| Revision as of 05:43, 4 September 2016 editXanthomelanoussprog (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users7,137 edits Undid revision 737643938 by 2804:7F7:2280:C500:0:0:0:1 (talk) disruption← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 06:47, 6 January 2025 edit undoTraumnovelle (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users8,308 edits Undid revision 1267691428 by 2600:1700:EF00:20D0:DD4C:9D2F:8881:1BCE (talk)Tag: Undo | ||
| (828 intermediate revisions by more than 100 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|American dog breed}} | |||
| {{about|the American Terrier|the family of dogs, including legal status worldwide|pit bull}} | |||
| {{About|the dog breed|the family of dogs, including legal status worldwide|Pit bull}} | |||
| {{Use mdy dates|date=April 2013}} | |||
| {{Distinguish|Staffordshire Bull Terrier|American Staffordshire Terrier}} | |||
| {{refimprove|date=March 2013}} | |||
| {{Use American English|date=August 2022}} | |||
| {{Use mdy dates|date=August 2020}} | |||
| {{Infobox dog breed | {{Infobox dog breed | ||
| |name=American Pit Bull Terrier | |name = American Pit Bull Terrier | ||
| |image = |
|image = 001 American Pit Bull Terrier.jpg | ||
| |caption = A female American Pit Bull Terrier | |||
| |image_caption = | |||
| | |
|image_alt = 001 American Pit Bull Terrier.jpg | ||
| |image_caption = | |||
| |country = United States,<br />United Kingdom<ref>{{cite web| title = Origin of American Pitbull Terrier | url = http://www.kennelclubusa.com/american_pit_bull_terrier.htm | date = November 1, 2008 | accessdate = 26 September 2013}}</ref> | |||
| |image2 = | |||
| | collapse_standards_and_traits = yes | |||
| |image_alt2 = | |||
| |image_caption2 = | |||
| |altname = {{flat list| | |||
| * Pit Bull | |||
| * Pitbull Terrier | |||
| * Pittie}} | |||
| |nickname = {{flat list| | |||
| * Pit | |||
| * APBT}} | |||
| |stock = {{ubl|]|]|]}} | |||
| |country = United States | |||
| <!-----Traits------> | <!-----Traits------> | ||
| |maleweight = {{convert| |
|maleweight = {{convert|15.8|-|27.2|kg|lb|abbr=on}} | ||
| |femaleweight = {{convert| |
|femaleweight = {{convert|13.6|-|22.6|kg|lb|abbr=on}} | ||
| |maleheight = {{convert| |
|maleheight = {{convert|45|-|53|cm|in|abbr=on}} | ||
| |femaleheight = {{convert|43|-| |
|femaleheight = {{convert|43|-|50|cm|in|abbr=on}} | ||
| |coat = smooth<br />thin<br />single | |coat = smooth<br />thin<br />single | ||
| |color = Multiple accepted colours and combinations (except merle).<br />Red, black and buckskin are the most common | |||
| |color = Red nose | |||
| |litter_size = 5–10 | |litter_size = 5–10 | ||
| <!-----Kennel club standards-----> | |||
| |life_span = 8-15 years | |||
| | kc_name = ] | |||
| | ukcgroup = Terrier | |||
| | |
| kc_std = https://www.ukcdogs.com/american-pit-bull-terrier | ||
| | |
| kc2_name = ] | ||
| | kc2_std = https://adbadog.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/07/2015-Heritage-conformation-standard-outline.pdf | |||
| |note = | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| The '''American Pit Bull Terrier''' ('''APBT''') is a ].<ref>{{cite web| title = Standard of American pit bull terrier | url = http://www.ukcdogs.com/Web.nsf/Breeds/Terrier/AmericanPitBullTerrier | date = 2015 |access-date= 8 October 2015}}</ref> It is a medium-sized, solidly-built, short-haired ] whose early ancestors came from the ]. A member of the ] breed group, both the ] and the American Pit Bull Terrier (APBT) were bred from the same lineage, but received different names from the two American kennel clubs; American Staffordshire Terrier was the name given by the ] (AKC), and American Pit Bull Terrier by the ] (UKC). When compared with the English ] (another breed within the ] commonly called ]s), the American Pit Bull Terrier is larger by margins of {{convert|6|-|8|in|cm|abbr=out}} in height and {{convert|25|-|35|lb|kg|abbr=out}} in weight. The American Pit Bull Terrier varies in size. Males normally are about 18-19 inches (45-48 cm) in height and around 35-63 pounds (15-29 kg) in weight. Females are normally around 17-18 inches (43-45 cm) in height and 30-57 pounds (13-26 kg) in weight. | |||
| The '''American Pit Bull Terrier''' ('''APBT''') is a ] recognized by the ] (UKC)<ref name="auto">{{cite web|url=https://www.ukcdogs.com/docs/breeds/american-pit-bull-terrier.pdf|title=UKC Standard of the American Pit Bull Terrier|date=2017|access-date=April 1, 2017}}</ref> and the ] (ADBA),<ref name="auto1">{{cite web|title=ADBA Standard of the American pit bull terrier |url=https://adbadog.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/07/2015-Heritage-conformation-standard-outline.pdf |date=2018 |access-date=February 2, 2018}}</ref> but not the ] (AKC).<ref>{{Cite news |title=Official list of all American Kennel Club dog breeds |publisher=American Kennel Club |url=https://www.akc.org/dog-breeds/ |access-date=March 14, 2019}}</ref> It is a medium-sized, short-haired dog, of a solid build, whose early ancestors came from ]. When compared with the English ], the American Pit Bull Terrier is larger by margins of {{convert|6|-|8|in|cm|abbr=out}} in height and {{convert|25|-|35|lb|kg|abbr=out}} in weight. The American Pit Bull Terrier varies in size: males are normally about 18–21 inches (45–53 cm) in height and around 35–60 pounds (15–27 kg) in weight, while females are normally around 17–20 inches (43–50 cm) in height and 30–50 pounds (13–22 kg) in weight.<ref name="auto" /> | |||
| The American Pit Bull is medium-sized, and has a short coat and smooth well-defined muscle structure. Its eyes are round to almond-shaped, and its ears are small to medium in length, typically half prick or rose in carriage. The tail is slightly thick and tapers to a point. The coat is glossy, smooth, short, and stiff to the touch. The accepted coat color can vary widely, but, both the AKC and UKC do not recognize merle coloring. Color patterns that are typical in the breed are spotted, brindled, solid, and with points. | |||
| According to the ADBA, the American Pit Bull is described to be medium-sized and has a short coat and smooth well-defined muscle structure, and its eyes are to be round to almond-shaped, and its ears are to be small to medium in length, typically ] in carriage. The tail is prescribed to be slightly thick and tapering to a point. The coat is required by the ADBA to be glossy, smooth, short, and stiff to the touch. Many colors, color patterns, and combinations of colors are acceptable to the ADBA, except that both the ADBA and UKC do not recognize ] coloring.<ref name="auto" /><ref name="auto1" /> ] that are typical in the breed are solid and tuxedo.<ref>{{cite web|title=Dog Coat Patterns – Caninest.com |url=http://www.caninest.com/dog-coat-patterns/ |date=2018 |access-date=February 5, 2018}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|title=ADBA – American Pit Bull Terrier Color Chart Gallery |url=https://adbadog.com/pit-bull-color-chart/ |date=2018 |access-date=February 5, 2018}}</ref> | |||
| Twelve countries in Europe, as well as Australia, Canada, Ecuador, Malaysia, New Zealand, Puerto Rico, Singapore, and Venezuela have enacted some form of ] on pit bull-type dogs, including American Pit Bull Terriers, ranging from outright bans to restrictions and conditions on ownership. The state of ] in Australia places restrictions on the breed, including mandatory sterilization. The breed is banned in the ], in the Canadian province of ],<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.attorneygeneral.jus.gov.on.ca/english/about/pubs/dola-pubsfty/dola-pubsfty.asp#TOC_01|title=Information on The Dog Owners' Liability Act and Public Safety Related to Dogs Statute Law Amendment Act, 2005|publisher=Ministry of the attorney general}}</ref> and in many locations in the United States. | |||
| Despite the colloquial use of the term "]" to encompass a whole category of dogs and the legal use of the term to include several breeds in legislation, some conservative professional breeders of the American Pit Bull Terrier as well as some experts and supporters claim that historically the APBT is the only true "pit bull" and the only breed that should be denominated as such.<ref name="The Real Pit Bull Breed Information Center">{{cite web |url=http://www.realpitbull.com/center.html |title=A Note on the Use of the Term, "Pit Bull" |publisher=The Real Pit Bull |access-date=July 27, 2018}}</ref><ref name="Pit Bull Informational Pages">{{cite web |url=https://www.workingpitbull.com/history.htm |title=History of the Pit Bull – Facts and Myths About Pit Bull History |publisher=Diane Jessup |access-date=July 27, 2018}}</ref><ref name="Pit Bulls Against Misinformation">{{cite web |url=http://www.pitbulltruth.org/what-is-a-pit-bull/ |title=What is a Pit Bull? |publisher=pitbulltruth.org |access-date=July 27, 2018}}</ref><ref name="Diane Jessup's educational site dedicated to the American pit bull">{{cite web |url=https://www.workingpitbull.com/ |title=Working Pit Bull |publisher=Diane Jessup |date=March 20, 2012 |access-date=July 27, 2018}}</ref> | |||
| == History == | |||
| ] poster featuring a pit bull as representation of the U.S.]] | |||
| The Pit Bull Terrier was created by breeding ]s and ]s together to produce a dog that combined the ] of the terrier with the strength and athleticism of the ].<ref name="United Kennel Club">{{cite web |url=http://www.ukcdogs.com/WebSite.nsf/Breeds/AmericanPitBullTerrierRevisedNovember12008 |title=American Pit Bull Terrier |publisher=United Kennel Club (UKC) |date=November 1, 2008 |accessdate=August 7, 2009}}</ref> These dogs were bred in England, and arrived in the United States where they became the direct ancestors of the American Pitbull Terrier. In the ], pit bulls were used in bloodsports such as ], bear baiting. These bloodsports were officially eliminated in 1835 as Britain began to introduce animal welfare laws. Since dogfights were cheaper to organise and far easier to conceal from the law than bull or bear baits, bloodsport proponents turned to pitting their dogs against each other instead. Dog fighting was used as both a bloodsport (often involving gambling) and a way to continue to test the quality of their stock. For decades afterwards, dog fighting clandestinely took place in small areas of Britain and America. In the early 20th century, pitbulls were used as ]s in America for semi-wild cattle and hogs, to hunt, and drive livestock, and as family companions.<ref name="United Kennel Club" /> Some have been selectively bred for their fighting prowess.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.aspca.org/fight-cruelty/dog-fighting/pit-bull-cruelty |title=Pit Bull Cruelty |publisher=] (ASPCA) |year=2013 |accessdate=February 3, 2014}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.aspca.org/fight-cruelty/dog-fighting |title=Dog Fighting |publisher=] (ASPCA) |year=2013 |accessdate=February 3, 2014}}</ref> | |||
| Twelve countries in Europe, as well as ], ], some parts of the ], ], ], ], ], ], and ], have enacted some form of ] on pit bull-type dogs, including American Pit Bull Terriers, ranging from outright bans to restrictions and conditions on ownership. Several states in Australia place restrictions on the breed, including mandatory sterilization. Pit Bull Terriers are banned in the ],<ref name=":6" /> in the Canadian province of ],<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.attorneygeneral.jus.gov.on.ca/english/about/pubs/dola-pubsfty/dola-pubsfty.asp#TOC_01|title=Information on The Dog Owners' Liability Act and Public Safety Related to Dogs Statute Law Amendment Act, 2005|publisher=Ministry of the Attorney General|access-date=July 25, 2007|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20091224033000/http://www.attorneygeneral.jus.gov.on.ca/english/about/pubs/dola-pubsfty/dola-pubsfty.asp#TOC_01|archive-date=December 24, 2009|url-status=dead}}</ref> and in many locations in the United States.<ref name="BSL Continues To Crumble">{{Cite web|title=BSL Continues To Crumble|url=https://www.pitbullinfo.org/bsl-continues-to-crumble.html|access-date=2021-11-15|website=Pitbullinfo.org|language=en}}</ref> | |||
