| Revision as of 12:53, 9 October 2007 view sourceŠvitrigaila (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, Pending changes reviewers3,473 editsm Vartan Oskanian --> Vardan Oskanyan← Previous edit | Revision as of 12:54, 9 October 2007 view source Švitrigaila (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, Pending changes reviewers3,473 editsm ու --> "u" (and not "ow")Next edit → | ||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
| |image_flag = Flag of Armenia.svg | |image_flag = Flag of Armenia.svg | ||
| |image_coat = Coat of Arms of Armenia.svg | |image_coat = Coat of Arms of Armenia.svg | ||
| |national_motto = <div style="line-height:1.33em;"> {{lang|hy|Մեկ Ազգ, Մեկ Մշակույթ}} <small>(])</small><br/>"{{lang|hy-Latn|''Mek Azg, Mek |
|national_motto = <div style="line-height:1.33em;"> {{lang|hy|Մեկ Ազգ, Մեկ Մշակույթ}} <small>(])</small><br/>"{{lang|hy-Latn|''Mek Azg, Mek Mshakuyt''"}}{{spaces|2}}<small>(])<br/>"One Nation, One Culture"</small></div> | ||
| |image_map = Europe location ARM2.png | |image_map = Europe location ARM2.png | ||
| |national_anthem = {{lang|hy-Latn|'']''}}<small><br/>''Our Fatherland''</small> | |national_anthem = {{lang|hy-Latn|'']''}}<small><br/>''Our Fatherland''</small> | ||
Revision as of 12:54, 9 October 2007
For other uses, see Armenia (disambiguation).
| Republic of Armenia Հայաստանի Հանրապետություն Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) | |
|---|---|
 Flag
Coat of arms of Armenia
Coat of arms
Flag
Coat of arms of Armenia
Coat of arms
| |
| Motto: Մեկ Ազգ, Մեկ Մշակույթ (Armenian) " Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) (transliteration) "One Nation, One Culture" | |
| Anthem: Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) Our Fatherland | |
 | |
| Capitaland largest city | Yerevan |
| Official languages | Armenian |
| Demonym(s) | Armenian |
| Government | Unitary republic |
| • President | Robert Kocharyan |
| • Prime Minister | Serzh Sargsyan |
| Formation and independence | |
| • Traditional | August 11 2492 BC |
| • Urartu under Aramu | 840s BC |
| • Tigranes Orontid | 560 BC |
| • Kingdom of Armenia formed | 190 BC |
| • Armenian Apostolic Church | 301 AD |
| • Democratic Republic of Armenia established | May 28 1918 |
| • Independence from the Soviet UnionDeclared Recognised Finalised | August 23 1990 September 21 1991 December 25 1991 |
| Area | |
| • Total | 29,800 km (11,500 sq mi) (141st) |
| • Water (%) | 4.71 |
| Population | |
| • 2005 estimate | 3,215,800 (136th) |
| • 2001 census | 3,002,594 |
| • Density | 101/km (261.6/sq mi) (98th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2005 estimate |
| • Total | $14.17 billion (127th) |
| • Per capita | $4,270 (115th) |
| Gini (2003) | 33.8 medium inequality |
| HDI (2004) | Error: Invalid HDI value (80th) |
| Currency | Dram (AMD) |
| Time zone | UTC+4 (UTC) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+5 (DST) |
| Calling code | 374 |
| ISO 3166 code | AM |
| Internet TLD | .am |
| |
Armenia (Template:Lang-hy Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help)), officially the Republic of Armenia, is a landlocked mountainous country in Eurasia between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, located in the Southern Caucasus. It shares borders with Turkey to the west, Georgia to the north, Azerbaijan to the east, and Iran and the Nakhchivan exclave of Azerbaijan to the south. A transcontinental country located at the juncture of Eastern Europe and Western Asia, Armenia has and continues to have extensive sociopolitical and cultural connections with Europe.
A former republic of the Soviet Union, Armenia is a unitary, multiparty, democratic nation-state with an ancient and historic cultural heritage. Historically, Armenia was the first nation to adopt Christianity as its state religion, Armenia is constitutionally a secular state today, although the Christian faith plays a major role in the history and identification of the Armenian people. Armenia is currently a member of more than 40 different international organizations, including the United Nations, the Council of Europe, the Asian Development Bank, the Commonwealth of Independent States, the World Trade Organization and the Organization of the Black Sea Economic Cooperation. It is a Partnership for Peace (PfP) member of NATO and also a member of the CSTO military alliance. It is also an observer member of the Eurasian Economic Community, La Francophonie, and the Non-Aligned Movement. Armenia is also active in the international sports community with full membership in the Union of European Football Associations and International Ice Hockey Federation. The country is an emerging democracy and because of its strategic location, it lies among both the Russian and Western spheres of influence.
Name
Main article: Armenia (name)The native Armenian name for the country is Hayk‘. The name in the Middle Ages was extended to Hayastan, by addition of the Persian suffix -stan "land". The name is obviously related to that of the mythical patriarch of the Armenians, according to Moses of Chorene a great-great-grandson of Noah, Hayk (Հայկ), but its further origin is uncertain.
The earliest Greek reference to Armenia (Ἀρμενία), was made by the historian Hecataeus of Miletus in 525 BC.* The exonym Armenia is attested in the Old Persian Behistun inscription as Armina. Herodotus mentioned the "Armenians" as Ἀρμένιοι, who in his review of the troops opposing the Greeks wrote that "the Armenians were armed like the Phrygians, being Phrygian settlers". About 50 years later, Xenophon upon traveling through Armenia, on his way back to Greece, said Armenians sounded like Persians.
