select source | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{short description|Painting by Leonardo da Vinci}} | |||
| {{otheruses}} | |||
| {{about|the painting}} | |||
| {{Infobox Painting| image_file=Mona Lisa.jpg | |||
| <noinclude>{{pp-semi-indef}}</noinclude> | |||
| | image_size=230px | |||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=September 2024}} | |||
| | title=Mona Lisa | |||
| {{Use Oxford spelling|date=September 2024}} | |||
| | other_language_1=Italian | |||
| {{Infobox artwork | |||
| | other_title_1=La Gioconda | |||
| | image_file = File:Mona Lisa, by Leonardo da Vinci, from C2RMF retouched.jpg | |||
| | other_language_2=French | |||
| | alt = See adjacent text. | |||
| | other_title_2=La Joconde | |||
| | title = Mona Lisa | |||
| | artist=] | |||
| | caption = The ''Mona Lisa'' digitally retouched to reduce the effects of ageing; ] has darkened over time.<ref>{{cite episode |url=https://www.npr.org/2012/02/02/146288063/painting-sheds-new-light-on-the-mona-lisa |title=The Mona Lisa's Twin Painting Discovered |series=] |network=] |date=2 February 2012 |quote=The original ''Mona Lisa'' in the Louvre is difficult to see—it's covered with layers of varnish, which has darkened over the decades and the centuries, and even cracked', Bailey says}}</ref><ref>{{cite episode |url=https://www.pbs.org/treasuresoftheworld/a_nav/mona_nav/main_monafrm.html |title=Theft of the Mona Lisa |network=PBS |series=Treasures of the World |quote=time has aged and darkened her complexion.}}</ref><ref name=varnish>{{cite book| last=Sassoon| first=Donald| title=Mona Lisa: The History of the World's Most Famous Painting| url=https://books.google.com/books?id=3twyAQAAIAAJ&q=actually+quite+dirty| publisher=HarperCollins| year=2001| pages=10| quote=It is actually quite dirty, partly due to age and partly to the darkening of a varnish applied in the sixteenth century.| isbn=978-0-00-710614-1}}</ref> | |||
| | year=circa ]–] | |||
| | other_language_1 = ] | |||
| | type=] | |||
| | other_title_1 = {{lang|it|la Gioconda}}, {{lang|it|Monna Lisa}} | |||
| | height=77 | |||
| | other_language_2 = <br>] | |||
| | width=53 | |||
| | other_title_2 = {{lang|fr|la Joconde}} | |||
| | height_inch=30 | |||
| | artist = ] | |||
| | width_inch=21 | |||
| | |
| subject = ] | ||
| | year = {{circa|1503–1506}}, perhaps continuing until {{circa|1517|lk=no}} | |||
| | museum=] | |||
| | material = ] on ] panel | |||
| | height_metric = 77 | |||
| | width_metric = 53 | |||
| | city = Paris | |||
| | museum = ] | |||
| | condition = | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| '''''Mona Lisa''''', or '''''La Gioconda (La Joconde)''''' is a 16th-century ] painted in ] on a ] ] by ] during the ]. It is arguably the most famous painting in the world, and few other works of art have been subject to as much scrutiny, study, mythologizing and parody. It is owned by the ] and hangs in the ] in ], ] with the title '''''Portrait of Lisa Gherardini, wife of Francesco del Giocondo'''''.<ref name="Louvre.fr">{{cite web|title=Portrait of Lisa Gherardini, wife of Francesco del Giocondo|url=http://www.louvre.fr/llv/oeuvres/detail_notice.jsp?CONTENT%3C%3Ecnt_id=10134198673226503&CURRENT_LLV_NOTICE%3C%3Ecnt_id=10134198673226503&amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;FOLDER%3C%3Efolder_id=9852723696500816&bmUID=1155229237450&bmLocale=en|publisher=Musée du Louvre|accessdate=2007-10-04}}</ref> The painting, a half-length portrait, depicts a woman whose gaze meets the viewer's with an expression often described as enigmatic.<ref name="paris1">{{Cite web|url=http://www.ibiblio.org/wm/paint/auth/vinci/joconde/|title=Leonardo da Vinci - La Joconde|accessyear=2007|accessmonthday=September 15|publisher=WebMuseum, Paris|year=2006|author=WebMuseum, Paris|language=English}}</ref><ref name="ns1">{{Cite web|url=http://www.newscientist.com/article.ns?id=dn6056|title=Noisy secret of Mona Lisa's smile|accessyear=2007|accessmonthday=September 15|publisher=NewScientist|year=2007|author=Philip Cohen|language=English}}</ref> It is considered by many to be Leonardo's ]. | |||
| The '''''Mona Lisa''''' ({{IPAc-en|ˌ|m|oʊ|n|ə|_|ˈ|l|iː|s|ə}} {{respell|MOH|nə|_|LEE|sə}}; {{langx|it|la Gioconda}} {{IPA|it|la dʒoˈkonda|}} or {{lang|it|Monna Lisa}} {{IPA|it|ˈmɔnna ˈliːza|}}; {{langx|fr|la Joconde}} {{IPA|fr|la ʒɔkɔ̃d|}}) is a half-length ] by Italian artist ]. Considered an archetypal ] of the ],<ref>{{cite episode |url=https://www.npr.org/2011/07/30/138800110/the-theft-that-made-the-mona-lisa-a-masterpiece |title=The Theft That Made Mona Lisa a Masterpiece |date=30 July 2011 |access-date=15 February 2019 |series=All Things Considered |network=NPR}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.timeshighereducation.com/news/why-i-think-mona-lisa-became-an-icon/164983.article |last=Sassoon |first=Donald |title=Why I think Mona Lisa became an icon |url-access=subscription |website=Times Higher Education |date=21 September 2001}}</ref> it has been described as "the best known, the most visited, the most written about, the most sung about, the most parodied work of art in the world."<ref>{{cite news |first=John |last=Lichfield |url=https://www.independent.co.uk/news/world/europe/the-moving-of-the-mona-lisa-530771.html |title=The Moving of the Mona Lisa |newspaper=] |location=London |date=1 April 2005 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161109110245/http://www.independent.co.uk/news/world/europe/the-moving-of-the-mona-lisa-530771.html |archive-date=9 November 2016 }}</ref> The painting's novel qualities include the subject's enigmatic expression,<ref name="ns1">{{cite magazine |access-date=27 April 2008 |url=https://www.newscientist.com/article.ns?id=dn6056 |title=Noisy secret of Mona Lisa's |magazine=] |date=23 June 2004 |author=Cohen, Philip |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080423031849/http://www.newscientist.com/article.ns?id=dn6056 |archive-date=23 April 2008}}</ref> monumentality of the composition, the subtle modelling of forms, and the atmospheric illusionism.<ref name="Louvre">{{cite web|title=Mona Lisa – Portrait of Lisa Gherardini, wife of Francesco del Giocondo|url=http://www.louvre.fr/en/oeuvre-notices/mona-lisa-–-portrait-lisa-gherardini-wife-francesco-del-giocondo|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140730003620/http://www.louvre.fr/en/oeuvre-notices/mona-lisa-%E2%80%93-portrait-lisa-gherardini-wife-francesco-del-giocondo|archive-date=30 July 2014|access-date=11 March 2012|publisher=Louvre}}</ref> | |||
| ==Artist and early history == | |||
| {{main|Leonardo da Vinci}} | |||
| ] (1452–1519)]] | |||
| ] immediately liked the ''Mona Lisa'' and borrowed it in his '']'' (1506).]] | |||
| Leonardo da Vinci began painting the ''Mona Lisa'' in ] (during the Italian Renaissance) and, according to Vasari, "after he had lingered over it four years, left it unfinished...."<ref name=Clark /> He is thought to have continued to work on it for three years after he moved to France and to have finished shortly before he died in 1519.<ref name=BBC-Faces>{{cite news|author=Chaundy, Bob|title=Faces of the Week|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/uk_news/magazine/5392000.stm|work=BBC News|publisher=BBC|date=]|accessdate=2007-10-05}}</ref> | |||
| The painting has been traditionally considered to depict the Italian noblewoman ].<ref>{{cite web |title=Mona Lisa – Heidelberger find clarifies identity |url=http://www.ub.uni-heidelberg.de/Englisch/news/monalisa.html |publisher=University Library Heidelberg |access-date=15 January 2008 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110508121954/http://www.ub.uni-heidelberg.de/Englisch/news/monalisa.html |archive-date=8 May 2011 }}</ref> It is painted in oil on a ] ].<ref>{{cite conference |last1=Uzielli |first1=Luca |last2=Gril |first2=Joseph |last3=Cocchi |first3=Linda |last4=Colmars |first4=Julien |last5=Dionisi Vici |first5=Paolo |last6=Dureisseix |first6=David |last7=Goli |first7=Giacomo |last8=Jullien |first8=Delphine |last9=Marcon |first9=Bertrand |last10=Mazzanti |first10=Paola |last11=Remond |first11=Romain |display-authors=5 |title=Experimental studies on the wooden support of the "Mona Lisa" |conference=The Safeguard of Cultural Heritage. A Challenge From the Past for the Europe of Tomorrow. COST strategic workshop |page=367 |date=July 2011 |location=Florence |url=https://hal.science/hal-00945958#:~:text=The%20%E2%80%9CMona%20Lisa%E2%80%9D%20(Louvre,cm%2C%20~%2013%20mm%20thick.|access-date=1 July 2024}}</ref> Leonardo never gave the painting to the Giocondo family.<ref>{{Cite web|date=22 April 2016|title=Was the 'Mona Lisa' Leonardo's Male Lover?|url=https://news.artnet.com/art-world/mona-lisa-leonardos-lover-salai-479783|access-date=20 May 2021|website=Artnet News|language=en-US}}</ref> It was believed to have been painted between 1503 and 1506; however, Leonardo may have continued working on it as late as 1517. King ] acquired the ''Mona Lisa'' after Leonardo's death in 1519, and it is now the property of the French Republic. It has normally been on display at the ] in Paris since 1797.<ref name=carrier>{{cite book |last=Carrier |first=David |date=2006 |title=Museum Skepticism: A History of the Display of Art in Public Galleries |publisher=Duke University Press |page=35 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=VIBoW6dDZgIC&q=Museum+Skepticism:+A+History+of+the+Display+of+Art+in+Public+Galleries |isbn=978-0-8223-3694-5}}</ref> | |||
| Leonardo took the painting from ] to ] in ] when King ] invited the painter to work at the ] near the king's castle in ]. The King bought the painting for 4,000 '']'' and kept it at ], where it remained until given to Louis XIV. | |||
| The painting's global fame and popularity partly stem from its 1911 theft by ], who attributed his actions to Italian patriotism—a belief it should belong to Italy. The theft and subsequent recovery in 1914 generated unprecedented publicity for an ], and led to the publication of many cultural depictions such as the 1915 opera ], two early 1930s films ('']'' and '']''), and the song "]" recorded by ]—one of the most successful songs of the 1950s.<ref name=Charney1>{{cite book | last1=Charney | first1=N. | last2=Fincham | first2=D. | last3=Charney | first3=U. | title=The Thefts of the Mona Lisa: On Stealing the World's Most Famous Painting | publisher=Arca Publications | year=2011 | isbn=978-0-615-51902-9 | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=QBMdygAACAAJ | access-date=4 November 2022}}</ref> | |||
| ] moved the painting to the ]. After the ], it was moved to the Louvre. ] had it moved to his bedroom in the ]; later it was returned to the Louvre. During the ] of ]–], it was moved from the Louvre to a hiding place elsewhere in France. | |||
| The ''Mona Lisa'' is one of the most valuable paintings in the world. It holds the ] for the highest known painting insurance valuation in history at US$100 million in 1962,<ref>{{Cite news |url=http://www.guinnessworldrecords.com/world-records/highest-insurance-valuation-for-a-painting |title=Highest insurance valuation for a painting |work=Guinness World Records |access-date=25 July 2017 |language=en-GB}}</ref> equivalent to $1 billion {{as of|2023|lc=y}}.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.inflationtool.com/us-dollar/1962-to-present-value?amount=100&year2=2023&frequency=yearly|title=Value of 1962 US Dollars today – Inflation Calculator|website=www.inflationtool.com}}</ref> | |||
| The painting was not well-known until the mid-19th century, when artists of the emerging ] movement began to appreciate it, and associated it with their ideas about feminine mystique. Critic ], in his ] essay on Leonardo, expressed this view by describing the figure in the painting as a kind of mythic embodiment of eternal femininity, who is "older than the rocks among which she sits" and who "has been dead many times and learned the secrets of the grave." | |||
| ==Title and subject== | ==Title and subject== | ||
| ] (visible at right) discovered in a book at ]. Dated 1503, it states that Leonardo was working on a portrait of ].<ref>{{cite news |date=14 January 2008 |title=German experts crack the ID of 'Mona Lisa' |work=] |agency=] |url=https://www.today.com/popculture/german-experts-crack-id-mona-lisa-wbna22652514 |access-date=21 August 2020}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |last=Nizza |first=Mike |date=15 January 2008 |title=Mona Lisa's Identity, Solved for Good? |work=The New York Times |url=https://thelede.blogs.nytimes.com/2008/01/15/mona-lisas-identity-solved-for-good/ |access-date=15 January 2008|issn=1553-8095}}</ref>]] | |||
| {{main|Lisa del Giocondo}} | |||
| ] (1479–1542 or c. 1551)]] | |||
| ''Mona Lisa'' is named for ] The wife of a wealthy Florentine merchant.<ref name=Kemp /> Lisa was a member of the Gherardini family of ] and ] who married Francesco del Giocondo, a successful silk merchant. The painting was commissioned for their new home and to celebrate the birth of their second son, Andrea.<ref>{{cite book|author=Zöllner, Frank|title=Leonardo Da Vinci, 1452-1519|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=fq8IHuJIKmoC&pg=PA72|date=2000|publisher=Taschen via Google Books limited preview|edition=also Slovart 2004, Edipresse Polska 2005 and Remzi 2005 and English via | |||
| Universität Leipzig Institut für Kunstgeschichte|pages=72|language=English|isbn=3-8228-5979-6|url=|accessdate=2007-10-14}}</ref> The title stems from the description of the painting by ] in his biography of Leonardo da Vinci, published 31 years after the artist's death. "Leonardo undertook to paint, for Francesco del Giocondo, the portrait of Mona Lisa, his wife...."<ref name=Clark>{{cite journal|author=Clark, Kenneth|title=Mona Lisa|journal=The Burlington Magazine|publisher=The Burlington Magazine Publications via JSTOR|volume=115|issue=840|url=http://links.jstor.org/sici?sici=0007-6287(197303)115%3A840%3C144%3AML%3E2.0.CO%3B2-Z|date=March 1973|pages=144|issn=00076287|accessdate=2007-10-05}}</ref> (one version in {{Lang-it|Prese Lionardo a fare per Francesco del Giocondo il ritratto di mona Lisa sua moglie}}).<ref>{{cite book|author=Vasari, Giorgio|others=Gaetano Milanesi | |||
| Published 1879|title=Le vite de' più eccellenti pittori, scultori ed architettori|volume=IV|pages=39|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=EroFAAAAQAAJ&pg=PA39|location=Firenze|publisher=G.C. Sansoni|origyear=1550, rev. ed. 1568|date=1879|accessdate=2007-10-05}}</ref> | |||
| The ], which is known in English as ''Mona Lisa'', is based on the presumption that it depicts ], although her likeness is uncertain. ] art historian ] wrote that "] undertook to paint, for Francesco del Giocondo, the portrait of Mona Lisa, his wife."<ref name="Vasari">{{Langx|it|Prese Lionardo a fare per Francesco del Giocondo il ritratto di monna Lisa sua moglie}} {{harvnb|Vasari|1879|p=39}}</ref><ref name="Clark">{{cite journal |last=Clark|first= Kenneth |title=Mona Lisa |journal=] |issue=840 |date=March 1973 |issn=0007-6287 |volume=115 |jstor=877242 |pages=144–151}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|title=Giorgio Vasari – Leonardo e la Gioconda|url=http://www.libriantichionline.com/divagazioni/giorgio_vasari_leonardo_gioconda|access-date=15 November 2021|website=Libri antichi online|language=it|date=2021}}</ref> {{lang|it|Monna}} in Italian is a polite form of address originating as {{lang|it|ma donna}}—similar to ''Ma'am'', ''Madam'', or '']'' in English. This became {{lang|it|]}}, and its contraction {{lang|it|monna}}. The title of the painting is spelled in Italian as ''Monna Lisa'' ('']'' being a vulgarity in Italian), which is rare in English,<ref>{{cite web|title=<!--Ricerca {{!}}--> Mona|url=https://www.garzantilinguistica.it/ricerca/?q=mona|access-date=5 December 2024|date=2013|website=Garzanti Linguistica}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|title=Mona – Parola, significato e traduzione|url=https://www.grandidizionari.it/Dizionario_Italiano/parola/M/mona_1.aspx?query=mona+(1)<!--Other url: https://dizionari.repubblica.it/Italiano/M/mona.html dead url: https://dizionari.hoepli.it/Dizionario_Italiano/parola/m/mona+(1).aspx-->|date=2018|access-date=5 December 2024|website=Dizionario Italiano online Hoepli|language=it}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|title=Mona – Definizione significato|url=https://www.collinsdictionary.com/it/dizionario/inglese/mona|date=2024|access-date=5 December 2024|website=Collins Online Dictionary|language=it}}</ref> where it is traditionally spelled ''Mona''.<ref name="Museo Leonardo Da Vinci Experience 2022">{{cite web |date=2022 |title=Gioconda o Monna Lisa |url=https://www.leonardodavincimuseo.com/prodotto/gioconda-o-monna-lisa/ |access-date=5 November 2024 |website=Museo Leonardo Da Vinci Experience |language=it}}</ref> | |||
| On Jan 14, 2008, Reuters reported that experts at the Heidelberg University library say dated notes scribbled in the margins of a book by its owner in October 1503 confirm once and for all that Lisa del Giocondo was indeed the model for one of the most famous portraits in the world. "All doubts about the identity of the Mona Lisa have been eliminated by a discovery by Dr. Armin Schlechter," a manuscript expert, the library said in a statement on Monday.<ref></ref> | |||
| Until then, only "scant evidence" from sixteenth-century documents had been available. "This left lots of room for interpretation and there were many different identities put forward," the library said." | |||
| Lisa del Giocondo was a member of the ] family of ] and ], and the wife of wealthy Florentine silk merchant Francesco del Giocondo.<ref name="Kemp">{{harvnb|Kemp|2006|pp=261–262}}</ref> The painting is thought to have been commissioned for their new home, and to celebrate the birth of their second son, Andrea.<ref>{{harvnb|Farago|1999|p=123}}</ref> The Italian name for the painting, {{lang|it|La Gioconda}}, means "jocund" ("happy" or "jovial"), or literally "the jocund one", a pun on the feminine form of Lisa's married name, Giocondo.<ref name="Kemp" />{{sfn|Bartz|König|2001|p=626}} In French, the title {{lang|fr|La Joconde}} has the same meaning.<ref name="Museo Leonardo Da Vinci Experience 2022"/> Vasari's account of the ''Mona Lisa'' comes from his biography of Leonardo published in 1550, 31 years after the artist's death. It has long been the best-known source of information on the ] of the work and identity of the sitter. Leonardo's assistant ], at his death in 1524, owned a portrait which in his personal papers was named ''la Gioconda'', a painting bequeathed to him by Leonardo.<ref name="Kemp Pallanti" /> | |||
| In Italian, ''ma donna'' from ''donna'' meaning '']'' which became '']'', and its contraction ''mona''. ''Mona'' is thus a polite form of address, similar to ''Madam'' or ''my lady'' in English. In modern Italian, the short form of ''madonna'' is usually spelled ''Monna'', so the title is sometimes ''Monna Lisa'', rarely in English and more commonly in ] such as French and Italian. | |||
| That Leonardo painted such a work, and its date, were confirmed in 2005 when a scholar at ] discovered a marginal note in a 1477 printing of a volume by ] philosopher ]. Dated October 1503, the note was written by Leonardo's contemporary ]. This note likens Leonardo to renowned Greek painter ], who is mentioned in the text, and states that Leonardo was at that time working on a painting of Lisa del Giocondo.<ref name="subject">{{cite web|title=Mona Lisa – Heidelberg discovery confirms identity |url=http://www.ub.uni-heidelberg.de/Englisch/news/monalisa.html |publisher=] |access-date=4 July 2010 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131105050239/http://www.ub.uni-heidelberg.de/Englisch/news/monalisa.html |archive-date=5 November 2013 }}</ref> In response to the announcement of the discovery of this document, Vincent Delieuvin, the ] representative, stated "Leonardo da Vinci was painting, in 1503, the portrait of a Florentine lady by the name of Lisa del Giocondo. About this we are now certain. Unfortunately, we cannot be absolutely certain that this portrait of Lisa del Giocondo is the painting of the Louvre."<ref name=Vincent>{{cite episode |first=Vincent |last=Delieuvin |title=Télématin |series=Journal Télévisé |network=France 2 Télévision |date=15 January 2008}}</ref> | |||
| At his death in 1525, Leonardo's assistant Salai owned the portrait named in his personal papers ''la Gioconda'' which had been bequeathed to him by the artist. Italian for jocund, happy or jovial, Gioconda was a nickname for the sitter, a pun on the feminine form of her married name Giocondo and her disposition.<ref name=Kemp>{{cite book|author=Kemp, Martin|title=Leonardo Da Vinci: The Marvellous Works of Nature And Man|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=1-t_dJh-_mUC&pg=PA261|pages=261|publisher=Oxford University Press via Google Books limited preview|isbn=0-1928-0725-0|date=2006|accessdate=2007-10-05}}</ref><ref name="louvre1">{{cite book |author= Bartz, Gabriele |title=Louvre | series=Art and Architecture|publisher=3C Publishing |location= |year=2006 |pages=626 |isbn=3-8331-1943-8}}</ref> In French, the title ''La Joconde'' has the same double meaning. | |||
| The ] ''Leonardo da Vinci'' (2019) confirms that the painting probably depicts Lisa del Giocondo, with ] being the only plausible alternative.<ref name="Zöllner">{{harvnb|Zöllner|2019|p=241}}</ref> Scholars have developed several ], arguing that Lisa del Giocondo was the subject of a different portrait, and identifying at least four other paintings referred to by Vasari as the ''Mona Lisa''.<ref name="monna bella">{{cite journal |last=Stites |first=Raymond S. |date=January 1936 |title=Mona Lisa – Monna Bella |journal=Parnassus |volume=8 |issue=1 |pages=7–10, 22–23 |doi=10.2307/771197 |jstor=771197|s2cid=195050582 | issn=1543-6314 }}</ref> Several other people have been proposed as the subject of the painting,<ref name="Wilson">{{harvnb|Wilson|2000|pp=364–366}}</ref> including ],<ref name="Debelle">{{cite news |last=Debelle |first=Penelope |date=25 June 2004 |title=Behind that secret smile |work=The Age |location=Melbourne |url=http://www.theage.com.au/articles/2004/06/24/1088046208817.html |url-status=dead |access-date=6 October 2007 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131125184249/http://www.theage.com.au/articles/2004/06/24/1088046208817.html |archive-date=25 November 2013}}</ref> ],<ref name="Johnston">{{cite news |last=Johnston |first=Bruce |date=8 January 2004 |title=Riddle of Mona Lisa is finally solved: she was the mother of five |newspaper=] |location=London |url=https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/main.jhtml?xml=/news/2004/08/01/wmona01.xml&sSheet=/news/2004/08/01/ixworld.html |url-status=dead |access-date=6 October 2007 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20071011082755/http://telegraph.co.uk/news/main.jhtml?xml=%2Fnews%2F2004%2F08%2F01%2Fwmona01.xml&sSheet=%2Fnews%2F2004%2F08%2F01%2Fixworld.html |archive-date=11 October 2007}}</ref> ],<ref name="Wilson" /> Pacifica Brandano/Brandino, Isabella Gualanda, ], ], Salaì, and even Leonardo himself.<ref name="myth">{{cite news |last=Nicholl|first= Charles |date=28 March 2002 |title=The myth of the Mona Lisa |work=The Guardian |url=http://books.guardian.co.uk/lrb/articles/0,6109,675653,00.html |url-status=dead |access-date=6 October 2007 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080905005401/http://books.guardian.co.uk/lrb/articles/0%2C6109%2C675653%2C00.html |archive-date=5 September 2008|issn=1756-3224}}</ref><ref name="BBC-Faces">{{cite news |author=Chaundy, Bob |date=29 September 2006 |title=Faces of the Week |publisher=BBC |url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/uk_news/magazine/5392000.stm |url-status=live |access-date=5 October 2007 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140803042520/http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/uk_news/magazine/5392000.stm |archive-date=3 August 2014}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |last1=Kington |first1=Tom |date=9 January 2011 |title=Mona Lisa backdrop depicts Italian town of Bobbio, claims art historian |work=The Guardian |url=https://www.theguardian.com/artanddesign/2011/jan/09/mona-lisa-bobbio-da-vinci|access-date=5 December 2024|issn=1756-3224}}</ref> Psychoanalyst ] theorized that Leonardo imparted an approving smile from his mother,<ref name="Spector 1968">{{cite web |last=Spector |first=Jack |date=1 April 1968 |title=Freud and Ducham: The Mona Lisa 'Exposed' |url=https://www.artforum.com/features/freud-and-duchamp-the-mona-lisa-exposed-211110/ |access-date=5 December 2024 |website=Artforum}}</ref><ref name="Dalí 1963">{{cite web |date=23 October 2019 |title=Salvador Dalí on Why People Attack Leonardo's 'Mona Lisa,' in 1963: From the Archives |url=https://www.artnews.com/art-news/retrospective/salvador-dali-mona-lisa-essay-13450/ |access-date=5 December 2024 |website=ARTnews.com }}</ref> Caterina, onto the ''Mona Lisa'' and other works like '']'', '']'', and '']''.<ref>{{cite journal |last=Kobbé |first=Gustav |author-link=Gustav Kobbé |date=1916 |title=The Smile of the 'Mona Lisa'|url=https://www.jstor.org/stable/20543781 |journal=The Lotus Magazine |volume=8 |issue=2 |pages=67–74 |jstor=20543781 |issn=2150-5977}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |last=Prisco|first=Salvatore|date=9 January 1987 |title=Opinion {{!}} Couldn't 'Mona Lisa' Just Stay a Mystery? |work=The New York Times |url=https://www.nytimes.com/1987/01/09/opinion/l-couldn-t-mona-lisa-just-stay-a-mystery-361987.html |access-date=10 July 2022 |issn=1553-8095}}</ref><ref name="Greenberger 2019">{{cite web |last=Greenberger |first=Alex |date=23 October 2019 |title=Salvador Dalí on Why People Attack Leonardo's 'Mona Lisa,' in 1963: From the Archives |url=https://www.artnews.com/art-news/retrospective/salvador-dali-mona-lisa-essay-13450/ |access-date=2 December 2024 |website=ARTnews}}</ref> | |||
| == Aesthetics == | |||
| ] | |||
| Leonardo used a pyramid design to place the woman simply and calmly in the space of the painting. Her folded hands form the front corner of the pyramid. Her breast, neck and face glow in the same light that softly models her hands. The light gives the variety of living surfaces an underlying geometry of spheres and circles. Leonardo referred to a seemingly simple formula for seated female figure: the images of seated Madonna, which were widely spread at the time. He effectively modified this formula in order to create the visual impression of distance between the sitter and the observer. The armrest of the chair functions as a dividing element between ''Mona Lisa'' and us. The woman sits markedly upright with her arms folded, which is also a sign of her reserved posture. Only her gaze is fixed on the observer and seems to welcome him to this silent communication. Since the brightly lit face is practically framed with various much darker elements (hair, veil, shadows), the observer's attraction to ''Mona Lisa'''s face is brought to even greater extent. Thus, the composition of the figure evokes an ambiguous effect: we are attracted to this mysterious woman but have to stay at a distance as if she were a divine creature. There is no indication of an intimate dialogue between the woman and the observer as is the case in the Portrait of Baldassare Castiglione (Louvre) painted by Raphael about ten years after ''Mona Lisa'' and undoubtedly influenced by Leonardo's portrait. | |||