| Pit Bull Terriers successfully fill the role of ]s, and ]s,<ref>{{cite journal |date=October 2002 |title=Cool K-9 Popsicle retires |journal=U.S. Customs Today |volume=38 |issue=10 |url=http://www.cbp.gov/xp/CustomsToday/2002/October/k9.xml |accessdate=August 7, 2009}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |first=Adrienne Mand |last=Lewin |title=Protecting the Nation – One Sniff at a Time |date=October 12, 2005 |publisher=] |url=http://abcnews.go.com/Technology/Terrorism/story?id=1200304&page=1 |accessdate=February 2, 2009}}</ref> and ].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.npr.org/templates/story/story.php?storyId=91769901 |first=Scott |last=Simon |title=Trainer turns pit bull into therapy dog |date=June 21, 2008 |publisher=] |accessdate=August 7, 2009}}</ref> Pit Bull Terriers also constitute the majority of dogs used for illegal ] in America<ref>{{cite web |title=Dog Fighting Fact Sheet |year=2009 |publisher=Humane Society of the United States |url=http://www.hsus.org/acf/fighting/dogfight/dogfighting_fact_sheet.html |accessdate=August 7, 2009}}</ref> In addition, law enforcement organisations report these dogs are used for other nefarious purposes, such as guarding illegal narcotics operations,<ref>{{cite news| url=http://www.dailymail.co.uk/news/article-2102608/Robin-Johnson-Known-prostitute-loses-left-arm-leg-pit-bull-attack.html | location=London | work=Daily Mail | title=Known prostitute' loses left arm and leg after pit bull 'viciously attacks her as she was shut inside a home with the beast | date=February 17, 2012}}</ref><ref name="SI 1987">{{cite news |first=E.M. |last=Swift |title=The pit bull: friend and killer |date=July 27, 1987 |periodical=] |volume=67 |issue=4 |url=http://sportsillustrated.cnn.com/vault/article/magazine/MAG1066224/1/index.htm |accessdate=December 2, 2009}}</ref> use against police,<ref>{{cite news |first1=Al |last1=Baker |first2=Mathew R. |last2=Warren |title=Shooting highlights the risks dogs pose to police, and vice versa |date=July 9, 2009 |place=New York, NY |newspaper=] |url=http://www.nytimes.com/2009/07/10/nyregion/10pitbull.html?_r=1 |accessdate=January 7, 2010}}</ref> and as ]s.<ref>{{cite news |title='Dangerous dogs' weapon of choice |date=December 2, 2009 |publisher=BBC News |url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/uk_news/england/west_midlands/8391909.stm |accessdate=December 2, 2009}}</ref> | |||
| == History == | |||
| In an effort to counter the fighting reputation of pit bull-type dogs, in 1996 the ] renamed pit bull terriers to "St. Francis Terriers", so that people might be more likely to adopt them.<ref>{{cite news |first=George |last=Cothran |title=Shouldn't we just kill this dog? |date=June 11, 1997 |place=] |periodical=] |url=http://www.sfweekly.com/1997-06-11/news/shouldn-t-we-just-kill-this-dog |accessdate=September 4, 2009}}</ref> 60 temperament-screened dogs were adopted until the program was halted, after several of the newly adopted pit bulls killed cats.<ref>{{cite news |title=Bring breeders of high-risk dogs to heel |date=January 2004 |periodical=Animal People News |url=http://www.animalpeoplenews.org/04/1/editorialHighRiskDogs1.04.html |accessdate=September 4, 2009}}</ref> The New York City ] tried a similar approach in 2004, relabeling their pit bulls as "New Yorkies", but dropped the idea in the face of overwhelming public opposition.<ref>{{cite news |first=Clyde |last=Haberman |title=NYC; Rebrand Fido? An idea best put down |date=January 13, 2004 |place=] |newspaper=] |url=http://www.nytimes.com/2004/01/13/nyregion/nyc-rebrand-fido-an-idea-best-put-down.html |accessdate=September 4, 2009}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |first=Charles |last=Laurence |title=Q: When is a pit bull terrier not a pit bull terrier? A: When it's a patriot terrier |date=January 4, 2004 |place=] |newspaper=] |url=http://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/northamerica/usa/1451409/Q-When-is-a-a-pit-bull-terrier-not-a-pit-bull-A-When-its-a-patriot-terrier.html |accessdate=November 14, 2009}}</ref> | |||
| ] type. Paris, 1863.]] | |||
| ] | |||
| Until the mid-19th century the since-extinct ]s and ]s were bred together to produce a dog that combined the ] of the terrier with the strength and athleticism of the ].<ref name="United Kennel Club">{{cite web |url=http://www.ukcdogs.com/WebSite.nsf/Breeds/AmericanPitBullTerrierRevisedNovember12008 |title=American Pit Bull Terrier |publisher=United Kennel Club (UKC) |date=November 1, 2008 |access-date=August 7, 2009 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090709081341/http://www.ukcdogs.com/WebSite.nsf/Breeds/AmericanPitBullTerrierRevisedNovember12008 |archive-date=July 9, 2009 |url-status=dead }}</ref><ref name="Dustman">{{cite web|title=Sporting Magazine: Dustman|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=YLsCAAAAYAAJ&q=1812,+Sporting+Magazine+Dustman&pg=PA97|date=June 1812|publisher=Rogerson & Tuxford|page=97|via=Google Books|access-date=May 23, 2020|volume=XI|issue=CCXXXVII}}</ref> This type of dog, which was bred in ], became known as the ].<ref name="Dustman" /> These dogs arrived in the United States in the late nineteenth century where they became the direct ancestors of the American Pit Bull Terrier.<ref name="auto" /> | |||
| In the United Kingdom, bull and terriers were used in ] such as ] and ]. These bloodsports were banned in 1835 when Britain introduced animal welfare laws. Since ] is cheaper to organize and far easier to conceal from the law than bull or bear baits, bloodsport proponents turned to pitting their dogs against each other instead.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Curnutt|first=Jordan|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=p2p0MptGeBkC&q=bull+baiting+1835&pg=PA284|title=Animals and the Law: A Sourcebook|date=2001|publisher=ABC-CLIO|isbn=978-1-57607-147-2|pages=284|language=en}}</ref> Dog fighting was used as both a bloodsport (often involving gambling) and a way to continue to test the quality of their stock. For decades afterwards, dog fighting clandestinely took place in small areas of Britain. These dogs arrived in America around 1845 to 1860, where the dog fighting practice had continuity.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Dickey|first=Bronwen|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=KNBfCgAAQBAJ&q=pit+bull+1845&pg=PA25|title=Pit Bull: The Battle over an American Icon|date=May 1, 2016|publisher=Knopf Doubleday Publishing Group|isbn=978-0-307-96177-8|pages=25|language=en}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book|last=Janish|first=Joseph|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=ltwJBgAAQBAJ&q=pit+bull+terrier+import&pg=PA14|title=American Staffordshire Terrier|date=January 2, 2012|publisher=i5 Publishing|isbn=978-1-59378-983-1|pages=13|language=en}}</ref> On February 10, 1898, the breed was recognized by the ] (UKC) named as American Pit Bull Terrier.<ref name="auto" /> | |||
| === Temperament === | |||
| The ] gives this description of the characteristics of the American Pit Bull Terrier: | |||
| For some time in the early part of the 20th century the UKC began to register the breed name with the word "pit" in parentheses (American (Pit) Bull Terrier), to facilitate public acceptance as an American Bull Terrier.<ref name=":0">{{Cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=SUsIAAAACAAJ&q=the+world+of+the+american+pit+bull+terrier|title=The World of the American Pit Bull Terrier|last=Stratton|first=Richard F.|date=1983|publisher=T.F.H. Publications|isbn=978-0-87666-851-1|language=en}}</ref> However this only lasted a short time and returned to the previous form.<ref name="auto" /> | |||
| <blockquote>The essential characteristics of the American Pit Bull Terrier are strength, confidence, and zest for life. This breed is eager to please and brimming over with enthusiasm. APBTs make excellent family companions and have always been noted for their love of children. Because most APBTs exhibit some level of ] and because of its powerful physique, the APBT requires an owner who will carefully socialize and obedience train the dog. The breed’s natural agility makes it one of the most capable canine climbers so good fencing is a must for this breed. The APBT is not the best choice for a guard dog since they are extremely friendly, even with strangers. Aggressive behavior toward humans is uncharacteristic of the breed and highly undesirable. This breed does very well in performance events because of its high level of intelligence and its willingness to work.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.ukcdogs.com/Web.nsf/Breeds/AmericanPitBullTerrier12012012 |title=American Pit Bull Terrier: Official UKC Breed Standard |publisher=] |date=December 1, 2012 |accessdate=March 21, 2013}}</ref></blockquote> | |||
| In the early 20th century, pit bulls were used as ]s in America for semi-wild cattle and hogs, to hunt hogs, and drive livestock, and as family companions.<ref name="United Kennel Club" /> | |||
| In September 2000, the United States ] (CDC) published a study which examined dog bite-related fatalities (human death caused by dog bite injuries) in order to "summarize breeds of dogs involved in fatal human attacks during a 20-year period and to assess policy implications."<ref name="CDC">{{cite web |url=http://www.cdc.gov/HomeandRecreationalSafety/images/dogbreeds-a.pdf |title=Breeds of dogs involved in fatal human attacks in the United States between 1979 and 1998 |publisher=] |date=April 1, 2008 |accessdate=July 8, 2009}}</ref> | |||
| Pit Bull Terriers fill the role of ]s, ]s, athletic sport dogs (], French Ring Sport, Top Dog), ]s,<ref>{{cite journal|date=October 2002 |title=Cool K-9 Popsicle retires |journal=U.S. Customs Today |volume=38 |issue=10 |url=http://www.cbp.gov/xp/CustomsToday/2002/October/k9.xml |access-date=August 7, 2009 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111024001344/http://www.cbp.gov/xp/CustomsToday/2002/October/k9.xml |archive-date=October 24, 2011 }}</ref><ref>{{cite news |first=Adrienne Mand |last=Lewin |title=Protecting the Nation – One Sniff at a Time |date=October 12, 2005 |work=] |url=https://abcnews.go.com/Technology/Terrorism/story?id=1200304&page=1 |access-date=February 2, 2009}}</ref> and ]s.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.npr.org/templates/story/story.php?storyId=91769901 |first=Scott |last=Simon |title=Trainer turns pit bull into therapy dog |date=June 21, 2008 |publisher=] |access-date=August 7, 2009}}</ref> Pit Bull Terriers also constitute the majority of dogs used for illegal ] in America<ref>{{cite web|title=Dog Fighting Fact Sheet |year=2009 |publisher=Humane Society of the United States |url=http://www.hsus.org/acf/fighting/dogfight/dogfighting_fact_sheet.html |access-date=August 7, 2009 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090719152149/http://www.hsus.org/acf/fighting/dogfight/dogfighting_fact_sheet.html |archive-date=July 19, 2009 }}</ref> In addition, law enforcement organizations report these dogs are used for other nefarious purposes, such as guarding illegal narcotics operations,<ref name="SI 1987">{{cite magazine |first=E.M. |last=Swift |title=The pit bull: friend and killer |date=July 27, 1987 |magazine=] |volume=67 |issue=4 |url=http://sportsillustrated.cnn.com/vault/article/magazine/MAG1066224/1/index.htm |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121104035617/http://sportsillustrated.cnn.com/vault/article/magazine/MAG1066224/1/index.htm |url-status=dead |archive-date=November 4, 2012 |access-date=December 2, 2009}}</ref> use against police,<ref>{{cite news |first1=Al |last1=Baker |first2=Mathew R. |last2=Warren |title=Shooting highlights the risks dogs pose to police, and vice versa |date=July 9, 2009 |place=New York, NY |newspaper=] |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2009/07/10/nyregion/10pitbull.html |access-date=January 7, 2010}}</ref> and as ]s.<ref>{{cite news |title='Dangerous dogs' weapon of choice |date=December 2, 2009 |work=BBC News |url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/uk_news/england/west_midlands/8391909.stm |access-date=December 2, 2009}}</ref> | |||
| The study examined 238 fatalities between 1979 and 1998 in which the breed of dog was known. It found that "the data indicates that Rottweilers and pit bull-type dogs accounted for 67% of human DBRF in the United States between 1997 and 1998" and that it was "extremely unlikely that they accounted for anywhere near 60% of dogs in the United States during that same period and, thus, there appears to be a breed-specific problem with fatalities."<ref name="CDC"/> | |||
| In an effort to counter the fighting reputation of pit bull–type dogs, in 1996 the ] renamed pit bull terriers "St. Francis Terriers", hoping that people would be more likely to adopt them.<ref>{{cite news |first=George |last=Cothran |title=Shouldn't we just kill this dog? |date=June 11, 1997 |place=San Francisco, California |periodical=] |url=http://www.sfweekly.com/1997-06-11/news/shouldn-t-we-just-kill-this-dog |access-date=September 4, 2009 |archive-date=February 9, 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120209215548/http://www.sfweekly.com/1997-06-11/news/shouldn-t-we-just-kill-this-dog/ |url-status=dead }}</ref> 60 temperament-screened dogs were adopted until the program was halted, after several of the newly adopted pit bulls killed cats.<ref>{{cite news |title=Bring breeders of high-risk dogs to heel |date=January 2004 |periodical=Animal People News |url=http://www.animalpeoplenews.org/04/1/editorialHighRiskDogs1.04.html |access-date=September 4, 2009 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100415213358/http://animalpeoplenews.org/04/1/editorialHighRiskDogs1.04.html |archive-date=April 15, 2010 |url-status=dead }}</ref> The New York City ] tried a similar approach in 2004, relabeling their pit bulls as "New Yorkies", but dropped the idea in the face of overwhelming public opposition.<ref>{{cite news |first=Clyde |last=Haberman |title=NYC; Rebrand Fido? An idea best put down |date=January 13, 2004 |place=New York City |newspaper=] |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2004/01/13/nyregion/nyc-rebrand-fido-an-idea-best-put-down.html |access-date=September 4, 2009}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |first=Charles |last=Laurence |title=Q: When is a pit bull terrier not a pit bull terrier? A: When it's a patriot terrier |date=January 4, 2004 |place=London, England |newspaper=] |url=https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/northamerica/usa/1451409/Q-When-is-a-a-pit-bull-terrier-not-a-pit-bull-A-When-its-a-patriot-terrier.html |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20220111/https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/northamerica/usa/1451409/Q-When-is-a-a-pit-bull-terrier-not-a-pit-bull-A-When-its-a-patriot-terrier.html |archive-date=January 11, 2022 |url-access=subscription |url-status=live |access-date=November 14, 2009}}{{cbignore}}</ref> | |||