History
Main article: History of ArmeniaAntiquity

Armenia has been populated since prehistoric times, and has been proposed as the site of the Biblical Garden of Eden. Armenia lies in the highlands surrounding the Biblical mountains of Ararat, upon which, as Judeo-Christian theology states, Noah's Ark came to rest after the flood. (Gen. 8:4). Archaeologists continue to uncover evidence that Armenia and the Armenian Highlands were among the earliest sites of human civilization and maybe even the birthplace of agriculture and civilization. From 6000 BC to 1000 BC, tools such as spears and axes and trinkets of copper, bronze, and iron were commonly produced in Armenia and traded in neighbouring lands where those metals were less abundant. Armenia is the main candidate for the legendary Aratta (Ararat), mentioned in Sumerian records. In the Bronze Age, several states flourished in the area of Greater Armenia, including the Hittite Empire (at the height of its power), Mitanni (South-Western historical Armenia), and Hayasa-Azzi (1500-1200 BC). Then, the Nairi people (twelfth to ninth centuries BC) and the Kingdom of Urartu (1000-600 BC) successively established their sovereignty over the Armenian Highland. Each of the aforementioned nations and tribes participated in the ethnogenesis of the Armenian people. Yerevan, the modern capital of Armenia, was founded in 782 BC by the Urartian king Argishti I.
Around 600 BC, the Kingdom of Armenia was established under the Orontid Dynasty, which existed under several local dynasties till 428 AD. The kingdom reached its height between 95 - 66 BC under Tigranes the Great, becoming one of the most powerful kingdoms of its time within the region. Throughout its history, the kingdom of Armenia enjoyed periods of independence intermitted with periods of autonomy subject to contemporary empires. Armenia's strategic location between two continents has subjected it to invasions by many peoples, including the Assyrians, Greeks, Romans, Byzantines, Arabs, Mongols, Persians, Ottoman Turks and Russians.


In 301, Armenia became the first country in the world to adopt Christianity as its official state religion, while a number of Christian communities have been established in Armenia since 40 AD. There had been various pagan communities before Christianity, but they were converted by an influx of Christian missionaries. Tiridates III (238-314 AD) was the first ruler to officially Christianise his people, his conversion ten years before the Roman Empire granted Christianity official toleration under Galerius, and 36 years before Constantine was baptised.
After the fall of the Armenian kingdom in 428 AD, most of Armenia was incorporated as a marzpanate within the Sassanid Empire, ruled by a marzpan. Following an Armenian rebellion in 451 AD, Christian Armenians maintained their religious freedom, while Armenia gained autonomy and the right to be ruled by an Armenian marzpan, whereas other imperial territories were ruled exclusively by Persians. The Marzpanate of Armenia lasted until the 630s, when Sassanid Persia was destroyed by the Arab Caliphate.
Medieval Armenia
Main article: Medieval ArmeniaAfter the Marzpanate period (428-636), Armenia emerged as The Emirate of Armenia, an autonomous principality within the Arabic Empire, reuniting Armenian lands previously taken by the Byzantine Empire as well. The principality was ruled by the Prince of Armenia, recognised by the Caliph and the Byzantine Emperor. It was part of the administrative division/emirate Arminiyya created by the Arabs, which also included parts of Georgia and Caucasian Albania, and had its center in the Armenian city Dvin. The Principality of Armenia lasted till 884, when it regained its independence from the weakened Arabic Empire.
The reemergent Armenian kingdom was ruled by the Bagratuni dynasty, and lasted till 1045. In time, several areas of the Bagratid Armenia separated as independent kingdoms and principalities such as the Kingdom of Vaspurakan ruled by the House of Artsruni, while still recognizing the supremacy of the Bagratid kings.
In 1045, the Byzantine Empire conquered Bagratid Armenia. Soon, the other Armenian states fell under Byzantine control as well. The Byzantine rule was short lived, as in 1071 Seljuk Turks defeated the Byzantines and conquered Armenia at the Battle of Manzikert, establishing the Seljuk Empire. To escape death or servitude at the hands of those who had assassinated his relative, Gagik II, King of Ani, an Armenian named Roupen with some of his countrymen went into the gorges of the Taurus Mountains and then into Tarsus of Cilicia. The Byzantine governor of the palace gave them shelter where the Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia was eventually established.
The Seljuk Empire soon started to collapse. In the early 1100s, Armenian princes of the Zakarid noble family established a semi-independent Armenian principality in Northern and Eastern Armenia, known as Zakarid Armenia. The noble family of Orbelians shared control with the Zakarids in various parts of the country, especially in Syunik and Vayots Dzor.
Foreign rule
During the 1230s, the Mongol Ilkhanate conquered the Zakaryan Principality, as well as the rest of Armenia. The Mongolian invasions were soon followed by those of other Central Asian tribes, which continued from the 1200s until the 1400s. After incessant invasions, each bringing destruction to the country, Armenia in time became weakened. During the 1500s, the Ottoman Empire and Safavid Persia divided Armenia among themselves. The Russian Empire later incorporated Eastern Armenia (consisting of the Erivan and Karabakh khanates within Persia) in 1813 and 1828.
Under Ottoman rule, the Armenians were granted considerable autonomy within their own enclaves and lived in relative harmony with other groups in the empire (including the ruling Turks). However, as Christians under a strict Muslim social system, Armenians faced pervasive discrimination. When they began pushing for more rights within the Ottoman Empire, Sultan ‘Abdu’l-Hamid II, in response, organised state-sponsored massacres against the Armenians between 1894 and 1896, resulting in an estimated death toll of 80,000 to 300,000 people. The Hamidian massacres, as they came to be known, gave Hamid international infamy as the "Red Sultan" or "Bloody Sultan."