| ==Description== | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| The painting was among the first ]s to depict the sitter before an imaginary landscape. The enigmatic woman is portrayed seated in what appears to be an open ] with dark pillar bases on either side. Behind her a vast landscape recedes to icy mountains. Winding paths and a distant bridge give only the slightest indications of human presence. The sensuous curves of the woman's hair and clothing, created through ], are echoed in the undulating imaginary valleys and rivers behind her. The blurred outlines, graceful figure, dramatic contrasts of light and dark, and overall feeling of calm are characteristic of Leonardo's style. Due to the expressive synthesis that Leonardo achieved between sitter and landscape it is arguable whether ''Mona Lisa'' should be considered as a traditional portrait, for it represents an ideal rather than a real woman. The sense of overall harmony achieved in the painting — especially apparent in the sitter's faint smile — reflects Leonardo's idea of the cosmic link connecting humanity and nature, making this painting an enduring record of Leonardo's vision and genius. | |||
| The ''Mona Lisa'' bears a strong resemblance to many Renaissance depictions of the ], who was at that time seen as an ideal for womanhood.<ref name="Zollner1" /> The woman sits markedly upright in a pozzetto armchair with her arms folded, a sign of her reserved posture. Her gaze is fixed on the observer. The woman appears alive to an unusual extent, which Leonardo achieved by his method of not drawing outlines. The soft blending ('']'') creates an ambiguous mood "mainly in two features: the corners of the mouth, and the corners of the eyes".<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.artchive.com/artchive/L/leonardo/monalisa_text.jpg.html |title=E.H. Gombrich, ''The Story of Art'' |publisher=Artchive.com |access-date=3 June 2013 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130603014150/http://www.artchive.com/artchive/L/leonardo/monalisa_text.jpg.html |archive-date=3 June 2013 }}</ref> | |||
| It is also notable that ''Mona Lisa'' has no visible facial hair at all - including eyebrows and eyelashes. Some researchers claim that it was common at this time for genteel women to pluck them off, since they were considered to be unsightly.<ref>Turudich, D. & Welch, L. (2003). Plucked, shaved and braided: Medieval and renaissance beauty and grooming practices 1000–1600. Leicester, England: Streamline Press. ISBN 1-930064-08-X</ref><ref>McMullen, R. (1975). Mona Lisa: The picture and the myth. Boston: Houghton Mifflin. ISBN 0-333-19169-2</ref>. For modern viewers the missing eyebrows add to the slightly semi-abstract quality of the face. | |||
| The depiction of the sitter in three-quarter profile is similar to late 15th-century works by ] and ].<ref name="Zollner1">{{cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=fq8IHuJIKmoC&pg=PA71|title=Leonardo Da Vinci, 1452–1519|author-link=Frank Zöllner|last=Zöllner|first=Frank|isbn=978-3-8228-5979-7|year=2000|publisher=Taschen }}</ref> ] notes that the sitter's general position can be traced back to ] models and that "in particular the vertical slices of columns at both sides of the panel had precedents in Flemish portraiture."<ref>{{cite web|url=http://archiv.ub.uni-heidelberg.de/artdok/157/1/Zoellner_GBA_93.pdf |last=Zöllner |first=Frank |title=Leonardo's Portrait of Mona Lisa del Giocondo |page=16 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141001152129/http://archiv.ub.uni-heidelberg.de/artdok/157/1/Zoellner_GBA_93.pdf |archive-date=1 October 2014 }}</ref> Woods-Marsden cites ]'s ] (1487) or Italian imitations such as ]'s ] for the use of a '']'', which has the effect of mediating between the sitter and the distant landscape, a feature missing from Leonardo's earlier portrait of '']''.<ref name="Marsden77">Woods-Marsden p. 77 n. 100</ref> | |||
| The painting has been restored numerous times; ] examinations have shown that there are three versions of the ''Mona Lisa'' hidden under the present one. The thin poplar backing is beginning to show signs of deterioration at a higher rate than previously thought, causing concern from museum curators about the future of the painting. | |||
| <gallery> | |||
| Image:Mona Lisa detail background left.jpg|Detail of the background (left side) | |||
| Image:Mona Lisa detail mouth.jpg|Detail of the mouth | |||
| Image:Mona Lisa detail eyes.jpg|Detail of the eyes | |||
| Image:Mona Lisa detail face.jpg|Detail of the face, showing the subtle shading effect of sfumato, particularly in the shadows around the eyes | |||
| ] | |||
| </gallery> | |||
| The painting was one of the first Italian portraits to depict the sitter in front of an imaginary landscape,<ref>], ''Renaissance Portraits, European Portrait-Painting in the 14th, 15th and 16th Centuries'', pp. 120–124, 1990, Yale, {{ISBN|0300046758}}</ref> although some scholars favour a realistic description,<ref name="Lisa#">{{cite news |title=Mystery of where Mona Lisa was painted has been solved, geologist claims |date=11 May 2024 |last=Alberge |first=Dalya |work= The Guardian |url=https://www.theguardian.com/artanddesign/article/2024/may/11/where-mona-lisa-was-painted-mystery-solved-geologist-claims |access-date=12 May 2024|issn=1756-3224}}</ref> and Leonardo was one of the first painters to use ].<ref>{{cite web|title=The Mona Lisa (La Gioconda) |url=http://www.bbc.co.uk/science/leonardo/gallery/monalisa.shtml |date=25 October 2009 |publisher=BBC |access-date=24 October 2009 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100626045642/http://www.bbc.co.uk/science/leonardo/gallery/monalisa.shtml |archive-date=26 June 2010 }}</ref> The enigmatic woman is portrayed seated in what appears to be an open loggia with dark pillar bases on either side. Behind her, a vast landscape recedes to icy mountains,<ref>According to the geologist and art historian Ann Pizzorusso, the mountains in the background would not be covered in snow because the white and gray color would be typical of the mountains that overlook ] and its lake. {{cite news |title=Mystery of where Mona Lisa was painted has been solved, geologist claims |date=11 May 2024 |last=Alberge |first=Dalya |work= The Guardian |url=https://www.theguardian.com/artanddesign/article/2024/may/11/where-mona-lisa-was-painted-mystery-solved-geologist-claims |access-date=12 May 2024|issn=1756-3224}}</ref> winding paths and a distant bridge, giving only the slightest indications of human presence. Leonardo chose to place the horizon line not at the neck, as he did with ''Ginevra de' Benci'', but on a level with the eyes, thus linking the figure with the landscape and emphasizing the mysterious nature of the painting.<ref name="Marsden77" /> The bridge in the background was identified by Silvano Vincenti as the four-arched ] from ]-] times near ], ], over the ] river.<ref name="Giuffrida-2023">{{cite news |last=Giuffrida |first=Angela |date=3 May 2023 |title=Italian historian claims to have identified bridge in Mona Lisa backdrop |work=The Guardian |url=https://www.theguardian.com/artanddesign/2023/may/03/italian-historian-claims-to-have-identified-bridge-in-mona-lisa-backdrop|access-date=5 December 2024|issn=1756-3224}}</ref> Other bridges with similar arches suggested as possible locations had more arches.<ref name="Giuffrida-2023" /> Some observers find similarities with the ].<ref name="Lisa#" /> | |||
| == Conservation == | |||
| The Mona Lisa has survived for more than 500 years, and an international commission convened in 1952 noted that "the picture is in a remarkable state of preservation."<ref name="mohen">{{cite book | last = Mohen | first = Jean-Pierre | title = Mona Lisa: inside the Painting | publisher = "Harry N. Abrams, Inc." | location = City | year = 2006 | pages=128|isbn = 0810943158 }}</ref> This is partly due to the result of a variety of conservation treatments the painting has undergone in its history. A detailed analysis of the picture in 1933 by Madame de Gironde revealed that earlier restorers had "acted with a great deal of restraint."<ref name="mohen" /> Nevertheless, applications of ] made to the painting had darkened even by the end of the 16th century, and an aggressive 1809 cleaning and re-varnish removed some of the uppermost portion of the paint layer, resulting in a washed-out appearance to the face of the figure. Despite these few unfortunate treatments, the Mona Lisa has been well cared for throughout its history, and the 2004-05 conservation team was optimistic about the future of the work.<ref name="mohen" /> | |||
| ''Mona Lisa'' has no clearly visible eyebrows or eyelashes, although Vasari describes the eyebrows in detail.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Vasari|first=Giorgio|url=https://archive.org/details/livesofartists0000vasa_k5j0/page/294/mode/2up|title=The Lives of the Artists|publisher=Oxford University Press|year=1991|isbn=0-19-283410-X|series=Oxford World's Classics|page=294|language=en|translator-last=Bondanella|translator-first=Peter|quote=The eyebrows could not be more natural, for they represent the way the hair grows in the skin—thicker in some places and thinner in others, following the pores of the skin.|author-link=Giorgio Vasari|orig-year=1568|translator-last2=Bondanella|translator-first2=Julia Conway}}</ref>{{efn|Some researchers argue that it was common at this time for genteel women to pluck these hairs, as they were considered unsightly.<ref>{{harvnb|Turudich|2003|p=198}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|title=Mona Lisa: The Picture and the Myth|author=McMullen, Roy|publisher=]|year=1976|isbn=978-0-333-19169-9}}</ref>}} In 2007, French engineer Pascal Cotte announced that his ultra-high resolution scans of the painting provide evidence that ''Mona Lisa'' was originally painted with eyelashes and eyebrows but that these had gradually disappeared over time, perhaps as a result of overcleaning.<ref>{{cite news|last=Holt|first=Richard|date=22 October 2007|title=Solved: Why Mona Lisa doesn't have eyebrows|work=The Daily Telegraph|location=UK|url=https://www.telegraph.co.uk/culture/art/3668700/Solved-Why-Mona-Lisa-doesnt-have-eyebrows.html|url-status=live|url-access=registration|access-date=11 March 2010|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100404082647/http://www.telegraph.co.uk/culture/art/3668700/Solved-Why-Mona-Lisa-doesnt-have-eyebrows.html|archive-date=4 April 2010}}</ref> Cotte discovered that the painting had been reworked several times, with changes made to the size of the face and the direction of gaze. He also found that in one layer the subject was depicted wearing numerous hairpins and a headdress adorned with pearls which was later scrubbed out and overpainted.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.livescience.com/53038-hidden-painting-real-mona-lisa.html |title=Lurking Beneath the 'Mona Lisa' May Be the Real One |website=Livescience.com |date=9 December 2015 |author=Ghose, Tia |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151211114103/http://www.livescience.com/53038-hidden-painting-real-mona-lisa.html |archive-date=11 December 2015 }}</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| There has been much speculation regarding the painting's sitter and landscape background. For example, Leonardo probably painted his sitter's appearance faithfully since her beauty is not seen as being among the best, "even when measured by late quattrocento (15th century) or even twenty-first century standards."<ref>Irene Earls, ''Artists of the Renaissance'', Greenwood Press, 2004, p. 113. {{ISBN|0-313-31937-5}}</ref> Some historians in Eastern art, such as ], argue that the landscape in the background of the picture was influenced by ];<ref name="Salgueiro" /> this thesis has been contested for lack of clear evidence.<ref name="Salgueiro">{{cite book|first=Heliana Angotti |last=Salgueiro|title=Paisaje y art|publisher=]|year= 2000|page= 74|isbn=978-85-901430-1-7}}</ref> | |||
| ====Poplar panel==== | |||
| At some point in its history, the Mona Lisa was removed from its original frame. The unconstrained poplar panel was allowed to warp freely with changes in humidity, and as a result, a crack began to develop near the top of the panel. The crack extends down to the hairline of the figure. In the mid 18th to early 19th century, someone attempted to stabilize the crack by inlaying two butterfly shaped walnut braces into the back of the panel to a depth of about 1/3 the thickness of the panel. This work was skillfully executed, and has successfully stabilized the crack. Sometime between 1888 and 1905, or perhaps at some point during the picture's theft, the upper brace fell out. A later restorer glued and lined the resulting socket and crack with cloth. | |||
| Research in 2003 by Professor ] of ] said that Mona Lisa's smile disappears when observed with direct vision, known as ]. Because of the way the human eye processes visual information, it is less suited to pick up shadows directly; however, ] can pick up shadows well.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/entertainment/2775817.stm |title=BBC News – Entertainment – Mona Lisa smile secrets revealed |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070831010359/http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/entertainment/2775817.stm |archive-date=31 August 2007 |date=18 February 2003 }}</ref> Research in 2008 by a geomorphology professor at ] and an artist-photographer revealed that ''Mona Lisa''{{`}}s landscape was similar to some views in the ] region in the Italian provinces of ], and ].<ref>Rosetta Borchia and Olivia Nesci, ''Codice P. Atlante illustrato del reale paesaggio della Gioconda'', Mondadori Electa, 2012, {{ISBN|978-88-370-9277-1}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.thetimes.co.uk/tto/arts/visualarts/article3612516.ece|title=Researchers identify landscape behind the Mona Lisa|newspaper=The Times |access-date=22 January 2014}}</ref> Research in 2023/2024 by geologist and art historian Ann Pizzorusso suggests that the landscape contains "several recognisable features of ], on the shores of ] in the ] region of ]."<ref>{{cite news|url=https://www.theguardian.com/artanddesign/article/2024/may/11/where-mona-lisa-was-painted-mystery-solved-geologist-claims|title=Mystery of where Mona Lisa was painted has been solved, geologist claims|work=The Guardian |access-date=11 May 2024|issn=1756-3224}}</ref> | |||
| The picture is currently kept under strict, climate controlled conditions in its bullet-proof glass case. The humidity is maintained at 50% ±10%, and the temperature is maintained between 18 and 21°C. To compensate for fluctuations in relative humidity, the case is supplemented with a bed of ] treated to provide 55% relative humidity.<ref name="mohen" /> | |||
| == |
==History== | ||
| ===Creation and date=== | |||
| Because the Mona Lisa's poplar support expands and contracts with changes in humidity, the picture has experienced some warping. In response to warping and swelling experienced during its storage during World War II, and to prepare the picture for an exhibit to honor the anniversary of Da Vinci's 500th birthday, the Mona Lisa was fitted in 1951 with a flexible oak frame with beech crosspieces. This flexible frame, which is used in addition to the decorative frame described below, exerts pressure on the panel to keep it from warping further. In 1970, the beech crosspieces were switched to maple after it was found that the beech wood had been infested with insects. In 2004-05, a conservation and study team replaced the maple crosspieces with sycamore ones, and an additional metal crosspiece was added for scientific measurement of the panel's warp. | |||
| Of ], the ''Mona Lisa'' is the only portrait whose authenticity has never been seriously questioned,{{sfn|Chiesa|1967|p=103}} and one of four works—the others being '']'', '']'' and '']''—whose attribution has avoided controversy.{{sfn|Chiesa|1967|p=87}} He had begun working on a portrait of ], the sitter for the ''Mona Lisa'', by October 1503.<ref name="subject"/><ref name=Vincent/> It is believed by some that the ''Mona Lisa'' was begun in 1503 or 1504 in Florence.<ref>{{cite book|last=Wiesner-Hanks|first=Merry E.|title=An Age of Voyages, 1350–1600|publisher=Oxford University Press|year=2005|isbn=978-0-19-517672-8|location=New York|page=26}}</ref> Although the Louvre states that it was "doubtless painted between 1503 and 1506",<ref name="Louvre" /> art historian ] says that there are some difficulties in confirming the dates with certainty.<ref name="Kemp" /> ] believes that the painting is characteristic of Leonardo's style in the final years of his life, post-1513.<ref name="Vezzosi 2007">{{cite book |last=Vezzosi |first=Alessandro |editor-last1=Vezzosi |editor-last2=Schwarz |editor-last3=Manetti |title=Mona Lisa: Leonardo's hidden face |publisher=Polistampa |year=2007 |chapter=The Gioconda mystery – Leonardo and the 'common vice of painters' |isbn=978-88-596-0258-3}}</ref> Other academics argue that, given the historical documentation, Leonardo would have painted the work from 1513.<ref name="Asmus Parfenov Elford">{{cite journal |last1=Asmus |first1=John F. |last2=Parfenov |first2=Vadim |last3=Elford |first3=Jessie |date= 28 November 2016 |title=Seeing double: Leonardo's Mona Lisa twin |journal=Optical and Quantum Electronics |volume=48 |issue=12 |pages=555 |doi=10.1007/s11082-016-0799-0|bibcode=2016OQEle..48..555A |s2cid=125226212 }}</ref> According to Vasari, "after he had lingered over it four years, left it unfinished".<ref name=Clark /> In 1516, Leonardo was invited by ] to work at the ] near the ]; it is believed that he took the ''Mona Lisa'' with him and continued to work on it after he moved to France.<ref name="BBC-Faces" /> Art historian Carmen C. Bambach has concluded that Leonardo probably continued refining the work until 1516 or 1517.<ref>Leonardo, Carmen Bambach, Rachel Stern, and Alison Manges (2003). ''Leonardo da Vinci, master draftsman''. New York: Metropolitan Museum of Art. p. 234. {{ISBN|1-58839-033-0}}</ref> Leonardo's right hand was paralytic {{Circa|1517}},<ref name="seeker">{{cite web|last=Lorenzi|first=Rossella|date=10 May 2016|title=Did a Stroke Kill Leonardo da Vinci?|url=https://www.seeker.com/did-a-stroke-kill-leonardo-da-vinci-1789047208.html|access-date=5 May 2019|website=Seeker}}</ref> which may indicate why he left the ''Mona Lisa'' unfinished.<ref name="guardian2005">{{cite news|last=McMahon|first=Barbara|date=1 May 2005|title=Da Vinci 'paralysis left Mona Lisa unfinished'|url=https://www.theguardian.com/world/2005/may/01/italy.arts|access-date=2 May 2019|work=The Guardian|issn=1756-3224}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|last=Saplakoglu|first=Yasemin|date=4 May 2019|title=A Portrait of Leonardo da Vinci May Reveal Why He Never Finished the Mona Lisa|url=https://www.livescience.com/65396-da-vinci-hand-injury.html|access-date=5 May 2019|website=Live Science}}</ref><ref name="fainting">{{cite news|last=Bodkin|first=Henry|date=4 May 2019|title=Leonardo da Vinci never finished the Mona Lisa because he injured his arm while fainting, experts say|newspaper=The Telegraph|url=https://www.telegraph.co.uk/science/2019/05/04/leonardo-da-vinci-never-finished-mona-lisa-injured-arm-fainting/ |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20220110/https://www.telegraph.co.uk/science/2019/05/04/leonardo-da-vinci-never-finished-mona-lisa-injured-arm-fainting/ |archive-date=10 January 2022 |url-access=subscription |url-status=live|access-date=6 May 2019}}{{cbignore}}</ref>{{efn|Leonardo, later in his life, is said to have regretted "never having completed a single work".<ref>{{cite book|first1=Henry |last1=Thomas |first2=Dana |last2=Lee Thomas|title=Living biographies of great painters|publisher= Garden City Publishing Co., Inc.|year=1940|page=49}}</ref>}} | |||
| The Mona Lisa has had many different decorative frames in its history, owing to changes in taste over the centuries. In 1906, the picture was given its current frame by the countess of Béarn, a Renaissance frame consistent with the historical period of the Mona Lisa. The edges of the painting have been trimmed at least once in its history to fit the picture into various frames, but none of the original paint layer has been trimmed.<ref name="mohen" /> | |||
| ]'s drawing ({{Circa|1505}}), after Leonardo; today in the ] along with the ''Mona Lisa''<ref name="Reynal">{{cite book|last=Becherucci|first=Luisa|title=The Complete Work of Raphael|date=1969|publisher=Reynal and Co., ]|location=New York|page=50}}</ref>]] | |||
| ====Insect treatment==== | |||
| ''Circa'' 1505,<ref name=Reynal/> ] executed a pen-and-ink sketch, in which the columns flanking the subject are more apparent. Experts universally agree that it is based on Leonardo's portrait.<ref>{{cite magazine|last=Clark|first=Kenneth|date=March 1973|title=Mona Lisa|magazine=Burlington Magazine|volume=115}}</ref><ref name="Lorusso Natali">{{cite journal |last1=Lorusso |first1=Salvatore |last2=Natali |first2=Andrea |year=2015 |title=Mona Lisa: A comparative evaluation of the different versions and copies |url= https://conservation-science.unibo.it/article/view/6168/5936 |journal=Conservation Science |volume=15 |pages=57–84 |access-date=26 July 2017}}</ref><ref name="Isbouts">{{cite book|last1=Isbouts|first1=Jean-Pierre|title=The Mona Lisa Myth|last2=Heath-Brown|first2=Christopher|date=2013|publisher=Pantheon Press|isbn=978-1-4922-8949-4|location=Santa Monica, California}}</ref> Other later copies of the ''Mona Lisa'', such as those in the ] and ], also display large flanking columns. As a result, it was thought that the ''Mona Lisa'' had been trimmed.<ref>{{cite book|last=Friedenthal|first=Richard|title=Leonardo da Vinci: a pictorial biography|date=1959|publisher=Viking Press|location=New York}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|last=Kemp|first=Martin|url=https://archive.org/details/leonardodavincim00kemp_0|title=Leonardo: The marvelous works of nature and man|date=1981|publisher=Harvard University Press|isbn=978-0-674-52460-6|location=Cambridge, Massachusetts}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|last=Bramly|first=Serge|url=https://archive.org/details/leonardoartistma00bram|title=Leonardo: The artist and the man|date=1995|publisher=Penguin books|isbn=978-0-14-023175-5|location=London}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|last=Marani|first=Pietro|title=Leonardo: The complete paintings|date=2003|publisher=Harry N. Abrams|isbn=978-0-8109-9159-0|location=New York}}</ref> By 1993, ] observed that the painting surface had never been trimmed;<ref name="Zollner 1993">{{cite journal|last=Zollner|first=Frank|year=1993|title=Leonardo da Vinci's portrait of Mona Lisa de Giocondo|url=http://archiv.ub.uni-heidelberg.de/artdok/4207/1/Zoellner_Leonardos_portrait_of_Mona_Lisa_1993.pdf|journal=Gazette des Beaux-Arts|volume=121|pages=115–138|access-date=3 August 2017}}</ref> this was confirmed through a series of tests in 2004.<ref name="mohen" /> In view of this, ], curator of 16th-century Italian painting at the Louvre, states that the sketch and these other copies must have been inspired by another version,<ref name="Delieuvin Tallec">{{cite book|last1=Delieuvin|first1=Vincent|title=What's so special about Mona Lisa|last2=Tallec|first2=Olivier|date=2017|publisher=Editions du musée du Louvre|isbn=978-2-35031-564-5|location=Paris}}</ref> while Zöllner states that the sketch may be after another Leonardo portrait of the same subject.<ref name="Zollner 1993" /> | |||
| In 1977, a new insect infestation was discovered in the back of the panel as a result of crosspieces installed to keep the painting from warping. This was treated on the spot with ], and later with an ] treatment. In 1985, the spot was again treated with carbon tetrachloride as a preventive measure.<ref name="mohen" /> | |||
| The record of an October 1517 visit by ] states that the ''Mona Lisa'' was executed for the deceased ], Leonardo's steward at ], between 1513 and 1516;<ref>{{cite book|last=De Beatis|first=Antonio|author-link=Antonio de Beatis|title=The travel journal of Antonio de Beatis: Germany, Switzerland, the Low Countries, France and Italy 1517–1518|date=1979|publisher=Haklyut Society|editor-last1=Hale|editor-first1=J.R.|location=London, England|orig-year=1st pub.:1517|editor-last2=Lindon|editor-first2=J.M.A.}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|last=Bacci|first=Mina|title=The Great Artists: Da Vinci|publisher=Funk & Wagnalls|year=1978|location=New York|translator-last=Tanguy|translator-first=J.|orig-year=1963}}<!--intro--></ref>{{efn|"... Messer Lunardo Vinci {{sic}} ... showed His Excellency three pictures, one of a certain Florentine lady done from life at the instance of the late Magnificent, Giuliano de' Medici."<ref name=Wallace>{{cite book |last=Wallace |first=Robert |title=The World of Leonardo: 1452–1519 |publisher=Time-Life Books |location=New York |year=1972|orig-year=1966 |pages=163–64}}</ref>}} this was likely an error.<ref name=Wallace/>{{efn|"Possibly it was another portrait of which no record and no copies exist—Giuliano de' Medici surely had nothing to do with the ''Mona Lisa''—the probability is that the secretary, overwhelmed as he must have been at the time, inadvertently dropped the Medici name in the wrong place."<ref name=Wallace/>}} According to Vasari, the painting was created for the sitter's husband, Francesco del Giocondo.<ref name="Vasari2">{{cite book|last=Vasari|first=Giorgio|title=Le Vite de' più eccellenti pittori, scultori, ed architettori|date=1550|publisher=]|location=Florence, Italy}}</ref> A number of experts have argued that Leonardo made two versions (because of the uncertainty concerning its dating and commissioner, as well as its fate following Leonardo's death in 1519, and the difference of details in Raphael's sketch—which may be explained by the possibility that he made the sketch from memory).<ref name=Reynal/><ref name=Isbouts/><ref name="Lorusso Natali"/><ref name="Boudin">{{cite book|last=Boudin de l'Arche|first=Gerard|title=A la recherche de Monna Lisa|date=2017|publisher=Edition de l'Omnibus|isbn=979-10-95833-01-7|location=Cannes, France}}</ref> The hypothetical first portrait, displaying prominent columns, would have been commissioned by Giocondo {{circa|1503}}, and left unfinished in Leonardo's pupil and assistant Salaì's possession until his death in 1524. The second, commissioned by Giuliano de' Medici {{circa|1513}}, would have been sold by Salaì to Francis I in 1518,{{efn|Along with '']'' and '']''}} and is the one in the Louvre today.<ref name=Isbouts/><ref name="Lorusso Natali"/><ref name=Boudin/><ref>{{cite web |title=Mona Lisa|url=http://www.louvre.fr/en/oeuvre-notices/mona-lisa-portrait-lisa-gherardini-wife-francesco-del-giocondo|access-date=3 August 2017|website=louvre.fr}}</ref> Others believe that there was only one true ''Mona Lisa'' but are divided as to the two aforementioned fates.<ref name="Kemp" /><ref name="Kemp Pallanti">{{cite book |last1=Kemp |first1=Martin |title=Mona Lisa: The people and the painting |last2=Pallanti |first2=Giuseppe |date=2017 |publisher=Oxford University Press |isbn=978-0-19-874990-5 |location=Oxford |pages=113}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal|last=Jestaz|first=Bertrand|year=1999|title=Francois 1er, Salai, et les tableaux de Léonard|journal=Revue de l'Art|language=fr|volume=76|issue=1 |pages=68–72|doi=10.3406/rvart.1999.348476}}</ref> At some point in the 16th century, a ] was applied to the painting.<ref name=varnish/> It was kept at the ] until ] moved it to the ], where it remained until the ].<ref name="Classics-2017">{{Cite book|last1=Classics|first1=Delphi|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=06KfDgAAQBAJ&q=moved+it+to+the+Palace+of+Versailles,+where+it+remained+until+the+French+Revolution&pg=PT95|title=The History of Art in 50 Paintings (Illustrated)|last2=Russell|first2=Peter|date=7 April 2017|publisher=Delphi Classics|isbn=978-1-78656-508-2|language=en}}</ref> In 1797, it went on permanent display at the Louvre.<ref name=carrier/> | |||