| However, the article continued, saying that care should be taken in drawing conclusions based on these data because: | |||
| * first, the study likely covered only about 74% of actual DBRF cases; | |||
| * second, records of DBRF may have been biased by the propensity of media to report attacks by certain breeds over others; | |||
| * third, it is not always straightforward to identify a dog's breed, and records may be biased towards reporting 'known' aggressive breeds; and | |||
| * fourth, it was not clear how to count mixed breeds. | |||
| * fifth, such breeds have traditionally been used in dog fighting at a far higher percentage than others. Thus, the disparity of docility versus aggressiveness tends to rank very highly in Rottweilers and pit bull-type dogs when compared to other breeds, with human training playing the primary role. | |||
| == Temperament == | |||
| The authors concluded by noting that "breeds responsible for human DBRF have varied over time" (for example, Great Danes caused the most reported DBRF between 1979 and 1980). In the face of this inconclusive data, the study authors recommended that breed should not be the "primary factor driving public policy", instead making the following policy recommendations: "adequate funding for animal control agencies, enforcement of existing animal control laws, and educational and policy strategies to reduce inappropriate dog and owner behaviors" as likely to be beneficial and specifically to decrease the occurrence of dog bites.<ref name="CDC"/> | |||
| The ] gives this description of the characteristic of the American Pit Bull dog: "The essential characteristics of the American Pit Bull Terrier are strength, confidence, and zest for life. This breed is eager to please and brimming over with enthusiasm. The breed's natural agility makes it one of the most capable canine climbers so good fencing is a must for this breed. This breed does very well in performance events because of its high level of intelligence and its willingness to work."<ref name="auto3">{{cite web |title=American Pit Bull Terrier |date=1 May 2017 |series=Official UKC breed standard |publisher=] |url=https://www.ukcdogs.com/american-pit-bull-terrier |access-date=April 13, 2019}}</ref> | |||
| The standard imposed by the ADBA and Old Family Red Nose Registry (OFRNR) considers human aggression a disqualification factor.<ref>{{cite report |publisher=] |date=July 2016 |title=APBT official standard |url=https://adbadog.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/07/2015-Heritage-conformation-standard-outline.pdf |access-date=September 30, 2018}}</ref> The American Preservation Dog Registry (APDR) standard points out that "the temperament '''''must''''' be totally reliable with people".<ref>{{cite web |title=American Pit Bull Terrier |publisher=American Preservation Dog Registry |url=http://www.apdrdogs.com/american-pit-bull-terrier.html |access-date=September 30, 2018}}</ref> | |||
| In a peer-reviewed literature review of 66 dog bite risk studies, the ] determined that "breed is a poor sole predictor of dog bites. Controlled studies reveal no increased risk for the group blamed most often for dog bites, ‘pit bull-type’ dogs. Accordingly, targeting this breed or any another as a basis for dog-bite prevention is unfounded. As stated by the National Animal Control Association: "Dangerous and/or vicious animals should be labeled as such as a result of their actions or behavior and not because of their breed."<ref name=avma2014>{{cite web |url=https://www.avma.org/KB/Resources/LiteratureReviews/Pages/The-Role-of-Breed-in-Dog-Bite-Risk-and-Prevention.aspx |publisher=American Veterinary Medical Association |title=Dog Bite Risk and Prevention: The Role of Breed |date=17 April 2012 |accessdate=October 2014}}</ref> | |||
| In September 2000, the United States ] (CDC) published a study that examined dog-bite–related fatalities (human death caused by dog-bite injuries) to "summarize breeds of dogs involved in fatal human attacks during a 20-year period and to assess policy implications."<ref name="CDC">{{cite web|url=https://www.cdc.gov/HomeandRecreationalSafety/images/dogbreeds-a.pdf |title=Breeds of dogs involved in fatal human attacks in the United States between 1979 and 1998 |publisher=] |date=April 1, 2008 |accessdate=July 8, 2009 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150411211206/http://www.cdc.gov/homeandrecreationalsafety/images/dogbreeds-a.pdf |archive-date=April 11, 2015 }}</ref> The study examined 238 fatalities between 1979 and 1998 in which the breed of dog was known. It found that "the data indicates that Rottweilers and pit bull–type dogs accounted for 67% of human DBRF (dog bite-related fatality) in the United States between 1979 and 1998" and that it was "extremely unlikely that they accounted for anywhere near 60% of dogs in the United States during that same period and, thus, there appears to be a breed-specific problem with fatalities."<ref name="CDC" /> | |||
| In 2014, new statistical evidence emerged regarding the province-wide ban on "pit bulls", more specifically the American Pit Bull Terrier and Staffordshire Terrier, in the Canadian province of Ontario. It was reported to show that since the ban had been implemented, dog bites involving the two breeds and dogs of their likeness had dropped considerably in the province's largest city Toronto,<ref>Jonathan Kay, , ''The National Post'', October 6, 2014</ref> yet overall dog bites hit their highest levels this century in 2013 and 2014.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://globalnews.ca/news/2527882/torontos-pit-bulls-are-almost-gone-so-why-are-there-more-dog-bites-than-ever/?sf21251600=1|title=Toronto’s pit bulls are almost gone. So why are there more dog bites than ever?|last=Cain|first=Patrick|website=Global News|access-date=2016-03-07}}</ref> | |||
| Media portrayal has significantly impacted how the American public views the temperament of APBT. A study from 2002 suggests that "news media exaggerates and exacerbates any real or potential problems that exist with Pit Bulls."<ref>{{cite news |first=Judy |last=Cohen |title=Pit Bull Panic |date=2002|publisher=Journal of Popular Culture, vol. 36, no. 2}}</ref> Other studies also note that many people, including experts such as animal control officers and veterinarians, falsely report any stocky short-haired dogs as Pit Bulls.<ref>{{cite news |first=Randall |last=Lockwood |title=Are 'Pit Bulls' Different? An Analysis of the Pit Bull Terrier Controversy. |date=1987|publisher=ANTHROlOOS, vol. 1.}}</ref> Consequently, Pit Bulls have a lower probability of adoption or even being taken into shelters for care.<ref>{{cite news |first=Hillary |last=Twining |title=Managing the Stigma of Outlaw Breeds: A Case Study of Pit Bull Owners.|date=2000|publisher=Society & Animals}}</ref> | |||
| === Health === | |||
| ] | |||
| == Health == | |||
| {{Expand section|date=November 2009}} | {{Expand section|date=November 2009}} | ||
| Due to their athleticism and diverse breeding background, the breed tends to be hardy, with an average lifespan of 12 to 14 years, longer than many breeds of a similar size. There are some genetic conditions to be watchful for. The breed tends to have bone diseases such as hip dysplasia, ] and kneecap dislocation. The breed can also have skin problems, such as mange and skin allergies, because of its short coat. Other health ailments seen in the breed include thyroid and congenital heart defects.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://animalhealthcenternh.com/client-resources/breed-info/american-pitbull-terrier/ |title = Breed Info – Animal Health Center| date=November 2, 2022 }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.petmd.com/dog/breeds/c_dg_american_pit_bull_terrier |title = American Pit Bull Terrier Dog Breed Hypoallergenic, Health and Life Span {{!}} PetMD}}</ref> | |||
| The breed tends to have a higher than average incidence of ].<ref>{{cite book|last=Stahlkuppe|first=Joe|title=American pit bull terriers/American Staffordshire terriers|publisher=Barron's Educational Series|year=2000|isbn=0-7641-1052-7|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=oYQPNdO17o0C&pg=PT35&dq=%22american+pit+bull+terrier%22+%22dysplasia%22#v=onepage&q=%22american%20pit%20bull%20terrier%22%20%22dysplasia%22&f=false}}</ref> | |||
| Culling for performance has helped eliminate this problem and others such as ] problems, ] dysfunction and ]s.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.offa.org/stats.html|title=Statistics and Data – American Pit Bull Terrier|publisher=Orthopedic Foundation for Animals|accessdate=November 5, 2009}}</ref> American Pit Bull Terriers with dilute coat colors have not had a higher occurrence of skin allergies as other breeds.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2156/6/34|publisher=Biomedcentral.com|title=Polymorphisms within the canine MLPH gene are associated with dilute coat color in dogs|date=23 December 2004}}</ref> As a breed they are more susceptible to parvovirus than others if not vaccinated, especially as puppies, so vaccination is imperative beginning at 39 days old and continuing every 2 weeks until 4 months old. Then again at 8 months. Once a year after that, as recommend for all breeds.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://vetmedicine.about.com/od/dogdiseasesconditions/a/CWParvo.htm |title=Parvovirus in Dogs -Signs - Diagnosis - Treatment of Parvovirus |publisher=Vetmedicine.about.com |date=2013-06-23 |accessdate=2013-07-12}}</ref> | |||
| The breed tends to have a higher than average incidence of ].<ref>{{cite book|last=Stahlkuppe|first=Joe|title=American pit bull terriers/American Staffordshire terriers|publisher=Barron's Educational Series|year=2000|isbn=0-7641-1052-7|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=oYQPNdO17o0C&q=%22american+pit+bull+terrier%22+%22dysplasia%22&pg=PT35}}</ref> | |||
| They are very prone to ] due to culling for performance. There are two different types of Demodex Mange, namely Localized and Generalized Demodex. Although it is not contagious it is sometimes difficult to treat due to immunodeficiency in some puppies. The Localized symptoms are usually loss of hair in small patches on the head and feet of the puppies. This type will usually heal as the puppies grow and their immune systems grow stronger. The second type which is Generalized Demodex mange is a more severe form of the sickness. The symptoms are more severe and include loss of hair throughout the entire body and the skin may also be scabby and bloody. Generalized are usually hereditary due to immunodeficiency genes that are passed on from Sire and Dam to their puppies. A simple skin scraping test will allow the vet to diagnose demodex mange. The most widely used method to treat Demodex Mange is ] injections or oral medications. Since Demodex Mange lives in the hair follicles of the dog, Ivermectin will kill these mites at the source.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.sheltermedicine.vet.cornell.edu//shelter/Ivermectin/demodex.htm |title=Shelter Medicine – Cornell Veterinary Medicine |publisher=Sheltermedicine.vet.cornell.edu |date=January 15, 2008 |accessdate=October 26, 2011}}</ref> | |||
| Culling for performance has helped eliminate this problem and others such as ] problems, ] dysfunction and ]s.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.offa.org/stats.html|title=Statistics and Data – American Pit Bull Terrier|publisher=Orthopedic Foundation for Animals|access-date=November 5, 2009|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100209042815/http://www.offa.org/stats.html|archive-date=February 9, 2010|url-status=dead}}</ref> American Pit Bull Terriers with dilute coat colors have not had a higher occurrence of skin allergies as other breeds.<ref>{{cite journal|publisher=Biomedcentral.com|title=Polymorphisms within the canine MLPH gene are associated with dilute coat color in dogs|journal=BMC Genetics|volume=6|pages=34|date=December 23, 2004|doi=10.1186/1471-2156-6-34|last1=Philipp|first1=Ute|last2=Hamann|first2=Henning |last3=Mecklenburg|first3=Lars|last4=Nishino|first4=Seiji|last5=Mignot|first5=Emmanuel|last6=Günzel-Apel|first6=Anne-Rose|last7=Schmutz|first7=Sheila M.|last8=Leeb|first8=Tosso|pmid=15960853|pmc=1183202 |doi-access=free }}</ref> As a breed they are more susceptible to ] than others if not vaccinated, especially as puppies, so vaccination is imperative beginning at 39 days old and continuing every 2 weeks until 4 months old, then again at 8 months, and once a year after that, as recommended for all breeds.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://vetmedicine.about.com/od/dogdiseasesconditions/a/CWParvo.htm |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130501090647/http://vetmedicine.about.com/od/dogdiseasesconditions/a/CWParvo.htm |url-status=dead |archive-date=May 1, 2013 |title=Parvovirus in Dogs -Signs – Diagnosis – Treatment of Parvovirus |publisher=Vetmedicine.about.com |date=June 2, 2013 |access-date=July 12, 2013 }}</ref> | |||