World War I and the Armenian Genocide
Main article: Armenian Genocide
As the Ottoman Empire began to collapse, the Young Turks overthrew the government of Sultan Hamid. Armenians living in the empire hoped that the Young Turk revolution would change their second-class status. However, with onslaught of World War I and the Ottoman Empire's assault on the Russian Empire, the new government began to look on the Armenians with distrust and suspicion. This was due to the fact that the Russian army contained a contingent of Armenian volunteers. On April 24, 1915, Armenian intellectuals were arrested by Ottoman authorities, and with the Tehcir Law, eventually a large proportion of Armenians living in Anatolia perished in what has become known as the Armenian Genocide. There was local Armenian resistance in the region, developed against the activities of the Ottoman Empire. The events of 1915 to 1917 are regarded by Armenians and the vast majority of Western historians to have been state-sponsored mass killings, or genocide. Turkish authorities maintain that the deaths were the result of a civil war coupled with disease and famine, with casualties incurred by both sides. Most estimates for the number of Armenians killed range from 650,000 to 1.5 million. Armenia and the Armenian diaspora have been campaigning for official recognition of the events as genocide for over 30 years. These events are traditionally commemorated yearly on April 24, the Armenian Martyr Day, or the Day of the Armenian Genocide.
Although the Russian army succeeded in gaining most of Ottoman Armenia during World War I, their gains were lost with the Russian Revolution of 1917. At the time, Russian-controlled Eastern Armenia, Georgia, and Azerbaijan attempted to bond together in the Transcaucasian Democratic Federative Republic. This federation, however, only lasted from February to May 1918, when all three parties decided to dissolve it. As a result, Eastern Armenia became independent as the Democratic Republic of Armenia (DRA) on May 28. Unfortunately, the DRA's short-lived independence was fraught with war, territorial disputes, a mass influx of refugees from Ottoman Armenia, spreading disease, and starvation. Still, the Entente Powers, appalled by the actions of the Ottoman government, sought to help the newly-found Armenian state through relief funds and other forms of support.
At the end of the war, the victorious Entente powers sought to divide up the Ottoman Empire. Signed between the Allied and Associated Powers and Ottoman Empire at Sèvres on August 10, 1920, the Treaty of Sèvres promised to maintain the existence of the DRA and to attach the former territories of Ottoman Armenia to it. Because the new borders of Armenia were to be drawn by United States President Woodrow Wilson, Ottoman Armenia is also referred to as "Wilsonian Armenia." There was even consideration of possibly making Armenia a mandate under the protection of the United States. The treaty, however, was rejected by the Turkish National Movement, and never came into effect. The movement, under Mustafa Kemal Atatürk, used the treaty as the occasion to declare itself the rightful government of Turkey, replacing the monarchy based in Istanbul with a republic based in Ankara.
Soviet Armenia
Main article: Armenian SSR
In 1920, Armenia and Turkey engaged in the Turkish-Armenian War, a violent conflict that ended with the Treaty of Alexandropol. Signed on December 2, the Alexandropol treaty forced Armenia to disarm most of its military forces, cede more than 50% of its pre-war territory, and to give up all the territories granted to it at the Sèvres treaty. Simultaneously, the Soviet Eleventh Army under the command of Grigoriy Ordzhonikidze, invaded Armenia at Karavansarai (present-day Ijevan) on November 29. By December 4, Ordzhonikidze's forces entered Yerevan and the short-lived Armenian republic collapsed. It was annexed by Bolshevist Russia and in 1922 was incorporated into the Soviet Union as part of the Transcaucasian SFSR along with Georgia and Azerbaijan. The Treaty of Alexandropol was then superseded by the Treaty of Kars, between Turkey and the Soviet Union. In it, Turkey allowed the Soviet Union to assume control over Ajara with the port city of Batumi in return for sovereignty over the cities of Kars, Ardahan, and Iğdır, all of which were part of Russian Armenia.
The TSFR existed from 1922 to 1936, when it was divided up into three separate entities (Armenian SSR, Azerbaijan SSR, and Georgian SSR). Armenians enjoyed a period of relative stability under Soviet rule. They received medicine, food, and other provisions from Moscow, and communist rule proved to be a soothing balm in contrast to the turbulent final years of the Ottoman Empire. The situation was difficult for the church, which struggled under Soviet rule. After the death of Vladimir Lenin, Joseph Stalin took the reins of power and began an era of renewed fear and terror for Armenians. As with various other ethnic minorities who lived in the Soviet Union during Stalin's Great Purge, tens of thousands of Armenians were either executed or deported.
Fears decreased when Stalin died in 1953 and Nikita Khruschev emerged as the Soviet Union's new leader. Soon, life in Soviet Armenia began to see rapid improvement. The church which suffered greatly under Stalin was revived when Catholicos Vazgen I assumed the duties of his office in 1955. In 1967, a memorial to the victims of the Armenian Genocide was built at the Tsitsernakaberd hill above the Hrazdan gorge in Yerevan. This occurred after mass demonstrations took place on the tragic event's fiftieth anniversary in 1965. During the Gorbachev era of the 1980s with the reforms of Glasnost and Perestroika, Armenians began to demand better environmental care for their country, opposing the pollution that Soviet-built factories brought. Tensions also developed between the Armenian and Azerbaijani republics over the region of Nagorno-Karabakh. Soviet Armenia suffered the devastating 1988 Spitak earthquake. Gorbachev's inability to solve Armenia's problems (especially Karabakh) led many Armenians to become disillusioned with the Soviet leader and only fed a growing hunger for independence.
In May 1990, the New Armenian Army (NAA) was established, serving as a defense force separate from the Soviet Red Army. Clashes soon broke out between the NAA and Soviet MVD troops based in Yerevan when Armenians decided to commemorate the establishment of the 1918 Democratic Republic of Armenia. The violence resulted in the deaths of five Armenians killed in a shootout between the MVD at the railway station. Witnesses there claimed that the MVD used excessive force and that they had instigated the fighting. Further firefights between Armenian militiamen and Soviet troops occurred in Sovetshen, near the capital and resulted in the deaths of over twenty-six people. On March 17, 1991, Armenia, along with the Baltic states, Georgia and Moldova, boycotted a union-wide referendum in which 78% of all voters voted for the retention of the Soviet Union in a reformed form.