| ====Cleaning and touch-up==== | |||
| The first and most extensive recorded cleaning, revarnishing, and touch up of the Mona Lisa was an 1809 wash and re-varnish undertaken by Jean-Marie Hooghstoel, who was responsible for restoration of paintings for the galleries of the ]. The work involved cleaning with spirits, touch up of color, and revarnishing the painting. In 1906, Louvre restorer ] performed watercolor retouches on areas of the paint layer disturbed by the crack in the panel. Denizard also retouched the edges of the picture with varnish, to mask areas that had been covered initially by an older frame. In 1913, when the painting was recovered after its theft, Denizard was again called upon to work on the Mona Lisa. Denizard was directed to clean the picture without ], and to lightly touch up several scratches to the painting with watercolor. In 1952, the varnish layer over the background in the painting was evened out. After the second 1956 attack, restorer Jean-Gabriel Goulinat was directed to touch up the damage to Mona Lisa's left elbow with watercolor.<ref name="mohen" /> | |||
| ===Refuge, theft, and vandalism=== | |||
| ] | |||
| ]'s 1911 painting depicting ''Mona Lisa'' displayed in the ] before the theft, which Béroud discovered and reported to the guards]] | |||
| ====Infrared scan==== | |||
| After the French Revolution, the painting was moved to the Louvre but spent a brief period in the bedroom of ] (d. 1821) in the ].<ref name="Classics-2017" /> Although the ''Mona Lisa'' was not widely known outside the art world, in the 1860s a portion of the French ] began to hail it as a masterwork of Renaissance painting.<ref>{{cite news|date=30 July 2011|title=The Theft That Made The 'Mona Lisa' A Masterpiece|work=]|url=https://www.npr.org/2011/07/30/138800110/the-theft-that-made-the-mona-lisa-a-masterpiece|url-status=live|access-date=26 August 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140827142640/http://www.npr.org/2011/07/30/138800110/the-theft-that-made-the-mona-lisa-a-masterpiece|archive-date=27 August 2014}}</ref> During the ] (1870–1871), the painting was moved from the Louvre to the ].<ref name="Bohm-Duchen2001p53">{{cite book|last=Bohm-Duchen|first=Monica|url=https://archive.org/details/isbn_9790520233781|title=The private life of a masterpiece|publisher=University of California Press|year=2001|isbn=978-0-520-23378-2|page=|access-date=10 October 2010|url-access=registration}}</ref> | |||
| In 2004 experts from the ] conducted a three-dimensional ] scan. Because of the aging of the varnish on the painting it has been difficult to discern details. Data from the scan and infrared ] were later used by Bruno Mottin of the French Museums' "Center for Research and Restoration" to argue that the transparent gauze veil worn by the sitter is a ], typically used by women while pregnant or just after giving birth. A similar guarnello was painted by ] in his ''Portrait of Smeralda Brandini'' (1470), depicting a pregnant woman (] in London]). Furthermore, this reflectography revealed that ''Mona Lisa'''s hair is not loosely hanging down, but seems attached at the back of the head to a bonnet or pinned back into a ] and covered with a veil, bordered with a sombre rolled hem. In the 16th century, hair hanging loosely down on the shoulders was the customary ] of unmarried young women or prostitutes. This apparent contradiction with her status as a married woman has now been resolved. | |||
| In 1911, the painting was still not popular among the lay-public.<ref name="ny2019">{{cite magazine|last=Halpern|first=Jack|date=9 January 2019|title=The French Burglar Who Pulled Off His Generation's Biggest Art Heist|url=https://www.newyorker.com/magazine/2019/01/14/the-french-burglar-who-pulled-off-his-generations-biggest-art-heist|magazine=The New Yorker|access-date=9 January 2019}}</ref> On 21 August 1911, the painting was ] from the Louvre.<ref name="Stoner-PBS">{{cite news|title=Theft of the Mona Lisa|publisher=Stoner Productions via Public Broadcasting Service (PBS)|url=https://www.pbs.org/treasuresoftheworld/a_nav/mona_nav/main_monafrm.html|url-status=live|access-date=24 October 2009|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20091029133742/http://www.pbs.org/treasuresoftheworld/a_nav/mona_nav/main_monafrm.html|archive-date=29 October 2009}}</ref> The painting was first reported missing the next day by painter ]. After some confusion as to whether the painting was being photographed somewhere, the Louvre was closed for a week for investigation. French poet ] came under suspicion and was arrested and imprisoned. Apollinaire implicated his friend ], who was brought in for questioning. Both were later exonerated.<ref name="Scotti2010">{{cite book|last=Scotti|first=R. A. |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=UmaaVuZMCAkC|title=Vanished Smile: The Mysterious Theft of the Mona Lisa|date=April 2010|publisher=Vintage Books|isbn=978-0-307-27838-8|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160102112800/https://books.google.com/books?id=UmaaVuZMCAkC|archive-date=2 January 2016|url-status=live}}</ref><ref name="monalisa25">{{cite magazine|date=2 December 2007|title=Top 25 Crimes of the Century: Stealing the Mona Lisa, 1911|magazine=Time|url=http://www.time.com/time/2007/crimes/2.html|url-status=dead|access-date=15 September 2007|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070714103850/http://www.time.com/time/2007/crimes/2.html|archive-date=14 July 2007}}</ref> The real culprit was Louvre employee ], who had helped construct the painting's glass case.<ref>{{cite news|last=Sale|first=Jonathan|date=8 May 2009|title=Review: The Lost Mona Lisa: The Extraordinary True Story of the Greatest Art Theft in History by RA Scotti|url=https://www.theguardian.com/books/2009/may/09/ra-scotti-lost-mona-lisa|access-date=23 July 2019|work=The Guardian|issn=1756-3224}}</ref> He carried out the theft by entering the building during regular hours, hiding in a broom closet, and walking out with the painting hidden under his coat after the museum had closed.{{sfn|Bartz|König|2001|p=626}} | |||
| Researchers also used the data to reveal details about the technique used and to predict that the painting will degrade very little if current conservation techniques are continued.<ref>CBC. (2006, September 26) Retrieved on September 27, 2006. </ref><ref>CNN. (2006, September 26). Retrieved on September 25, 2006.</ref><ref>Edmonton Journal (September 23) Retrieved on September 27, 2006</ref> During 2006, ''Mona Lisa'' underwent a major scientific observation that proved through infrared cameras she is wearing a bonnet and clenching her chair (something that Leonardo decided to change as an afterthought).<ref>{{cite news |first= Ian|last= Austen|title= New Look at ‘Mona Lisa’ Yields Some New Secrets |url= http://www.nytimes.com/2006/09/27/arts/design/27mona.html?ex=1317009600&en=9b5bc3405c3c4c03&ei=5090&partner=rssuserland&emc=rss |work=] |publisher=] |date=2006-09-27 |accessdate=2007-06-08}}</ref> | |||
| {{multiple image | |||
| | perrow = 2 | |||
| | image1 = Mona Lisa stolen-1911.jpg | |||
| | caption1 = Vacant wall in the Louvre's Salon Carré after the painting was stolen in 1911 | |||
| | image2 = Mona Lisa Found, La Joconde est Retrouvée, Le Petit Parisien, Numéro 13559, 13 December 1913.jpg | |||
| | caption2 = "La Joconde est Retrouvée" ("Mona Lisa is Found"), '']'', 13 December 1913 | |||
| | image3 = Monalisa uffizi 1913.jpg | |||
| | caption3 = The ''Mona Lisa'' in the ] in ], 1913. Museum director Giovanni Poggi ''(right)'' inspects the painting. | |||
| | image4 = Excelsior, journal illustré quotidien, La Joconde est Revenue, 1 January 1914.jpg | |||
| | caption4 = ''Excelsior'', "La Joconde est Revenue" ("The Mona Lisa has returned"), 1 January 1914 | |||
| }} | |||
| Peruggia was an Italian patriot who believed that Leonardo's painting should have been returned to an Italian museum.<ref>{{cite news|last1=Iqbal|first1=Nosheen|last2=Jonze|first2=Tim|date=22 January 2020|title=In pictures: The greatest art heists in history|work=The Guardian|url=https://www.theguardian.com/artanddesign/gallery/2009/feb/19/greatest-art-heists-in-pictures|access-date=17 April 2021|issn=0261-3077}}</ref> Peruggia may have been motivated by an associate whose copies of the original would significantly rise in value after the painting's theft.<ref name="lost">{{cite book |last=Scotti |first=R. A. |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=kSdYINRtkWEC |title=The Lost Mona Lisa: The Extraordinary True Story of the Greatest Art Theft in History |publisher=Bantam Books |year=2010 |isbn=978-0-5538-1830-7 |edition=reprinted}}</ref>{{page needed|date=July 2019}} After having kept the ''Mona Lisa'' in his apartment for two years, Peruggia grew impatient and was caught when he attempted to sell it to ], director of the ] in ]. It was exhibited in the Uffizi Gallery for over two weeks and returned to the Louvre on 4 January 1914.<ref>{{cite web|title=Noah Charney, ''Chronology of the Mona Lisa: History and Thefts'', The Secret History of Art, Blouin Artinfo Blogs|url=http://blogs.artinfo.com/secrethistoryofart/2011/08/09/chronology-of-the-mona-lisa-history-and-thefts/|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151027061739/http://blogs.artinfo.com/secrethistoryofart/2011/08/09/chronology-of-the-mona-lisa-history-and-thefts/|archive-date=27 October 2015|access-date=25 October 2015}}</ref> Peruggia served six months in prison for the crime and was hailed for his patriotism in Italy.<ref name="monalisa25" /> A year after the theft, '']'' journalist ] wrote that he met an alleged accomplice named ], who claimed to have masterminded the theft. Forger ] was to have created six copies of the painting to sell in the US while concealing the location of the original.<ref name=lost/> Decker published this account of the theft in 1932.<ref>{{cite web|last=Nilsson|first=Jeff|date=7 December 2013|title=100 Years Ago: The Mastermind Behind the Mona Lisa Heist {{!}} The Saturday Evening Post|url=https://www.saturdayeveningpost.com/2013/12/the-mona-lisa-heist/|access-date=23 July 2019|website=Saturday Evening Post}}</ref><ref name=Charney1 /> | |||
| During ], it was again removed from the Louvre and taken first to the Château d'Amboise, then to the ] and ], then finally to the ] in ].<ref name=Charney1 /><ref>{{cite news|url=https://theguardian.com/artanddesign/2013/nov/12/nazis-steal-mona-lisa-louvre|date=12 November 2013|title=Did the Nazis steal the Mona Lisa?|last=Charney|first=Noah|work=The Guardian|issn=1756-3224}}</ref> Since the 1990s, the painting has been temporarily moved to accommodate renovations to the Louvre on three occasions: between 1992 and 1995, from 2001 to 2005, and again in 2019.<ref>{{cite web|last=Guenfoud|first=Ibtissem|date=17 July 2019|title='Mona Lisa' relocated within Louvre for 1st time since 2005|url=https://abcnews.go.com/International/mona-lisa-relocated-louvre-1st-time-2005/story?id=64384961|access-date=23 July 2019|website=ABC News}}</ref> A new queuing system introduced in 2019 reduces the amount of time museum visitors have to wait in line to see the painting. After going through the queue, a group has about 30 seconds to see the painting.<ref>{{cite news|last=Samuel|first=Henry|date=7 October 2019|title=Will new Mona Lisa queuing system in restored Louvre gallery bring a smile back to visitors' faces?|newspaper=The Telegraph|url=https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/2019/10/07/shorter-wait-intimacy-mona-lisa-can-forget-selfies/ |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20220110/https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/2019/10/07/shorter-wait-intimacy-mona-lisa-can-forget-selfies/ |archive-date=10 January 2022 |url-access=subscription |url-status=live|access-date=12 October 2019}}{{cbignore}}</ref> | |||
| ====Display==== | |||
| On ], ] — following a period of curatorial maintenance, recording, and analysis — the painting was moved, within the Louvre, to a new home in the museum's Salle des États. It is displayed in a purpose-built, climate-controlled enclosure behind bullet proof glass.<ref>BBC News. (2005, April 6). Retrieved on June 20, 2006.</ref> About 6 million people view the painting at the Louvre each year.<ref name=BBC-Faces /> | |||
| On 30 December 1956, Bolivian Ugo Ungaza Villegas threw a rock at the ''Mona Lisa'' while it was on display at the Louvre. He did so with such force that it shattered the glass case and dislodged a speck of pigment near the left elbow.<ref>{{cite web|title=Mona FAQ|url=http://www.monalisamania.com/faq.htm|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090601155641/http://www.monalisamania.com/faq.htm|archive-date=1 June 2009|access-date=7 January 2010|publisher=Mona Lisa Mania}}</ref> The painting was protected by glass because a few years earlier a man who claimed to be in love with the painting had cut it with a razor blade and tried to steal it.<ref>{{cite news|date=31 December 1956|url=https://www.nytimes.com/1956/12/31/archives/tourist-damages-the-mona-lisa-stone-breaks-glass-in-louvrepaint.html|title=Tourist Damages the 'Mona Lisa'; Stone Breaks Glass in Louvre--Paint Slightly Chipped Tourist Damages Louve Painting Portrait Deemed Uriceless|work=The New York Times|page=1|access-date=5 December 2024|issn=1553-8095}}</ref> After this attack, ] wrote in 1963 an essay titled "Why they attack the Mona Lisa", referencing earlier Freud theories.<ref name="Greenberger 2019"/><ref name="Dalí 1963"/> | |||
| ==Theft and vandalism== | |||
| ]]] | |||
| The Mona Lisa painting now hangs in the Musée du Louvre in Paris, France. The painting's increasing fame was further emphasized when it was ] on ], ]. The next day, Louis Béroud, a painter, walked into the Louvre and went to the Salon Carré where the ''Mona Lisa'' had been on display for five years. However, where the ''Mona Lisa'' should have stood, he found four iron pegs. | |||
| Since the 1956 attack, ] has been used to shield the painting from any further attacks, and in all subsequent cases the painting was undamaged. On 21 April 1974, while the painting was on display at the ], a woman sprayed it with red paint as a protest against that museum's failure to provide access for disabled people.<ref>{{cite news|date=21 April 1974|title='Mona Lisa' Still Smiling, Undamaged After Woman's Spray Attack in Tokyo|newspaper=Sarasota Herald-Tribune|url=https://news.google.com/newspapers?nid=1755&dat=19740421&id=qkg0AAAAIBAJ&pg=7136,1955839|access-date=9 October 2012}}</ref> On 2 August 2009, a Russian woman, distraught over being denied French citizenship, threw a ceramic teacup purchased at the Louvre; the vessel shattered against the glass enclosure.<ref>{{cite web|date=12 August 2009|title=Mona Lisa attacked by Russian woman|url=http://news.xinhuanet.com/english/2009-08/12/content_11868974.htm|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120302172144/http://news.xinhuanet.com/english/2009-08/12/content_11868974.htm|archive-date=2 March 2012|access-date=12 August 2009|publisher=Xinhua News Agency}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|date=11 August 2009|title=Russian tourist hurls mug at Mona Lisa in Louvre|agency=Associated Press|work=Deseret|url=https://www.deseret.com/2009/8/11/20333993/russian-tourist-hurls-mug-at-mona-lisa-in-louvre/<!--original dead url https://www.google.com/hostednews/ap/article/ALeqM5jVp53azA2HoJZZCxJ8aul8d9tJhgD9A0PM900 https://web.archive.org/web/20100716204935/https://www.google.com/hostednews/ap/article/ALeqM5jVp53azA2HoJZZCxJ8aul8d9tJhgD9A0PM900-->|access-date=5 December 2024}}</ref> | |||
| Béroud contacted the section head of the guards, who thought the painting was being photographed for marketing purposes. A few hours later, Béroud checked back with the section head of the museum, and it was confirmed that the ''Mona Lisa'' was not with the photographers. The Louvre was closed for an entire week to aid in investigation of the theft. | |||
| On 29 May 2022, a male activist, disguised as a woman in a wheelchair, threw ] at the protective glass covering the painting in an apparent attempt to raise awareness for ];<ref>{{cite news |date=30 May 2022 |title=Man in wig throws cake at glass protecting Mona Lisa |agency=] |publisher=] |url=https://abcnews.go.com/Weird/wireStory/man-wig-throws-cake-glass-protecting-mona-lisa-85064273 |access-date=30 May 2022}}</ref> the painting was not damaged.<ref>{{cite news |last=Hummel |first=Tassilo |date=30 May 2022 |title=Mona Lisa left unharmed but smeared in cream in climate protest stunt |work=] |editor-last=Stonestreet |editor-first=John |url=https://www.reuters.com/world/europe/mona-lisa-left-unharmed-smeared-cream-climate-protest-stunt-2022-05-30/ |access-date=30 May 2022}}</ref> The man was arrested and placed in psychiatric care in the police headquarters,<ref>{{cite news |date=30 May 2022 |title=Man arrested after Mona Lisa smeared with cake |work=The Guardian |url=https://www.theguardian.com/world/2022/may/30/mona-lisa-smeared-cake-suspected-climate-protester |access-date=7 June 2022|issn=1756-3224}}</ref> and an investigation was opened after the Louvre filed a complaint.<ref>{{cite news |last=Palumbo |first=Jacqui |date=31 May 2022 |title=The 'Mona Lisa' has been caked in attempted vandalism stunt |url=https://www.cnn.com/style/article/mona-lisa-louvre-cake-attack/index.html |access-date=31 May 2022 |work=CNN }}</ref> On 28 January 2024, two attackers from the environmentalist group Riposte Alimentaire (Food Retaliation) threw soup at the painting's protective glass, demanding the right to "healthy and sustainable food" and criticizing the contemporary state of agriculture; the painting was not damaged.<ref>{{cite web |date=28 January 2024 |title=Environmental activists hurl soup at the Mona Lisa in Paris's Louvre Museum |url=https://www.france24.com/en/france/20240128-activists-hurl-soup-on-glass-protected-mona-lisa-at-paris-s-louvre-museum |access-date=28 January 2024 |website=France 24}}</ref> | |||
| French poet ], who had once called for the ] to be "burnt down," came under suspicion; he was arrested and put in jail. Apollinaire pointed to his friend ], who was also brought in for questioning, but both were later exonerated.<ref name="monalisa25">{{cite news |first= |last= |authorlink= |coauthors= |title=Top 25 Crimes of the Century: Stealing the Mona Lisa, 1911 |url=http://www.time.com/time/2007/crimes/2.html |quote=She had been the chattel of French monarchs. Francois I bought her. Louis XIV set her up in Versailles. Napoleon moved her into his bedroom. She was Italian, created by Leonardo da Vinci over four years' labor in Florence, but France was her home and there she stayed for four centuries. Then on ], ], the space she occupied on the walls of the Louvre was discovered bare. |language=English|author=Time Magazine|publisher=] |date=2007 |accessdate=2007-09-15 }}</ref> | |||
| === Modern analysis === | |||
| At the time, the painting was believed to be lost forever, and it would be two years before the real thief was discovered. Louvre employee ] stole it by entering the building during regular hours, hiding in a broom closet and walking out with it hidden under his coat after the museum had closed.<ref name="louvre1" /> Peruggia was an ] patriot who believed ] painting should be returned to Italy for display in an Italian museum. Peruggia may have also been motivated by a friend who sold copies of the painting, which would skyrocket in value after the theft of the original. After having kept the painting in his apartment for two years, Peruggia grew impatient and was finally caught when he attempted to sell it to the directors of the ] in ]; it was exhibited all over Italy and returned to the Louvre in ]. Peruggia was hailed for his patriotism in Italy and only served a few months in jail for the crime.<ref name="monalisa25" /> | |||
| In the early 21st century, French scientist Pascal Cotte hypothesized a hidden portrait underneath the surface of the painting. He analysed the painting in the Louvre with reflective light technology beginning in 2004, and produced ] for his theory.<ref name="bbc">{{cite web|date=8 December 2015|title=Hidden portrait 'found under Mona Lisa', says French scientist|url=https://www.bbc.com/news/entertainment-arts-35031997|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151208131512/http://www.bbc.com/news/entertainment-arts-35031997|archive-date=8 December 2015|access-date=8 December 2015|work=BBC News}}</ref><ref name="Cotte">{{cite book|last=Cotte|first=Pascal|title=Lumiere on the Mona Lisa: Hidden portraits|date=2015|publisher=Vinci Editions|isbn=978-2-9548-2584-7|location=Paris}}</ref><ref name="Apollo">{{cite journal|last=McAloon|first=Jonathan|date=10 December 2015|title=The Missing Mona Lisa|url=http://www.apollo-magazine.com/the-missing-mona-lisa/|url-status=live|journal=]|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151215033419/http://www.apollo-magazine.com/the-missing-mona-lisa/|archive-date=15 December 2015}}</ref> Cotte admits that his investigation was carried out only in support of his hypotheses and should not be considered as definitive proof.<ref name="Cotte" /><ref name="Kemp Pallanti" /> The underlying portrait appears to be of a sitter looking to the side, and lacks flanking columns,<ref>{{cite magazine|date=8 December 2015|title=Secret Portrait Hidden Under Mona Lisa, Claims French Scientist|url=http://europe.newsweek.com/secret-portrait-hidden-under-mona-lisa-claims-french-scientist-402422?rm=eu|magazine=Newsweek|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151208232213/http://europe.newsweek.com/secret-portrait-hidden-under-mona-lisa-claims-french-scientist-402422?rm=eu|archive-date=8 December 2015|access-date=8 December 2015|url-status=live}}</ref> but it does not fit with historical descriptions of the painting. Both Vasari and ] describe the subject as smiling,<ref name="Vasari" /><ref>{{cite book|last=Lomazzo|first=Gian Paolo|title=Treatise on the art of painting|date=1584|location=Milan}}</ref> unlike the subject in Cotte's supposed portrait.<ref name="Cotte" /><ref name="Kemp Pallanti" /> In 2020, Cotte published a study alleging that the painting has an ], transferred from a preparatory drawing via the ] technique.<ref>{{Cite journal|last1=Cotte|first1=Pascal|last2=Simonot|first2=Lionel|date=1 September 2020|title=Mona Lisa's spolvero revealed|url=https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1296207420304362|journal=Journal of Cultural Heritage|language=en|volume=45|pages=1–9|doi=10.1016/j.culher.2020.08.004|s2cid=225304838|issn=1296-2074}}</ref> | |||
| ==Conservation== | |||
| During ], the painting was again removed from the Louvre and taken safely, first to ], then to the ] and finally to the ] in ]. | |||
| ] | |||
| The ''Mona Lisa'' has survived for more than 500 years, and an international commission convened in 1952 noted that "the picture is in a remarkable state of preservation."<ref name="mohen">{{cite book |last=Mohen |first=Jean-Pierre |title=Mona Lisa: inside the Painting |publisher=] |year=2006 |page=128 |isbn=978-0-8109-4315-5}}</ref> It has never been fully restored,<ref>{{cite journal |url=https://www.nationalgeographic.com/magazine/2019/05/leonardo-da-vinci-artistic-brilliance-endures-500-years-after-death/ |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190415142512/https://www.nationalgeographic.com/magazine/2019/05/leonardo-da-vinci-artistic-brilliance-endures-500-years-after-death/ |url-status=dead |archive-date=15 April 2019 |title=Why Leonardo da Vinci's brilliance endures, 500 years after his death |last=Kalb |first=Claudia |date=1 May 2019 |journal=] |access-date=21 August 2020 |url-access=subscription}}</ref> so the current condition is partly due to a variety of conservation treatments the painting has undergone. A detailed analysis in 1933 by Madame de Gironde revealed that earlier restorers had "acted with a great deal of restraint."<ref name="mohen" /> Nevertheless, applications of ] made to the painting had darkened even by the end of the 16th century, and an aggressive 1809 cleaning and revarnishing removed some of the uppermost portion of the paint layer, resulting in a washed-out appearance to the face of the figure. Despite the treatments, the ''Mona Lisa'' has been well cared for throughout its history, and although the panel's warping caused the curators "some worry",<ref>{{cite news |title=Ageing Mona Lisa worries Louvre |url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/entertainment/3660143.stm |date=26 April 2004 |work=BBC News |access-date=24 October 2009 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090816062240/http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/entertainment/3660143.stm |archive-date=16 August 2009}}</ref> the 2004–05 conservation team was optimistic about the future of the work.<ref name="mohen" /> | |||
| ===Poplar panel=== | |||
| In ], the lower part of the painting was severely damaged when someone doused it with acid. On ] of that same year, Ugo Ungaza Villegas, a young ], damaged the painting by throwing a rock at it. This resulted in the loss of a speck of pigment near the left elbow, which was later painted over. The painting is now covered with bulletproof security glass. | |||
| At some point, the ''Mona Lisa'' was removed from its original frame. The unconstrained poplar panel warped freely with changes in humidity, and as a result, a crack developed near the top of the panel, extending down to the hairline of the figure. In the mid-18th century to early 19th century, two ] walnut braces were inserted into the back of the panel to a depth of about one third the thickness of the panel. This intervention was skilfully executed, and successfully stabilized the crack. Sometime between 1888 and 1905, or perhaps during the picture's theft, the upper brace fell out. A later restorer glued and lined the resulting socket and crack with cloth.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Bramly|first=Serge|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=9uNHAAAACAAJ|title=Mona Lisa|date=1996|publisher=Thames and Hudson|isbn=978-0-500-23717-5|language=en}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book|last=Sassoon|first=Donald|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Nc7rAAAACAAJ|title=Leonardo and the Mona Lisa Story: The History of a Painting Told in Pictures|date=2006|publisher=Allen & Unwin|isbn=978-1-74114-902-9|language=en}}</ref> The picture is kept under strict, climate-controlled conditions in its bulletproof glass case. The humidity is maintained at 50% ±10%, and the temperature is maintained between {{convert|18|C|F}} and {{convert|21|C|F}}. To compensate for fluctuations in relative humidity, the case is supplemented with a bed of ] treated to provide 55% relative humidity.<ref name="mohen" /> | |||
| == |
===Frame=== | ||