| They are prone to ] due to culling for performance. There are two different types of demodex mange, namely localized and generalized demodex. Although it is not contagious, it is sometimes difficult to treat due to immunodeficiency in some puppies. The localized symptoms are usually loss of hair in small patches on the head and feet of the puppies. This type will usually heal as the puppies grow and their immune systems grow stronger. The second type, which is generalized demodex mange, is a more severe form of the sickness. The symptoms include loss of hair throughout the entire body and the skin may also be scabby and bloody. Generalized mange is usually hereditary due to immunodeficiency genes that are passed on from sire and dam to their puppies. A simple skin scraping test will allow the vet to diagnose demodex mange. The most widely used method to treat demodex mange is ] injections or oral medications. Since demodex mange lives in the hair follicles of the dog, ivermectin will kill these mites at the source.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.sheltermedicine.vet.cornell.edu//shelter/Ivermectin/demodex.htm |title=Shelter Medicine – Cornell Veterinary Medicine |publisher=Sheltermedicine.vet.cornell.edu |date=January 15, 2008 |access-date=October 26, 2011}}</ref> | |||
| == Varieties == | |||
| == Bloodlines == | |||
| The APBT has several ], many originating in "professional" ] throughout the 20th century. | |||
| Others developed for the ]s of the United Kennel Club in the 1980s.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.fiapbt.net/ingles17.html|title=Fiapbt – Bloodlines|access-date=September 30, 2018}}</ref> While the history and ancestry of the APBT bloodlines can provide context and insight into the breed's development, it is essential to prioritize responsible breeding practices and the well-being of the individual dogs. | |||
| === Castillo Pit Bulls === | |||
| Founded by Tekla Castillo in the early 1980s,<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.californiapits.com/|title=Tekla Castillo's California Pits|website=California Pits|accessdate=May 9, 2023}}</ref> her program focused on conformation standards within the UKC. The Castillo bloodline is a lineage of American Pit Bull Terriers known for its unique combination of different breeding lines, resulting in dogs with desirable traits such as strength, intelligence, and temperament. The bloodline's foundation includes dogs such as "PR" Nelson's Hazard Joe, born from breeding between Camarano's Buster Jo and Coonie's Bonnie. | |||
| The Castillo bloodline features a mix of other well-known bloodlines, with connections to influential dog breeders like Earl Tudor, Joe Corvino, J.P. Colby, and others. Due to the interconnected nature of the breeding community and the various influences on the bloodline, the Castillo lineage has expanded as a result of the collective efforts of multiple breeders who contributed to its development over time. | |||
| === Colby Pit Bulls === | |||
| ] | |||
| The Colby dogs are an ancient black-nosed bloodline that served as one of the pillars of the APBT breed. Considered one of the most important and famous bloodlines, the Colby dogs were started by John Pritchard Colby in 1889, who acquired the best fighting dogs (]s) imported from Ireland and England.<ref>{{Cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=5ja2NLfjEDAC&q=the+world+of+the+american+pit+bull+terrier|title=Colby's Book of the American Pit Bull Terrier|last1=Colby|first1=Louis B.|last2=Jessup|first2=Diane|date=1997|publisher=T.F.H. Publications|isbn=978-0-7938-2091-7|language=en}}</ref> One of the most famous dogs of his bloodline was ''Colby's Pincher''. Pincher was widely used as a ]. For this reason, Pincher is present in the pedigree of the vast majority of APBT specimens. The Colby dogs bloodline remains preserved by the family of John P. Colby.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.colbypitbull.com/|title=Colby kennel (Official Site) – History and pedigree. 2017|access-date=September 30, 2018}}</ref> | |||
| === Old Family Red Nose === | === Old Family Red Nose === | ||
| Old Family Red Nose (OFRN) is an old ] or a family of bloodlines originating in Ireland, and known for their specific and unique reddish coloration. Many dogs of the OFRN strain has a copper-red nose and coat, red lips, red toe nails, and red or amber eyes.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.apbt.info/tiki-index.php?page=Red+Nose+History|archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20120321142626/http://www.apbt.info/tiki-index.php?page=Red+Nose+History|url-status=dead|title=''Red Nose History'', The Encyclopedia of the American Pit Bull Terrier|archivedate=March 21, 2012|accessdate=May 9, 2023}}</ref> Not every American Pit Bull Terrier with these characteristics is necessarily an OFRN, since for this the dog must have a high percentage of the recognized bloodlines of this family in its pedigree.]In the middle of the 19th century, there was a strain of ] in Ireland that were known as "Old Family". At that time, all the bloodlines were closely inbred with each family clan. Since red is recessive to all colors but white, the strain was known as "Irish Old Family Reds". When the dogs began coming to America, they were already showing the red nose.<ref name="auto2">{{cite web|url=http://www.oldfamilyreds.com/red-history|title=Reds History – Old Family Reds|first=Robert|last=Vining|website=www.oldfamilyreds.com|access-date=September 30, 2018}}</ref><ref name="southerninfernokennels.com">{{cite web|url=http://www.southerninfernokennels.com/ofrnhistory.htm|title=- OFRN History|website=www.southerninfernokennels.com|access-date=September 30, 2018|archive-date=May 8, 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210508045053/https://www.southerninfernokennels.com/ofrnhistory.htm|url-status=dead}}</ref> The "Old Family Reds" dogs found their way to America in the 19th century, mainly via Irish immigrants, though many in the United States did import the breed.<ref name="auto2" /><ref name="southerninfernokennels.com" /> | |||
| Old Family Red Nose (OFRN) is an old ] of ] known for their specific reddish coloration. A dog of the red-nosed strain has a copper-red nose and coat, red lips, red toe nails, and red or amber eyes.<ref> {{wayback|url=http://www.apbt.info/tiki-index.php?page=Red+Nose+History |date=20120321142626 }}</ref> | |||
| Many strains have been crossed with the Old Family Reds at some time in their existence. Consequently, nearly any strain will occasionally throw a red-nosed pup. This means that not every red-nose dog is a true OFRN. The Old Family Reds produced more than their share of good ones unlike other strains are known. Old Family Reds were sought after for their gameness. The original strain continues to be bred. | |||
| ==== History ==== | |||
| ]In the middle of the 19th century, there was a breed of pit dogs in Ireland that were known as "Old Family." At that time, all the strains were closely inbred with each family clan. Since red is recessive to all colors but white, the breed was known as "Irish Old Family Reds." When the dogs began coming to America, they were already showing the red nose. | |||
| Although once renowned for its ], it was later bred to maintain its unique reddish color. Some of the most reputable breeders of the past, such as Lightner, McClintock, Hemphill, Williams, Menefee, Norrod and Wallace have contributed to the preservation and development of the strain. Finally, as McNolty said in his ''30-30 Journal'' (1967), "Regardless of one's historical perspective, these old amber-eyed, red-nosed, red-toe-nailed, red-coated dogs represent some of the most significant pit bull history and tradition that stands on four legs today."<ref name="southerninfernokennels.com" /> | |||
| The "Old Family Reds" dogs found their way to America mainly via Irish immigrants though many in the United States did import the breed. | |||
| == American Staffordshire Terrier == | |||
| Many strains have been crossed with the Old Family Reds at some time in their existence. | |||
| {{Main|American Staffordshire Terrier}} | |||
| This is how the breed of American Pit Bull Terrier was created. Consequently, nearly any strain will occasionally throw a red-nosed pup. To many dog owners, these red-nosed individuals are Old Family Red Noses even though the great preponderance of their blood is that of other strains. Sometimes such individuals will fail to measure up and thereby reflect undeserved discredit on the red-nosed strain. However the Old Family Reds produced more than their share of good ones unlike other strains are known. Old Family Reds were sought after for their high percentage in ability to produce deep gameness. | |||
| In 1935 in England a ] ] strain was accepted and registered as a purebred breed by ] as ].<ref>{{Cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=6pk5DAAAQBAJ&q=Staffordshire+Bull+Terriers:+a+practical+guide+for+owners+and+breeders|title=Staffordshire Bull Terriers: A Practical Guide for Owners and Breeders|last=Beaufoy|first=James|date=February 2, 2016|publisher=Crowood|isbn=978-1-78500-097-3|language=en}}</ref> One year later in America the ] (AKC) noted the growing popularity and acceptance of a similar breed already registered years earlier by the ] (UKC), the American Pit Bull Terrier. The AKC finally decided to accept to register and recognize the American breed, but would rename the breed with the commitment that the associate breeders would not breed dogs for dogfighting.<ref name=":1">{{Cite web|url=https://medium.com/@neylorz/the-origin-and-differences-between-the-american-staffordshire-terrier-and-the-american-pit-bull-a55f1c514b1b|title=The origin and differences between the American Staffordshire Terrier and the American Pit Bull…|last=Zaurisio|first=Neylor|date=November 2, 2019|website=Medium|language=en|access-date=December 28, 2019}}</ref> | |||
| American Bull Terrier without the "pit" (a word that referred to dogfighting arenas) was the first name considered by the AKC, but quickly dismissed due to protests by ]'s breeders.<ref name=":0" /> Yankee Terrier was another option, also dismissed.<ref name=":0" /> The name "Staffordshire Terrier" was chosen with the claim that the breed originally came from ] in England.<ref name=":2">{{Cite book|url=https://archive.org/details/americanpitbullt00joes|url-access=registration|quote=staffordshire.|title=American Pit Bull Terrier Handbook|last=Stahlkuppe |first=Joe|date=April 2000|publisher=Barron's Educational Series|isbn=978-1-4380-8141-0|language=en}}</ref> On June 10, 1936, around 50 UKC dogs entered the AKC ] under the name Staffordshire Terrier. Wilfred Truman Brandon founded the AKC Staffordshire Terrier Club of America (STCA). The Colby dog named Colby's Primo was one of the first to be regarded as an ideal model of the breed standard in the AKC. The AKC stud book was opened a few more times until it was last closed around the 1970s. In 1972 the AKC changed the name of the breed to American Staffordshire Terrier<ref name=":2" /> as it already intended to recognize the British Staffordshire Bull Terrier as a separate breed in subsequent years.<ref name=":4">{{Cite web|url=https://cdn.akc.org/AmericanStaffordshireTerrier-club-flier.pdf|title=Congratulations on Your New American Staffordshire Terrier|website=Staffordshire Terrier Club of America (])|date=June 10, 1936}}</ref> | |||
| Originally renowned for its gameness, it continues to be bred to maintain its unique reddish color. Some of the most reputable breeders in all Pit Bull history such as Lightner, McClintock, Hemphill, Williams, Menefee, Norrod and Wallace have contributed to the preservation and development of the strain. Finally, as McNolty said in his 30-30 Journal (1967) "Regardless of one's historical perspective, these old amber-eyed, red-nosed, red-toe-nailed, red-coated dogs represent some of the most significant pit bull history and tradition that stands on four legs today." | |||