Independence
In 1991, the Soviet Union broke apart and Armenia re-established its independence. Declaring independence on August 23, it was the first non-Baltic republic to secede. However, the initial post-Soviet years were marred by economic difficulties as well as the break-out of a full-scale armed confrontation between the Armenian population of Nagorno-Karabakh and Azerbaijan. The economic problems had their roots early in the Karabakh conflict when the Azerbaijani Popular Front managed to pressure the Azerbaijan SSR to instigate a railway and air blockade against Armenia. This move effectively crippled Armenia's economy as 85% of its cargo and goods arrived through rail traffic. In 1993, Turkey joined the blockade against Armenia in support of Azerbaijan.
The Karabakh war ended after a Russian-brokered cease-fire was put in place in 1994. The war was a success for the Karabakh Armenian forces who managed to secure 14% of Azerbaijan's internationally recognised territory including Nagorno-Karabakh itself. Since then, Armenia and Azerbaijan have held peace talks, mediated by the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE). The status over Karabakh has yet to be determined. The economies of both countries have been hurt in the absence of a complete resolution and Armenia's borders with Turkey and Azerbaijan remain closed.
As it enters the twenty-first century, Armenia faces many hardships. Still, despite high unemployment, it has managed to make some economic improvements. It has made a full switch to a market economy and as of 2007, remains the 32nd most economically free nation in the world. Its relations with Europe, the Middle East, and the Commonwealth of Independent States have allowed Armenia to increase trade. Gas, oil, and other supplies come through two vital routes: Iran and Georgia. Armenia maintains cordial relations with both countries.
Politics and government
Main article: Politics of ArmeniaPolitics of Armenia takes place in a framework of a presidential representative democratic republic. According to the Constitution of Armenia, the President is the head of government and of a pluriform multi-party system. Executive power is exercised by the government. Legislative power is vested in both the government and parliament. The unicameral parliament (also called the Azgayin Zhoghov or National Assembly) is controlled by a coalition of three political parties: the conservative Republican party, the Prosperous Armenia party, and the Armenian Revolutionary Federation. The main opposition parties include Artur Baghdasarian's Rule of Law party and Raffi Hovannisian's Heritage party, both of which favor eventual Armenian membership in the European Union and NATO.
The Armenian government's stated aim is to build a Western-style parliamentary democracy as the basis of its form of government. However, international observers of Council of Europe and U.S. Department of State have questioned the fairness of Armenia's parliamentary and presidential elections and constitutional referendum since 1995, citing polling deficiencies, lack of cooperation by the Electoral Commission, and poor maintenance of electoral lists and polling places. Freedom House ranked Armenia as "partly free" in its 2007 report, though it did not categorise Armenia as an "electoral democracy", indicating an absence of relatively free and competitive elections. It has universal suffrage above the age of eighteen.
Foreign relations
Main articles: Foreign relations of Armenia and Armenia and the European Union
Armenia presently maintains good relations with almost every country in the world, with two major exceptions being its immediate neighbors, Turkey and Azerbaijan. Tensions were running high between Armenians and Azerbaijanis during the final years of the Soviet Union. The Nagorno-Karabakh War dominated the region's politics throughout the 1990s. The border between the two rival countries remains closed up to this day, and a permanent solution for the conflict has not been reached despite the mediation provided by organizations such as the OSCE. Foreign Minister Vardan Oskanyan represents Armenia in the peace negotiations.
Turkey also has a long history of poor relations with Armenia over its refusal to acknowledge the Armenian Genocide of 1915. The Karabakh conflict became an excuse for Turkey to close its border with Armenia in 1993. It has not lifted its blockade despite pressure from the powerful Turkish business lobby interested in Armenian markets.
Due to its position between two unfriendly neighbors, Armenia has close security ties with Russia. At the request of the Armenian government, Russia maintains a military base in the northwestern Armenian city of Gyumri as a deterrent against Turkey. Despite this, Armenia has also been looking toward Euro-Atlantic structures in recent years. It maintains good relations with the United States especially through its Armenian diaspora. According to the 2000 US census, there are 385,488 Armenians living in the country.
Armenia is also a member of the NATO Partnership for Peace as well as the Council of Europe, maintaining friendly relations with the European Union, especially with its member states such as France and Greece. A 2005 survey reported that 64% of Armenia's population would be in favor of joining the EU. Several Armenian officials have also expressed the desire for their country to eventually become an EU member state, some predicting that it will make an official bid for membership in a few years. Some too have also looked with favour in joining NATO. President Robert Kocharyan, however, wants to keep Armenia tied to Russia and the CIS and the CSTO, becoming partners, not members of the EU and NATO.
Military
Main article: Armed Forces of ArmeniaThe Armenian Army, Air Force, Air Defense, and Border Guard comprise the four branches of the Armed Forces of the Republic of Armenia. The Armenian military was formed after the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991 and with the establishment of the Ministry of Defense in 1992. The Commander-in-Chief of the military is the President of Armenia, Robert Kocharyan. The Ministry of Defense is in charge of political leadership, currently headed by Colonel-General Mikael Harutyunyan, while military command remains in the hands of the General Staff, headed by the Chief of Staff, who is currently Lieutenant-General Seyran Ohanian .
Active forces now number about 60,000 soldiers, with an additional reserve of 32,000, and a "reserve of the reserve" of 350,000 troops. Armenian border guards are in charge of patrolling the country's borders with Georgia and Azerbaijan, while Russian troops continue to monitor its borders with Iran and Turkey. In the case of an eventual attack, Armenia is prepared to mobilise every able-bodied man between the age of 15 and 59, with military preparedness.