| Because the ''Mona Lisa''{{'}}s poplar ] expands and contracts with changes in humidity, the picture has experienced some warping. In response to warping and swelling experienced during its storage during World War II, and to prepare the picture for an exhibit to honour the anniversary of Leonardo's 500th birthday, the ''Mona Lisa'' was fitted in 1951 with a flexible oak frame with beech ]. This flexible frame, which is used in addition to the decorative frame, exerts pressure on the panel to keep it from warping further. In 1970, the beech crosspieces were switched to maple after it was found that the ] had been infested with insects. In 2004–05, a conservation and study team replaced the maple crosspieces with sycamore ones, and an additional metal crosspiece was added for scientific measurement of the panel's warp.{{citation needed|date=November 2016}} The ''Mona Lisa'' has had many different decorative frames in its history. In 1909, the art collector ] gave the portrait its current frame,<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.pastellists.com/Collectors.htm |title=Biographical index of collectors of pastels |publisher=Pastellists.com |access-date=3 June 2013 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130615060320/http://www.pastellists.com/Collectors.htm |archive-date=15 June 2013}}</ref> a Renaissance-era work consistent with the historical period of the ''Mona Lisa''. The edges of the painting have been trimmed at least once in its history to fit the picture into various frames, albeit no part of the original paint layer has been trimmed.<ref name="mohen" /> | |||
| ], Mrs. Malraux, ] French Minister of Culture, ], and ] with ''Mona Lisa'' at the ] in the United States]] | |||
| ''Mona Lisa'' was used as an instrument of ].<ref name=BBC-Faces /> From ] ] to March of ], the French government lent the painting to the ] to be displayed at the ] in ] and the ] in ]. In ], the painting was exhibited at the ] in ], ], and the ] in ], ]. About 3.6 million visitors viewed the ''Mona Lisa'' during its travels outside France.<ref>{{cite web|author=|title=Treasures of the World: Mona Lisa Timeline|url=http://www.pbs.org/treasuresoftheworld/mona_lisa/mlevel_1/mtimeline.html|publisher=Stoner Productions via Public Broadcasting Service (PBS)|date=1999|accessdate=2007-10-05}}</ref> | |||
| ===Cleaning and touch-up=== | |||
| ==Value== | |||
| The first and most extensive recorded cleaning, revarnishing, and touch-up of the ''Mona Lisa'' was an 1809 wash and revarnishing undertaken by Jean-Marie Hooghstoel, who was responsible for the restoration of paintings for the galleries of the ]. The work involved cleaning with spirits, touch-ups of colour, and revarnishing the painting. In 1906, Louvre restorer Eugène Denizard performed watercolour retouches on areas of the paint layer disturbed by the crack in the panel. Denizard also retouched the edges of the picture with varnish to mask areas that had been covered initially by an older frame. In 1913, when the painting was recovered after its theft, Denizard was again called upon to work on the ''Mona Lisa''. Denizard was directed to clean the picture without ] and to lightly touch up several scratches on the painting with watercolour. In 1952, the varnish layer over the background in the painting was evened out. After the second 1956 attack, restorer Jean-Gabriel Goulinat was directed to touch up the damage to ''Mona Lisa''{{'}}s left elbow with watercolour.<ref name="mohen" /> In 1977, a new insect infestation was discovered in the back of the panel as a result of crosspieces installed to keep the painting from warping. This was treated on the spot with ], and later with an ] treatment. In 1985, the spot was again treated with carbon tetrachloride as a preventive measure.<ref name="mohen" /> | |||
| Prior to the 1962–1963 tour, the painting was assessed for insurance purposes at $100 million. According to the '']'', this makes the ''Mona Lisa'' the most valuable painting ever insured. As an ], it has only recently been surpassed (in terms of actual dollar price) by three other paintings, the '']'' by ], which was sold for $135 million (£73 million), the '']'' by ] sold for $137.5 million in November of 2006, and most recently '']'' by ] sold for a record $140 million on ], 2006. Although these figures are greater than that which the ''Mona Lisa'' was insured for, the comparison does not account for the change in prices due to inflation -- $100 million in 1962 is approximately $670 million in 2006 when adjusted for inflation using the US Consumer Price Index.<ref>E.H. Net. Accessed on June 20, 2006.</ref> | |||
| == |
===Display=== | ||
| On 6 April 2005—following a period of curatorial maintenance, recording, and analysis—the painting was moved to a new location within the museum's Salle des États. It is displayed in a purpose-built, climate-controlled enclosure behind bulletproof glass.<ref>{{cite news|access-date=27 April 2008 |url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/entertainment/arts/4413303.stm |title=Mona Lisa gains new Louvre home |publisher=BBC |date=6 April 2005 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080201011609/http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/entertainment/arts/4413303.stm |archive-date=1 February 2008}}</ref> Since 2005, the painting has been illuminated by an ], and a new 20-watt LED lamp that was specially designed for this painting was installed in 2013. The lamp has a ] of up to 98 and minimizes ] and ] radiation, which could otherwise degrade the painting.<ref>Fontoynont, Marc et al. " {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140308035208/http://www.sbi.dk/indeklima/lys/ny-lampe-til-mona-lisa/Microsoft%20Word%20-%2013-06-2%20Publication-Joconde-ENGLISH%20-MF.docx.pdf |date=8 March 2014}}" {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140829194442/http://www.sbi.dk/indeklima/lys/ny-lampe-til-mona-lisa/Microsoft%20Word%20-%2013-03-Joconde-Summary%20docx%20-2.pdf |date=29 August 2014}}. ] / ], June 2013.</ref> The renovation of the gallery where the painting now resides was financed by the Japanese broadcaster ].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.ntv.co.jp/english/an/06pr/05/20050406.html |title=Nippon Television Network Corporation |publisher=Ntv.co.jp |date=6 April 2005 |access-date=21 November 2010 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20101008134129/http://www.ntv.co.jp/english/an/06pr/05/20050406.html |archive-date=8 October 2010}}</ref> As of 2019, about 10.2 million people view the painting at the Louvre each year.<ref>{{cite news |title=Mona Lisa fans decry brief encounter with their idol in Paris |url=https://www.theguardian.com/world/2019/aug/13/mona-lisa-fans-face-scandalous-queues-after-portrait-relocated |access-date=24 August 2020 |work=The Guardian |date=13 August 2019 |issn=1756-3224}}</ref> | |||
| ] 2005. Visitors generally spend about 15 seconds viewing the ''Mona Lisa''.<ref>{{cite news|author=Gentleman, Amelia|title=Smile, please|url=http://arts.guardian.co.uk/features/story/0,,1330413,00.html|work=The Guardian|publisher=Guardian News and Media|date=] ]|accessdate=2007-10-13}}</ref>]] | |||
| Historian Donald Sassoon cataloged the growth of the painting's fame. During the mid-1800s, ] and the ] poets were able to write about ''Mona Lisa'' as a '']'' because Lisa was an ordinary person. ''Mona Lisa'' "...was an open text into which one could read what one wanted; probably because she was not a religious image; and, probably, because the literary gazers were mainly men who subjected her to an endless stream of male fantasies." During the 20th century, the painting was stolen, an object for mass reproduction, merchandising, lampooning and speculation, and was reproduced in "300 paintings and 2,000 advertisements".<ref name=Sassoon>{{cite journal|author=Sassoon, Donald |title=Mona Lisa: the Best-Known Girl in the Whole Wide World|journal=]|publisher=]|date=2001|volume=2001|issue=51|issn=1477-4569|pages=|url=http://hwj.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/content/abstract/2001/51/1|accessdate=2007-10-09}}</ref> The subject was described as deaf, in mourning,<ref>{{cite book|Littlefield, Walter|title=The Two "Mona Lisas"|publisher=The Century: A Popular Quarterly by Making of America Project via Google Books scan from University of Michigan copy|date=1914|pages=525|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=ux0MAAAAMAAJ&pg=PA525&vq=mona+lisa#PPA528,M1|accessdate=2007-10-09}}</ref> toothless, a "highly-paid tart", various people's lover, a reflection of the artist's neuroses, and a victim of syphilis, infection, paralysis, palsy, cholesterol or a toothache.<ref name=Sassoon /> Scholarly as well as amateur speculation assigned Lisa's name to at least four different paintings<ref>{{cite journal|author=Stites, Raymond S.|title=Mona Lisa--Monna Bella|url=http://links.jstor.org/sici?sici=1543-6314(193601)8%3A1%3C7%3AMLB%3E2.0.CO%3B2-5|journal=Parnassus|volume=8|issue=1|pages=7-10+22-23|publisher=College Art Association via JSTOR|date=January 1936|doi=10.2307/771197|accessdate=2007-10-06}} and {{cite book|Littlefield, Walter|title=The Two "Mona Lisas"|publisher=The Century: A Popular Quarterly by Making of America Project via Google Books scan from University of Michigan copy|date=1914|pages=525|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=ux0MAAAAMAAJ&pg=PA525&vq=mona+lisa#PPA528,M1|accessdate=2007-10-09}} and {{cite book|author=Wilson, Colin|title=The Mammoth Encyclopedia of the Unsolved|publisher=Carroll & Graf via Google Books limited preview|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=Mf7ujOGDzZ8C&pg=PA364|date=2000|pages=364–366|isbn=0-7867-0793-3}}</ref> and the sitter's identity to at least ten different people.<ref>{{cite news|author=Debelle, Penelope|title=Behind that secret smile|url=http://www.theage.com.au/articles/2004/06/24/1088046208817.html|work=The Age|publisher=The Age Company|date=]|accessdate=2007-10-06}} and {{cite news|author=Johnston, Bruce|title= Riddle of Mona Lisa is finally solved: she was the mother of five|work=Telegraph.co.uk|publisher=Telegraph Media Group|url=http://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/main.jhtml?xml=/news/2004/08/01/wmona01.xml&sSheet=/news/2004/08/01/ixworld.html|date=]|accessdate=2007-10-06}} and {{cite news|author=Nicholl, Charles (review of Mona Lisa: The History of the World's Most Famous Painting by Donald Sassoon)|title=The myth of the Mona Lisa|work=Guardian Unlimited|publisher=London Review of Books via Guardian News and Media|url=http://books.guardian.co.uk/lrb/articles/0,6109,675653,00.html|date=]|accessdate=2007-10-06}} and {{cite news|author=Chaundy, Bob|title=Faces of the Week|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/uk_news/magazine/5392000.stm|work=BBC News|publisher=BBC|date=]|accessdate=2007-10-05}}</ref> | |||
| On the 500th anniversary of the master's death, the Louvre held the largest ever single exhibit of Leonardo's works from 24 October 2019 to 24 February 2020. The ''Mona Lisa'' was not included because it is in such great demand among visitors to the museum; the painting remained on display in its gallery.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://aleteia.org/2019/12/01/louvre-exhibit-has-most-da-vinci-paintings-ever-assembled/ |title=Leonardo da Vinci's Unexamined Life as a Painter |date=1 December 2019 |publisher=The Atlantic |access-date=1 December 2019}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.theatlantic.com/entertainment/archive/2019/12/leonardo-da-vinci-louvre-museum-his-life-painter/602800/ |title=Louvre exhibit has most da Vinci paintings ever assembled |date=1 December 2019 |publisher=Aleteia |access-date=1 December 2019}}</ref> In 2024, it was decided to place the panel in a separate room. This change will require significant construction changes, including a new entrance to the Louvre and two rooms in the basement under the museum's square courtyard. Due to the renovation, visitors will be able to pass directly to the painting, which will reduce queues at the ].<ref>{{cite web |title="Моне Лизе" обещают свою комнату. В Лувре считают, что полотно "плохо расположено" |date=25 April 2024 |url=https://ru.euronews.com/culture/2024/04/25/culture-louvre-to-give-disappointing |accessdate=7 May 2024 |publisher=ru.euronews.com |lang=ru}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.npr.org/2024/04/28/1247666904/louvre-museum-mona-lisa-renovations-paris-olympics |title=The Louvre Museum looks to rehouse the 'Mona Lisa' in its own room — underground |first=Chloe |last=Veltman |website=] |date=28 April 2024 |access-date=22 August 2024}}</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| Until the 20th century, ''Mona Lisa'' was one among many and certainly not the "most famous painting"<ref>{{cite news|author=Riding, Alan|title=In Louvre, New Room With View of 'Mona Lisa'|url=http://www.nytimes.com/2005/04/06/arts/design/06lisa.html|work=The New York Times|publisher=The New York Times Company|date=]|accessdate=2007-10-07}}</ref> in the world as it is termed today. Among works in the Louvre, in 1852 its market value was 90,000 francs compared to works by Raphael valued at up to 600,000 francs. In 1878, the ] guide called it "the most celebrated work of Leonardo in the Louvre". Between 1851 and 1880, artists who visited the Louvre copied ''Mona Lisa'' roughly half as many times as certain works by ], ], ], ], ] and ].<ref name=Sassoon /> | |||
| ==Legacy== | |||
| == References in art == | |||
| {{See also|Mona Lisa replicas and reinterpretations}} | |||
| The ] art world has also taken note of the undeniable fact of the ''Mona Lisa's'' popularity. Because of the painting's overwhelming stature, ]ists and ] often produce modifications and ]s. In ], ], one of the most influential Dadaists, made a ''Mona Lisa'' ] by adorning a cheap reproduction with a moustache and a goatee, as well as adding the rude inscription L.H.O.O.Q., when read out loud in ] sounds like "Elle a chaud au cul" (translating to "she has a hot arse" as a manner of implying the woman in the painting is in a state of sexual excitement and availability). This was intended as a Freudian joke, referring to Leonardo's alleged ]. According to Rhonda R. Shearer, the apparent reproduction is in fact a copy partly modelled on Duchamp's own face.<ref name="asrl">{{Cite web|url=http://www.artscienceresearchlab.org/articles/panorama.htm|title=Mona Lisa: Who is Hidden Behind the Woman with the Mustache?|accessyear=2007|accessmonthday=September 15|publisher=Art Science Research Laboratory|year=2003|author=Marco De Marting - Translated by Camillo Olivetti|language=English}}</ref> ], famous for his pioneering surrealist work, painted ''Self portrait as Mona Lisa'' in ]. | |||
| The ''Mona Lisa'' began influencing contemporary ] even before its completion. ], who had been to Leonardo's workshop several times, promptly used elements of the portrait's composition and format in several of his works, such as '']'' ({{Circa|1506}}),<ref>Zollner gives a date of c. 1504, most others say c. 1506</ref> and '']'' ({{Circa|1506}}).<ref name="Reynal" /> Later paintings by Raphael, such as {{lang|it|]}} (1515–16) and '']'' ({{Circa|1514–15}}), continued to borrow from Leonardo's painting. Zollner states that "None of Leonardo's works would exert more influence upon the evolution of the genre than the ''Mona Lisa''. It became the definitive example of the Renaissance portrait and perhaps for this reason is seen not just as the likeness of a real person, but also as the embodiment of an ideal."<ref>{{cite book|page=161|title=Leonardo Da Vinci, 1452–1519|author-link=Frank Zöllner|last=Zöllner|first=Frank}}</ref> | |||
| Where earlier critics such as ] in the 16th century and ] in the 17th praised the picture for its ], by the mid-19th century, writers began to regard the ''Mona Lisa'' as imbued with a sense of mystery and ]. In 1859, ] wrote that the ''Mona Lisa'' was a "sphinx of beauty who smiles so mysteriously" and that "Beneath the form expressed one feels a thought that is vague, infinite, inexpressible. One is moved, troubled ... repressed desires, hopes that drive one to despair, stir painfully." ]'s essay of 1869 described the sitter as "older than the rocks among which she sits; like the vampire, she has been dead many times, and learned the secrets of the grave; and has been a diver in the deep seas, and keeps their fallen day about her."<ref>{{cite book|chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=1mCBiu2yFUgC&pg=PA214|title=Leonardo Da Vinci, Selected Scholarship: Leonardo's projects, c. 1500–1519|chapter=Mona Lisa|author=Clark, Kenneth|author-link=Kenneth Clark|editor=Farago, Claire J.|page=214 |isbn=978-0-8153-2935-0|year=1999|publisher=Taylor & Francis}}</ref> | |||
| In ], ]ist ] started making colorful ] prints of the ''Mona Lisa''. Warhol thus consecrated her as a modern icon, similar to ] or ]. At the same time, his use of a stencil process and crude colors implies a criticism of the debasement of aesthetic values in a society of mass production and mass consumption. | |||
| By the early 20th century, some critics started to feel the painting had become a repository for subjective ] and theories.<ref name="auto">{{cite news|url=https://www.theguardian.com/books/2002/mar/28/londonreviewofbooks |work=The Guardian |title=The myth of the Mona Lisa |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170710090649/https://www.theguardian.com/books/2002/mar/28/londonreviewofbooks |archive-date=10 July 2017 |date=28 March 2002|access-date=5 December 2024|issn=1756-3224}}</ref> Upon the painting's theft in 1911, Renaissance historian ] admitted that it had "simply become an incubus, and <!-- original: "I" --> was glad to be rid of her."<ref name="auto" /><ref>{{cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=fzdlbNBUsJsC&pg=PA215|page=215|title=Bernard Berenson, the Making of a Legend|isbn=978-0-674-06779-0|last1=Samuels |first1=Ernest|last2=Samuels|first2=Jayne|year=1987|publisher=Harvard University Press}}</ref> ]'s '']'' was exhibited at the 1911 ] and was sarcastically described as "la Joconde à la cuiller" (Mona Lisa with a spoon) by art critic ] on the front page of ].<ref name="Vauxcelles 1911">{{Cite web|url=https://gallica.bnf.fr/ark:/12148/bpt6k7536510d|title=Gil Blas / dir. A. Dumont|date=30 September 1911|website=Gallica}}</ref> ] subsequently described the painting as "The Mona Lisa of Cubism".<ref name="auto1">{{cite web|url=http://archive.org/details/lartvivant00salm|title=L'Art vivant|first=André|last=Salmon|date=15 September 1920|publisher=Paris : G. Crès|via=Internet Archive}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.philamuseum.org/collections/permanent/51056.html|title=Philadelphia Museum of Art – Collections Object : Tea Time (Woman with a Teaspoon)|website=www.philamuseum.org}}</ref> | |||
| A reproduction of the Mona Lisa was discovered painted onto a hillside near ] on August 15th, 2006. It was created by artist Samuel Clemens using a tarp stencil and water-based paint. <ref name="seattlepi">{{Cite web|url=http://seattlepi.nwsource.com/local/281739_monalisa18.html|title=Artist brings 'Mona Lisa' smile to an Oregon hillside|accessyear=2007|accessmonthday=September 15|publisher=Seattle Post Intelligencer|year=2006|author=Associated Press|language=English}}</ref> | |||
| The ] art world has made note of the ''Mona Lisa''{{'}}s undeniable popularity. Because of the painting's overwhelming stature, ]ists and ] often produce modifications and ]s. In 1883, ''Le rire,'' an image of a ''Mona Lisa'' smoking a pipe, by ] (Eugène Bataille), was shown at the "]" show in Paris. In 1919, ], one of the most influential modern artists, created '']'', a ''Mona Lisa'' parody made by adorning a cheap reproduction with a moustache and goatee.<ref name="Spector 1968"/><ref name="Dalí 1963"/> Duchamp added an inscription, which when read out loud in French sounds like "Elle a chaud au cul" (meaning "she has a hot ass"), implying the woman in the painting is in a state of sexual excitement and intended as a ].<ref>{{cite news |last=Jones |first=Jonathan |title=L.H.O.O.Q., Marcel Duchamp (1919) |work=The Guardian |date=26 May 2001 |url=https://www.theguardian.com/culture/2001/may/26/art |access-date=12 June 2009 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140509202948/http://www.theguardian.com/culture/2001/may/26/art |archive-date=9 May 2014|issn=1756-3224}}</ref> According to ], the apparent reproduction is in fact a copy partly modelled on Duchamp's own face.<ref name="asrl">{{cite web |url=http://www.artscienceresearchlab.org/articles/panorama.htm |title=Mona Lisa: Who is Hidden Behind the Woman with the Mustache? |access-date=27 April 2008 |publisher=Art Science Research Laboratory |year=2003 |author=Marting, Marco De |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080320203734/http://www.artscienceresearchlab.org/articles/panorama.htm |archive-date=20 March 2008}}</ref> | |||
| ==Theories and speculation== | |||
| ], famous for his surrealist work, painted ''Self portrait as Mona Lisa'' in 1954.<ref>{{cite web |author=Dalí, Salvador |title=Self Portrait as Mona Lisa |url=http://www.studiolo.org/Mona/MONA14.htm |publisher=Mona Lisa Images for a Modern World by Robert A. Baron (from the catalog of an exhibition at the Museum of Modern Art and the Philadelphia Museum of Art, 1973, p. 195) |access-date=24 October 2009 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20091028014015/http://www.studiolo.org/Mona/MONA14.htm |archive-date=28 October 2009}}</ref> ] created ] prints of multiple ''Mona Lisa''s, called ''Thirty Are Better than One'', following the painting's visit to the United States in 1963.<ref>{{cite book|author=Sassoon, Donald|title=Becoming Mona Lisa|page=251 |year=2003|publisher=Harvest Books via Amazon Search Inside|isbn=978-0-15-602711-3}}</ref> The French urban artist known pseudonymously as ] has created versions of the ''Mona Lisa'' on city walls in Paris and Tokyo using a mosaic style.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://metro.co.uk/2009/01/29/the-20000-rubiks-cube-mona-lisa-406655/ |title=The £20,000 Rubik's Cube Mona Lisa |work=Metro |date=29 January 2009 |access-date=18 July 2014 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140726093359/http://metro.co.uk/2009/01/29/the-20000-rubiks-cube-mona-lisa-406655/ |archive-date=26 July 2014}}</ref> A 2014 '']'' magazine cartoon parodies the supposed enigma of the ''Mona Lisa'' smile in an animation showing progressively more maniacal smiles.<ref>{{cite news |last=Schwartz |first=Benjamin |date=3 October 2014 |title=Daily Cartoon: Friday, October 3rd |url=https://www.newyorker.com/cartoons/daily-cartoon/daily-cartoon-friday-october-3rd |access-date=5 December 2024 |work=The New Yorker |issn=0028-792X}}</ref> | |||
| ===Columns and trimming=== | |||
| <gallery mode="packed" widths="200px" heights="200px" class="center"> | |||
| ], Baltimore]] | |||
| File:Raffael 046FXD.jpg|'']'' by ], {{Circa|1506}} | |||
| File:Baldassare Castiglione, by Raffaello Sanzio, from C2RMF retouched.jpg|'']'' by Raphael, {{Circa|1514–15}} | |||
| File:Sapeck-La Joconde fumant la pipe.jpg|''Le rire'' (''The Laugh'') by Eugène Bataille or Sapeck, 1883 | |||
| File:Jean Metzinger, Le goûter, Tea Time, 1911, 75.9 x 70.2 cm, Philadelphia Museum of Art.jpg|'']'' by ], 1911, ], 75.9 × 70.2 cm, ] | |||
| File:Marguerite Agniel as Mona Lisa by Robert Henri.jpg|''] "As Mona Lisa"'' by ], {{Circa|1929}} | |||
| </gallery> | |||
| ===Fame=== | |||
| It has for a long time been argued that after Leonardo's death the painting was cut down by having part of the panel at both sides removed. Early copies depict columns on both sides of the figure. Only the edges of the bases can be seen in the original.<ref name="vern">{{Cite web|url=http://www.kleio.org/monalisa/mlpics/787ae.htm|title=The Mona Lisa of the Vernon Collection is still showing the columns|accessyear=2007|accessmonthday=September 15|publisher=kleio.org|year=2007|author=Maike Vogt-Luerssen|language=English}}</ref><ref name="walt">{{Cite web|url=http://www.thewalters.org/wcontent/files/pages_new/mona_lisa.aspx|title=The Walters' Mona Lisa|accessyear=2007|accessmonthday=September 15|publisher=The Walters Art Museum|year=2007|author=The Walters Art Museum|language=English}}</ref> However, some art historians, such as ], now argue that the painting has not been altered, and that the columns depicted in the copies were added by the copyists. The latter view was bolstered during 2004 and 2005 when an international team of 39 specialists undertook the most thorough scientific examination of the ''Mona Lisa'' yet undertaken. Beneath the frame (the current one was fitted to the ''Mona Lisa'' in 2004) there was discovered a "reserve" around all four edges of the panel. A reserve is an area of bare wood surrounding the ] and painted portion of the panel. That this is a genuine reserve, and not the result of removal of the gesso or paint is demonstrated by a raised edge still existing around the gesso, the result of build up from the edge of brush strokes at the edge of the gesso area. | |||
| In the 21st century, the ''Mona Lisa'' is considered the most famous painting in the world, a ]. Until the 20th century, it was one among many highly regarded artworks.<ref name="riding">{{cite news|author=Riding, Alan|date=6 April 2005|title=In Louvre, New Room With View of 'Mona Lisa'|work=The New York Times|url=https://www.nytimes.com/2005/04/06/arts/design/06lisa.html|url-status=live|access-date=7 October 2007|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110625130936/http://www.nytimes.com/2005/04/06/arts/design/06lisa.html|archive-date=25 June 2011|issn=1553-8095}}</ref> Once part of ]'s collection, the ''Mona Lisa'' was among the first artworks to be exhibited in the Louvre, which became a national museum after the French Revolution. Leonardo began to be revered as a genius, and the painting's popularity grew in the mid-19th century when French intelligentsia praised it as mysterious and a representation of the ].<ref>{{cite web|last=Sassoon|first=Donald|title=Why is the Mona Lisa Famous?|url=http://podcast.blogs.latrobe.edu.au/2014/01/21/26-why-is-the-mona-lisa-famous/|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150704044849/http://www.latrobe.edu.au/marketing/assets/podcasts/2008/opinion-nov2808-audio.mp3|archive-date=4 July 2015|access-date=20 January 2014|publisher=La Trobe University Podcast}}</ref> The ] guide in 1878 called it "the most celebrated work of Leonardo in the Louvre",<ref name="Sassoon">{{cite journal|author=Sassoon, Donald|year=2001|title=Mona Lisa: the Best-Known Girl in the Whole Wide World|journal=]|edition=vol 2001|volume=2001|issue=51|page=1|doi=10.1093/hwj/2001.51.1|issn=1477-4569}}</ref> but the painting was known more by the ] than the general public.<ref name="npr2011">{{cite news|date=30 July 2011|title=The Theft That Made The 'Mona Lisa' A Masterpiece|language=en|work=All Things Considered|publisher=NPR|url=https://www.npr.org/2011/07/30/138800110/the-theft-that-made-the-mona-lisa-a-masterpiece|access-date=24 August 2020}}</ref> | |||
