| Revision as of 10:27, 21 May 2012 view sourceBrightStarSky (talk | contribs)29,585 edits →Politics← Previous edit | Revision as of 19:22, 22 May 2012 view source Ottomanist (talk | contribs)383 editsm →Ottoman and Austrian ruleNext edit → | ||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 123: | Line 123: | ||
| ===Ottoman and Austrian rule=== | ===Ottoman and Austrian rule=== | ||
| {{See also|History of Ottoman Serbia|Great Serb Migrations|Kingdom of Serbia (1718–1739)|Koča's frontier}} | {{See also|History of Ottoman Serbia|Great Serb Migrations|Kingdom of Serbia (1718–1739)|Koča's frontier}} | ||
| After the loss of independence to the ] and the Ottoman Empire, Serbia briefly regained sovereignty under ] in the 16th century. Three Austrian invasions and numerous rebellions, such as the ] (1595), constantly challenged Ottoman rule. Vojvodina endured a century long Ottoman occupation before being ceded to the ] in the 17th–18th centuries under the ]. As the ] depopulated most of southern Serbia, the Serbs sought refuge across the Danube river in ] to the north and the ] in the west where they were granted rights by the Austrian crown under measures such as the ''Statuta Wallachorum'' of 1630. |
After the loss of independence to the ] and the Ottoman Empire, Serbia briefly regained sovereignty under ] in the 16th century. Three Austrian invasions and numerous rebellions, such as the ] (1595), constantly challenged Ottoman rule. Vojvodina endured a century long Ottoman occupation before being ceded to the ] in the 17th–18th centuries under the ]. As the ] depopulated most of southern Serbia,{{Citation needed|date=May 2012}} the Serbs sought refuge across the Danube river in ] to the north and the ] in the west where they were granted rights by the Austrian crown under measures such as the ''Statuta Wallachorum'' of 1630. | ||
| However, modern Ottomanist and post-constructivist scholars have refuted such a claim of a massive migration<ref>Noel Malcolm, Kosovo: a short history, London : Macmillan, 1998 </ref><ref>Anscombe, Frederick F. (2006). The Ottoman empire in recent international politics - II: the case of Kosovo. The International History Review 28 (4) 758-793.</ref> The Ottoman persecutions of Christians culminated in the abolition and plunder of the ] in 1766.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.rastko.org.rs/kosovo/crucified/cr_heritage.html |title=Crucified Kosovo: Ljubisa Folic: Crucified Heritage |publisher={{lang|sr|Пројекат Растко: Библиотека српске културе; Proјekat Rastko: Biblioteka srpske kulture}} |accessdate=28 April 2010}}</ref> However, most post-constructivist scholars have argued that the Ottoman Empire was in fact 'liberal' towards its Christians subjects relative to other parts of Europe at the time, but also that the Ottoman sultan enjoyed widespread legitimacy from the Orthodox clergy. The Ottoman Empire facilitated for a shared sense of time among Orthodox Christians, defined the ecclesiastical calendar: time revolve around succession feast days in Orthodox calendar; Saint’s days, the marking of changing seasons, harvests, fairs and family events. This was linked to the Idea of legitimate Ottoman rule rule and a ‘shared vision of the world’ among Orthodox Balkans in the 18th century which brought political unity and created commonalities.<ref>P. Kitromilides, ‘“Imagined Communities” and the Origins of the National Question in the Balkans’, in P. Kitromilides, Enlightenment, National- ism, Orthodoxy: Studies in the Culture and Political Thought of South-Eastern Europe (Aldershot, 1994).</ref> | |||
| According to the nationalist reading of history, as Ottoman rule in the ] grew ever more brutal, the ] ] formally granted the Serbs the right to their autonomous crownland following several petitions.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.ceeol.com/aspx/getdocument.aspx?logid=5&id=da7facf9c68246a7820bfdf1f9d9eaaf|title=CEEOL Balcanica, Issue XXXVI /2005|publisher=Central and Eastern European Online Library|accessdate=28 April 2010}}</ref> | |||
| ===Revolution and independence=== | ===Revolution and independence=== | ||
Revision as of 19:22, 22 May 2012
For other uses, see Serbia (disambiguation). Not to be confused with Republika Srpska.