The Treaty on Conventional Armed Forces in Europe, which establishes comprehensive limits on key categories of military equipment, was ratified by the Armenian parliament in July 1992. In March 1993, Armenia signed the multilateral Chemical Weapons Convention, which calls for the eventual elimination of chemical weapons. Armenia acceded to the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT) as a non-nuclear weapons state in July 1993. Armenia is member of Collective Security Treaty Organization (CSTO) along with Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, Tajikistan and Uzbekistan. It participates in NATO's Partnership for Peace (PiP) program and is in a NATO organization called Euro-Atlantic Partnership Council (EAPC). Armenia has engaged in peacekeeping mission in Kosovo as part of non-NATO KFOR troops under Greek command. Armenia has 46 members of its military forces as a part of the Coalition Forces in Iraq War.
Regions
Main article: Administrative divisions of Armenia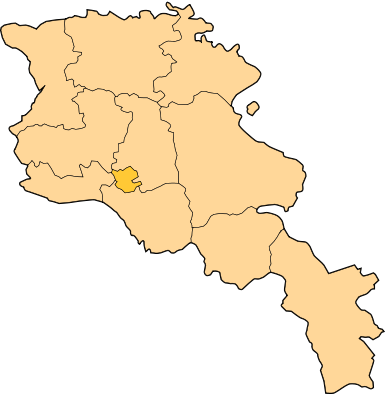 Shirak
Lori
Tavush
Aragatsotn
Armavir
Yerevan
Ararat
Kotayk
Gegharkunik
Vayots
Shirak
Lori
Tavush
Aragatsotn
Armavir
Yerevan
Ararat
Kotayk
Gegharkunik
VayotsDzor Syunik
Armenia is divided into ten marzes (regions, singular marz), with the city of Yerevan (Երևան) having special administrative status as the country's capital. The chief executive in each of then ten marzes is the marzpet (marz governor), appointed by the government of Armenia. In Yerevan, the chief executive is the mayor, appointed by the president.
| Marz | Capital | Area | Population |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aragatsotn (Արագածոտն) | Ashtarak (Աշտարակ) | 2,753 km² | 126,278 |
| Ararat (Արարատ) | Artashat (Արտաշատ) | 2,096 km² | 252,665 |
| Armavir (Արմավիր) | Armavir (Արմավիր) | 1,242 km² | 255,861 |
| Gegharkunik (Գեղարքունիք) | Gavar (Գավառ) | 5,348 km² | 215,371 |
| Kotayk (Կոտայք) | Hrazdan (Հրազդան) | 2,089 km² | 241,337 |
| Lori (Լոռի) | Vanadzor (Վանաձոր) | 3,789 km² | 253,351 |
| Shirak (Շիրակ) | Gyumri (Գյումրի) | 2,681 km² | 257,242 |
| Syunik (Սյունիք) | Kapan (Կապան) | 4,506 km² | 134,061 |
| Tavush (Տավուշ) | Ijevan (Իջևան) | 2,704 km² | 121,963 |
| Vayots Dzor (Վայոց Ձոր) | Yeghegnadzor (Եղեգնաձոր) | 2,308 km² | 53,230 |
| Yerevan (Երևան) | – | 227 km² | 1,091,235 |
Geography
Main article: Geography of Armenia
Armenia is a landlocked country in the southern Caucasus. Located between the Black and Caspian Seas, the country is bordered on the north and east by Georgia and Azerbaijan, and on the south and west by Iran and Turkey.
Topography
The Republic of Armenia, covering an area of 30 000 square kilometres (11,600 sq. mi), is located in the north-east of the Armenian Highland (covering 400 000 km² or 154,000 sq. mi), otherwise known as historical Armenia and considered as the original homeland of Armenians. The terrain is mostly mountainous, with fast flowing rivers and few forests. The climate is highland continental, which means that the country is subjected to hot summers and cold winters. The land rises to 4095 metres (13,435 ft) above sea-level at Mount Aragats, and no point is below 400 meters (1,312 ft) above sea level.
Mount Ararat, which was historically part of Armenia, is the highest mountain in the region. Now located in Turkey, but clearly viewable in Armenia, it is regarded by the Armenians as a symbol of their land. Because of this, the mountain is present on the Armenian national emblem today.
Environmental problems
Armenia is trying to address its environmental problems. It has established a Ministry of Nature Protection and introduced taxes for air and water pollution and solid waste disposal, whose revenues are used for environmental protection activities. Armenia is interested in cooperating with other members of the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS, a group of eleven former Soviet republics) and with members of the international community on environmental issues. The Armenian Government is working toward closing its Nuclear Power Plant at Medzamor near Yerevan as soon as alternative energy sources are identified.
Climate
The climate in Armenia is markedly continental. Summers are dry and sunny, lasting from June to mid-September. The temperature fluctuates between 22° and 36°C. However, the low humidity level mitigates the effect of high temperatures. Evening breezes blowing down the mountains provide a welcome refreshing and cooling effect. Springs are short, while falls are long. Autumns are known for their vibrant and colorful foliage. Winters are quite cold with plenty of snow, with temperatures ranging between -5° and -10°C. Winter sports enthusiasts enjoy skiing down the hills of Tsakhkadzor, located thirty minutes outside Yerevan. Lake Sevan nestled up in the Armenian highlands, is the second largest lake in the world relative to its altitude, 1,900 meters above sea level.
Economy
Main article: Economy of ArmeniaBefore independence, Armenia's economy was largely industry-based – chemicals, electronics, machinery, processed food, synthetic rubber, and textile – and highly dependent on outside resources. Agriculture contributed only 20% of net material product and 10% of employment before the breakup of the Soviet Union in 1991. The republic had developed a modern industrial sector, supplying machine tools, textiles, and other manufactured goods to sister republics in exchange for raw materials and energy.