| An argument persists concerning whether the American Pit Bull Terrier and the American Staffordshire Terrier are two separate breeds or still the same breed.<ref name=":2" /> Pit Bull and AmStaff breeders have distanced themselves from each other by pursuing different goals over the last 30 years, producing dogs with physical and temperament differences. Since 2015, the ] (ADBA), which has registered the American Pit Bull Terrier since 1909,<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://adbadog.com/history-of-the-adba/|title=History of the ADBA|last=Bullock|first=Tyler|date=May 1, 2016|website=American Dog Breeders Association|language=en-US|access-date=December 28, 2019}}</ref> considers the American Staffordshire Terrier to be a separate breed.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://adbadog.com/adba-apbt-stud-book-corrections/|title=American Dog Breeders Assoc APBT Stud Book Corrections|last=Bullock|first=Tyler|date=May 1, 2016|website=American Dog Breeders Association|language=en-US|access-date=December 28, 2019}}</ref><ref name=":5">{{Cite web|url=https://adbadog.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/07/Breed_Reclassification.pdf|title=Breed Reclassification Process Underway|date=2015|website=American Dog Breeders Association|access-date=December 28, 2019}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://adbadog.com/heritage-american-pit-bull-terrier-conformation-standard/|title=Heritage American Pit Bull Terrier Conformation Standard®|last=Bullock|first=Tyler|date=January 2, 2018|website=American Dog Breeders Association|language=en-US|access-date=December 28, 2019}}</ref> The UKC is the only kennel club at the moment to accept to register American Staffordshire Terriers as American Pit Bull Terriers.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.ukcdogs.com/single-registration-requirements-american-pit-bull-terrier|title=Single Registration Requirements : American Pit Bull Terrier {{!}} United Kennel Club (UKC)|website=www.ukcdogs.com|access-date=December 28, 2019}}</ref><ref> United Kennel Club.</ref> The UKC ] champions are very similar to those of the AKC, as both clubs share many judges. The AKC has not accepted to register American Pit Bull Terrier as American Staffordshire Terriers since the late 20th century.<ref name=":3">{{Cite web|url=https://medium.com/@neylorz/the-so-called-modern-bloodlines-9ad44ea6553|title=The so-called "modern" bloodlines|last=Zaurisio|first=Neylor|date=November 1, 2019|website=Medium|language=en|access-date=December 28, 2019}}</ref> | |||
| To this day there are dogs called dual registered, dogs registered at the same time as American Staffordshire Terrier in the AKC and American Pit Bull Terrier in the UKC, due to past breeders who decided to keep the two pedigree registers parallel.<ref name=":1" /><ref name=":3" /> Since 2015 the ADBA classifies most (or all) of these dual registered (AKC-UKC) dogs as American Staffordshire Terriers.<ref name=":5" /> | |||
| The ADBA conformation champion dogs differ greatly from UKC and AKC champion dogs. The AKC standard does not accept red nose dogs.<ref name=":4" /> The UKC dogs and the AmStaff are generally heavier and more robust and bulky than the ADBA American Pit Bull Terrier dogs.<ref name=":1" /> | |||
| == Activities == | == Activities == | ||
| American Pit Bull Terriers excel in many ], including ], ], ], ], and advanced ]. Out of the 115 dogs who have earned ] "superdog" status (by gaining championship titles in conformation, obedience, agility, and weightpull), 34 have been American Pit Bull Terriers, and another 13 were American Staffordshire Terriers.<ref name="aspca">{{cite web|url=http://www.aspca.org/site/PageServer?pagename=pets_pitbull |title=ASPCA: Pet Care: Dog Care: Pit Bull Information |access-date=December 22, 2008 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080801154956/http://www.aspca.org/site/PageServer?pagename=pets_pitbull |archive-date=August 1, 2008 |url-status=live }}</ref><ref name="UKC">{{cite web|url = http://www.ukcdogs.com/WebSite.nsf/WebPages/DogSuperdog|title = UKC Superdog!|access-date = November 22, 2015|archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20120626000455/http://www.ukcdogs.com/WebSite.nsf/WebPages/DogSuperdog|archive-date = June 26, 2012|url-status = dead|df = mdy-all}}</ref> | |||
| ]]]] | |||
| American Pit Bull Terriers excel in many ], including ], ], ], ], and advanced ]. Out of the 115 dogs who have earned UKC "superdog" status (by gaining championship titles in conformation, obedience, agility, and weightpull), 34 have been American Pit Bull Terriers, and another 13 were American Staffordshire Terriers.<ref name="aspca">{{cite web|url=http://www.aspca.org/site/PageServer?pagename=pets_pitbull|title=ASPCA: Pet Care: Dog Care: Pit Bull Information|accessdate=December 22, 2008|archiveurl=http://web.archive.org/web/20080801154956/http://www.aspca.org/site/PageServer?pagename=pets_pitbull <!-- Bot retrieved archive --> |archivedate = August 1, 2008}}</ref><ref name="UKC">{{cite web|url = http://www.ukcdogs.com/WebSite.nsf/WebPages/DogSuperdog|title = UKC Superdog!|accessdate = November 22, 2015}}</ref> | |||
| The American Pit Bull Terrier is a ] and is suitable for a wide range of working disciplines due to their intelligence, high energy, and endurance. In the United States they have been used as ]s,<ref name="forpittsake">{{cite web|url=http://www.forpitssake.org/sar.html|title=So That Others May Live...|access-date=December 22, 2008|archive-url=https://archive.today/20120731064506/http://www.forpitssake.org/sar.html|archive-date=July 31, 2012|url-status=dead}}</ref> ]s performing narcotics and explosives ],<ref name="cbp">{{cite web|url=http://www.cbp.gov/xp/CustomsToday/2002/October/k9.xml |title=Kool K-9 Popsicle retires |date=October 2002 |access-date=December 22, 2008 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111024001344/http://www.cbp.gov/xp/CustomsToday/2002/October/k9.xml |archive-date=October 24, 2011 }}</ref><ref name="lawdogsusa">{{cite web|url=http://www.lawdogsusa.org/whypitbulls1.html |archive-url=https://archive.today/20090114034620/http://www.lawdogsusa.org/whypitbulls1.html |url-status=dead |archive-date=January 14, 2009 |title=LawDogsUSA // Detection Dogs Made In America |access-date=December 22, 2008 }}</ref> ] dogs, ]s to provide services to the deaf, as well as general ]s, including ]s. | |||
| In some places they are often a favorite dog for catching feral pigs.<ref>{{Cite web|last=M|first=Logan|date=2021-06-18|title=Are Pit Bulls Good Hunting Dogs? - (Answered & Explained)|url=https://notabully.org/are-pitbulls-good-hunting-dogs/|access-date=2022-01-21|language=en-US}}</ref> Although, the ] (RSPCA) describes how this practice can be dangerous for the hunting dogs, noting that the dogs may experience severe injuries, "heat exhaustion, poisoning, vehicular trauma, snake bite, and accidental shooting".<ref>{{Cite web|title=What happens when dogs are used to hunt feral pigs? – RSPCA Knowledgebase|url=https://kb.rspca.org.au/knowledge-base/what-happens-when-dogs-are-used-to-hunt-feral-pigs/|access-date=2020-10-24|language=en-AU}}</ref> | |||
| == Breed-specific legislation == | |||
| The American Pit Bull Terrier is a ], and is suitable for a wide range of working disciplines due to their intelligence, high energy, and endurance. In the United States they have been used as ]s,<ref name="forpittsake">{{cite web|url=http://www.forpitssake.org/sar.html|title=So That Others May Live...|accessdate=December 22, 2008}}</ref> ]s performing narcotics and explosives ],<ref name="cbp">{{cite web|url=http://www.cbp.gov/xp/CustomsToday/2002/October/k9.xml|title=Kool K-9 Popsicle retires|date=October 2002|accessdate=December 22, 2008}}</ref><ref name="lawdogsusa">{{cite web|url=http://www.lawdogsusa.org/whypitbulls1.html|title=LawDogsUSA // Detection Dogs Made In America|accessdate=December 22, 2008<!--DASHBot-->}}{{dead link|date=May 2016|bot=medic}}{{cbignore|bot=medic}}</ref> ] dogs, ]s to provide services to the deaf, as well as general ]s. In the South they are often a favorite dog for catching feral pigs. | |||
| {{Main|Breed-specific legislation}} | |||
| United Kingdom,<ref name=":6">{{Cite web |title=Controlling your dog in public |url=https://www.gov.uk/control-dog-public/banned-dogs |access-date=2022-10-21 |website=GOV.UK |language=en}}</ref> Brazil,<ref>{{Cite web |title=Portaria n.o 422/2004 de 24 de Abril |url=https://files.dre.pt/1s/2004/04/097b00/25462546.pdf |access-date=2023-02-14 |language=pt}}</ref> Australia,<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.austlii.edu.au/au/legis/cth/consol_reg/cir1956432/sch1.html |title=Customs (Prohibited Imports) Regulations 1956 No. 90, as amended – Schedule 1|publisher=Commonwealth of Australia |date=July 6, 2009 |access-date=July 18, 2009|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090619213318/http://www.austlii.edu.au/au/legis/cth/consol_reg/cir1956432/sch1.html| archive-date= June 19, 2009 |url-status= live}}</ref> Ecuador,<ref>{{cite news|title=Ecuador descalifica a perros pit bull y rottweiler como mascotas |date=February 4, 2009 |place=Ecuador |publisher=Diaro Hoy |language=es |url=http://www.hoy.com.ec/noticias-ecuador/ecuador-descalifica-a-perros-pit-bull-y-rottweiler-como-mascotas-332398.html |access-date=August 24, 2009 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090312052256/http://www.hoy.com.ec/noticias-ecuador/ecuador-descalifica-a-perros-pit-bull-y-rottweiler-como-mascotas-332398.html |archive-date=March 12, 2009 }}</ref> Malaysia,<ref>{{cite news |first=Rashita|last=A. Hamid |title=Pit bull kills jogger |date=May 9, 2012 |newspaper=The Star |place=Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia|url=http://thestar.com.my/news/story.asp?file=/2012/5/9/nation/11255532&sec=nation |access-date=May 9, 2012}}</ref> New Zealand,<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.dia.govt.nz/diawebsite.nsf/wpg_URL/Resource-material-Dog-Control-Dog-Control-Amendment-Act-2003?OpenDocument&ExpandView |title=Dog Control Amendment Act of 2003 |publisher=New Zealand Department of Internal Affairs |date=July 2, 2009 |access-date=August 2, 2009}}</ref> the territory of Puerto Rico,<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.oslpr.org/download/en/1998/0158.pdf |title=H.B. 595 (Law 198) – Approved July 23, 1998 |publisher=Puerto Rico Office of Legislative Services |date=July 23, 1998 |access-date=August 4, 2009 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110927121655/http://www.oslpr.org/download/en/1998/0158.pdf |archive-date=September 27, 2011 }}</ref> Singapore,<ref> {{webarchive |url=https://web.archive.org/web/20091229013242/http://www.ava.gov.sg/NR/rdonlyres/0CA18578-7610-4917-BB67-C7DF4B96504B/17971/ABDogLicensingandControlRules2007.pdf |date=December 29, 2009 }}</ref> Venezuela,<ref>{{cite news|title=Venezuela restringe tenencia de perros Pit Bull |date=January 6, 2010 |location=Managua, Nicaragua |newspaper=La Prensa |language=es |url=http://www.laprensa.com.ni/2010/01/06/internacionales/12316 |access-date=January 8, 2010 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100720091321/http://www.laprensa.com.ni/2010/01/06/internacionales/12316 |archive-date=July 20, 2010 }}</ref> Trinidad and Tobago,<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.guardian.co.tt/news/2014-07-14/dog-control-act|title=The Dog Control Act|access-date=September 30, 2018}}</ref> Denmark, Israel,<ref>{{cite web|url=https://petolog.com/articles/banned-dogs?CODE=banned-dogs#israel|title=List of Banned Dogs by Countries|date=October 29, 2022 |publisher=PETolog}}</ref> France, Germany, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Spain, Switzerland,<ref name="vancouver">{{cite web|url=http://vancouver.ca/ctyclerk/cclerk/20050217/pe2.htm|title=Administrative report|publisher=Vancouver City Council|date=February 17, 2005}}</ref> and Turkey<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.tarimorman.gov.tr/DKMP/Haber/209/Tehlike-Arz-Eden-Hayvanlara-Iliskin-Genelge |title=Tehlike Arz Eden Hayvanlara İlişkin Genelge |trans-title=Directive on Dangerous Animals |publisher=] |language=tr |date=9 December 2021 |access-date=7 January 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211209103042/https://www.tarimorman.gov.tr/DKMP/Haber/209/Tehlike-Arz-Eden-Hayvanlara-Iliskin-Genelge |archive-date=9 December 2021}}</ref> have enacted some form of ] on pit bull–type dogs, including American Pit Bull Terriers, ranging from outright bans to restrictions on import and conditions on ownership.<ref name="vancouver" /><ref name="dogbite">{{cite web|url=http://www.dogbitelaw.com/PAGES/danger.htm#meaning|title=Vicious dogs|publisher=Dog bite law}}</ref> The state of ] in Australia places restrictions on the breed, including mandatory sterilization.<ref>{{cite news |first=Karen |last=Barlow |title=NSW bans pit bull terrier breed |date=May 3, 2005 |publisher=Australian Broadcasting Corporation |location=Sydney, Australia |url=http://www.abc.net.au/pm/content/2005/s1359018.htm |access-date=December 23, 2009}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |first=Gary |last=Hughes |title=Pit bull bite prompts call for national approach to dangerous dog breeds |date=October 20, 2009 |newspaper=The Australian |place=Sydney, Australia |url=http://www.theaustralian.com.au/news/pit-bull-bite-prompts-call-for-national-approach-to-dangerous-dog-breeds/story-e6frg6of-1225788552051 |access-date=December 23, 2009}}</ref> | |||