| The 1911 theft of the ''Mona Lisa'' and its subsequent return was reported worldwide, leading to a massive increase in public recognition of the painting. During the 20th century, it was an object for mass reproduction, merchandising, lampooning, and speculation, and was claimed to have been reproduced in "300 paintings and 2,000 advertisements".<ref name="Sassoon" /> The ''Mona Lisa'' was regarded as "just another Leonardo until early last century, when the scandal of the painting's theft from the Louvre and subsequent return kept a spotlight on it over several years."<ref>{{cite news|last=Gopnik|first=Blake|date=7 May 2004|title=A Record Picasso and the Hype Price of Status Objects|newspaper=The Washington Post|url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/archive/lifestyle/2004/05/07/a-record-picasso-and-the-hype-price-of-status-objects/91826269-6a9e-42a4-91e8-3ec3aed10510/|url-status=live|access-date=28 November 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161129023833/https://www.washingtonpost.com/archive/lifestyle/2004/05/07/a-record-picasso-and-the-hype-price-of-status-objects/91826269-6a9e-42a4-91e8-3ec3aed10510/|archive-date=29 November 2016}}</ref> | |||
| The reserve area, which was likely to have been as much as 20 mm originally appears to have been trimmed at some point probably to fit a frame (we know that in the 1906 framing it was the frame itself which was trimmed, not the picture, so it must have been earlier), however at no point has any of Leonardo's actual paint been trimmed. Therefore the columns in early copies must be inventions of those artists, or copies of another (unknown) studio version of ''Mona Lisa''. The round objects each side of the sill remain as mysterious as so much of this painting. | |||
| ], ], ], ], and ] at the unveiling of the ''Mona Lisa'' at the ] during its visit to Washington, D.C., 8 January 1963]] | |||
| ===Other versions=== | |||
| From December 1962 to March 1963, the French government lent it to the United States to be displayed in New York City and Washington, D.C.<ref>{{cite web|title=The Mona Lisa|url=https://www.metmuseum.org/pubs/bulletins/1/pdf/3257982.pdf.bannered.pdf|access-date=8 January 2018|publisher=]|archive-date=19 March 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180319165706/https://metmuseum.org/pubs/bulletins/1/pdf/3257982.pdf.bannered.pdf|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref name="Stolow1987">{{cite book|last=Stolow|first=Nathan|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=AwbGoXofgtYC|title=Conservation and exhibitions: packing, transport, storage, and environmental consideration|publisher=Butterworths|year=1987|isbn=978-0-408-01434-2|page=188|access-date=10 October 2010|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121005110125/http://books.google.com/books?id=AwbGoXofgtYC|archive-date=5 October 2012|url-status=live}}</ref> It was shipped on the new ocean liner ].<ref>{{cite web|date=4 February 2013|title=Today in Met History: February 4|url=https://www.metmuseum.org/blogs/now-at-the-met/features/2013/today-in-met-history-february-4|access-date=8 January 2018|publisher=]}}</ref> In New York, an estimated 1.7 million people queued "in order to cast a glance at the ''Mona Lisa'' for 20 seconds or so."<ref name="Sassoon" /> While exhibited in the ], the painting was nearly drenched in water because of a faulty sprinkler; the painting's bullet-proof glass case protected it.<ref>{{cite web|date=13 January 2013|title=Another art anniversary: Mona Lisa comes to New York! And she's almost drowned in a sprinkler malfunction|url=http://www.boweryboyshistory.com/2013/01/another-art-anniversary-mona-lisa-comes.html|access-date=8 January 2018|publisher=boweryboyshistory.com}}</ref> In 1974, the painting was exhibited in Tokyo and Moscow.<ref name="Bohm-Duchen2001">{{cite book|last=Bohm-Duchen|first=Monica|url=https://archive.org/details/isbn_9790520233781|title=The private life of a masterpiece|publisher=University of California Press|year=2001|isbn=978-0-520-23378-2|page=|access-date=10 October 2010|url-access=registration}}</ref> In 2014, 9.3 million people visited the Louvre.<ref>{{cite web|author=The French Ministry of Foreign affairs|title=The Louvre, the most visited museum in the world (01.15)|url=http://www.diplomatie.gouv.fr/en/french-foreign-policy/tourism/events/article/the-louvre-the-most-visited-museum|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151222074901/http://www.diplomatie.gouv.fr/en/french-foreign-policy/tourism/events/article/the-louvre-the-most-visited-museum|archive-date=22 December 2015|website=France Diplomatie :: Ministry of Foreign Affairs and International Development}}</ref> Former director ] reckoned that "80 percent of the people only want to see the ''Mona Lisa''."<ref>{{cite news|date=11 October 2009|title=On a Mission to Loosen Up the Louvre|url=https://www.nytimes.com/2009/10/11/arts/design/11voge.html|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161224172935/http://www.nytimes.com/2009/10/11/arts/design/11voge.html|archive-date=24 December 2016|work=The New York Times|access-date=5 December 2024|issn=1553-8095}}</ref> | |||
| ===Financial worth=== | |||
| It has been suggested that Leonardo created more than one version of the painting. The owners of the version known as the '']'' claim that it is an original, though the great majority of art historians believe it to be a later copy by an unknown artist. The same claim has been made for a version in the Vernon collection.<ref name="lair">{{Cite web|url=http://www.lairweb.org.nz/leonardo/mona.html |title=Mona Lisa|accessyear=2007|accessmonthday=September 15|publisher=Loadstar's Lair| year=2007|author=Loadstar's Lair|language=English}}</ref> Another version, dating from c.1616 was given in c.] to ] by the ] in exchange for a Reynolds self-portrait. Reynolds thought it to be the real painting and the French one a copy, which has now been disproved. It is, however, useful in that it was copied when the original's colors were far brighter than they are now, and so it gives some sense of the original's appearance 'as new'. It is in a private collection, but was exhibited in 2006 at the ].<ref name="guard">{{Cite web|url=http://arts.guardian.co.uk/news/story/0,,1879254,00.html|title=Unveiled: early copy that reveals Mona Lisa as her creator intended|accessyear=2007|accessmonthday=September 15|publisher=The Guardian Unlimited|year=2006|author=Charlotte Higgins|language=English}}</ref> There are also copies of the image in which the figure appears nude. These have also led to speculation that they were copied from a lost Leonardo original depicting Lisa naked.<ref name="nigel">{{Cite web|url=http://www.nigel-cawthorne.com/projects.htm|title=Mona Lisa Nude - Nigel Cawthorne.com|accessyear=2007|accessmonthday=September 15|publisher=Nigel Cawthorne.com|year=2002|author=Nigel Cawthorne.com|language=English}}</ref> | |||
| Before the 1962–1963 tour, the painting was assessed for insurance at $100 million (equivalent to {{nowrap|${{inflation|US-GDP|100|1962|r=-1|fmt=c}} million}} in {{inflation/year|US-GDP}}), making it, in practice, the ] in the world. The insurance was not purchased; instead, more was spent on security.<ref>{{cite book|title=The Guinness Book of World Records 1999|title-link=Guinness Book of World Records|publisher=Bantam Books|year=1999|isbn=978-0-553-58075-4|editor-last=Young|editor-first=Mark|page=381}}</ref> In 2014, a ] article suggested that the painting could be sold to help ease the national debt, although it was observed that the ''Mona Lisa'' and other such art works were prohibited from being sold by French heritage law, which states that, "Collections held in museums that belong to public bodies are considered public property and cannot be otherwise."<ref>{{cite web|date=2 September 2014|title=Culture – Could France sell the Mona Lisa to pay off its debts?|url=http://www.france24.com/en/20140902-could-france-sell-mona-lisa-pay-off-its-debts|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151130092248/http://www.france24.com/en/20140902-could-france-sell-mona-lisa-pay-off-its-debts|archive-date=30 November 2015|website=France 24}}</ref> | |||
| ===Cultural depictions=== | |||
| ] | |||
| Cultural depictions of the ''Mona Lisa'' include: | |||
| * The 1915 '']'' by German composer Max von Schillings. | |||
| * Two 1930s films written about the theft, ('']'' and '']''). | |||
| * The 1950 song "]" recorded by ]. | |||
| * The 1952 short story "The Smile" by Ray Bradbury, published in his 1959 collection '']'' | |||
| * The 1984 song "]" recorded by ]. | |||
| * The 2011 song "]" by American rock band ]. | |||
| * The 2018 song "]" by rapper ]. | |||
| * The 2022 mystery film '']'' depicts the destruction of the ''Mona Lisa'', which has been borrowed from its location by a billionaire. | |||
| * '']'' released a set called ''Mona Lisa 31213'' as part of their Lego Art theme. The set includes 1503 pieces to build it.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.lego.com/en-us/product/mona-lisa-31213|title=Mona Lisa 31213|publisher=Lego Art|website=Lego.com|access-date=22 August 2024}}</ref> | |||
| * During the ] the ''Mona Lisa'' got "stolen" by the ] from the ] museum and later ended up floating in the ] river waters.<ref> https://ge.globo.com/google/amp/olimpiadas/noticia/2024/07/26/olimpiadas-minions-aparecem-em-cerimonia-e-viralizam-nas-redes-assista.ghtml </ref> <ref> https://www.espn.com.br/olimpiadas/artigo/_/id/13956114/olimpiadas-cerimonia-abertura-minions-roubam-monalisa </ref> | |||
| ==Early versions and copies== | |||
| ===Smile=== | |||
| {{main|Mona Lisa replicas and reinterpretations}} | |||
| <!-- what are these images? Visual WP:OR? | |||
| {{multiple image | |||
| | align = right | |||
| | image1 = Mona lisa Prado PERSPECTIVA.jpg | |||
| | width1 = 150 | |||
| | caption1 = Perspective of ''Mona Lisa'', Museo del Prado | |||
| | image2 = Mona Lisa Louvre PERSPECTIVA.jpg | |||
| | width2 = 150 | |||
| | caption2 = Perspective of ''Mona Lisa'', Louvre | |||
| }} | |||
| --> | |||
| ===''Prado Museum La Gioconda''=== | |||
| ''Mona Lisa'''s smile has repeatedly been a subject of many - greatly varying - interpretations. ] interpreted the 'smile' as signifying Leonardo's erotic attraction to his mother.<ref name="virg">{{Cite web|url=http://www.people.virginia.edu/~djr4r/freud.html|title=Leonardo Da Vinci and a Memory of his Childhood|accessyear=2007|accessmonthday=September 15|publisher=Damian Judge Rollison - Department of English, University of Virginia|author=Sigmund Freud|language=English}}</ref> Others have described the smile as both innocent and inviting. | |||
| {{main|Mona Lisa (Prado's version)}} | |||
| Many researchers have tried to explain why the smile is seen so differently by people. The explanations range from scientific theories about human vision to curious supposition about ''Mona Lisa's'' identity and feelings. Professor Margaret Livingstone of ] has argued that the smile is mostly drawn in low ], and so can best be seen from a distance or with one's ].<ref name="bbc">{{Cite web|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/entertainment/2775817.stm|title=Mona Lisa smile secrets revealed|accessyear=2007|accessmonthday=September 15|publisher=BBC News|year=2003|author=BBC News|language=English}}</ref> Thus, for example, the smile appears more striking when looking at the portrait's eyes than when looking at the mouth itself. Christopher Tyler and Leonid Kontsevich of the ] in ] believe that the changing nature of the smile is caused by variable levels of random noise in human ].<ref name="ns1" /> Dina Goldin, Adjunct Professor at ], has argued that the secret is in the dynamic position of ''Mona Lisa's'' facial muscles, where our mind's eye unconsciously extends her smile; the result is an unusual dynamicity to the face that invokes subtle yet strong emotions in the viewer of the painting.<ref name="goldin">{{Cite web|url=http://www.cse.uconn.edu/~dqg/papers/monalisa.htm|title=Mona Lisa's Secret Revealed|accessyear=2007|accessmonthday=September 15|publisher=Brown University Faculty Bulletin|year=2002|author=Dina Q. Goldin|language=English}}</ref> | |||
| A version of ''Mona Lisa'' known as {{lang|es|Mujer de mano de Leonardo Abince}} ("Woman by Leonardo da Vinci's hand", ], Madrid) was for centuries considered to be a work by Leonardo. Since its restoration in 2012, it is now thought to have been executed by one of ] in his studio at the same time as ''Mona Lisa'' was being painted.<ref>{{cite web |title=La Gioconda, Leonardo's atelier |url=https://www.museodelprado.es/en/exhibitions/exhibitions/at-the-museum/instalacion-temporal-de-la-gioconda-copia/la-gioconda-del-museo-nacional-del-prado/ |website=Museo Nacional del Prado |access-date=7 December 2015 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151208204026/https://www.museodelprado.es/en/exhibitions/exhibitions/at-the-museum/instalacion-temporal-de-la-gioconda-copia/la-gioconda-del-museo-nacional-del-prado/ |archive-date=8 December 2015}}</ref> The Prado's conclusion that the painting is probably by ] (1480–1524) or by ] (1493–1572) has been called into question by others.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://monalisa.org/2012/09/11/prado/ |title=The 'Prado Mona Lisa' – The Mona Lisa Foundation |website=The Mona Lisa Foundation |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151217034527/http://monalisa.org/2012/09/11/prado/ |archive-date=17 December 2015 |date=11 September 2012 |access-date=11 December 2015}}</ref> The restored painting is from a slightly different perspective than the original ''Mona Lisa'', leading to the ] that it is part of the world's first ] pair;<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Carbon |first1=C. C. |last2=Hesslinger |first2=V. M. |title=Da Vinci's Mona Lisa Entering the Next Dimension |journal=Perception |date=August 2013 |volume=42 |issue=8 |pages=887–893 |pmid=24303752 |doi=10.1068/p7524 |doi-access=free}}</ref><ref> {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170207001407/http://www.experimental-psychology.de/ccc/material/SOM/CarbonHesslinger-Perception-MonaLisa3D/09-Transitions%20animated/MonaLisaLouvrePrado_AnimatedTransition.gif |date=7 February 2017}} by Carbon and Hesslinger</ref> however, a 2017 report demonstrated that this stereoscopic pair in fact gives no reliable stereoscopic depth.<ref>{{Cite journal |author=Brooks, K. R. |date=1 January 2017 |title=Depth Perception and the History of Three-Dimensional Art: Who Produced the First Stereoscopic Images? |journal=i-Perception |volume=8 |issue=1 |pages=204166951668011 |doi=10.1177/2041669516680114 |pmid=28203349 |pmc=5298491}}</ref> | |||
| In late 2005, Dutch researchers from the University of Amsterdam ran the painting's image through "emotion recognition" computer software developed in collaboration with the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. The technology demonstration found the smile to be 83% happy, 9% disgusted, 6% fearful, 2% angry, less than 1% neutral, and 0% surprised.<ref>{{cite web|title="Mona Lisa 'happy', computer finds"|publisher=BBC|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/entertainment/4530650.stm|accessdate=2007-08-27}}</ref><ref name="livescience">{{cite web|last=Sterling|first=Toby|publisher=Associated Press|accessdate=2007-08-17|url=http://www.livescience.com/history/ap_051215_mona_lisa.html|title="Mona LIsa Was 83 Percent Happy"|date=2007-12-27}} </ref> | |||
| ===''Isleworth Mona Lisa''=== | |||
| There are many speculations regarding Mona Lisa and Her smile, and many new artists tend to agree that the reason behind her smile is to be questioned. By looking at her eyes; before the smile, the thought that comes first, to many minds, is that her eyes hold a certain sadness, again which reason is left for discussion. However, this leads people to question whether her smile was of a positive reason, and it leads many critics to suggest more deeper reasoning into Mona Lisa and her smile. | |||
| {{main|Isleworth Mona Lisa}} | |||
| A version of the ''Mona Lisa'' known as the '']'' was first bought by an English nobleman in 1778 and was rediscovered in 1913 by ], an art connoisseur. The painting was presented to the media in 2012 by the Mona Lisa Foundation.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.independent.co.uk/arts-entertainment/art/news/early-mona-lisa-unveiling-the-oneinamillion-identical-twin-to-leonardo-da-vinci-painting-9926951.html |title='Early Mona Lisa': Unveiling the one-in-a-million identical twin to Leonardo da Vinci painting |first=Kunal |last=Dutta |website=] |date=15 December 2014 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141216084610/http://www.independent.co.uk/arts-entertainment/art/news/early-mona-lisa-unveiling-the-oneinamillion-identical-twin-to-leonardo-da-vinci-painting-9926951.html |archive-date=16 December 2014}}</ref> It is a painting of the same subject as Leonardo da Vinci's ''Mona Lisa''. The current scholarly consensus on attribution is unclear.<ref>{{cite news |last=Rosenbaum |first=Matthew |date=27 September 2012 |title=Second Mona Lisa Unveiled for First Time in 40 Years |work=] |publisher=ABC News Internet Ventures |access-date=12 June 2020 |url=https://abcnews.go.com/blogs/headlines/2012/09/second-mona-lisa-unveiled-for-first-time-in-40-years/}}</ref> Some experts, including ], ], and ] denied the attribution to Leonardo;<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.bbc.com/culture/story/20150216-a-second-mona-lisa |title=The Isleworth Mona Lisa: A second Leonardo masterpiece? |author=Alastair Sooke |publisher=BBC |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160102112800/http://www.bbc.com/culture/story/20150216-a-second-mona-lisa |archive-date=2 January 2016}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url= https://www.reuters.com/article/entertainment-us-art-monalisa-idUSBRE91C11H20130213 |title= New proof said found for "original" Mona Lisa – |publisher= Reuters.com |date= 13 February 2013 |access-date= 26 July 2017}}</ref> professors such as Salvatore Lorusso, Andrea Natali,<ref>{{cite journal|last1=Lorusso|first1=Salvatore|last2=Natali|first2=Andrea|date=January 2015|title=Mona Lisa: A Comparative Evaluation of the Different Versions and Their Copies|journal=]|volume=15|pages=80|doi=10.6092/issn.1973-9494/6168|url=https://conservation-science.unibo.it/article/view/6168/5936}}</ref> and John F Asmus supported it;<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Asmus |first1=John F.|date=1 July 1989 |title=Computer Studies of the Isleworth and Louvre Mona Lisas |url= http://opticalengineering.spiedigitallibrary.org/article.aspx?articleid=1223582 |journal= Optical Engineering |volume=28 |issue=7 |pages=800–804 |doi=10.1117/12.7977036 |bibcode=1989OptEn..28..800A |access-date= 26 July 2017}}</ref> others like ] and ] were uncertain.<ref>{{harvnb|Kemp|2018}}: "], who spoke at the launch in ], and ], the great Leonardo specialist, made encouraging but noncommittal statements about the picture being of high quality and worthy of further research."</ref> | |||
| ===Eyebrows and eyelashes=== | |||
| ===''Hermitage Mona Lisa''=== | |||
| One long-standing mystery of the painting is why Mona Lisa apparently does not have any eyebrows or eyelashes. In October 2007, Pascal Cotte, a French engineer and inventor, says that he discovered with a high-definition camera that Leonardo da Vinci originally did paint eyebrows and eyelashes. Creating an ultra-high resolution close-up that magified Mona Lisa's face 24 times, Cotte says he found a single brushstroke of a single hair above the left brow. "One day I say, if I can find only one hair, only one hair of the eyebrow, I will have definitively the proof that originally Leonardo da Vinci had painted eyelash and eyebrow," said Cotte. The engineer claims that other eyebrows that potentially could have appeared on the painting may have faded or been inadvertently erased by a poor attempt to clean the painting. In addition, Cotte says his work uncovered proof that her hands were originally painted in a slightly different position than in the final portrait. <ref>{{cite web|title="High resolution image hints at 'Mona Lisa's' eyebrows"|publisher=CNN|url=http://www.cnn.com/2007/US/10/17/monalisa.mystery/index.html}}</ref> | |||
| {{main|Mona Lisa (Hermitage)}} | |||
| A version known as the '']'' is in the ] and it was made by an unknown 16th-century artist.<ref>, hermitagemuseum.org.</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.arteworld.it/analisi-la-gioconda-di-leonardo-da-vinci/|title=La Gioconda (o Monna Lisa) di Leonardo da Vinci: analisi|first=Dario|last=Mastromattei|date=16 February 2016}}</ref> | |||
| <gallery mode="packed" widths="200px" heights="200px" class="center"> | |||
| ]''.]] | |||
| File:Mona Lisa (copy, Thalwil, Switzerland).JPG|Copy of ''Mona Lisa'' commonly attributed to ] | |||
| File:Gioconda (copia del Museo del Prado restaurada).jpg|The ''Prado Museum La Gioconda'' | |||
| File:Isleworthml.JPG|The '']'' | |||
| File:Mona Lisa (copy, Hermitage).jpg|'']'' | |||
| </gallery> | |||
| ==''Mona Lisa'' illusion== | |||
| ===Subject=== | |||
| If a person being photographed looks into the camera lens, the image produced provides an illusion that viewers perceive as the subject looking at them, irrespective of the photograph's position. It is presumably for this reason that many people, while taking photographs, ask subjects to look at the camera rather than anywhere else. In psychology, this is known as the "''Mona Lisa'' illusion", which was named after the famous painting that also presents the same illusion.<ref name="Horstmann_2019">{{cite journal |vauthors=Horstmann G, Loth S |title=The Mona Lisa Illusion-Scientists See Her Looking at Them Though She Isn't |journal=Iperception |volume=10 |issue=1 |pages= |date=2019 |doi=10.1177/2041669518821702 |url= |pmid=30671222 |pmc=6327345}}</ref> | |||
| ==See also== | |||
| Various alternatives to the traditional sitter have been proposed. During the last years of his life, Leonardo spoke of a portrait "of a certain Florentine lady done from life at the request of the magnificent ]." No evidence has been found that indicates a link between Lisa del Giocondo and Giuliano de' Medici, but then the comment could instead refer to one of the two other portraits of women executed by Leonardo. A later anonymous statement created confusion when it linked the ''Mona Lisa'' to a portrait of Francesco del Giocondo himself — perhaps the origin of the controversial idea that it is the portrait of a man. | |||
| {{portal|Painting}} | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| {{clear}} | |||
| ==Footnotes== | |||
| Dr. ] of ] suggests that the ''Mona Lisa'' is actually a self-portrait. She supports this theory with the results of a digital analysis of the facial features of Leonardo's face and that of the famous painting. When flipping a self-portrait drawing by Leonardo and then merging that with an image of the ''Mona Lisa'' using a computer, the features of the faces align perfectly.<ref></ref> Critics of this theory suggest that the similarities are due to both portraits being painted by the same person using the same style. Additionally, the drawing on which she based the comparison may not be a self-portrait. | |||
| {{notelist}} | |||
| ], in his biography of Leonardo, discusses the possibility that the portrait depicts the artist's mother Caterina. This would account for the resemblance between artist and subject observed by Dr. Schwartz, and would explain why Leonardo kept the portrait with him wherever he traveled, until his death. | |||
| ==References== | |||
| ] ]] | |||
| {{reflist|30em}} | |||
| Art historians have also suggested the possibility that the ''Mona Lisa'' may only resemble Leonardo by accident: as an artist with a great interest in the human form, Leonardo would have spent a great deal of time studying and drawing the human face, and the face most often accessible to him was his own, making it likely that he would have the most experience with drawing his own features. The similarity in the features of the people depicted in paintings such as the ''Mona Lisa'' and ''St. John the Baptist'' may thus result from Leonardo's familiarity with his own facial features, causing him to draw other, less familiar faces in a similar light. | |||
| ==Sources== | |||
| The art expert Dr. Henry Pulitzer suggested that the portrait was possibly that of ], duchess of ], a patroness of Leonardo, and mistress of Giuliano de Medici. D'Avalos, coincidentally, was also nicknamed 'La Gioconda'.<ref name="pol">{{Cite web|url=http://www.politicaonline.net/forum/showthread.php?t=45653|title= La Gioconda Di Leonardo Da Vinci (1452-1510)|accessyear=2007|accessmonthday=September 15|publisher=Politica Online Forums|year=2003|author=Politica Online Forum Moderator|language=Italian}}</ref> | |||
| {{refbegin}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Bartz |first1=Gabriele |last2=König |first2=Eberhard |title=Art and Architecture, Louvre |year=2001 |publisher=] |location=New York |isbn=978-0-7607-2577-1 |url={{google books|plainurl=y|id=A37g3x3cXOgC}} }} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Bohm-Duchen |first=Monica |year=2001 |title=The Private Life of a Masterpiece |publisher=] |location=Berkeley, California |isbn=978-0-520-23378-2 |url=https://archive.org/details/isbn_9790520233781 |url-access=registration }} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Chiesa |first=Angela Ottino della |year=1967 |title=The Complete Paintings of Leonardo da Vinci |series=Penguin Classics of World Art |publisher=] |location=London |isbn=978-0-14-008649-2}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Farago |first=Claire J. |year=1999 |title=Leonardo's Projects, c. 1500–1519 |publisher=] |location=Oxford |isbn=978-0-8153-2935-0 |url={{google books|plainurl=y|id=1mCBiu2yFUgC}} }} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Kemp |first=Martin |author-link=Martin Kemp (art historian) |year=2006 |title=Leonardo da Vinci: The Marvelous Works of Nature and Man |publisher=] |location=Oxford |isbn=978-0-19-280725-0 |url={{google books|plainurl=y|id=Vdu0ynmoRc8C}} }} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Kemp |first=Martin |author-link=Martin Kemp |year=2018 |title=Living with Leonardo: Fifty Years of Sanity and Insanity in the Art World and Beyond |publisher=] |location=London |isbn=978-0-500-77423-6 |url={{google books|plainurl=y|id=K99XDwAAQBAJ}} }} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Kemp |first=Martin |author-link=Martin Kemp (art historian) |year=2019 |title=Leonardo da Vinci: The 100 Milestones |publisher=] |location=New York |isbn=978-1-4549-304-26}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Marani |first=Pietro C. |year=2003 |orig-year=2000 |title=Leonardo da Vinci: The Complete Paintings |publisher=] |location=New York |isbn=978-0-8109-3581-5 }} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Turudich |first=Daniela |year=2003 |title=Plucked, Shaved & Braided: Medieval and Renaissance Beauty and Grooming Practices 1000–1600 |publisher=Streamline Press |location=North Branford, Connecticut |isbn=978-1-930064-08-9 |url={{google books|plainurl=y|id=moKItgAACAAJ}} }} | |||