Armenian mines produce copper, zinc, gold, and lead. The vast majority of energy is produced with fuel imported from Russia, including gas and nuclear fuel (for its one nuclear power plant); the main domestic energy source is hydroelectric. Small amounts of coal, gas, and petroleum have not yet been developed.
Like other newly independent states of the former Soviet Union, Armenia's economy suffers from the legacy of a centrally planned economy and the breakdown of former Soviet trading patterns. Soviet investment in and support of Armenian industry has virtually disappeared, so that few major enterprises are still able to function. In addition, the effects of the 1988 Spitak Earthquake, which killed more than 25,000 people and made 500,000 homeless, are still being felt. The conflict with Azerbaijan over Nagorno-Karabakh has not been resolved. The closure of Azerbaijani and Turkish borders has devastated the economy, because Armenia depends on outside supplies of energy and most raw materials. Land routes through Georgia and Iran are inadequate or unreliable. GDP fell nearly 60% from 1989 until 1992–1993. The national currency, the dram, suffered hyperinflation for the first years after its introduction in 1993.
Nevertheless, the government was able to make wide-ranging economic reforms that paid off in dramatically lower inflation and steady growth. The 1994 cease-fire in the Nagorno-Karabakh conflict has also helped the economy. Armenia has had strong economic growth since 1995, building on the turnaround that began the previous year, and inflation has been negligible for the past several years. New sectors, such as precious stone processing and jewelry making, information and communication technology, and even tourism are beginning to supplement more traditional sectors in the economy, such as agriculture.
This steady economic progress has earned Armenia increasing support from international institutions. The International Monetary Fund (IMF), World Bank, European Bank for Reconstruction and Development (EBRD), and other international financial institutions (IFIs) and foreign countries are extending considerable grants and loans. Loans to Armenia since 1993 exceed $1.1 billion. These loans are targeted at reducing the budget deficit, stabilizing the currency; developing private businesses; energy; the agriculture, food processing, transportation, and health and education sectors; and ongoing rehabilitation in the earthquake zone. The government joined the World Trade Organization on February 5, 2003. But one of the main sources of foreign direct investments remains the Armenian diaspora, which finances major parts of the reconstruction of infrastructure and other public projects. Being a growing democratic state, Armenia also hopes to get more financial aid from the Western World.
A liberal foreign investment law was approved in June 1994, and a Law on Privatization was adopted in 1997, as well as a program on state property privatization. Continued progress will depend on the ability of the government to strengthen its macroeconomic management, including increasing revenue collection, improving the investment climate, and making strides against corruption. However unemployment still remains a major problem due to the influx of thousands of refugees from the Karabakh conflict, which currently stands at around 15%.
In the 2006 Transparency International Corruption Perceptions Index (CPI), Armenia ranked 93rd of 163 countries. According to this poll, corruption in Armenia has increased only slightly since it was first ranked in the 2003 report. Armenia ranked 80th on the 2006 UNDP Human Development Index, the highest among the Transcaucasian republics. In the 2007 Index of Economic Freedom, Armenia ranked 32nd, ahead of countries like Portugal and Italy.
Demographics
Main articles: Demographics of Armenia, Religion in Armenia, and Peoples of the Caucasus
Armenia has a population of 3,215,800 (April 2006 est.) and is the second most densely populated of the former Soviet republics. There has been a problem of population decline due to elevated levels of emigration after the break-up of the USSR. The rates of emigration and population decline, however, have decreased drastically in the recent years, and a moderate influx of Armenians returning to Armenia have been the main reasons for the trend, which is expected to continue. In fact Armenia is expected to resume its positive population growth by 2010.
Ethnic Armenians make up 97.9% of the population. Yazidis make up 1.3%, and Russians 0.5%. Other minorities include Assyrians, Ukrainians, Greeks, Kurds, Georgians, and Belarusians. There are also smaller communities of Vlachs, Mordvins, Ossetians, Udis, and Tats. Minorities of Poles and Caucasus Germans also exist though they are heavily Russified. During the Soviet era, Azerbaijanis were historically the second largest population in the country (forming about 10% in 1939). However, due to hostilities with neighboring Azerbaijan over the disputed region of Nagorno-Karabakh virtually all of them emigrated from Armenia. Conversely, Armenia received a large influx of Armenian refugees from Azerbaijan, thus giving Armenia a more homogeneous character.
Armenia has a relatively large diaspora (8 million by some estimates, greatly exceeding the 3 million population of Armenia itself), with communities existing across the globe. The largest Armenian communities outside of Armenia can be found in Russia, France, Iran, the United States, Georgia, Syria, Lebanon, Argentina, Australia, Canada, Cyprus, Ukraine, Israel, and Ukraine. 40,000 to 70,000 Armenians still live in Turkey (mostly in and around Istanbul). Also, about 1,000 Armenians reside in the Armenian Quarter in the Old City of Jerusalem in Israel, a remnant of a once-larger community. In addition, approximately 130,000 Armenians live in the disputed Nagorno-Karabakh region where they form a majority.
The predominant religion in Armenia is Christianity. The roots of the Armenian Church go back to the first century. According to tradition, the Armenian Church was founded by two of Jesus' twelve apostles -- Thaddaeus and Bartholomew -- who preached Christianity in Armenia between 40-60 AD. Because of these two founding apostles, the official name of the Armenian Church is Armenian Apostolic Church. Armenia was the first nation to adopt Christianity as a state religion, in 301. Over 93% of Armenian Christians belong to the Armenian Apostolic Church, a form of Oriental (Non-Chalcedonian) Orthodoxy, which is a very ritualistic, conservative church, roughly comparable to the Coptic and Syriac churches. Armenia also has a population of Catholics (both Roman and Mekhitarist - Armenian Uniate (180,000)), evangelical Protestants and followers of the Armenian traditional religion. The Yazidi Kurds, who live in the western part of the country, practice Yazidism. The Armenian Catholic Church is headquartered in Bzoummar, Lebanon. The non-Yazidi Kurds practice Sunni Islam. The Jewish community in Armenia has diminished to 750 persons since independence due to Armenia's economic difficulties, with most emigrants leaving for Israel. There are currently two synagogues operating in Armenia - in the capital, Yerevan, and in the city of Sevan located near Lake Sevan. Intermarriage with Christian Armenians is frequent. Still, despite these difficulties, a lot of enthusiasm exists to help the community meet its needs.