| Certain cities in the United States, as well as the province of ], Canada, have banned ownership of the American Pit Bull Terrier.<ref name="vancouver" /><ref>{{cite web |title=Information on The Dog Owners' Liability Act and Public Safety Related to Dogs Statute Law Amendment Act, 2005 |publisher=Ministry of the Attorney General of Ontario |url=http://www.attorneygeneral.jus.gov.on.ca/english/about/pubs/dola-pubsfty/dola-pubsfty.asp#TOC_15 |access-date=January 8, 2010 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20091224033000/http://www.attorneygeneral.jus.gov.on.ca/english/about/pubs/dola-pubsfty/dola-pubsfty.asp#TOC_15 |archive-date=December 24, 2009 |url-status=dead}}</ref> In the United Kingdom, it is against the law to own, sell, abandon, give away, or breed a Pit Bull Terrier.<ref name=":6" /> {{asof|September 2023}}, restrictions have been declining with at least 120 repeals since 2018.<ref name="BSL Continues To Crumble"/> | |||
| == Law == | |||
| {{main|Breed-specific legislation|Pit Bull}} | |||
| Australia,<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.austlii.edu.au/au/legis/cth/consol_reg/cir1956432/sch1.html |title=Customs (Prohibited Imports) Regulations 1956 No. 90, as amended – Schedule 1|publisher=Commonwealth of Australia |date=July 6, 2009 |accessdate=July 18, 2009|archiveurl=http://web.archive.org/web/20090619213318/http://www.austlii.edu.au/au/legis/cth/consol_reg/cir1956432/sch1.html| archivedate= June 19, 2009 <!--DASHBot-->| deadurl= no}}</ref> ],<ref>{{cite news |title=Ecuador descalifica a perros pit bull y rottweiler como mascotas |date=February 4, 2009 |place=Ecuador |publisher=Diaro Hoy |language=Spanish |url=http://www.hoy.com.ec/noticias-ecuador/ecuador-descalifica-a-perros-pit-bull-y-rottweiler-como-mascotas-332398.html |accessdate=August 24, 2009}}</ref> ],<ref>{{cite news |first=Rashita|last=A. Hamid |title=Pit bull kills jogger |date=May 9, 2012 |newspaper=The Star |place=Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia|url=http://thestar.com.my/news/story.asp?file=/2012/5/9/nation/11255532&sec=nation |accessdate=May 9, 2012}}</ref> New Zealand,<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.dia.govt.nz/diawebsite.nsf/wpg_URL/Resource-material-Dog-Control-Dog-Control-Amendment-Act-2003?OpenDocument&ExpandView |title=Dog Control Amendment Act of 2003 |publisher=New Zealand Department of Internal Affairs |date=July 2, 2009 |accessdate=August 2, 2009}}</ref> the territory of ],<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.oslpr.org/download/en/1998/0158.pdf|title=H.B. 595 (Law 198) – Approved July 23, 1998 |publisher=Puerto Rico Office of Legislative Services |date=July 23, 1998 |accessdate=August 4, 2009}}</ref> ],<ref></ref> ]<ref>{{cite news |title=Venezuela restringe tenencia de perros Pit Bull |date=January 6, 2010 |location=Managua, Nicaragua |newspaper=La Prensa |language=Spanish |url=http://www.laprensa.com.ni/2010/01/06/internacionales/12316 |accessdate=January 8, 2010}}</ref> Denmark, Israel,<ref>{{cite web|url=https://petolog.com/articles/banned-dogs?CODE=banned-dogs#israel|title=List of Banned Dogs by Countries|publisher=PETolog}}</ref> France, Germany, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Spain and Switzerland<ref name="vancouver">{{cite web|url=http://vancouver.ca/ctyclerk/cclerk/20050217/pe2.htm|title=Administrative report|publisher=Vancouver City Council|date=17 February 2005}}</ref> have enacted some form of ] on pit bull-type dogs, including American Pit Bull Terriers, ranging from outright bans to restrictions on import and conditions on ownership.<ref name="vancouver" /><ref name="dogbite">{{cite web|url=http://www.dogbitelaw.com/PAGES/danger.htm#meaning|title=Vicious dogs|publisher=Dog bite law}}</ref> The state of ] in Australia places restrictions on the breed, including mandatory sterilization.<ref>{{cite news |first=Karen |last=Barlow |title=NSW bans pit bull terrier breed |date=May 3, 2005 |publisher=Australian Broadcasting Corporation |location=Sydney, Australia |url=http://www.abc.net.au/pm/content/2005/s1359018.htm |accessdate=December 23, 2009}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |first=Gary |last=Hughes |title=Pit bull bite prompts call for national approach to dangerous dog breeds |date=October 20, 2009 |newspaper=The Australian |place=Sydney, Australia |url=http://www.theaustralian.com.au/news/pit-bull-bite-prompts-call-for-national-approach-to-dangerous-dog-breeds/story-e6frg6of-1225788552051 |accessdate=December 23, 2009}}</ref> | |||
| In 2014, new statistical evidence emerged regarding the province-wide ban on "pit bulls", more specifically the American Pit Bull Terrier and ], in the Canadian province of Ontario. Since the ban had been implemented, dog bites involving pit bull types, as identified by the owners or city investigators, had dropped considerably as the registered populations of these breeds decreased in the province's largest city, Toronto.<ref>Kay, Jonathan. (6 October 2014). . '']''.</ref> However, "Toronto's reported dog bites have been rising since 2012, and in 2013 and 2014, reached their highest levels this century, even as pit bulls and similar dogs neared local extinction," and evidence published in '']'' implicates several other dog breeds had contributed to the rise.<ref name=Cain-2016-GN>{{cite news |last=Cain |first=Patrick |date=20 February 2016 |title=Toronto's pit bulls are almost gone. So why are there more dog bites than ever? |newspaper=] |url=http://globalnews.ca/news/2527882/torontos-pit-bulls-are-almost-gone-so-why-are-there-more-dog-bites-than-ever/?sf21251600=1 |access-date=7 March 2016}}</ref> | |||
| Certain counties and cities in the United States have banned ownership of the American Pit Bull Terrier, as well as the province of Ontario in Canada.<ref name="vancouver"/><ref>{{cite web |title=Information on The Dog Owners' Liability Act and Public Safety Related to Dogs Statute Law Amendment Act, 2005 |publisher=Ministry of the Attorney General of Ontario |url=http://www.attorneygeneral.jus.gov.on.ca/english/about/pubs/dola-pubsfty/dola-pubsfty.asp#TOC_15 |accessdate=January 8, 2010| archiveurl= http://web.archive.org/web/20091224033000/http://www.attorneygeneral.jus.gov.on.ca/english/about/pubs/dola-pubsfty/dola-pubsfty.asp| archivedate= December 24, 2009 <!--DASHBot-->| deadurl= no}}</ref> American Pit Bull Terriers are also on a list of four breeds that are banned in the UK.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.gov.uk/control-dog-public/banned-dogs |title=Banned dogs |date=August 5, 2015 |work= |publisher=] |accessdate=January 26, 2016}}</ref> | |||
| == |
==See also== | ||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] (ancestor of the APBT) | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * '']'' | |||
| * ] | |||
| * '']'' (TV series) | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| {{clear}} | {{clear}} | ||
| == References == | == References == | ||
| {{ |
{{Reflist}} | ||
| == Further reading == | == Further reading == | ||
| {{ |
{{Refbegin}} | ||
| *{{cite book|last=Capp|first=Dawn M. |title=American Pit Bull Terriers: Fact or Fiction: The Truth Behind One of America's Most Popular Breeds|publisher=Doral Publishing|year=2004|isbn=0-9745407-1-4}} | *{{cite book|last=Capp|first=Dawn M. |title=American Pit Bull Terriers: Fact or Fiction: The Truth Behind One of America's Most Popular Breeds|publisher=Doral Publishing|year=2004|isbn=0-9745407-1-4}} | ||
| *{{cite book|last=Foster|first=Ken|title=The Dogs Who Found Me: What I've Learned from Pets Who Were Left Behind|publisher=Lyons Press|year=2006|isbn=1-59228-749-2}} | *{{cite book|last=Foster|first=Ken|title=The Dogs Who Found Me: What I've Learned from Pets Who Were Left Behind|publisher=Lyons Press|year=2006|isbn=1-59228-749-2|url=https://archive.org/details/dogswhofoundme00kenf}} | ||
| *{{cite book|last=Stahlkuppe|first=Joe|title=American Pit Bull Terrier Handbook|publisher=Barron's Educational Series|year=2000|isbn=0-7641-1233-3}} | *{{cite book|last=Stahlkuppe|first=Joe|title=American Pit Bull Terrier Handbook|publisher=Barron's Educational Series|year=2000|isbn=0-7641-1233-3|url=https://archive.org/details/americanpitbullt00joes}} | ||
| {{ |
{{Refend}} | ||
| == External links == | == External links == | ||
| {{Commons}} | |||
| {{commons|American Pit Bull Terrier}} | |||
| * |
* | ||
| * | |||
| {{Terriers}} | {{Terriers}} | ||
| {{American dogs}} | {{American dogs}} | ||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 06:47, 6 January 2025
American dog breed This article is about the dog breed. For the family of dogs, including legal status worldwide, see Pit bull. Not to be confused with Staffordshire Bull Terrier or American Staffordshire Terrier.Dog breed
| American Pit Bull Terrier | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other names |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common nicknames |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Origin | United States | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Foundation stock | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dog (domestic dog) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The American Pit Bull Terrier (APBT) is a dog breed recognized by the United Kennel Club (UKC) and the American Dog Breeders Association (ADBA), but not the American Kennel Club (AKC). It is a medium-sized, short-haired dog, of a solid build, whose early ancestors came from England. When compared with the English Staffordshire Bull Terrier, the American Pit Bull Terrier is larger by margins of 6–8 inches (15–20 cm) in height and 25–35 pounds (11–16 kg) in weight. The American Pit Bull Terrier varies in size: males are normally about 18–21 inches (45–53 cm) in height and around 35–60 pounds (15–27 kg) in weight, while females are normally around 17–20 inches (43–50 cm) in height and 30–50 pounds (13–22 kg) in weight.
According to the ADBA, the American Pit Bull is described to be medium-sized and has a short coat and smooth well-defined muscle structure, and its eyes are to be round to almond-shaped, and its ears are to be small to medium in length, typically half prick or rose in carriage. The tail is prescribed to be slightly thick and tapering to a point. The coat is required by the ADBA to be glossy, smooth, short, and stiff to the touch. Many colors, color patterns, and combinations of colors are acceptable to the ADBA, except that both the ADBA and UKC do not recognize merle coloring. Color patterns that are typical in the breed are solid and tuxedo.
Despite the colloquial use of the term "pit bull" to encompass a whole category of dogs and the legal use of the term to include several breeds in legislation, some conservative professional breeders of the American Pit Bull Terrier as well as some experts and supporters claim that historically the APBT is the only true "pit bull" and the only breed that should be denominated as such.
Twelve countries in Europe, as well as Australia, Canada, some parts of the United States, Ecuador, Malaysia, New Zealand, Puerto Rico, Singapore, and Venezuela, have enacted some form of breed-specific legislation on pit bull-type dogs, including American Pit Bull Terriers, ranging from outright bans to restrictions and conditions on ownership. Several states in Australia place restrictions on the breed, including mandatory sterilization. Pit Bull Terriers are banned in the United Kingdom, in the Canadian province of Ontario, and in many locations in the United States.
History


Until the mid-19th century the since-extinct Old English Terriers and Old English Bulldogs were bred together to produce a dog that combined the gameness of the terrier with the strength and athleticism of the bulldog. This type of dog, which was bred in England, became known as the bull and terrier. These dogs arrived in the United States in the late nineteenth century where they became the direct ancestors of the American Pit Bull Terrier.
In the United Kingdom, bull and terriers were used in bloodsports such as bull baiting and bear baiting. These bloodsports were banned in 1835 when Britain introduced animal welfare laws. Since dog fighting is cheaper to organize and far easier to conceal from the law than bull or bear baits, bloodsport proponents turned to pitting their dogs against each other instead. Dog fighting was used as both a bloodsport (often involving gambling) and a way to continue to test the quality of their stock. For decades afterwards, dog fighting clandestinely took place in small areas of Britain. These dogs arrived in America around 1845 to 1860, where the dog fighting practice had continuity. On February 10, 1898, the breed was recognized by the United Kennel Club (UKC) named as American Pit Bull Terrier.
For some time in the early part of the 20th century the UKC began to register the breed name with the word "pit" in parentheses (American (Pit) Bull Terrier), to facilitate public acceptance as an American Bull Terrier. However this only lasted a short time and returned to the previous form.
In the early 20th century, pit bulls were used as catch dogs in America for semi-wild cattle and hogs, to hunt hogs, and drive livestock, and as family companions.
Pit Bull Terriers fill the role of companion dogs, working dogs, athletic sport dogs (weight pulling, French Ring Sport, Top Dog), police dogs, and therapy dogs. Pit Bull Terriers also constitute the majority of dogs used for illegal dog fighting in America In addition, law enforcement organizations report these dogs are used for other nefarious purposes, such as guarding illegal narcotics operations, use against police, and as attack dogs.