| Republic of Serbia Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) | |
|---|---|
 Flag
Flag
 Coat of arms
Coat of arms
| |
| Anthem: Боже правде / Bože pravde God of Justice | |
 Location of Serbia (green) – Kosovo (light green) Location of Serbia (green) – Kosovo (light green)on the European continent (dark grey) | |
| Capitaland largest city | Belgrade |
| Official languages | Serbian |
| Ethnic groups (2002) | 82.9% Serbs, 3.9% Hungarians, 1.8% Bosniaks, 1.4% Roma, 10.0% others (excluding Kosovo) |
| Demonym(s) | Serbian |
| Government | Parliamentary republic |
| • Acting President | Slavica Đukić Dejanović |
| • Prime Minister | Mirko Cvetković |
| • President-elect | Tomislav Nikolić |
| Legislature | National Assembly |
| Formation | |
• First state {{citation}}: Empty citation (help) | 768 |
| • Kingdom | 1217 |
| • Empire | 1346 |
| • Suzerain monarchy | 1817 |
| • De-jure independence | 1878 |
| • Independent republic | 2006 |
| Area | |
| • Total | 88,361 km (34,116 sq mi) (113th) |
| • Water (%) | 0.13 (including Kosovo) |
| Population | |
| • 2011 estimate | 7,120,666 (excluding Kosovo) (100th) |
| • 2002 census | 7,498,001 (excluding Kosovo) |
| • Density | 919/km (2,380.2/sq mi) (112th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2011 estimate |
| • Total | $78.869 billion (76th) |
| • Per capita | $10,642 (excluding Kosovo) (79th) |
| GDP (nominal) | 2011 estimate |
| • Total | $45.064 billion (79th) |
| • Per capita | $6,080 (excluding Kosovo) (81st) |
| Gini (2008) | 26 low inequality |
| HDI (2011) | 0.766 Error: Invalid HDI value (59th) |
| Currency | Serbian dinar (RSD) |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) |
| Drives on | Right |
| Calling code | 381 |
| ISO 3166 code | RS |
| Internet TLD | .rs, .срб |
| See also regional minority languages recognized by the ECRML | |
Serbia /ˈsɜːrbiə/ , officially the Republic of Serbia (Template:Lang-sr), is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central and Southeast Europe, covering the southern part of the Carpathian basin and the central part of the Balkans. Serbia borders Hungary to the north; Romania and Bulgaria to the east; the Republic of Macedonia to the south; and Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, and Montenegro to the west; additionally, it borders Albania through Kosovo, whose status as part of Serbia is disputed. Serbia covers an area of 88,361 km and has a population of just over 7.1 million, while the capital and largest city is Belgrade.
The arrival of the Serbs to the Balkans in the 7th century, established several states, eventually forming the Serbian Empire in the 14th century. By the 16th century, Serbia was conquered and occupied by the Ottoman Empire, at times interrupted by the Habsburgs. In the early 19th century the Serbian revolution re-established the country as the region's first constitutional monarchy, which subsequently expanded its territory and pioneered the abolition of feudalism in the Balkans. The former Habsburg crownland of Vojvodina united with Serbia in 1918. Following World War I, Serbia formed Yugoslavia with other South Slavic peoples which existed in several forms up until 2006, when the National Assembly of Serbia declared independence and the legal succession to the former State Union. In February 2008 the parliament of UNMIK-governed Kosovo, Serbia's southern province, declared independence, with mixed responses from international governments.
Serbia is a member of the UN, Council of Europe, OSCE, PfP, BSEC and CEFTA. It is also an official candidate for membership in the European Union and a neutral country.