Culture
Armenians have their own distinctive alphabet and language. The alphabet was invented in 405 AD by Saint Mesrob Mashtots and consists of thirty-eight letters, two of which were added during the Cilician period. 96% of the people in the country speak Armenian, while 75.8% of the population additionally speaks Russian although English is becoming increasingly popular.
Music and the arts

The National Art Gallery in Yerevan has more than 16,000 works that date back to the Middle Ages. The Modern Art Museum, the Children’s Picture Gallery, and the Martiros Saryan Museum are only a few of the other noteworthy collections. Moreover, many private galleries are in operation, with many more opening each year. They feature rotating exhibitions and sales.
The Armenian Philharmonic Orchestra performs at the refurbished city Opera House. In addition, several chamber ensembles are highly regarded for their musicianship, including the National Chamber Orchestra of Armenia and the Serenade Orchestra. Classical music can also be heard at one of several smaller venues, including the Yerevan Komitas State Conservatory and the Chamber Orchestra Hall. Jazz is popular, especially in the summer when live performances are a regular occurrence at one of the city’s many outdoor cafés.
Yerevan’s Vernisage (arts and crafts market), close to Republic Square, bustles with hundreds of vendors selling a variety of crafts on weekends and Wednesdays (though the selection is much reduced mid-week). The market offers woodcarving, antiques, fine lace, and the hand-knotted wool carpets and kilims that are a Caucasus specialty. Obsidian, which is found locally, is crafted into assortment of jewelry and ornamental objects. Armenian gold smithery enjoys a long tradition, populating one corner of the market with a selection of gold items. Soviet relics and souvenirs of recent Russian manufacture—nesting dolls, watches, enamel boxes and so on, are also available at the Vernisage.
Across from the Opera House, a popular art market fills another city park on the weekends. Armenia’s long history as a crossroads of the ancient world has resulted in a landscape with innumerable fascinating archaeological sites to explore. Medieval, Iron Age, Bronze Age and even Stone Age sites are all within a few hours drive from the city. All but the most spectacular remain virtually undiscovered, allowing visitors to view churches and fortresses in their original settings.

The American University of Armenia has graduate programs in Business and Law, among others. The institution owes its existence to the combined efforts of the Government of Armenia, the Armenian General Benevolent Union, U.S. Agency for International Development, and the University of California. The extension programs and the library at AUA form a new focal point for English-language intellectual life in the city.
Many famous names in the music world are of Armenian descent including classical composer Aram Khachaturian and French singer Charles Aznavour. The members of the alternative metal band System of a Down all have Armenian backgrounds as well, although only bassist Shavo Odadjian was born in the country.
Hospitality and wedding ceremonies
Armenian hospitality is legendary and stems from ancient tradition. Social gatherings focused around sumptuous presentations of course after course of elaborately prepared and well-seasoned food. The hosts will often put morsels on a guest's plate whenever it is empty or fill his or her glass when it gets low. After a helping or two it is acceptable to refuse politely or, more simply, just leave a little uneaten food. Alcohol such as cognac, vodka, and red wine are usually served during meals and gatherings. It is considered rare and unusual for one to go inside an Armenian household and not be offered coffee, pastry, food, or even water.
The elaborate Armenian wedding process begins when the man and woman are "promised". The man's immediate family (parents, grandparents, and often uncles and aunts) go over to the woman's house to ask for permission from the woman's father for the relationship to continue and hopefully prosper. Once permission is granted by the father, the man gives the woman a "promise ring" to make it official. To celebrate the mutual family agreement, the woman's family opens a bottle of Armenian cognac. After being promised, most families elect to have a semi-large engagement party as well. The girl's family is the one who plans, organises and pays for the party. There is very little involvement by the man's family. At the party, a priest is summoned to pray for the soon-to-be husband and wife and give his blessings. Once the words of prayer have concluded, the couple slide wedding bands on each other's right hands (the ring is moved to the left hand once a formal marriage ceremony is conducted by the Armenian church). The customary time to wait for the marriage is about one year. Unlike in other cultures, the man and his family pay for the wedding. The planning and organization process is usually done by the bride and groom to be.
See also
References
- date of the Battle of Dyutsaznamart of Khorenac‘i's History as calculated by Mikayel Chamchian (1784); see Razmik Panossian, The Armenians: From Kings And Priests to Merchants And Commissars, Columbia University Press (2006), ISBN 978-0231139267, p. 106.