In an effort to counter the fighting reputation of pit bull–type dogs, in 1996 the San Francisco Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals renamed pit bull terriers "St. Francis Terriers", hoping that people would be more likely to adopt them. 60 temperament-screened dogs were adopted until the program was halted, after several of the newly adopted pit bulls killed cats. The New York City Center for Animal Care and Control tried a similar approach in 2004, relabeling their pit bulls as "New Yorkies", but dropped the idea in the face of overwhelming public opposition.
Temperament
The UKC gives this description of the characteristic of the American Pit Bull dog: "The essential characteristics of the American Pit Bull Terrier are strength, confidence, and zest for life. This breed is eager to please and brimming over with enthusiasm. The breed's natural agility makes it one of the most capable canine climbers so good fencing is a must for this breed. This breed does very well in performance events because of its high level of intelligence and its willingness to work."
The standard imposed by the ADBA and Old Family Red Nose Registry (OFRNR) considers human aggression a disqualification factor. The American Preservation Dog Registry (APDR) standard points out that "the temperament must be totally reliable with people".
In September 2000, the United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) published a study that examined dog-bite–related fatalities (human death caused by dog-bite injuries) to "summarize breeds of dogs involved in fatal human attacks during a 20-year period and to assess policy implications." The study examined 238 fatalities between 1979 and 1998 in which the breed of dog was known. It found that "the data indicates that Rottweilers and pit bull–type dogs accounted for 67% of human DBRF (dog bite-related fatality) in the United States between 1979 and 1998" and that it was "extremely unlikely that they accounted for anywhere near 60% of dogs in the United States during that same period and, thus, there appears to be a breed-specific problem with fatalities."
Media portrayal has significantly impacted how the American public views the temperament of APBT. A study from 2002 suggests that "news media exaggerates and exacerbates any real or potential problems that exist with Pit Bulls." Other studies also note that many people, including experts such as animal control officers and veterinarians, falsely report any stocky short-haired dogs as Pit Bulls. Consequently, Pit Bulls have a lower probability of adoption or even being taken into shelters for care.
Health
| This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (November 2009) |
Due to their athleticism and diverse breeding background, the breed tends to be hardy, with an average lifespan of 12 to 14 years, longer than many breeds of a similar size. There are some genetic conditions to be watchful for. The breed tends to have bone diseases such as hip dysplasia, canine degenerative myelopathy and kneecap dislocation. The breed can also have skin problems, such as mange and skin allergies, because of its short coat. Other health ailments seen in the breed include thyroid and congenital heart defects.
The breed tends to have a higher than average incidence of hip dysplasia. Culling for performance has helped eliminate this problem and others such as patella problems, thyroid dysfunction and congenital heart defects. American Pit Bull Terriers with dilute coat colors have not had a higher occurrence of skin allergies as other breeds. As a breed they are more susceptible to parvovirus than others if not vaccinated, especially as puppies, so vaccination is imperative beginning at 39 days old and continuing every 2 weeks until 4 months old, then again at 8 months, and once a year after that, as recommended for all breeds.
They are prone to demodex mange due to culling for performance. There are two different types of demodex mange, namely localized and generalized demodex. Although it is not contagious, it is sometimes difficult to treat due to immunodeficiency in some puppies. The localized symptoms are usually loss of hair in small patches on the head and feet of the puppies. This type will usually heal as the puppies grow and their immune systems grow stronger. The second type, which is generalized demodex mange, is a more severe form of the sickness. The symptoms include loss of hair throughout the entire body and the skin may also be scabby and bloody. Generalized mange is usually hereditary due to immunodeficiency genes that are passed on from sire and dam to their puppies. A simple skin scraping test will allow the vet to diagnose demodex mange. The most widely used method to treat demodex mange is ivermectin injections or oral medications. Since demodex mange lives in the hair follicles of the dog, ivermectin will kill these mites at the source.
Bloodlines
The APBT has several bloodlines, many originating in "professional" dog fighting throughout the 20th century.
Others developed for the conformation shows of the United Kennel Club in the 1980s. While the history and ancestry of the APBT bloodlines can provide context and insight into the breed's development, it is essential to prioritize responsible breeding practices and the well-being of the individual dogs.
Castillo Pit Bulls
Founded by Tekla Castillo in the early 1980s, her program focused on conformation standards within the UKC. The Castillo bloodline is a lineage of American Pit Bull Terriers known for its unique combination of different breeding lines, resulting in dogs with desirable traits such as strength, intelligence, and temperament. The bloodline's foundation includes dogs such as "PR" Nelson's Hazard Joe, born from breeding between Camarano's Buster Jo and Coonie's Bonnie.
The Castillo bloodline features a mix of other well-known bloodlines, with connections to influential dog breeders like Earl Tudor, Joe Corvino, J.P. Colby, and others. Due to the interconnected nature of the breeding community and the various influences on the bloodline, the Castillo lineage has expanded as a result of the collective efforts of multiple breeders who contributed to its development over time.
Colby Pit Bulls
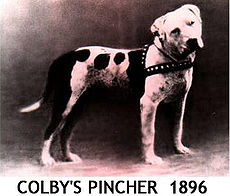
The Colby dogs are an ancient black-nosed bloodline that served as one of the pillars of the APBT breed. Considered one of the most important and famous bloodlines, the Colby dogs were started by John Pritchard Colby in 1889, who acquired the best fighting dogs (bull and terriers) imported from Ireland and England. One of the most famous dogs of his bloodline was Colby's Pincher. Pincher was widely used as a stud dog. For this reason, Pincher is present in the pedigree of the vast majority of APBT specimens. The Colby dogs bloodline remains preserved by the family of John P. Colby.
Old Family Red Nose
Old Family Red Nose (OFRN) is an old strain or a family of bloodlines originating in Ireland, and known for their specific and unique reddish coloration. Many dogs of the OFRN strain has a copper-red nose and coat, red lips, red toe nails, and red or amber eyes. Not every American Pit Bull Terrier with these characteristics is necessarily an OFRN, since for this the dog must have a high percentage of the recognized bloodlines of this family in its pedigree.

In the middle of the 19th century, there was a strain of pit dogs in Ireland that were known as "Old Family". At that time, all the bloodlines were closely inbred with each family clan. Since red is recessive to all colors but white, the strain was known as "Irish Old Family Reds". When the dogs began coming to America, they were already showing the red nose. The "Old Family Reds" dogs found their way to America in the 19th century, mainly via Irish immigrants, though many in the United States did import the breed.
Many strains have been crossed with the Old Family Reds at some time in their existence. Consequently, nearly any strain will occasionally throw a red-nosed pup. This means that not every red-nose dog is a true OFRN. The Old Family Reds produced more than their share of good ones unlike other strains are known. Old Family Reds were sought after for their gameness. The original strain continues to be bred.
Although once renowned for its gameness, it was later bred to maintain its unique reddish color. Some of the most reputable breeders of the past, such as Lightner, McClintock, Hemphill, Williams, Menefee, Norrod and Wallace have contributed to the preservation and development of the strain. Finally, as McNolty said in his 30-30 Journal (1967), "Regardless of one's historical perspective, these old amber-eyed, red-nosed, red-toe-nailed, red-coated dogs represent some of the most significant pit bull history and tradition that stands on four legs today."
American Staffordshire Terrier
Main article: American Staffordshire TerrierIn 1935 in England a Cradley Heath bull and terrier strain was accepted and registered as a purebred breed by The Kennel Club as Staffordshire Bull Terrier. One year later in America the American Kennel Club (AKC) noted the growing popularity and acceptance of a similar breed already registered years earlier by the United Kennel Club (UKC), the American Pit Bull Terrier. The AKC finally decided to accept to register and recognize the American breed, but would rename the breed with the commitment that the associate breeders would not breed dogs for dogfighting.
American Bull Terrier without the "pit" (a word that referred to dogfighting arenas) was the first name considered by the AKC, but quickly dismissed due to protests by English Bull Terrier's breeders. Yankee Terrier was another option, also dismissed. The name "Staffordshire Terrier" was chosen with the claim that the breed originally came from Staffordshire in England. On June 10, 1936, around 50 UKC dogs entered the AKC stud book under the name Staffordshire Terrier. Wilfred Truman Brandon founded the AKC Staffordshire Terrier Club of America (STCA). The Colby dog named Colby's Primo was one of the first to be regarded as an ideal model of the breed standard in the AKC. The AKC stud book was opened a few more times until it was last closed around the 1970s. In 1972 the AKC changed the name of the breed to American Staffordshire Terrier as it already intended to recognize the British Staffordshire Bull Terrier as a separate breed in subsequent years.
An argument persists concerning whether the American Pit Bull Terrier and the American Staffordshire Terrier are two separate breeds or still the same breed. Pit Bull and AmStaff breeders have distanced themselves from each other by pursuing different goals over the last 30 years, producing dogs with physical and temperament differences. Since 2015, the American Dog Breeders Association (ADBA), which has registered the American Pit Bull Terrier since 1909, considers the American Staffordshire Terrier to be a separate breed. The UKC is the only kennel club at the moment to accept to register American Staffordshire Terriers as American Pit Bull Terriers. The UKC conformation champions are very similar to those of the AKC, as both clubs share many judges. The AKC has not accepted to register American Pit Bull Terrier as American Staffordshire Terriers since the late 20th century.
To this day there are dogs called dual registered, dogs registered at the same time as American Staffordshire Terrier in the AKC and American Pit Bull Terrier in the UKC, due to past breeders who decided to keep the two pedigree registers parallel. Since 2015 the ADBA classifies most (or all) of these dual registered (AKC-UKC) dogs as American Staffordshire Terriers.
The ADBA conformation champion dogs differ greatly from UKC and AKC champion dogs. The AKC standard does not accept red nose dogs. The UKC dogs and the AmStaff are generally heavier and more robust and bulky than the ADBA American Pit Bull Terrier dogs.
Activities
American Pit Bull Terriers excel in many dog sports, including weight pulling, dog agility, flyball, lure coursing, and advanced obedience competition. Out of the 115 dogs who have earned UKC "superdog" status (by gaining championship titles in conformation, obedience, agility, and weightpull), 34 have been American Pit Bull Terriers, and another 13 were American Staffordshire Terriers.
The American Pit Bull Terrier is a working dog and is suitable for a wide range of working disciplines due to their intelligence, high energy, and endurance. In the United States they have been used as search and rescue dogs, police dogs performing narcotics and explosives detection, Border Patrol dogs, hearing dogs to provide services to the deaf, as well as general service dogs, including therapy dogs.
In some places they are often a favorite dog for catching feral pigs. Although, the Australian Royal Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals (RSPCA) describes how this practice can be dangerous for the hunting dogs, noting that the dogs may experience severe injuries, "heat exhaustion, poisoning, vehicular trauma, snake bite, and accidental shooting".
Breed-specific legislation
Main article: Breed-specific legislationUnited Kingdom, Brazil, Australia, Ecuador, Malaysia, New Zealand, the territory of Puerto Rico, Singapore, Venezuela, Trinidad and Tobago, Denmark, Israel, France, Germany, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Spain, Switzerland, and Turkey have enacted some form of breed-specific legislation on pit bull–type dogs, including American Pit Bull Terriers, ranging from outright bans to restrictions on import and conditions on ownership. The state of New South Wales in Australia places restrictions on the breed, including mandatory sterilization.
Certain cities in the United States, as well as the province of Ontario, Canada, have banned ownership of the American Pit Bull Terrier. In the United Kingdom, it is against the law to own, sell, abandon, give away, or breed a Pit Bull Terrier. As of September 2023, restrictions have been declining with at least 120 repeals since 2018.
In 2014, new statistical evidence emerged regarding the province-wide ban on "pit bulls", more specifically the American Pit Bull Terrier and American Staffordshire Terrier, in the Canadian province of Ontario. Since the ban had been implemented, dog bites involving pit bull types, as identified by the owners or city investigators, had dropped considerably as the registered populations of these breeds decreased in the province's largest city, Toronto. However, "Toronto's reported dog bites have been rising since 2012, and in 2013 and 2014, reached their highest levels this century, even as pit bulls and similar dogs neared local extinction," and evidence published in Global News implicates several other dog breeds had contributed to the rise.
See also
- Dogs portal
- List of dog breeds
- American Staffordshire Terrier
- Bull and terrier (ancestor of the APBT)
- Bull-type terriers
- Dog fighting in the United States
- Old English Bulldog
- Pit Boss
- Pit Bulls & Parolees (TV series)
References
- ^ "UKC Standard of the American Pit Bull Terrier" (PDF). 2017. Retrieved April 1, 2017.
- ^ "ADBA Standard of the American pit bull terrier" (PDF). 2018. Retrieved February 2, 2018.
- "Official list of all American Kennel Club dog breeds". American Kennel Club. Retrieved March 14, 2019.
- "Dog Coat Patterns – Caninest.com". 2018. Retrieved February 5, 2018.