| * {{cite book|last=Vasari |first=Giorgio |year=1879 |orig-year=1550 |title=Le vite de' più eccellenti pittori, scultori ed architettori |volume=4 |publisher=] |location=Florence |language=it |url={{google books|plainurl=y|id=EroFAAAAQAAJ}} }} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Wilson |first=Colin |author-link=Colin Wilson |year=2000 |title=The Mammoth Encyclopedia of the Unsolved |publisher=] |location=New York |isbn=978-0-7867-0793-5 |url=https://archive.org/details/isbn_9780786707935 |url-access=registration}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Woods-Marsden |first=Joanna |editor-last=Brown |editor-first=David Alan |year=2001 |title=Virtue & Beauty |pages=64–87 |contribution=Portrait of the Lady, 1430–1520 |contribution-url=https://inpress.lib.uiowa.edu/feminae/DetailsPage.aspx?Feminae_ID=7158 |place=London |publisher=Princeton University Press |isbn=978-0-691-09057-3}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Zöllner |first=Frank |author-link=Frank Zöllner |year=2015 |title=Leonardo |edition=2nd |publisher=] |location=Cologne |isbn=978-3-8365-0215-3}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Zöllner |first=Frank |author-link=Frank Zöllner |year=2019 |title=Leonardo da Vinci: The Complete Paintings and Drawings |edition=Anniversary |publisher=Taschen |location=Cologne |isbn=978-3-8365-7625-3}} | |||
| {{refend}} | |||
| ==Further reading== | |||
| Maike Vogt-Lüerssen argues that the woman behind the famous smile is ], the ]. Leonardo was the court painter for the Duke of Milan for 11 years. The pattern on ''Mona Lisa's'' dark green dress, Vogt-Lüerssen believes, indicates that she was a member of the ]. Her theory is that the ''Mona Lisa'' was the first official portrait of the new Duchess of Milan, which requires that it was painted in spring or summer ] (and not ]). This theory is allegedly supported by another portrait of Isabella of Aragon, painted by ], (Doria Pamphilj Gallery, ]). | |||
| * McMullen, Roy (1975). ''Mona Lisa: The Picture and the Myth''. Boston: Houghton Mifflin Company. | |||
| * Sassoon, Donald (2001). ''Becoming Mona Lisa: The Making of a Global Icon''. New York: Harcourt, Inc. | |||
| ==External links== | |||
| Historian Giuseppe Pallanti published ''Monna Lisa, Mulier Ingenua'' (''Mona Lisa: Real Woman'', published in English under the title ''Mona Lisa Revealed: The True Identity of Leonardo's Model'').<ref name="pallanti">{{cite book |author=Giuseppe Pallanti |title=Mona Lisa Revealed: The True Identity of Leonardo's Model |publisher=Skira |location=Geneve |year= |pages= |isbn=88-7624-659-2 |oclc= |doi=}}</ref> The book gathered archival evidence in support of the traditional identification of the model as Lisa. According to Pallanti, the evidence suggests that Leonardo's father was a friend of del Giocondo. "The portrait of ''Mona Lisa'', done when Lisa del Giocondo was aged about 24, was probably commissioned by Leonardo's father himself for his friends as he is known to have done on at least one other occasion."<ref name="teleg">{{Cite web|url=http://news.telegraph.co.uk/news/main.jhtml?xml=/news/2004/08/01/wmona01.xml|title= Riddle of Mona Lisa is finally solved: she was the mother of five|accessyear=2007|accessmonthday=September 15|publisher=Telegraph.co.uk|year=2004|author=Bruce Johnston|language=English}}</ref> <ref name="convent">{{Cite web|url=http://www.dominicantoday.com/app/article.aspx?id=21684|title='Mona Lisa' died in 1542, was buried in convent|accessyear=2007|accessmonthday=September 15|publisher=The Dominican Republic News|year=2007|author=Giuseppe Pallanti / Associated Press|language=English}}</ref> In 2007, genealogist Domenico Savini identified the princesses Natalia and Irina Strozzi as descendants of Lisa del Giocondo.<ref name="indep">{{Cite web|url=http://news.independent.co.uk/europe/article2192983.ece|title= The prince, the PM and the Mona Lisa|accessyear=2007|accessmonthday=September 15|publisher=The Independent|year=2007|author=Peter Popham|language=English}}</ref> Scan data obtained in 2004 suggested that the painting dated from around 1503 and commemorated the birth of the Giocondo's second son.<ref name="nrcc">{{Cite web|url=http://iit-iti.nrc-cnrc.gc.ca/projects-projets/monalisa-lajoconde_e.html|title=3D Examination of the Mona Lisa|accessyear=2007|accessmonthday=September 15|publisher=Nataional Research Council of Canada|year=2006|author=Nataional Research Council of Canada|language=English}}</ref><ref name="edmonton">{{Cite web|url=http://www.canada.com/edmontonjournal/news/story.html?id=45cc0dcc-7a3d-4256-8c67-2a4e5d1645d3&k=75720|title=Canadian researchers set to reveal Mona Lisa mysteries|accessyear=2007|accessmonthday=September 15|publisher=The Edmonton Journal|year=2006|author=Randy Boswell|language=English}}</ref> | |||
| {{Commons category|Mona Lisa}} | |||
| {{Wikiquote}} | |||
| * {{cite AV media|url=http://www.latrobe.edu.au/marketing/assets/podcasts/2008/opinion-nov2808-audio.mp3 |title=#26: Why is the ''Mona Lisa'' Famous? |date=21 January 2014 |first=Donald |last=Sassoon |publisher=] podcast blog |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150704044849/http://www.latrobe.edu.au/marketing/assets/podcasts/2008/opinion-nov2808-audio.mp3 |archive-date=4 July 2015 |url-status=live }} of the podcast audio. | |||
| * {{cite web |url=http://monalisa.org/the-earlier-version/ |title=''Mona Lisa'', Leonardo's Earlier Version |date=14 October 2012 |publisher=The Mona Lisa Foundation |location=Zürich, Switzerland |access-date=5 November 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150626203122/http://monalisa.org/the-earlier-version/ |archive-date=26 June 2015 |url-status=live}} | |||
| * {{cite press release |url=http://www.lumiere-technology.com/Pages/News/news3.htm |title=True Colors of the ''Mona Lisa'' Revealed |publisher=Lumiere Technology |location=Paris |date=19 October 2006 |access-date=5 November 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150626141217/http://www.lumiere-technology.com/Pages/News/news3.htm |archive-date=26 June 2015 |url-status=dead}} | |||
| * Compare layers of the painting as revealed by x-radiography, infrared reflectography and ultraviolet fluorescence | |||
| * . Dorothy & Thomas Hoobler. May 2009. excerpt of book. ''Vanity Fair'' | |||
| * Discussion by ] and ]: | |||
| * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141104113539/http://smarthistory.khanacademy.org/leonardo-mona-lisa.html |date=4 November 2014 }}, Smarthistory (video) | |||
| * , Discovery Channel documentary on YouTube | |||
| * . Xavier d'Hérouville & Aurore Caulier. December 2023. ''HAL Open Science'' | |||
| {{Mona Lisa}} | |||
| ===Other theories=== | |||
| {{Leonardo da Vinci}} | |||
| ''Mona Lisa'' certainly never belonged to the Giocondi, as Leonardo had it with him in France and it was sold to King ] there. Why Leonardo should have painted it remains unclear; it would have been an unusual portrait commission from a family such as the Giocondi at this date - most portraits of the "borghesia", even the ], were still much smaller and simpler. | |||
| {{High Renaissance}} | |||
| {{Louvre Museum}} | |||
| {{Portal bar|Painting|Visual arts}} | |||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| <noinclude> | |||
| == In popular culture == | |||
| ]''', '''How To Explain Great Art in The Age of Sports (Mona Lisa)''', 30 x 50”, Mixed Media on Canvas, Ed of 10.]] | |||
| The ''Mona Lisa'' has acquired an iconic status in ]. In "The Mountain Eaters", an episode of the British radio show '']'' broadcast on ] ], the character Neddy Seagoon signed an ] on the ''Mona Lisa''. Today the ''Mona Lisa'' is frequently reproduced, finding its way on to everything from carpets to mouse pads. | |||
| It has been a subject of many songs, including: | |||
| * '']'', a song from ] by ]. | |||
| * "Mona Lisa", the first track on ] singer ]'s ] album, '']''. The album rose to #1 on the ] Top Country Albums chart.<!-- Invalid reference<ref>Vitous, P., Pikora, V., Frantik, F., & Gololobov, M. (completion). (1999–2006). Retrieved on June 20, 2006.</ref>Invalid reference--> | |||
| * "]" was recorded by ] for his album ]. | |||
| * '']'' (ISBN 0-8362-1831-0) by ] features a ] version of the painting. | |||
| * "A Mona Lisa", an unreleased song by the ] ]. It was written by ] ] and recorded in ].<ref name="boot">{{Cite web|url=http://users.rcn.com/rfuss/ccboots1.html|title=Counting Crows bootleg guide|accessyear=2007|accessmonthday=September 15|publisher=Fuss, R. (compiler)|year=2002|author=Richard Fuss|language=English}}</ref> | |||
| * The 1995 "Mona Lisa And The Last Supper" is a song by ] encompassing two of Leonardo's most famous works. | |||
| * "]" is also a rare song by ]. | |||
| * ], directed by Mike Newell and featuring Julia Roberts, Kirsten Dunst, and Maggie Gyllenhaal, was released in 2003. | |||
| * Song by Wyclef Jean | |||
| * "Mona Lisa", a song by the ] music group ] suggests her smile is the result of the singer's hand underneath her skirt.<ref>Unheilig. (2003). . Official website. Retrieved on June 21, 2006. (Choose "Das 2. Gebot" under "LYRICS"). An audio sample can be heard at ASIN B00008K4EL</ref><ref>Unheilig. (2003). . Retrieved on June 21, 2006.</ref> | |||
| * Song by Chris Clouse. | |||
| In 1979 BBC TV series ] spoofed the painting's 1911 robbery in ], a storyline involving an alien forcing Leonardo to paint 6 extra copies of the Mona Lisa back in 1505. He then steals the original from the Louvre to sell to 7 different contemporary black market art collectors. | |||
| In the 1990 film ], an innocent first year student Clark Kellogg, played by ], is stunned to see the Mona Lisa hanging in the living room of his new employer, Carmine Sabatini, aka Jimmy The Toucan, played by ]. Carmine's daughter, Tina Sabatini, played by ], matter-of-factly states it to be the real one, and the one in Paris being a expert copy. | |||
| The ], ] edition of '']'' ran for its cover Dean Rohrer's Mona Monica,<ref name="newyorker">{{Cite web|url=http://www.studiolo.org/Mona/images/NewYorkerMonaMonicaA.jpg|title=New Yorker Cover image|accessyear=2007|accessmonthday=September 15|publisher=Robert A. Baron|author=Robert A. Baron|language=English}}</ref> an amalgamation of the ''Mona Lisa'' and ]. | |||
| In 2005, ], along with ], published '''' which features the Mona Lisa painting as a football play diagram -- and poses the question: "What if Art Lovers were as serious about art as sports fans are about sports?" | |||
| The painting plays a role in both the book and the movie versions of the fictional '']'' by ]. The novel says that the Mona Lisa is named so because it is an anagram of ], Egyptian god of male fertility, and L'Isa, the French name for ], Egyptian goddess of female fertility. | |||
| In the 1990s PBS game show '']'' Vic the Slick stole the Mona Lisa from the ]. | |||
| Parody and imitative versions of the Mona Lisa include a cow, gorilla, mouse, rabbit, and ] as Mona Lisa.<ref name="farside">{{Cite web|url=http://www.studiolo.org/Mona/MONASV07.htm|title=Mona Lisa Images for a Modern World - 7|accessyear=2007|accessmonthday=September 15|publisher=Robert A. Baron Arts Information Consultant|year=2007|author=Robert A. Baron|language=English}}</ref> | |||
| In the television show '']'', several episodes were named after the Mona Lisa, including "Moaning Lisa" and "Moe'N'a Lisa". | |||
| In the ] one artist used ] as a model for a rather busty--for Betty, anyway--version of the subject. | |||
| ''] Magazine'' ran an article suggesting how the ''Mona Lisa'' would look if modern cartoonists had drawn her: The high-cheekboned "Dragon Lady" of ]'s "Terry and the Pirates"; the macabre Morticia Addams of ]; the hatchet-faced Maggie of ]' "Bringing Up Father," etc. | |||
| The tabloid '']'' ran a Mona Lisa look-alike contest. A ''male'' entrant came in second. | |||
| == References == | |||
| {{reflist|2}} | |||
| <!-- READ ME!! PLEASE DO NOT JUST ADD NEW NOTES AT THE BOTTOM. See the instructions above on ordering. --> | |||
| == External links == | |||
| {{portal|Visual arts}} | |||
| {{Commonscat|Mona Lisa}} | |||
| *{{cite web|title=Portrait of Lisa Gherardini, wife of Francesco del Giocondo|url=http://www.louvre.fr/llv/oeuvres/detail_notice.jsp?CONTENT%3C%3Ecnt_id=10134198673226503&CURRENT_LLV_NOTICE%3C%3Ecnt_id=10134198673226503&amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;amp;FOLDER%3C%3Efolder_id=9852723696500816&bmUID=1155229237450&bmLocale=en|publisher=Musée du Louvre|accessdate=2007-10-04}} | |||
| * | |||
| * , a large Mona Lisa fan site | |||
| * , from the ] website for ''Treasures Of The World'' | |||
| * , an April 2004 ] article | |||
| * , another BBC article | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * , ''Cosmos'' magazine, September 2006 | |||
| * | |||
| {{Leonardo da Vinci}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| {{Link FA|es}} | |||
| ] | |||
| {{Link FA|pt}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| </noinclude> | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 19:41, 5 January 2025
Painting by Leonardo da Vinci This article is about the painting. For other uses, see Mona Lisa (disambiguation).
| Mona Lisa | |
|---|---|
| Italian: la Gioconda, Monna Lisa, French: la Joconde | |
 The Mona Lisa digitally retouched to reduce the effects of ageing; the original painting has darkened over time. The Mona Lisa digitally retouched to reduce the effects of ageing; the original painting has darkened over time. | |
| Artist | Leonardo da Vinci |
| Year | c. 1503–1506, perhaps continuing until c. 1517 |
| Medium | Oil on poplar panel |
| Subject | Lisa del Giocondo |
| Dimensions | 77 cm × 53 cm (30 in × 21 in) |
| Location | Louvre, Paris |
The Mona Lisa (/ˌmoʊnə ˈliːsə/ MOH-nə LEE-sə; Italian: la Gioconda [la dʒoˈkonda] or Monna Lisa [ˈmɔnna ˈliːza]; French: la Joconde [la ʒɔkɔ̃d]) is a half-length portrait painting by Italian artist Leonardo da Vinci. Considered an archetypal masterpiece of the Italian Renaissance, it has been described as "the best known, the most visited, the most written about, the most sung about, the most parodied work of art in the world." The painting's novel qualities include the subject's enigmatic expression, monumentality of the composition, the subtle modelling of forms, and the atmospheric illusionism.
The painting has been traditionally considered to depict the Italian noblewoman Lisa del Giocondo. It is painted in oil on a white poplar panel. Leonardo never gave the painting to the Giocondo family. It was believed to have been painted between 1503 and 1506; however, Leonardo may have continued working on it as late as 1517. King Francis I of France acquired the Mona Lisa after Leonardo's death in 1519, and it is now the property of the French Republic. It has normally been on display at the Louvre in Paris since 1797.
The painting's global fame and popularity partly stem from its 1911 theft by Vincenzo Peruggia, who attributed his actions to Italian patriotism—a belief it should belong to Italy. The theft and subsequent recovery in 1914 generated unprecedented publicity for an art theft, and led to the publication of many cultural depictions such as the 1915 opera Mona Lisa, two early 1930s films (The Theft of the Mona Lisa and Arsène Lupin), and the song "Mona Lisa" recorded by Nat King Cole—one of the most successful songs of the 1950s.
The Mona Lisa is one of the most valuable paintings in the world. It holds the Guinness World Record for the highest known painting insurance valuation in history at US$100 million in 1962, equivalent to $1 billion as of 2023.
Title and subject

The title of the painting, which is known in English as Mona Lisa, is based on the presumption that it depicts Lisa del Giocondo, although her likeness is uncertain. Renaissance art historian Giorgio Vasari wrote that "Leonardo undertook to paint, for Francesco del Giocondo, the portrait of Mona Lisa, his wife." Monna in Italian is a polite form of address originating as ma donna—similar to Ma'am, Madam, or my lady in English. This became madonna, and its contraction monna. The title of the painting is spelled in Italian as Monna Lisa (mona being a vulgarity in Italian), which is rare in English, where it is traditionally spelled Mona.
Lisa del Giocondo was a member of the Gherardini family of Florence and Tuscany, and the wife of wealthy Florentine silk merchant Francesco del Giocondo. The painting is thought to have been commissioned for their new home, and to celebrate the birth of their second son, Andrea. The Italian name for the painting, La Gioconda, means "jocund" ("happy" or "jovial"), or literally "the jocund one", a pun on the feminine form of Lisa's married name, Giocondo. In French, the title La Joconde has the same meaning. Vasari's account of the Mona Lisa comes from his biography of Leonardo published in 1550, 31 years after the artist's death. It has long been the best-known source of information on the provenance of the work and identity of the sitter. Leonardo's assistant Salaì, at his death in 1524, owned a portrait which in his personal papers was named la Gioconda, a painting bequeathed to him by Leonardo.
That Leonardo painted such a work, and its date, were confirmed in 2005 when a scholar at Heidelberg University discovered a marginal note in a 1477 printing of a volume by ancient Roman philosopher Cicero. Dated October 1503, the note was written by Leonardo's contemporary Agostino Vespucci. This note likens Leonardo to renowned Greek painter Apelles, who is mentioned in the text, and states that Leonardo was at that time working on a painting of Lisa del Giocondo. In response to the announcement of the discovery of this document, Vincent Delieuvin, the Louvre representative, stated "Leonardo da Vinci was painting, in 1503, the portrait of a Florentine lady by the name of Lisa del Giocondo. About this we are now certain. Unfortunately, we cannot be absolutely certain that this portrait of Lisa del Giocondo is the painting of the Louvre."
The catalogue raisonné Leonardo da Vinci (2019) confirms that the painting probably depicts Lisa del Giocondo, with Isabella d'Este being the only plausible alternative. Scholars have developed several alternative views, arguing that Lisa del Giocondo was the subject of a different portrait, and identifying at least four other paintings referred to by Vasari as the Mona Lisa. Several other people have been proposed as the subject of the painting, including Isabella of Aragon, Cecilia Gallerani, Costanza d'Avalos, Duchess of Francavilla, Pacifica Brandano/Brandino, Isabella Gualanda, Caterina Sforza, Bianca Giovanna Sforza, Salaì, and even Leonardo himself. Psychoanalyst Sigmund Freud theorized that Leonardo imparted an approving smile from his mother, Caterina, onto the Mona Lisa and other works like The Baptism of Christ, Virgin of the Rocks, and The Virgin and Child with Saint Anne.
Description

The Mona Lisa bears a strong resemblance to many Renaissance depictions of the Virgin Mary, who was at that time seen as an ideal for womanhood. The woman sits markedly upright in a pozzetto armchair with her arms folded, a sign of her reserved posture. Her gaze is fixed on the observer. The woman appears alive to an unusual extent, which Leonardo achieved by his method of not drawing outlines. The soft blending (sfumato) creates an ambiguous mood "mainly in two features: the corners of the mouth, and the corners of the eyes".
The depiction of the sitter in three-quarter profile is similar to late 15th-century works by Lorenzo di Credi and Agnolo di Domenico del Mazziere. Frank Zöllner notes that the sitter's general position can be traced back to Flemish models and that "in particular the vertical slices of columns at both sides of the panel had precedents in Flemish portraiture." Woods-Marsden cites Hans Memling's portrait of Benedetto Portinari (1487) or Italian imitations such as Sebastiano Mainardi's pendant portraits for the use of a loggia, which has the effect of mediating between the sitter and the distant landscape, a feature missing from Leonardo's earlier portrait of Ginevra de' Benci.

The painting was one of the first Italian portraits to depict the sitter in front of an imaginary landscape, although some scholars favour a realistic description, and Leonardo was one of the first painters to use aerial perspective. The enigmatic woman is portrayed seated in what appears to be an open loggia with dark pillar bases on either side. Behind her, a vast landscape recedes to icy mountains, winding paths and a distant bridge, giving only the slightest indications of human presence. Leonardo chose to place the horizon line not at the neck, as he did with Ginevra de' Benci, but on a level with the eyes, thus linking the figure with the landscape and emphasizing the mysterious nature of the painting. The bridge in the background was identified by Silvano Vincenti as the four-arched Romito di Laterina bridge from Etruscan-Roman times near Laterina, Arezzo, over the Arno river. Other bridges with similar arches suggested as possible locations had more arches. Some observers find similarities with the Azzone Visconti Bridge.
Mona Lisa has no clearly visible eyebrows or eyelashes, although Vasari describes the eyebrows in detail. In 2007, French engineer Pascal Cotte announced that his ultra-high resolution scans of the painting provide evidence that Mona Lisa was originally painted with eyelashes and eyebrows but that these had gradually disappeared over time, perhaps as a result of overcleaning. Cotte discovered that the painting had been reworked several times, with changes made to the size of the face and the direction of gaze. He also found that in one layer the subject was depicted wearing numerous hairpins and a headdress adorned with pearls which was later scrubbed out and overpainted.
There has been much speculation regarding the painting's sitter and landscape background. For example, Leonardo probably painted his sitter's appearance faithfully since her beauty is not seen as being among the best, "even when measured by late quattrocento (15th century) or even twenty-first century standards." Some historians in Eastern art, such as Yukio Yashiro, argue that the landscape in the background of the picture was influenced by Chinese paintings; this thesis has been contested for lack of clear evidence.
Research in 2003 by Professor Margaret Livingstone of Harvard University said that Mona Lisa's smile disappears when observed with direct vision, known as foveal. Because of the way the human eye processes visual information, it is less suited to pick up shadows directly; however, peripheral vision can pick up shadows well. Research in 2008 by a geomorphology professor at Urbino University and an artist-photographer revealed that Mona Lisa's landscape was similar to some views in the Montefeltro region in the Italian provinces of Pesaro and Urbino, and Rimini. Research in 2023/2024 by geologist and art historian Ann Pizzorusso suggests that the landscape contains "several recognisable features of Lecco, on the shores of Lake Como in the Lombardy region of northern Italy."
History
Creation and date
Of Leonardo da Vinci's works, the Mona Lisa is the only portrait whose authenticity has never been seriously questioned, and one of four works—the others being Saint Jerome in the Wilderness, Adoration of the Magi and The Last Supper—whose attribution has avoided controversy. He had begun working on a portrait of Lisa del Giocondo, the sitter for the Mona Lisa, by October 1503. It is believed by some that the Mona Lisa was begun in 1503 or 1504 in Florence. Although the Louvre states that it was "doubtless painted between 1503 and 1506", art historian Martin Kemp says that there are some difficulties in confirming the dates with certainty. Alessandro Vezzosi believes that the painting is characteristic of Leonardo's style in the final years of his life, post-1513. Other academics argue that, given the historical documentation, Leonardo would have painted the work from 1513. According to Vasari, "after he had lingered over it four years, left it unfinished". In 1516, Leonardo was invited by King Francis I to work at the Clos Lucé near the Château d'Amboise; it is believed that he took the Mona Lisa with him and continued to work on it after he moved to France. Art historian Carmen C. Bambach has concluded that Leonardo probably continued refining the work until 1516 or 1517. Leonardo's right hand was paralytic c. 1517, which may indicate why he left the Mona Lisa unfinished.
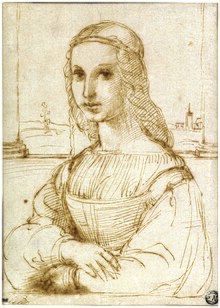
Circa 1505, Raphael executed a pen-and-ink sketch, in which the columns flanking the subject are more apparent. Experts universally agree that it is based on Leonardo's portrait. Other later copies of the Mona Lisa, such as those in the National Museum of Art, Architecture and Design and The Walters Art Museum, also display large flanking columns. As a result, it was thought that the Mona Lisa had been trimmed. By 1993, Frank Zöllner observed that the painting surface had never been trimmed; this was confirmed through a series of tests in 2004. In view of this, Vincent Delieuvin, curator of 16th-century Italian painting at the Louvre, states that the sketch and these other copies must have been inspired by another version, while Zöllner states that the sketch may be after another Leonardo portrait of the same subject.
The record of an October 1517 visit by Louis d'Aragon states that the Mona Lisa was executed for the deceased Giuliano de' Medici, Leonardo's steward at Belvedere, Vienna, between 1513 and 1516; this was likely an error. According to Vasari, the painting was created for the sitter's husband, Francesco del Giocondo. A number of experts have argued that Leonardo made two versions (because of the uncertainty concerning its dating and commissioner, as well as its fate following Leonardo's death in 1519, and the difference of details in Raphael's sketch—which may be explained by the possibility that he made the sketch from memory). The hypothetical first portrait, displaying prominent columns, would have been commissioned by Giocondo c. 1503, and left unfinished in Leonardo's pupil and assistant Salaì's possession until his death in 1524. The second, commissioned by Giuliano de' Medici c. 1513, would have been sold by Salaì to Francis I in 1518, and is the one in the Louvre today. Others believe that there was only one true Mona Lisa but are divided as to the two aforementioned fates. At some point in the 16th century, a varnish was applied to the painting. It was kept at the Palace of Fontainebleau until Louis XIV moved it to the Palace of Versailles, where it remained until the French Revolution. In 1797, it went on permanent display at the Louvre.
Refuge, theft, and vandalism

After the French Revolution, the painting was moved to the Louvre but spent a brief period in the bedroom of Napoleon (d. 1821) in the Tuileries Palace. Although the Mona Lisa was not widely known outside the art world, in the 1860s a portion of the French intelligentsia began to hail it as a masterwork of Renaissance painting. During the Franco-Prussian War (1870–1871), the painting was moved from the Louvre to the Brest Arsenal.
In 1911, the painting was still not popular among the lay-public. On 21 August 1911, the painting was stolen from the Louvre. The painting was first reported missing the next day by painter Louis Béroud. After some confusion as to whether the painting was being photographed somewhere, the Louvre was closed for a week for investigation. French poet Guillaume Apollinaire came under suspicion and was arrested and imprisoned. Apollinaire implicated his friend Pablo Picasso, who was brought in for questioning. Both were later exonerated. The real culprit was Louvre employee Vincenzo Peruggia, who had helped construct the painting's glass case. He carried out the theft by entering the building during regular hours, hiding in a broom closet, and walking out with the painting hidden under his coat after the museum had closed.