- As a transcontinental country, Armenia may be considered to be in Asia and/or Europe. The UN classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , National Geographic, and Encyclopædia Britannica also place Armenia in Asia. Conversely, numerous sources place Armenia in Europe such as the BBC , Oxford Reference Online , Merriam-Webster's Collegiate Dictionary (though it also places the historical Kingdom of Armenia in Asia), and www.worldatlas.com. Moreover, the Armenian government and the general population generally self-identify as European and a part of Europe . Minister of Foreign Affairs of Armenia Vardan Oskanyan iterated recently that: "Armenia is Europe. This is a fact, it's not a response to a question." . Mr. Torben Holtze, head of the European Commission's representation in Armenia and Georgia and Ambassador of the European Union with residence in Tbilisi, stated recently: "As a matter of principle, Armenia is a European country..." ; Juergen-Zahorka, Hans. "How Armenia Could Approach the European Union" (PDF). LIBERTAS - Europaeisches Institut GmbH. Retrieved December 23.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help); Unknown parameter|accessyear=ignored (|access-date=suggested) (help); "EUROPE AND ARMENIA". Inside Europe. Retrieved December 23.{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help); Unknown parameter|accessyear=ignored (|access-date=suggested) (help) - ^ Plunkett, Richard. Masters, Tom. Lonely Planet: Georgia, Armenia, and Azerbaijan, pp. 104-105. (ISBN 1740591380)
- Chahin, Mark (2001). The Kingdom of Armenia. London: Routledge. p. 177. ISBN 0-7007-1452-9.
- Herodotus, History, 7.73: Ἀρμένιοι δὲ κατά περ Φρύγες ἐσεσάχατο, ἐόντες Φρυγῶν ἄποικοι.
- Xenophon, Anabasis, IV.v.2-9.
- David M. Lang, Armenia: Cradle of Civilization (London: George Allen & Unwin, 1970) 50-1, 58-59.; Hovick Nersessian, "Highlands of Armenia", Los Angeles, 1998, Mr. Nersessian is in the New York Academy of Sciences
- Vahan Kurkjian, "History of Armenia", Michigan, 1968, ; Armenian Soviet Encyclopedia, v. 12, Yerevan 1987; Artak Movsisyan, "Sacred Highland: Armenia in the spiritual conception of the Near East", Yerevan, 2000; Martiros Kavoukjian, "The Genesis of Armenian People", Montreal, 1982
- ^ CIA World Factbook: Armenia
- Brunner, Borgna. Time Almanac with Information Please 2007, p. 685 (ISBN 1933405228).
- "Baltic states, Armenia, Georgia, and Moldova boycott USSR referendum". Retrieved 2007-02-06.
- Croissant, Michael P. (1998). The Armenia-Azerbaijan Conflict: Causes and Implications. London: Praeger. ISBN 0-275-96241-5.
- GlobalHeritageFund.org The Ties That Divide
- Thomas De Waal. Black Garden: Armenia And Azerbaijan Through Peace and War. New York: New York University Press, p. 240. ISBN 0-8147-1945-7
- "Freedom in the World 2007" (PDF). Freedom House. Retrieved 2007-02-20.
- "Nagorno-Karabakh: The Crisis in the Caucasus". Retrieved 2007-04-06.
- "Nagorno-Karabakh: The Crisis in the Caucasus". Retrieved 2007-04-06.
- ^ "Baku and Moscow - 'One Hundred Percent Strategic Partners'". Hetq Online. 2006-02-27. Retrieved 2006-02-27.
- See Armenian-American; EuroAmerican.net presents official data from the 2000 U.S. Census (including state-by-state data), which states that there are 385,488 people of Armenian ancestry currently living in the United States. The 2001 Canadian Census determined that there are 40,505 persons of Armenian ancestry currently living in Canada. However, these are liable to be low numbers, since people of mixed ancestry, very common in North America tend to be under-counted: the 1990 census U.S. indicates 149,694 people who speak Armenian at home. The Armenian Embassy in Canada estimates 1 million ethnic Armenians in the U.S. and 100,000 in Canada. The Armenian Church of America makes a similar estimate. By all accounts, over half of the Armenians in the United States live in California.
- RFE/RL Caucasus Report, Armenian Ministry of Foreign Affairs, 7 January 2005
- http://www.arminfo.am/political-issue22.html
- http://www.findarticles.com/p/articles/mi_go1493/is_200307/ai_n9111910
- http://news.xinhuanet.com/english/2006-04/24/content_4468385.htm
- "KFOR Contingent: Armenia". Official Web Site of the Kosovo Force. 24 January 2006. Retrieved 2007-03-11.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Armenian defense minister to visit Iraq as Armenia to extend small troop presence". The Associated Press. 13 November 2006. Retrieved 2007-02-20.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Transparency International Corruption Perceptions Index 2006
- Transparency International Corruption Perceptions Index 2003
- 2005 UN Human Development Report 2006 - Country Fact Sheets - Armenia
- Index of Economic Freedom 2007
- Garnik Asatryan and Victoria Arakelova, The Ethnic Minorities of Armenia, Routledge, part of the OSCE, 2002
- Template:Ru icon The All-Union Population Census of 1939. Demoscope.ru
- Turay, Anna. "Tarihte Ermeniler". Bolsohays:Istanbul Armenians. Retrieved 2007-01-04.
{{cite web}}: External link in|publisher= - Jewish Virtual Library: Jerusalem - The Old City: The Armenian Quarter
- Nationmaster.com: Azerbaijan
- Advocates on Behalf of Jews in Russia, Ukraine, the Baltic States, and Eurasia: Armenia and Jews
External links

- Government
(In alphabetical order of the domain name.)
- Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Armenia
- Public Television of Armenia
- National Statistical Service of Armenia
- Ministry of Health of Armenia
- Central Bank of Armenia
- Constitutional Court of Armenia
- Government of Armenia
- Ministry of Nature Protection of Armenia
- National Assembly of Armenia
- Administration of the President of Armenia
- Other
(In alphabetical order.)
- Armenia-Diaspora official WEB site
- Armenian Embassies, Consulates And Representations
- Armeniapedia.org - Armenian wiki (primarily English)
- Armeniainfo.am Information for tourists
- "Armenia". The World Factbook (2025 ed.). Central Intelligence Agency.
- Constitution of the Republic of Armenia.
- Electronic Visa (eVisa) for tourists
- Data
- HyeTad - The Online Armenian Cause In English and Spanish
| Within Armenia | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| International membership | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||