- "ADBA – American Pit Bull Terrier Color Chart Gallery". 2018. Retrieved February 5, 2018.
- "A Note on the Use of the Term, "Pit Bull"". The Real Pit Bull. Retrieved July 27, 2018.
- "History of the Pit Bull – Facts and Myths About Pit Bull History". Diane Jessup. Retrieved July 27, 2018.
- "What is a Pit Bull?". pitbulltruth.org. Retrieved July 27, 2018.
- "Working Pit Bull". Diane Jessup. March 20, 2012. Retrieved July 27, 2018.
- ^ "Controlling your dog in public". GOV.UK. Retrieved October 21, 2022.
- "Information on The Dog Owners' Liability Act and Public Safety Related to Dogs Statute Law Amendment Act, 2005". Ministry of the Attorney General. Archived from the original on December 24, 2009. Retrieved July 25, 2007.
- ^ "BSL Continues To Crumble". Pitbullinfo.org. Retrieved November 15, 2021.
- ^ "American Pit Bull Terrier". United Kennel Club (UKC). November 1, 2008. Archived from the original on July 9, 2009. Retrieved August 7, 2009.
- ^ "Sporting Magazine: Dustman". Rogerson & Tuxford. June 1812. p. 97. Retrieved May 23, 2020 – via Google Books.
- Curnutt, Jordan (2001). Animals and the Law: A Sourcebook. ABC-CLIO. p. 284. ISBN 978-1-57607-147-2.
- Dickey, Bronwen (May 1, 2016). Pit Bull: The Battle over an American Icon. Knopf Doubleday Publishing Group. p. 25. ISBN 978-0-307-96177-8.
- Janish, Joseph (January 2, 2012). American Staffordshire Terrier. i5 Publishing. p. 13. ISBN 978-1-59378-983-1.
- ^ Stratton, Richard F. (1983). The World of the American Pit Bull Terrier. T.F.H. Publications. ISBN 978-0-87666-851-1.
- "Cool K-9 Popsicle retires". U.S. Customs Today. 38 (10). October 2002. Archived from the original on October 24, 2011. Retrieved August 7, 2009.
- Lewin, Adrienne Mand (October 12, 2005). "Protecting the Nation – One Sniff at a Time". ABC News. Retrieved February 2, 2009.
- Simon, Scott (June 21, 2008). "Trainer turns pit bull into therapy dog". National Public Radio. Retrieved August 7, 2009.
- "Dog Fighting Fact Sheet". Humane Society of the United States. 2009. Archived from the original on July 19, 2009. Retrieved August 7, 2009.
- Swift, E.M. (July 27, 1987). "The pit bull: friend and killer". Sports Illustrated. Vol. 67, no. 4. Archived from the original on November 4, 2012. Retrieved December 2, 2009.
- Baker, Al; Warren, Mathew R. (July 9, 2009). "Shooting highlights the risks dogs pose to police, and vice versa". The New York Times. New York, NY. Retrieved January 7, 2010.
- "'Dangerous dogs' weapon of choice". BBC News. December 2, 2009. Retrieved December 2, 2009.
- Cothran, George (June 11, 1997). "Shouldn't we just kill this dog?". San Francisco Weekly. San Francisco, California. Archived from the original on February 9, 2012. Retrieved September 4, 2009.
- "Bring breeders of high-risk dogs to heel". Animal People News. January 2004. Archived from the original on April 15, 2010. Retrieved September 4, 2009.
- Haberman, Clyde (January 13, 2004). "NYC; Rebrand Fido? An idea best put down". The New York Times. New York City. Retrieved September 4, 2009.
- Laurence, Charles (January 4, 2004). "Q: When is a pit bull terrier not a pit bull terrier? A: When it's a patriot terrier". The Daily Telegraph. London, England. Archived from the original on January 11, 2022. Retrieved November 14, 2009.
- "American Pit Bull Terrier". Official UKC breed standard. United Kennel Club. May 1, 2017. Retrieved April 13, 2019.
- APBT official standard (PDF) (Report). American Dog Breeders Association. July 2016. Retrieved September 30, 2018.
- "American Pit Bull Terrier". American Preservation Dog Registry. Retrieved September 30, 2018.
- ^ "Breeds of dogs involved in fatal human attacks in the United States between 1979 and 1998" (PDF). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. April 1, 2008. Archived from the original (PDF) on April 11, 2015. Retrieved July 8, 2009.
- Cohen, Judy (2002). "Pit Bull Panic". Journal of Popular Culture, vol. 36, no. 2.
- Lockwood, Randall (1987). "Are 'Pit Bulls' Different? An Analysis of the Pit Bull Terrier Controversy". ANTHROlOOS, vol. 1.
- Twining, Hillary (2000). "Managing the Stigma of Outlaw Breeds: A Case Study of Pit Bull Owners". Society & Animals.
- "Breed Info – Animal Health Center". November 2, 2022.
- "American Pit Bull Terrier Dog Breed Hypoallergenic, Health and Life Span | PetMD".
- Stahlkuppe, Joe (2000). American pit bull terriers/American Staffordshire terriers. Barron's Educational Series. ISBN 0-7641-1052-7.
- "Statistics and Data – American Pit Bull Terrier". Orthopedic Foundation for Animals. Archived from the original on February 9, 2010. Retrieved November 5, 2009.
- Philipp, Ute; Hamann, Henning; Mecklenburg, Lars; Nishino, Seiji; Mignot, Emmanuel; Günzel-Apel, Anne-Rose; Schmutz, Sheila M.; Leeb, Tosso (December 23, 2004). "Polymorphisms within the canine MLPH gene are associated with dilute coat color in dogs". BMC Genetics. 6. Biomedcentral.com: 34. doi:10.1186/1471-2156-6-34. PMC 1183202. PMID 15960853.
- "Parvovirus in Dogs -Signs – Diagnosis – Treatment of Parvovirus". Vetmedicine.about.com. June 2, 2013. Archived from the original on May 1, 2013. Retrieved July 12, 2013.
- "Shelter Medicine – Cornell Veterinary Medicine". Sheltermedicine.vet.cornell.edu. January 15, 2008. Retrieved October 26, 2011.
- "Fiapbt – Bloodlines". Retrieved September 30, 2018.
- "Tekla Castillo's California Pits". California Pits. Retrieved May 9, 2023.
- Colby, Louis B.; Jessup, Diane (1997). Colby's Book of the American Pit Bull Terrier. T.F.H. Publications. ISBN 978-0-7938-2091-7.
- "Colby kennel (Official Site) – History and pedigree. 2017". Retrieved September 30, 2018.
- "Red Nose History, The Encyclopedia of the American Pit Bull Terrier". Archived from the original on March 21, 2012. Retrieved May 9, 2023.
- ^ Vining, Robert. "Reds History – Old Family Reds". www.oldfamilyreds.com. Retrieved September 30, 2018.
- ^ "- OFRN History". www.southerninfernokennels.com. Archived from the original on May 8, 2021. Retrieved September 30, 2018.
- Beaufoy, James (February 2, 2016). Staffordshire Bull Terriers: A Practical Guide for Owners and Breeders. Crowood. ISBN 978-1-78500-097-3.
- ^ Zaurisio, Neylor (November 2, 2019). "The origin and differences between the American Staffordshire Terrier and the American Pit Bull…". Medium. Retrieved December 28, 2019.
- ^ Stahlkuppe, Joe (April 2000). American Pit Bull Terrier Handbook. Barron's Educational Series. ISBN 978-1-4380-8141-0.
staffordshire.
- ^ "Congratulations on Your New American Staffordshire Terrier" (PDF). Staffordshire Terrier Club of America (AKC parent club). June 10, 1936.
- Bullock, Tyler (May 1, 2016). "History of the ADBA". American Dog Breeders Association. Retrieved December 28, 2019.
- Bullock, Tyler (May 1, 2016). "American Dog Breeders Assoc APBT Stud Book Corrections". American Dog Breeders Association. Retrieved December 28, 2019.
- ^ "Breed Reclassification Process Underway" (PDF). American Dog Breeders Association. 2015. Retrieved December 28, 2019.
- Bullock, Tyler (January 2, 2018). "Heritage American Pit Bull Terrier Conformation Standard®". American Dog Breeders Association. Retrieved December 28, 2019.
- "Single Registration Requirements : American Pit Bull Terrier | United Kennel Club (UKC)". www.ukcdogs.com. Retrieved December 28, 2019.
- UKC Application for American Pit Bull Terrier Single Registration United Kennel Club.
- ^ Zaurisio, Neylor (November 1, 2019). "The so-called "modern" bloodlines". Medium. Retrieved December 28, 2019.
- "ASPCA: Pet Care: Dog Care: Pit Bull Information". Archived from the original on August 1, 2008. Retrieved December 22, 2008.
- "UKC Superdog!". Archived from the original on June 26, 2012. Retrieved November 22, 2015.
- "So That Others May Live..." Archived from the original on July 31, 2012. Retrieved December 22, 2008.
- "Kool K-9 Popsicle retires". October 2002. Archived from the original on October 24, 2011. Retrieved December 22, 2008.
- "LawDogsUSA // Detection Dogs Made In America". Archived from the original on January 14, 2009. Retrieved December 22, 2008.
- M, Logan (June 18, 2021). "Are Pit Bulls Good Hunting Dogs? - (Answered & Explained)". Retrieved January 21, 2022.
- "What happens when dogs are used to hunt feral pigs? – RSPCA Knowledgebase". Retrieved October 24, 2020.
- "Portaria n.o 422/2004 de 24 de Abril" (PDF) (in Portuguese). Retrieved February 14, 2023.
- "Customs (Prohibited Imports) Regulations 1956 No. 90, as amended – Schedule 1". Commonwealth of Australia. July 6, 2009. Archived from the original on June 19, 2009. Retrieved July 18, 2009.
- "Ecuador descalifica a perros pit bull y rottweiler como mascotas" (in Spanish). Ecuador: Diaro Hoy. February 4, 2009. Archived from the original on March 12, 2009. Retrieved August 24, 2009.
- A. Hamid, Rashita (May 9, 2012). "Pit bull kills jogger". The Star. Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Retrieved May 9, 2012.
- "Dog Control Amendment Act of 2003". New Zealand Department of Internal Affairs. July 2, 2009. Retrieved August 2, 2009.
- "H.B. 595 (Law 198) – Approved July 23, 1998" (PDF). Puerto Rico Office of Legislative Services. July 23, 1998. Archived from the original (PDF) on September 27, 2011. Retrieved August 4, 2009.
- AVA.gov.sg Archived December 29, 2009, at the Wayback Machine
- "Venezuela restringe tenencia de perros Pit Bull". La Prensa (in Spanish). Managua, Nicaragua. January 6, 2010. Archived from the original on July 20, 2010. Retrieved January 8, 2010.
- "The Dog Control Act". Retrieved September 30, 2018.
- "List of Banned Dogs by Countries". PETolog. October 29, 2022.
- ^ "Administrative report". Vancouver City Council. February 17, 2005.
- "Tehlike Arz Eden Hayvanlara İlişkin Genelge" [Directive on Dangerous Animals] (in Turkish). Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry. December 9, 2021. Archived from the original on December 9, 2021. Retrieved January 7, 2022.
- "Vicious dogs". Dog bite law.
- Barlow, Karen (May 3, 2005). "NSW bans pit bull terrier breed". Sydney, Australia: Australian Broadcasting Corporation. Retrieved December 23, 2009.
- Hughes, Gary (October 20, 2009). "Pit bull bite prompts call for national approach to dangerous dog breeds". The Australian. Sydney, Australia. Retrieved December 23, 2009.
- "Information on The Dog Owners' Liability Act and Public Safety Related to Dogs Statute Law Amendment Act, 2005". Ministry of the Attorney General of Ontario. Archived from the original on December 24, 2009. Retrieved January 8, 2010.
- Kay, Jonathan. (6 October 2014). "Vindication for Ontario's pit bull ban". The National Post.
- Cain, Patrick (February 20, 2016). "Toronto's pit bulls are almost gone. So why are there more dog bites than ever?". Global News. Retrieved March 7, 2016.
Further reading
- Capp, Dawn M. (2004). American Pit Bull Terriers: Fact or Fiction: The Truth Behind One of America's Most Popular Breeds. Doral Publishing. ISBN 0-9745407-1-4.
- Foster, Ken (2006). The Dogs Who Found Me: What I've Learned from Pets Who Were Left Behind. Lyons Press. ISBN 1-59228-749-2.
- Stahlkuppe, Joe (2000). American Pit Bull Terrier Handbook. Barron's Educational Series. ISBN 0-7641-1233-3.
External links
- ADBA Heritage American Pit Bull Terrier Conformation Standard
- United Kennel Club American Pit Bull Terrier
| Dogs originating in the United States | |
|---|---|
| Extant |
|
| Extinct | |