 Vacant wall in the Louvre's Salon Carré after the painting was stolen in 1911
Vacant wall in the Louvre's Salon Carré after the painting was stolen in 1911 "La Joconde est Retrouvée" ("Mona Lisa is Found"), Le Petit Parisien, 13 December 1913
"La Joconde est Retrouvée" ("Mona Lisa is Found"), Le Petit Parisien, 13 December 1913 The Mona Lisa in the Uffizi Gallery in Florence, 1913. Museum director Giovanni Poggi (right) inspects the painting.
The Mona Lisa in the Uffizi Gallery in Florence, 1913. Museum director Giovanni Poggi (right) inspects the painting. Excelsior, "La Joconde est Revenue" ("The Mona Lisa has returned"), 1 January 1914
Excelsior, "La Joconde est Revenue" ("The Mona Lisa has returned"), 1 January 1914
Peruggia was an Italian patriot who believed that Leonardo's painting should have been returned to an Italian museum. Peruggia may have been motivated by an associate whose copies of the original would significantly rise in value after the painting's theft. After having kept the Mona Lisa in his apartment for two years, Peruggia grew impatient and was caught when he attempted to sell it to Giovanni Poggi, director of the Uffizi Gallery in Florence. It was exhibited in the Uffizi Gallery for over two weeks and returned to the Louvre on 4 January 1914. Peruggia served six months in prison for the crime and was hailed for his patriotism in Italy. A year after the theft, Saturday Evening Post journalist Karl Decker wrote that he met an alleged accomplice named Eduardo de Valfierno, who claimed to have masterminded the theft. Forger Yves Chaudron was to have created six copies of the painting to sell in the US while concealing the location of the original. Decker published this account of the theft in 1932.
During World War II, it was again removed from the Louvre and taken first to the Château d'Amboise, then to the Loc-Dieu Abbey and Château de Chambord, then finally to the Musée Ingres in Montauban. Since the 1990s, the painting has been temporarily moved to accommodate renovations to the Louvre on three occasions: between 1992 and 1995, from 2001 to 2005, and again in 2019. A new queuing system introduced in 2019 reduces the amount of time museum visitors have to wait in line to see the painting. After going through the queue, a group has about 30 seconds to see the painting.
On 30 December 1956, Bolivian Ugo Ungaza Villegas threw a rock at the Mona Lisa while it was on display at the Louvre. He did so with such force that it shattered the glass case and dislodged a speck of pigment near the left elbow. The painting was protected by glass because a few years earlier a man who claimed to be in love with the painting had cut it with a razor blade and tried to steal it. After this attack, Salvador Dalí wrote in 1963 an essay titled "Why they attack the Mona Lisa", referencing earlier Freud theories.
Since the 1956 attack, bulletproof glass has been used to shield the painting from any further attacks, and in all subsequent cases the painting was undamaged. On 21 April 1974, while the painting was on display at the Tokyo National Museum, a woman sprayed it with red paint as a protest against that museum's failure to provide access for disabled people. On 2 August 2009, a Russian woman, distraught over being denied French citizenship, threw a ceramic teacup purchased at the Louvre; the vessel shattered against the glass enclosure.
On 29 May 2022, a male activist, disguised as a woman in a wheelchair, threw cake at the protective glass covering the painting in an apparent attempt to raise awareness for climate change; the painting was not damaged. The man was arrested and placed in psychiatric care in the police headquarters, and an investigation was opened after the Louvre filed a complaint. On 28 January 2024, two attackers from the environmentalist group Riposte Alimentaire (Food Retaliation) threw soup at the painting's protective glass, demanding the right to "healthy and sustainable food" and criticizing the contemporary state of agriculture; the painting was not damaged.
Modern analysis
In the early 21st century, French scientist Pascal Cotte hypothesized a hidden portrait underneath the surface of the painting. He analysed the painting in the Louvre with reflective light technology beginning in 2004, and produced circumstantial evidence for his theory. Cotte admits that his investigation was carried out only in support of his hypotheses and should not be considered as definitive proof. The underlying portrait appears to be of a sitter looking to the side, and lacks flanking columns, but it does not fit with historical descriptions of the painting. Both Vasari and Gian Paolo Lomazzo describe the subject as smiling, unlike the subject in Cotte's supposed portrait. In 2020, Cotte published a study alleging that the painting has an underdrawing, transferred from a preparatory drawing via the spolvero technique.
Conservation

The Mona Lisa has survived for more than 500 years, and an international commission convened in 1952 noted that "the picture is in a remarkable state of preservation." It has never been fully restored, so the current condition is partly due to a variety of conservation treatments the painting has undergone. A detailed analysis in 1933 by Madame de Gironde revealed that earlier restorers had "acted with a great deal of restraint." Nevertheless, applications of varnish made to the painting had darkened even by the end of the 16th century, and an aggressive 1809 cleaning and revarnishing removed some of the uppermost portion of the paint layer, resulting in a washed-out appearance to the face of the figure. Despite the treatments, the Mona Lisa has been well cared for throughout its history, and although the panel's warping caused the curators "some worry", the 2004–05 conservation team was optimistic about the future of the work.
Poplar panel
At some point, the Mona Lisa was removed from its original frame. The unconstrained poplar panel warped freely with changes in humidity, and as a result, a crack developed near the top of the panel, extending down to the hairline of the figure. In the mid-18th century to early 19th century, two butterfly-shaped walnut braces were inserted into the back of the panel to a depth of about one third the thickness of the panel. This intervention was skilfully executed, and successfully stabilized the crack. Sometime between 1888 and 1905, or perhaps during the picture's theft, the upper brace fell out. A later restorer glued and lined the resulting socket and crack with cloth. The picture is kept under strict, climate-controlled conditions in its bulletproof glass case. The humidity is maintained at 50% ±10%, and the temperature is maintained between 18 °C (64 °F) and 21 °C (70 °F). To compensate for fluctuations in relative humidity, the case is supplemented with a bed of silica gel treated to provide 55% relative humidity.
Frame
Because the Mona Lisa's poplar support expands and contracts with changes in humidity, the picture has experienced some warping. In response to warping and swelling experienced during its storage during World War II, and to prepare the picture for an exhibit to honour the anniversary of Leonardo's 500th birthday, the Mona Lisa was fitted in 1951 with a flexible oak frame with beech crosspieces. This flexible frame, which is used in addition to the decorative frame, exerts pressure on the panel to keep it from warping further. In 1970, the beech crosspieces were switched to maple after it was found that the beechwood had been infested with insects. In 2004–05, a conservation and study team replaced the maple crosspieces with sycamore ones, and an additional metal crosspiece was added for scientific measurement of the panel's warp. The Mona Lisa has had many different decorative frames in its history. In 1909, the art collector Comtesse de Béhague gave the portrait its current frame, a Renaissance-era work consistent with the historical period of the Mona Lisa. The edges of the painting have been trimmed at least once in its history to fit the picture into various frames, albeit no part of the original paint layer has been trimmed.
Cleaning and touch-up
The first and most extensive recorded cleaning, revarnishing, and touch-up of the Mona Lisa was an 1809 wash and revarnishing undertaken by Jean-Marie Hooghstoel, who was responsible for the restoration of paintings for the galleries of the Musée Napoléon. The work involved cleaning with spirits, touch-ups of colour, and revarnishing the painting. In 1906, Louvre restorer Eugène Denizard performed watercolour retouches on areas of the paint layer disturbed by the crack in the panel. Denizard also retouched the edges of the picture with varnish to mask areas that had been covered initially by an older frame. In 1913, when the painting was recovered after its theft, Denizard was again called upon to work on the Mona Lisa. Denizard was directed to clean the picture without solvent and to lightly touch up several scratches on the painting with watercolour. In 1952, the varnish layer over the background in the painting was evened out. After the second 1956 attack, restorer Jean-Gabriel Goulinat was directed to touch up the damage to Mona Lisa's left elbow with watercolour. In 1977, a new insect infestation was discovered in the back of the panel as a result of crosspieces installed to keep the painting from warping. This was treated on the spot with carbon tetrachloride, and later with an ethylene oxide treatment. In 1985, the spot was again treated with carbon tetrachloride as a preventive measure.
Display
On 6 April 2005—following a period of curatorial maintenance, recording, and analysis—the painting was moved to a new location within the museum's Salle des États. It is displayed in a purpose-built, climate-controlled enclosure behind bulletproof glass. Since 2005, the painting has been illuminated by an LED lamp, and a new 20-watt LED lamp that was specially designed for this painting was installed in 2013. The lamp has a Colour Rendering Index of up to 98 and minimizes infrared and ultraviolet radiation, which could otherwise degrade the painting. The renovation of the gallery where the painting now resides was financed by the Japanese broadcaster Nippon Television. As of 2019, about 10.2 million people view the painting at the Louvre each year.
On the 500th anniversary of the master's death, the Louvre held the largest ever single exhibit of Leonardo's works from 24 October 2019 to 24 February 2020. The Mona Lisa was not included because it is in such great demand among visitors to the museum; the painting remained on display in its gallery. In 2024, it was decided to place the panel in a separate room. This change will require significant construction changes, including a new entrance to the Louvre and two rooms in the basement under the museum's square courtyard. Due to the renovation, visitors will be able to pass directly to the painting, which will reduce queues at the Louvre.
Legacy
See also: Mona Lisa replicas and reinterpretationsThe Mona Lisa began influencing contemporary Florentine painting even before its completion. Raphael, who had been to Leonardo's workshop several times, promptly used elements of the portrait's composition and format in several of his works, such as Young Woman with Unicorn (c. 1506), and Portrait of Maddalena Doni (c. 1506). Later paintings by Raphael, such as La velata (1515–16) and Portrait of Baldassare Castiglione (c. 1514–15), continued to borrow from Leonardo's painting. Zollner states that "None of Leonardo's works would exert more influence upon the evolution of the genre than the Mona Lisa. It became the definitive example of the Renaissance portrait and perhaps for this reason is seen not just as the likeness of a real person, but also as the embodiment of an ideal."
Where earlier critics such as Vasari in the 16th century and André Félibien in the 17th praised the picture for its realism, by the mid-19th century, writers began to regard the Mona Lisa as imbued with a sense of mystery and romance. In 1859, Théophile Gautier wrote that the Mona Lisa was a "sphinx of beauty who smiles so mysteriously" and that "Beneath the form expressed one feels a thought that is vague, infinite, inexpressible. One is moved, troubled ... repressed desires, hopes that drive one to despair, stir painfully." Walter Pater's essay of 1869 described the sitter as "older than the rocks among which she sits; like the vampire, she has been dead many times, and learned the secrets of the grave; and has been a diver in the deep seas, and keeps their fallen day about her."
By the early 20th century, some critics started to feel the painting had become a repository for subjective exegeses and theories. Upon the painting's theft in 1911, Renaissance historian Bernard Berenson admitted that it had "simply become an incubus, and was glad to be rid of her." Jean Metzinger's Le goûter (Tea Time) was exhibited at the 1911 Salon d'Automne and was sarcastically described as "la Joconde à la cuiller" (Mona Lisa with a spoon) by art critic Louis Vauxcelles on the front page of Gil Blas. André Salmon subsequently described the painting as "The Mona Lisa of Cubism".
The avant-garde art world has made note of the Mona Lisa's undeniable popularity. Because of the painting's overwhelming stature, Dadaists and Surrealists often produce modifications and caricatures. In 1883, Le rire, an image of a Mona Lisa smoking a pipe, by Sapeck (Eugène Bataille), was shown at the "Incoherents" show in Paris. In 1919, Marcel Duchamp, one of the most influential modern artists, created L.H.O.O.Q., a Mona Lisa parody made by adorning a cheap reproduction with a moustache and goatee. Duchamp added an inscription, which when read out loud in French sounds like "Elle a chaud au cul" (meaning "she has a hot ass"), implying the woman in the painting is in a state of sexual excitement and intended as a Freudian joke. According to Rhonda R. Shearer, the apparent reproduction is in fact a copy partly modelled on Duchamp's own face.
Salvador Dalí, famous for his surrealist work, painted Self portrait as Mona Lisa in 1954. Andy Warhol created serigraph prints of multiple Mona Lisas, called Thirty Are Better than One, following the painting's visit to the United States in 1963. The French urban artist known pseudonymously as Invader has created versions of the Mona Lisa on city walls in Paris and Tokyo using a mosaic style. A 2014 New Yorker magazine cartoon parodies the supposed enigma of the Mona Lisa smile in an animation showing progressively more maniacal smiles.
-
 Young Woman with Unicorn by Raphael, c. 1506
Young Woman with Unicorn by Raphael, c. 1506
-
 Portrait of Baldassare Castiglione by Raphael, c. 1514–15
Portrait of Baldassare Castiglione by Raphael, c. 1514–15
-
 Le rire (The Laugh) by Eugène Bataille or Sapeck, 1883
Le rire (The Laugh) by Eugène Bataille or Sapeck, 1883
-
 Le goûter (Tea Time) by Jean Metzinger, 1911, oil on canvas, 75.9 × 70.2 cm, Philadelphia Museum of Art
Le goûter (Tea Time) by Jean Metzinger, 1911, oil on canvas, 75.9 × 70.2 cm, Philadelphia Museum of Art
-
 Marguerite Agniel "As Mona Lisa" by Robert Henri, c. 1929
Marguerite Agniel "As Mona Lisa" by Robert Henri, c. 1929
Fame
In the 21st century, the Mona Lisa is considered the most famous painting in the world, a destination painting. Until the 20th century, it was one among many highly regarded artworks. Once part of King Francis I of France's collection, the Mona Lisa was among the first artworks to be exhibited in the Louvre, which became a national museum after the French Revolution. Leonardo began to be revered as a genius, and the painting's popularity grew in the mid-19th century when French intelligentsia praised it as mysterious and a representation of the femme fatale. The Baedeker guide in 1878 called it "the most celebrated work of Leonardo in the Louvre", but the painting was known more by the intelligentsia than the general public.
The 1911 theft of the Mona Lisa and its subsequent return was reported worldwide, leading to a massive increase in public recognition of the painting. During the 20th century, it was an object for mass reproduction, merchandising, lampooning, and speculation, and was claimed to have been reproduced in "300 paintings and 2,000 advertisements". The Mona Lisa was regarded as "just another Leonardo until early last century, when the scandal of the painting's theft from the Louvre and subsequent return kept a spotlight on it over several years."

From December 1962 to March 1963, the French government lent it to the United States to be displayed in New York City and Washington, D.C. It was shipped on the new ocean liner SS France. In New York, an estimated 1.7 million people queued "in order to cast a glance at the Mona Lisa for 20 seconds or so." While exhibited in the Metropolitan Museum of Art, the painting was nearly drenched in water because of a faulty sprinkler; the painting's bullet-proof glass case protected it. In 1974, the painting was exhibited in Tokyo and Moscow. In 2014, 9.3 million people visited the Louvre. Former director Henri Loyrette reckoned that "80 percent of the people only want to see the Mona Lisa."
Financial worth
Before the 1962–1963 tour, the painting was assessed for insurance at $100 million (equivalent to $770 million in 2023), making it, in practice, the most highly-valued painting in the world. The insurance was not purchased; instead, more was spent on security. In 2014, a France 24 article suggested that the painting could be sold to help ease the national debt, although it was observed that the Mona Lisa and other such art works were prohibited from being sold by French heritage law, which states that, "Collections held in museums that belong to public bodies are considered public property and cannot be otherwise."
Cultural depictions
Cultural depictions of the Mona Lisa include:
- The 1915 Mona Lisa by German composer Max von Schillings.
- Two 1930s films written about the theft, (The Theft of the Mona Lisa and Arsène Lupin).
- The 1950 song "Mona Lisa" recorded by Nat King Cole.
- The 1952 short story "The Smile" by Ray Bradbury, published in his 1959 collection A Medicine for Melancholy
- The 1984 song "Mona Lisa Lost Her Smile" recorded by David Allan Coe.
- The 2011 song "The Ballad of Mona Lisa" by American rock band Panic! at the Disco.
- The 2018 song "Mona Lisa" by rapper Lil Wayne.
- The 2022 mystery film Glass Onion: A Knives Out Mystery depicts the destruction of the Mona Lisa, which has been borrowed from its location by a billionaire.
- Lego released a set called Mona Lisa 31213 as part of their Lego Art theme. The set includes 1503 pieces to build it.
- During the 2024 Summer Olympics opening ceremony the Mona Lisa got "stolen" by the Minions from the Louvre museum and later ended up floating in the Seine river waters.
Early versions and copies
Main article: Mona Lisa replicas and reinterpretationsPrado Museum La Gioconda
Main article: Mona Lisa (Prado's version)A version of Mona Lisa known as Mujer de mano de Leonardo Abince ("Woman by Leonardo da Vinci's hand", Museo del Prado, Madrid) was for centuries considered to be a work by Leonardo. Since its restoration in 2012, it is now thought to have been executed by one of Leonardo's pupils in his studio at the same time as Mona Lisa was being painted. The Prado's conclusion that the painting is probably by Salaì (1480–1524) or by Melzi (1493–1572) has been called into question by others. The restored painting is from a slightly different perspective than the original Mona Lisa, leading to the speculation that it is part of the world's first stereoscopic pair; however, a 2017 report demonstrated that this stereoscopic pair in fact gives no reliable stereoscopic depth.
Isleworth Mona Lisa
Main article: Isleworth Mona LisaA version of the Mona Lisa known as the Isleworth Mona Lisa was first bought by an English nobleman in 1778 and was rediscovered in 1913 by Hugh Blaker, an art connoisseur. The painting was presented to the media in 2012 by the Mona Lisa Foundation. It is a painting of the same subject as Leonardo da Vinci's Mona Lisa. The current scholarly consensus on attribution is unclear. Some experts, including Frank Zöllner, Martin Kemp, and Luke Syson denied the attribution to Leonardo; professors such as Salvatore Lorusso, Andrea Natali, and John F Asmus supported it; others like Alessandro Vezzosi and Carlo Pedretti were uncertain.
Hermitage Mona Lisa
Main article: Mona Lisa (Hermitage)A version known as the Hermitage Mona Lisa is in the Hermitage Museum and it was made by an unknown 16th-century artist.
-
Copy of Mona Lisa commonly attributed to Salaì
-
 The Prado Museum La Gioconda
The Prado Museum La Gioconda
-
The Isleworth Mona Lisa
-
 Hermitage Mona Lisa
Hermitage Mona Lisa
Mona Lisa illusion
If a person being photographed looks into the camera lens, the image produced provides an illusion that viewers perceive as the subject looking at them, irrespective of the photograph's position. It is presumably for this reason that many people, while taking photographs, ask subjects to look at the camera rather than anywhere else. In psychology, this is known as the "Mona Lisa illusion", which was named after the famous painting that also presents the same illusion.
See also
- List of works by Leonardo da Vinci
- List of most expensive paintings
- List of stolen paintings
- Speculations about Mona Lisa
- Male Mona Lisa theories
- Two-Mona Lisa theory
Footnotes
- Some researchers argue that it was common at this time for genteel women to pluck these hairs, as they were considered unsightly.
- Leonardo, later in his life, is said to have regretted "never having completed a single work".
- "... Messer Lunardo Vinci [sic] ... showed His Excellency three pictures, one of a certain Florentine lady done from life at the instance of the late Magnificent, Giuliano de' Medici."
- "Possibly it was another portrait of which no record and no copies exist—Giuliano de' Medici surely had nothing to do with the Mona Lisa—the probability is that the secretary, overwhelmed as he must have been at the time, inadvertently dropped the Medici name in the wrong place."
- Along with The Virgin and Child with St. Anne and St. John the Baptist
References
- "The Mona Lisa's Twin Painting Discovered". All Things Considered. 2 February 2012. National Public Radio.
The original Mona Lisa in the Louvre is difficult to see—it's covered with layers of varnish, which has darkened over the decades and the centuries, and even cracked', Bailey says
- "Theft of the Mona Lisa". Treasures of the World. PBS.
time has aged and darkened her complexion.
- ^ Sassoon, Donald (2001). Mona Lisa: The History of the World's Most Famous Painting. HarperCollins. p. 10. ISBN 978-0-00-710614-1.
It is actually quite dirty, partly due to age and partly to the darkening of a varnish applied in the sixteenth century.
- "The Theft That Made Mona Lisa a Masterpiece". All Things Considered. 30 July 2011. NPR. Retrieved 15 February 2019.
- Sassoon, Donald (21 September 2001). "Why I think Mona Lisa became an icon". Times Higher Education.
- Lichfield, John (1 April 2005). "The Moving of the Mona Lisa". The Independent. London. Archived from the original on 9 November 2016.
- Cohen, Philip (23 June 2004). "Noisy secret of Mona Lisa's". New Scientist. Archived from the original on 23 April 2008. Retrieved 27 April 2008.
- ^ "Mona Lisa – Portrait of Lisa Gherardini, wife of Francesco del Giocondo". Louvre. Archived from the original on 30 July 2014. Retrieved 11 March 2012.
- "Mona Lisa – Heidelberger find clarifies identity". University Library Heidelberg. Archived from the original on 8 May 2011. Retrieved 15 January 2008.
- Uzielli, Luca; Gril, Joseph; Cocchi, Linda; Colmars, Julien; Dionisi Vici, Paolo; et al. (July 2011). Experimental studies on the wooden support of the "Mona Lisa". The Safeguard of Cultural Heritage. A Challenge From the Past for the Europe of Tomorrow. COST strategic workshop. Florence. p. 367. Retrieved 1 July 2024.
- "Was the 'Mona Lisa' Leonardo's Male Lover?". Artnet News. 22 April 2016. Retrieved 20 May 2021.
- ^ Carrier, David (2006). Museum Skepticism: A History of the Display of Art in Public Galleries. Duke University Press. p. 35. ISBN 978-0-8223-3694-5.
- ^ Charney, N.; Fincham, D.; Charney, U. (2011). The Thefts of the Mona Lisa: On Stealing the World's Most Famous Painting. Arca Publications. ISBN 978-0-615-51902-9. Retrieved 4 November 2022.
- "Highest insurance valuation for a painting". Guinness World Records. Retrieved 25 July 2017.
- "Value of 1962 US Dollars today – Inflation Calculator". www.inflationtool.com.
- "German experts crack the ID of 'Mona Lisa'". Today. Reuters. 14 January 2008. Retrieved 21 August 2020.
- Nizza, Mike (15 January 2008). "Mona Lisa's Identity, Solved for Good?". The New York Times. ISSN 1553-8095. Retrieved 15 January 2008.
- ^ Italian: Prese Lionardo a fare per Francesco del Giocondo il ritratto di monna Lisa sua moglie Vasari 1879, p. 39
- ^ Clark, Kenneth (March 1973). "Mona Lisa". The Burlington Magazine. 115 (840): 144–151. ISSN 0007-6287. JSTOR 877242.
- "Giorgio Vasari – Leonardo e la Gioconda". Libri antichi online (in Italian). 2021. Retrieved 15 November 2021.
- "Mona". Garzanti Linguistica. 2013. Retrieved 5 December 2024.
- "Mona – Parola, significato e traduzione". Dizionario Italiano online Hoepli (in Italian). 2018. Retrieved 5 December 2024.
- "Mona – Definizione significato". Collins Online Dictionary (in Italian). 2024. Retrieved 5 December 2024.
- ^ "Gioconda o Monna Lisa". Museo Leonardo Da Vinci Experience (in Italian). 2022. Retrieved 5 November 2024.
- ^ Kemp 2006, pp. 261–262
- Farago 1999, p. 123
- ^ Bartz & König 2001, p. 626.
- ^ Kemp, Martin; Pallanti, Giuseppe (2017). Mona Lisa: The people and the painting. Oxford: Oxford University Press. p. 113. ISBN 978-0-19-874990-5.
- ^ "Mona Lisa – Heidelberg discovery confirms identity". University of Heidelberg. Archived from the original on 5 November 2013. Retrieved 4 July 2010.
- ^ Delieuvin, Vincent (15 January 2008). "Télématin". Journal Télévisé. France 2 Télévision.
- Zöllner 2019, p. 241
- Stites, Raymond S. (January 1936). "Mona Lisa – Monna Bella". Parnassus. 8 (1): 7–10, 22–23. doi:10.2307/771197. ISSN 1543-6314. JSTOR 771197. S2CID 195050582.
- ^ Wilson 2000, pp. 364–366
- Debelle, Penelope (25 June 2004). "Behind that secret smile". The Age. Melbourne. Archived from the original on 25 November 2013. Retrieved 6 October 2007.
- Johnston, Bruce (8 January 2004). "Riddle of Mona Lisa is finally solved: she was the mother of five". The Daily Telegraph. London. Archived from the original on 11 October 2007. Retrieved 6 October 2007.
- Nicholl, Charles (28 March 2002). "The myth of the Mona Lisa". The Guardian. ISSN 1756-3224. Archived from the original on 5 September 2008. Retrieved 6 October 2007.
- ^ Chaundy, Bob (29 September 2006). "Faces of the Week". BBC. Archived from the original on 3 August 2014. Retrieved 5 October 2007.
- Kington, Tom (9 January 2011). "Mona Lisa backdrop depicts Italian town of Bobbio, claims art historian". The Guardian. ISSN 1756-3224. Retrieved 5 December 2024.
- ^ Spector, Jack (1 April 1968). "Freud and Ducham: The Mona Lisa 'Exposed'". Artforum. Retrieved 5 December 2024.
- ^ "Salvador Dalí on Why People Attack Leonardo's 'Mona Lisa,' in 1963: From the Archives". ARTnews.com. 23 October 2019. Retrieved 5 December 2024.
- Kobbé, Gustav (1916). "The Smile of the 'Mona Lisa'". The Lotus Magazine. 8 (2): 67–74. ISSN 2150-5977. JSTOR 20543781.
- Prisco, Salvatore (9 January 1987). "Opinion | Couldn't 'Mona Lisa' Just Stay a Mystery?". The New York Times. ISSN 1553-8095. Retrieved 10 July 2022.
- ^ Greenberger, Alex (23 October 2019). "Salvador Dalí on Why People Attack Leonardo's 'Mona Lisa,' in 1963: From the Archives". ARTnews. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
- ^ Zöllner, Frank (2000). Leonardo Da Vinci, 1452–1519. Taschen. ISBN 978-3-8228-5979-7.
- "E.H. Gombrich, The Story of Art". Artchive.com. Archived from the original on 3 June 2013. Retrieved 3 June 2013.
- Zöllner, Frank. "Leonardo's Portrait of Mona Lisa del Giocondo" (PDF). p. 16. Archived (PDF) from the original on 1 October 2014.
- ^ Woods-Marsden p. 77 n. 100
- Farago 1999, p. 372
- Campbell, Lorne, Renaissance Portraits, European Portrait-Painting in the 14th, 15th and 16th Centuries, pp. 120–124, 1990, Yale, ISBN 0300046758
- ^ Alberge, Dalya (11 May 2024). "Mystery of where Mona Lisa was painted has been solved, geologist claims". The Guardian. ISSN 1756-3224. Retrieved 12 May 2024.
- "The Mona Lisa (La Gioconda)". BBC. 25 October 2009. Archived from the original on 26 June 2010. Retrieved 24 October 2009.