Etymology
Main article: Names of the Serbs and SerbiaThe name "Serbia" was first mentioned as Template:Lang-gr, meaning "land of the Serbs". There are many theories regarding the origin of the name of the Serbs. The most likely is that it is derived from the Old Slavic root *serb-, meaning "same". Another proposed etymology is that of the Indo-European root *ser- "to watch over, protect", akin to Latin servare "to keep, guard, protect, preserve, observe".
History
Main article: History of SerbiaEarly history
Main articles: Prehistoric Serbia and Roman era Serbia
The Neolithic Starčevo and Vinča cultures existed in or near Belgrade and dominated the Balkans (as well as parts of Central Europe and Asia Minor) 8,500 years ago. Lepenski Vir and Vinča-Belo Brdo are two important sites of these cultures, located at the banks of the Danube. Around 1000 BC, the Paleo-Balkan peoples known as Thracians, Dacians, Illyrians developed in the Balkans. Ancient Greeks expanded into the south of modern Serbia in the 4th century BC, the north-westernmost point of Alexander the Great's empire being the town of Kale-Krševica. The Celtic tribe of Scordisci settled throughout Serbia in the 3rd century BC and built several fortifications, including Singidunum, present-day Belgrade, and Naissos, present-day Niš. Scordisci formed their own tribal state in this area and capital of that state was Singidunum (Belgrade). The Romans conquered parts of Serbia in the 2nd century BC; in 167 BC when conquering the west, establishing the province of Illyricum, and the rest of central part of present-day Serbia in 75 BC, establishing the province of Moesia Superior. Srem was conquered in 9 BC and Bačka and Banat in 106 AD after the Dacian wars. Despite its small size, contemporary Serbia extends fully or partially over several Roman provinces such as Moesia, Pannonia, Praevalitana, Dalmatia, Dacia and Macedonia. The chief towns of Serbian Upper Moesia (and wider) in the principate were: Singidunum, Viminacium, Remesiana, Naissus and especially, Sirmium which served as a Roman capital during the Tetrarchy. Seventeen Roman Emperors were born in Serbia, second only to Italy. The most famous of these was Constantine the Great, the first Christian Emperor, who issued religious tolerance throughout the Empire. When the Roman Empire was divided in 395, the region remained under the East, Byzantine Empire. After the 520s, Slavs appeared in the Byzantine Empire in great numbers.

Roman complex of palaces and temples,
built by Emperor Galerius (305–311)
Middle Ages
Main article: Serbia in the Middle AgesThe Serbs, as Slavs in the vicinity of the Byzantine Empire, lived in so-called Sklavinia ("Slav lands"), territories initially out of Byzantine control and independent. In the 8 century, the Vlastimirović dynasty established the Serbian Principality. In 822, Serbia "stretched over the greater part of Dalmatia", and Christianity was adopted as state-religion in ca 870. In the mid 10 century the state had emerged into a tribal confederation that stretched to the shores of the Adriatic Sea by the Neretva, the Sava, the Morava, and Skadar. The state disintegrated after the death of the last known Vlastimirid ruler – the Byzantines annexed the region and held it for a century, until 1040 when the Serbs under the Vojislavljević dynasty revolted in Duklja (Pomorje). In 1091, the Vukanović dynasty established the Serbian Grand Principality, based in Rascia (Zagorje). The two halves were reunited in 1142.