- According to the geologist and art historian Ann Pizzorusso, the mountains in the background would not be covered in snow because the white and gray color would be typical of the mountains that overlook Lecco and its lake. Alberge, Dalya (11 May 2024). "Mystery of where Mona Lisa was painted has been solved, geologist claims". The Guardian. ISSN 1756-3224. Retrieved 12 May 2024.
- ^ Giuffrida, Angela (3 May 2023). "Italian historian claims to have identified bridge in Mona Lisa backdrop". The Guardian. ISSN 1756-3224. Retrieved 5 December 2024.
- Vasari, Giorgio (1991) . The Lives of the Artists. Oxford World's Classics. Translated by Bondanella, Peter; Bondanella, Julia Conway. Oxford University Press. p. 294. ISBN 0-19-283410-X.
The eyebrows could not be more natural, for they represent the way the hair grows in the skin—thicker in some places and thinner in others, following the pores of the skin.
- Turudich 2003, p. 198
- McMullen, Roy (1976). Mona Lisa: The Picture and the Myth. Macmillan Publishers. ISBN 978-0-333-19169-9.
- Holt, Richard (22 October 2007). "Solved: Why Mona Lisa doesn't have eyebrows". The Daily Telegraph. UK. Archived from the original on 4 April 2010. Retrieved 11 March 2010.
- Ghose, Tia (9 December 2015). "Lurking Beneath the 'Mona Lisa' May Be the Real One". Livescience.com. Archived from the original on 11 December 2015.
- Irene Earls, Artists of the Renaissance, Greenwood Press, 2004, p. 113. ISBN 0-313-31937-5
- ^ Salgueiro, Heliana Angotti (2000). Paisaje y art. University of São Paulo. p. 74. ISBN 978-85-901430-1-7.
- "BBC News – Entertainment – Mona Lisa smile secrets revealed". 18 February 2003. Archived from the original on 31 August 2007.
- Rosetta Borchia and Olivia Nesci, Codice P. Atlante illustrato del reale paesaggio della Gioconda, Mondadori Electa, 2012, ISBN 978-88-370-9277-1
- "Researchers identify landscape behind the Mona Lisa". The Times. Retrieved 22 January 2014.
- "Mystery of where Mona Lisa was painted has been solved, geologist claims". The Guardian. ISSN 1756-3224. Retrieved 11 May 2024.
- Chiesa 1967, p. 103.
- Chiesa 1967, p. 87.
- Wiesner-Hanks, Merry E. (2005). An Age of Voyages, 1350–1600. New York: Oxford University Press. p. 26. ISBN 978-0-19-517672-8.
- Vezzosi, Alessandro (2007). "The Gioconda mystery – Leonardo and the 'common vice of painters'". In Vezzosi; Schwarz; Manetti (eds.). Mona Lisa: Leonardo's hidden face. Polistampa. ISBN 978-88-596-0258-3.
- Asmus, John F.; Parfenov, Vadim; Elford, Jessie (28 November 2016). "Seeing double: Leonardo's Mona Lisa twin". Optical and Quantum Electronics. 48 (12): 555. Bibcode:2016OQEle..48..555A. doi:10.1007/s11082-016-0799-0. S2CID 125226212.
- Leonardo, Carmen Bambach, Rachel Stern, and Alison Manges (2003). Leonardo da Vinci, master draftsman. New York: Metropolitan Museum of Art. p. 234. ISBN 1-58839-033-0
- Lorenzi, Rossella (10 May 2016). "Did a Stroke Kill Leonardo da Vinci?". Seeker. Retrieved 5 May 2019.
- McMahon, Barbara (1 May 2005). "Da Vinci 'paralysis left Mona Lisa unfinished'". The Guardian. ISSN 1756-3224. Retrieved 2 May 2019.
- Saplakoglu, Yasemin (4 May 2019). "A Portrait of Leonardo da Vinci May Reveal Why He Never Finished the Mona Lisa". Live Science. Retrieved 5 May 2019.
- Bodkin, Henry (4 May 2019). "Leonardo da Vinci never finished the Mona Lisa because he injured his arm while fainting, experts say". The Telegraph. Archived from the original on 10 January 2022. Retrieved 6 May 2019.
- Thomas, Henry; Lee Thomas, Dana (1940). Living biographies of great painters. Garden City Publishing Co., Inc. p. 49.
- ^ Becherucci, Luisa (1969). The Complete Work of Raphael. New York: Reynal and Co., William Morrow and Company. p. 50.
- Clark, Kenneth (March 1973). "Mona Lisa". Burlington Magazine. Vol. 115.
- ^ Lorusso, Salvatore; Natali, Andrea (2015). "Mona Lisa: A comparative evaluation of the different versions and copies". Conservation Science. 15: 57–84. Retrieved 26 July 2017.
- ^ Isbouts, Jean-Pierre; Heath-Brown, Christopher (2013). The Mona Lisa Myth. Santa Monica, California: Pantheon Press. ISBN 978-1-4922-8949-4.
- Friedenthal, Richard (1959). Leonardo da Vinci: a pictorial biography. New York: Viking Press.
- Kemp, Martin (1981). Leonardo: The marvelous works of nature and man. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-674-52460-6.
- Bramly, Serge (1995). Leonardo: The artist and the man. London: Penguin books. ISBN 978-0-14-023175-5.
- Marani, Pietro (2003). Leonardo: The complete paintings. New York: Harry N. Abrams. ISBN 978-0-8109-9159-0.
- ^ Zollner, Frank (1993). "Leonardo da Vinci's portrait of Mona Lisa de Giocondo" (PDF). Gazette des Beaux-Arts. 121: 115–138. Retrieved 3 August 2017.
- ^ Mohen, Jean-Pierre (2006). Mona Lisa: inside the Painting. Harry N. Abrams, Inc. p. 128. ISBN 978-0-8109-4315-5.
- Delieuvin, Vincent; Tallec, Olivier (2017). What's so special about Mona Lisa. Paris: Editions du musée du Louvre. ISBN 978-2-35031-564-5.
- De Beatis, Antonio (1979) . Hale, J.R.; Lindon, J.M.A. (eds.). The travel journal of Antonio de Beatis: Germany, Switzerland, the Low Countries, France and Italy 1517–1518. London, England: Haklyut Society.
- Bacci, Mina (1978) . The Great Artists: Da Vinci. Translated by Tanguy, J. New York: Funk & Wagnalls.
- ^ Wallace, Robert (1972) . The World of Leonardo: 1452–1519. New York: Time-Life Books. pp. 163–64.
- Vasari, Giorgio (1550). Le Vite de' più eccellenti pittori, scultori, ed architettori. Florence, Italy: Lorenzo Torrentino.
- ^ Boudin de l'Arche, Gerard (2017). A la recherche de Monna Lisa. Cannes, France: Edition de l'Omnibus. ISBN 979-10-95833-01-7.
- "Mona Lisa". louvre.fr. Retrieved 3 August 2017.
- Jestaz, Bertrand (1999). "Francois 1er, Salai, et les tableaux de Léonard". Revue de l'Art (in French). 76 (1): 68–72. doi:10.3406/rvart.1999.348476.
- ^ Classics, Delphi; Russell, Peter (7 April 2017). The History of Art in 50 Paintings (Illustrated). Delphi Classics. ISBN 978-1-78656-508-2.
- "The Theft That Made The 'Mona Lisa' A Masterpiece". NPR. 30 July 2011. Archived from the original on 27 August 2014. Retrieved 26 August 2014.
- Bohm-Duchen, Monica (2001). The private life of a masterpiece. University of California Press. p. 53. ISBN 978-0-520-23378-2. Retrieved 10 October 2010.
- Halpern, Jack (9 January 2019). "The French Burglar Who Pulled Off His Generation's Biggest Art Heist". The New Yorker. Retrieved 9 January 2019.
- "Theft of the Mona Lisa". Stoner Productions via Public Broadcasting Service (PBS). Archived from the original on 29 October 2009. Retrieved 24 October 2009.
- Scotti, R. A. (April 2010). Vanished Smile: The Mysterious Theft of the Mona Lisa. Vintage Books. ISBN 978-0-307-27838-8. Archived from the original on 2 January 2016.
- ^ "Top 25 Crimes of the Century: Stealing the Mona Lisa, 1911". Time. 2 December 2007. Archived from the original on 14 July 2007. Retrieved 15 September 2007.
- Sale, Jonathan (8 May 2009). "Review: The Lost Mona Lisa: The Extraordinary True Story of the Greatest Art Theft in History by RA Scotti". The Guardian. ISSN 1756-3224. Retrieved 23 July 2019.
- Iqbal, Nosheen; Jonze, Tim (22 January 2020). "In pictures: The greatest art heists in history". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 17 April 2021.
- ^ Scotti, R. A. (2010). The Lost Mona Lisa: The Extraordinary True Story of the Greatest Art Theft in History (reprinted ed.). Bantam Books. ISBN 978-0-5538-1830-7.
- "Noah Charney, Chronology of the Mona Lisa: History and Thefts, The Secret History of Art, Blouin Artinfo Blogs". Archived from the original on 27 October 2015. Retrieved 25 October 2015.
- Nilsson, Jeff (7 December 2013). "100 Years Ago: The Mastermind Behind the Mona Lisa Heist | The Saturday Evening Post". Saturday Evening Post. Retrieved 23 July 2019.
- Charney, Noah (12 November 2013). "Did the Nazis steal the Mona Lisa?". The Guardian. ISSN 1756-3224.
- Guenfoud, Ibtissem (17 July 2019). "'Mona Lisa' relocated within Louvre for 1st time since 2005". ABC News. Retrieved 23 July 2019.
- Samuel, Henry (7 October 2019). "Will new Mona Lisa queuing system in restored Louvre gallery bring a smile back to visitors' faces?". The Telegraph. Archived from the original on 10 January 2022. Retrieved 12 October 2019.
- "Mona FAQ". Mona Lisa Mania. Archived from the original on 1 June 2009. Retrieved 7 January 2010.
- "Tourist Damages the 'Mona Lisa'; Stone Breaks Glass in Louvre--Paint Slightly Chipped Tourist Damages Louve Painting Portrait Deemed Uriceless". The New York Times. 31 December 1956. p. 1. ISSN 1553-8095. Retrieved 5 December 2024.
- "'Mona Lisa' Still Smiling, Undamaged After Woman's Spray Attack in Tokyo". Sarasota Herald-Tribune. 21 April 1974. Retrieved 9 October 2012.
- "Mona Lisa attacked by Russian woman". Xinhua News Agency. 12 August 2009. Archived from the original on 2 March 2012. Retrieved 12 August 2009.
- "Russian tourist hurls mug at Mona Lisa in Louvre". Deseret. Associated Press. 11 August 2009. Retrieved 5 December 2024.
- "Man in wig throws cake at glass protecting Mona Lisa". ABC News. Associated Press. 30 May 2022. Retrieved 30 May 2022.
- Hummel, Tassilo (30 May 2022). Stonestreet, John (ed.). "Mona Lisa left unharmed but smeared in cream in climate protest stunt". Reuters. Retrieved 30 May 2022.
- "Man arrested after Mona Lisa smeared with cake". The Guardian. 30 May 2022. ISSN 1756-3224. Retrieved 7 June 2022.
- Palumbo, Jacqui (31 May 2022). "The 'Mona Lisa' has been caked in attempted vandalism stunt". CNN. Retrieved 31 May 2022.
- "Environmental activists hurl soup at the Mona Lisa in Paris's Louvre Museum". France 24. 28 January 2024. Retrieved 28 January 2024.
- "Hidden portrait 'found under Mona Lisa', says French scientist". BBC News. 8 December 2015. Archived from the original on 8 December 2015. Retrieved 8 December 2015.
- ^ Cotte, Pascal (2015). Lumiere on the Mona Lisa: Hidden portraits. Paris: Vinci Editions. ISBN 978-2-9548-2584-7.
- McAloon, Jonathan (10 December 2015). "The Missing Mona Lisa". Apollo. Archived from the original on 15 December 2015.
- "Secret Portrait Hidden Under Mona Lisa, Claims French Scientist". Newsweek. 8 December 2015. Archived from the original on 8 December 2015. Retrieved 8 December 2015.
- Lomazzo, Gian Paolo (1584). Treatise on the art of painting. Milan.
- Cotte, Pascal; Simonot, Lionel (1 September 2020). "Mona Lisa's spolvero revealed". Journal of Cultural Heritage. 45: 1–9. doi:10.1016/j.culher.2020.08.004. ISSN 1296-2074. S2CID 225304838.
- Kalb, Claudia (1 May 2019). "Why Leonardo da Vinci's brilliance endures, 500 years after his death". National Geographic. Archived from the original on 15 April 2019. Retrieved 21 August 2020.
- "Ageing Mona Lisa worries Louvre". BBC News. 26 April 2004. Archived from the original on 16 August 2009. Retrieved 24 October 2009.
- Bramly, Serge (1996). Mona Lisa. Thames and Hudson. ISBN 978-0-500-23717-5.
- Sassoon, Donald (2006). Leonardo and the Mona Lisa Story: The History of a Painting Told in Pictures. Allen & Unwin. ISBN 978-1-74114-902-9.
- "Biographical index of collectors of pastels". Pastellists.com. Archived from the original on 15 June 2013. Retrieved 3 June 2013.
- "Mona Lisa gains new Louvre home". BBC. 6 April 2005. Archived from the original on 1 February 2008. Retrieved 27 April 2008.
- Fontoynont, Marc et al. "Lighting Mona Lisa with LEDs Archived 8 March 2014 at the Wayback Machine" Note Archived 29 August 2014 at the Wayback Machine. SBI / Aalborg University, June 2013.
- "Nippon Television Network Corporation". Ntv.co.jp. 6 April 2005. Archived from the original on 8 October 2010. Retrieved 21 November 2010.
- "Mona Lisa fans decry brief encounter with their idol in Paris". The Guardian. 13 August 2019. ISSN 1756-3224. Retrieved 24 August 2020.
- "Leonardo da Vinci's Unexamined Life as a Painter". The Atlantic. 1 December 2019. Retrieved 1 December 2019.
- "Louvre exhibit has most da Vinci paintings ever assembled". Aleteia. 1 December 2019. Retrieved 1 December 2019.
- ""Моне Лизе" обещают свою комнату. В Лувре считают, что полотно "плохо расположено"" (in Russian). ru.euronews.com. 25 April 2024. Retrieved 7 May 2024.
- Veltman, Chloe (28 April 2024). "The Louvre Museum looks to rehouse the 'Mona Lisa' in its own room — underground". NPR. Retrieved 22 August 2024.
- Zollner gives a date of c. 1504, most others say c. 1506
- Zöllner, Frank. Leonardo Da Vinci, 1452–1519. p. 161.
- Clark, Kenneth (1999). "Mona Lisa". In Farago, Claire J. (ed.). Leonardo Da Vinci, Selected Scholarship: Leonardo's projects, c. 1500–1519. Taylor & Francis. p. 214. ISBN 978-0-8153-2935-0.
- ^ "The myth of the Mona Lisa". The Guardian. 28 March 2002. ISSN 1756-3224. Archived from the original on 10 July 2017. Retrieved 5 December 2024.
- Samuels, Ernest; Samuels, Jayne (1987). Bernard Berenson, the Making of a Legend. Harvard University Press. p. 215. ISBN 978-0-674-06779-0.
- "Gil Blas / dir. A. Dumont". Gallica. 30 September 1911.
- Salmon, André (15 September 1920). "L'Art vivant". Paris : G. Crès – via Internet Archive.
- "Philadelphia Museum of Art – Collections Object : Tea Time (Woman with a Teaspoon)". www.philamuseum.org.
- Jones, Jonathan (26 May 2001). "L.H.O.O.Q., Marcel Duchamp (1919)". The Guardian. ISSN 1756-3224. Archived from the original on 9 May 2014. Retrieved 12 June 2009.
- Marting, Marco De (2003). "Mona Lisa: Who is Hidden Behind the Woman with the Mustache?". Art Science Research Laboratory. Archived from the original on 20 March 2008. Retrieved 27 April 2008.
- Dalí, Salvador. "Self Portrait as Mona Lisa". Mona Lisa Images for a Modern World by Robert A. Baron (from the catalog of an exhibition at the Museum of Modern Art and the Philadelphia Museum of Art, 1973, p. 195). Archived from the original on 28 October 2009. Retrieved 24 October 2009.
- Sassoon, Donald (2003). Becoming Mona Lisa. Harvest Books via Amazon Search Inside. p. 251. ISBN 978-0-15-602711-3.
- "The £20,000 Rubik's Cube Mona Lisa". Metro. 29 January 2009. Archived from the original on 26 July 2014. Retrieved 18 July 2014.
- Schwartz, Benjamin (3 October 2014). "Daily Cartoon: Friday, October 3rd". The New Yorker. ISSN 0028-792X. Retrieved 5 December 2024.
- Riding, Alan (6 April 2005). "In Louvre, New Room With View of 'Mona Lisa'". The New York Times. ISSN 1553-8095. Archived from the original on 25 June 2011. Retrieved 7 October 2007.
- Sassoon, Donald. "Why is the Mona Lisa Famous?". La Trobe University Podcast. Archived from the original on 4 July 2015. Retrieved 20 January 2014.
- ^ Sassoon, Donald (2001). "Mona Lisa: the Best-Known Girl in the Whole Wide World". History Workshop Journal. 2001 (51) (vol 2001 ed.): 1. doi:10.1093/hwj/2001.51.1. ISSN 1477-4569.
- "The Theft That Made The 'Mona Lisa' A Masterpiece". All Things Considered. NPR. 30 July 2011. Retrieved 24 August 2020.
- Gopnik, Blake (7 May 2004). "A Record Picasso and the Hype Price of Status Objects". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on 29 November 2016. Retrieved 28 November 2016.
- "The Mona Lisa" (PDF). Metropolitan Museum of Art. Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 March 2018. Retrieved 8 January 2018.
- Stolow, Nathan (1987). Conservation and exhibitions: packing, transport, storage, and environmental consideration. Butterworths. p. 188. ISBN 978-0-408-01434-2. Archived from the original on 5 October 2012. Retrieved 10 October 2010.
- "Today in Met History: February 4". Metropolitan Museum of Art. 4 February 2013. Retrieved 8 January 2018.
- "Another art anniversary: Mona Lisa comes to New York! And she's almost drowned in a sprinkler malfunction". boweryboyshistory.com. 13 January 2013. Retrieved 8 January 2018.
- Bohm-Duchen, Monica (2001). The private life of a masterpiece. University of California Press. p. 65. ISBN 978-0-520-23378-2. Retrieved 10 October 2010.
- The French Ministry of Foreign affairs. "The Louvre, the most visited museum in the world (01.15)". France Diplomatie :: Ministry of Foreign Affairs and International Development. Archived from the original on 22 December 2015.
- "On a Mission to Loosen Up the Louvre". The New York Times. 11 October 2009. ISSN 1553-8095. Archived from the original on 24 December 2016. Retrieved 5 December 2024.
- Young, Mark, ed. (1999). The Guinness Book of World Records 1999. Bantam Books. p. 381. ISBN 978-0-553-58075-4.
- "Culture – Could France sell the Mona Lisa to pay off its debts?". France 24. 2 September 2014. Archived from the original on 30 November 2015.
- "Mona Lisa 31213". Lego.com. Lego Art. Retrieved 22 August 2024.
- https://ge.globo.com/google/amp/olimpiadas/noticia/2024/07/26/olimpiadas-minions-aparecem-em-cerimonia-e-viralizam-nas-redes-assista.ghtml
- https://www.espn.com.br/olimpiadas/artigo/_/id/13956114/olimpiadas-cerimonia-abertura-minions-roubam-monalisa
- "La Gioconda, Leonardo's atelier". Museo Nacional del Prado. Archived from the original on 8 December 2015. Retrieved 7 December 2015.
- "The 'Prado Mona Lisa' – The Mona Lisa Foundation". The Mona Lisa Foundation. 11 September 2012. Archived from the original on 17 December 2015. Retrieved 11 December 2015.
- Carbon, C. C.; Hesslinger, V. M. (August 2013). "Da Vinci's Mona Lisa Entering the Next Dimension". Perception. 42 (8): 887–893. doi:10.1068/p7524. PMID 24303752.
- Tweened animated gif of Mona Lisa and Prado version Archived 7 February 2017 at the Wayback Machine by Carbon and Hesslinger
- Brooks, K. R. (1 January 2017). "Depth Perception and the History of Three-Dimensional Art: Who Produced the First Stereoscopic Images?". i-Perception. 8 (1): 204166951668011. doi:10.1177/2041669516680114. PMC 5298491. PMID 28203349.
- Dutta, Kunal (15 December 2014). "'Early Mona Lisa': Unveiling the one-in-a-million identical twin to Leonardo da Vinci painting". Independent.co.uk. Archived from the original on 16 December 2014.
- Rosenbaum, Matthew (27 September 2012). "Second Mona Lisa Unveiled for First Time in 40 Years". ABC News. ABC News Internet Ventures. Retrieved 12 June 2020.
- Alastair Sooke. "The Isleworth Mona Lisa: A second Leonardo masterpiece?". BBC. Archived from the original on 2 January 2016.
- "New proof said found for "original" Mona Lisa –". Reuters.com. 13 February 2013. Retrieved 26 July 2017.
- Lorusso, Salvatore; Natali, Andrea (January 2015). "Mona Lisa: A Comparative Evaluation of the Different Versions and Their Copies". Conservation Science in Cultural Heritage. 15: 80. doi:10.6092/issn.1973-9494/6168.
- Asmus, John F. (1 July 1989). "Computer Studies of the Isleworth and Louvre Mona Lisas". Optical Engineering. 28 (7): 800–804. Bibcode:1989OptEn..28..800A. doi:10.1117/12.7977036. Retrieved 26 July 2017.
- Kemp 2018: "Alessandro Vezzosi, who spoke at the launch in Geneva, and Carlo Pedretti, the great Leonardo specialist, made encouraging but noncommittal statements about the picture being of high quality and worthy of further research."
- Portrait of Gioconda (copy), hermitagemuseum.org.
- Mastromattei, Dario (16 February 2016). "La Gioconda (o Monna Lisa) di Leonardo da Vinci: analisi".
- Horstmann G, Loth S (2019). "The Mona Lisa Illusion-Scientists See Her Looking at Them Though She Isn't". Iperception. 10 (1). doi:10.1177/2041669518821702. PMC 6327345. PMID 30671222.
Sources
- Bartz, Gabriele; König, Eberhard (2001). Art and Architecture, Louvre. New York: Barnes & Noble Books. ISBN 978-0-7607-2577-1.
- Bohm-Duchen, Monica (2001). The Private Life of a Masterpiece. Berkeley, California: University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-23378-2.
- Chiesa, Angela Ottino della (1967). The Complete Paintings of Leonardo da Vinci. Penguin Classics of World Art. London: Penguin Books. ISBN 978-0-14-008649-2.
- Farago, Claire J. (1999). Leonardo's Projects, c. 1500–1519. Oxford: Taylor & Francis. ISBN 978-0-8153-2935-0.
- Kemp, Martin (2006). Leonardo da Vinci: The Marvelous Works of Nature and Man. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-280725-0.
- Kemp, Martin (2018). Living with Leonardo: Fifty Years of Sanity and Insanity in the Art World and Beyond. London: Thames & Hudson. ISBN 978-0-500-77423-6.
- Kemp, Martin (2019). Leonardo da Vinci: The 100 Milestones. New York: Sterling. ISBN 978-1-4549-304-26.
- Marani, Pietro C. (2003) . Leonardo da Vinci: The Complete Paintings. New York: Harry N. Abrams. ISBN 978-0-8109-3581-5.
- Turudich, Daniela (2003). Plucked, Shaved & Braided: Medieval and Renaissance Beauty and Grooming Practices 1000–1600. North Branford, Connecticut: Streamline Press. ISBN 978-1-930064-08-9.
- Vasari, Giorgio (1879) . Le vite de' più eccellenti pittori, scultori ed architettori (in Italian). Vol. 4. Florence: G.C. Sansoni.
- Wilson, Colin (2000). The Mammoth Encyclopedia of the Unsolved. New York: Carroll & Graf Publishers. ISBN 978-0-7867-0793-5.
- Woods-Marsden, Joanna (2001). "Portrait of the Lady, 1430–1520". In Brown, David Alan (ed.). Virtue & Beauty. London: Princeton University Press. pp. 64–87. ISBN 978-0-691-09057-3.
- Zöllner, Frank (2015). Leonardo (2nd ed.). Cologne: Taschen. ISBN 978-3-8365-0215-3.
- Zöllner, Frank (2019). Leonardo da Vinci: The Complete Paintings and Drawings (Anniversary ed.). Cologne: Taschen. ISBN 978-3-8365-7625-3.
Further reading
- McMullen, Roy (1975). Mona Lisa: The Picture and the Myth. Boston: Houghton Mifflin Company.
- Sassoon, Donald (2001). Becoming Mona Lisa: The Making of a Global Icon. New York: Harcourt, Inc.
External links
- Sassoon, Donald (21 January 2014). #26: Why is the Mona Lisa Famous?. La Trobe University podcast blog. Archived from the original on 4 July 2015. of the podcast audio.
- "Mona Lisa, Leonardo's Earlier Version". Zürich, Switzerland: The Mona Lisa Foundation. 14 October 2012. Archived from the original on 26 June 2015. Retrieved 5 November 2015.
- "True Colors of the Mona Lisa Revealed" (Press release). Paris: Lumiere Technology. 19 October 2006. Archived from the original on 26 June 2015. Retrieved 5 November 2015.
- Scientific analyses conducted by the Center for Research and Restoration of the Museums of France (C2RMF) Compare layers of the painting as revealed by x-radiography, infrared reflectography and ultraviolet fluorescence
- "Stealing Mona Lisa". Dorothy & Thomas Hoobler. May 2009. excerpt of book. Vanity Fair
- Discussion by Janina Ramirez and Martin Kemp: Art Detective Podcast, 18 Jan 2017
- Leonardo's Mona Lisa Archived 4 November 2014 at the Wayback Machine, Smarthistory (video)
- Secrets of the Mona Lisa, Discovery Channel documentary on YouTube
- The Tricks of Leonardo da Vinci & Hieronymus Bosch. Xavier d'Hérouville & Aurore Caulier. December 2023. HAL Open Science
| Leonardo da Vinci's Mona Lisa | |
|---|---|
| |
| Replicas |
|
| Related | |
| 1911 theft | |
| On screen |
|
| Music |
|
| Literature |
|
| Leonardo da Vinci | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paintings |
| ||||||
| Sculptures |
| ||||||
| Works on paper |
| ||||||
| Manuscripts | |||||||
| Other projects | |||||||
| Leonardeschi | |||||||
| Museums | |||||||
| Related | |||||||
| |||||||
| High Renaissance | |
|---|---|
| Principal proponents | |
| Other artists |
|
| Major works |
|
| Related | |