In 1166, Stefan Nemanja assumed the throne, marking the beginning of a prospering Serbia, henceforth under the rule of the Nemanjić dynasty. Nemanja's son Rastko (posth. Saint Sava), gained autocephaly for the Serbian Church in 1217 and authored the oldest known constitution, and in the same year Stefan II was crowned King, establishing the Serbian Kingdom. The Serbian Empire was established in 1346 by Stephen Dušan the Mighty, during which time Serbia reached its territorial peak, becoming one of the most powerful states in Europe and the most powerful in the Balkans. Dušan's Code, a universal system of law, was enacted. The reign of his son Stephen Uroš V the Weak saw the Empire fragment into a confederation of principalities. Emperor Uroš died childless in December 1371, after much of the nobility had been destroyed by the Ottomans in the Battle of Maritsa earlier that year. The Mrnjavčević, Lazarević and Branković ruled the Serbian lands in the 15th and 16th centuries. Constant struggles took place between various Serbian provinces and the Ottoman Empire. After the fall of Constantinople to the Ottomans in 1453 and the Siege of Belgrade, the Serbian Despotate fell in 1459 following the siege of the provisional capital of Smederevo. After repelling Ottoman attacks for over 70 years, Belgrade finally fell in 1521, opening the way for Ottoman expansion into Central Europe.
Ottoman and Austrian rule
See also: History of Ottoman Serbia, Great Serb Migrations, Kingdom of Serbia (1718–1739), and Koča's frontierAfter the loss of independence to the Kingdom of Hungary and the Ottoman Empire, Serbia briefly regained sovereignty under Jovan Nenad in the 16th century. Three Austrian invasions and numerous rebellions, such as the Banat Uprising (1595), constantly challenged Ottoman rule. Vojvodina endured a century long Ottoman occupation before being ceded to the Habsburg Empire in the 17th–18th centuries under the Treaty of Karlowitz. As the Great Serb Migrations depopulated most of southern Serbia, the Serbs sought refuge across the Danube river in Vojvodina to the north and the Military Frontier in the west where they were granted rights by the Austrian crown under measures such as the Statuta Wallachorum of 1630.
However, modern Ottomanist and post-constructivist scholars have refuted such a claim of a massive migration The Ottoman persecutions of Christians culminated in the abolition and plunder of the Patriarchate of Peć in 1766. However, most post-constructivist scholars have argued that the Ottoman Empire was in fact 'liberal' towards its Christians subjects relative to other parts of Europe at the time, but also that the Ottoman sultan enjoyed widespread legitimacy from the Orthodox clergy. The Ottoman Empire facilitated for a shared sense of time among Orthodox Christians, defined the ecclesiastical calendar: time revolve around succession feast days in Orthodox calendar; Saint’s days, the marking of changing seasons, harvests, fairs and family events. This was linked to the Idea of legitimate Ottoman rule rule and a ‘shared vision of the world’ among Orthodox Balkans in the 18th century which brought political unity and created commonalities.
According to the nationalist reading of history, as Ottoman rule in the Sanjak of Smederevo grew ever more brutal, the Holy Roman Emperor Leopold I formally granted the Serbs the right to their autonomous crownland following several petitions.
Revolution and independence
Main articles: Serbian revolution, Principality of Serbia, and Kingdom of Serbia See also: Serbian Vojvodina and May Overthrow
 Karađorđe Petrović and Miloš Obrenović, leaders of the Serbian Revolution
Karađorđe Petrović and Miloš Obrenović, leaders of the Serbian Revolution
The quest for national emancipation was first undertaken during the Serbian national revolution, in 1804 until 1815. The national liberation war was followed by a period of formalization, negotiations and finally, the Constitutionalization, effectively ending the process in 1835. For the first time in Ottoman history, the entire Serbian Christian population had risen up against the Sultan. The entrenchment of French troops in western Balkans, the incessant political crises in the Ottoman Empire, the growing intensity of the Austro–Russian rivalry in the Balkans, the intermittent warfare which consumed the energies of French and Russian Empires and the outbreak of protracted hostilities between the Porte and Russia are but a few of the major international developments which directly or indirectly influenced the course of the Serbian revolt.
During the First Serbian Uprising, led by Duke Karađorđe Petrović, Serbia was independent for almost a decade before the Ottoman army was able to reoccupy the country. Shortly after this, the Second Serbian Uprising began. Led by Miloš Obrenović, it ended in 1815 with a compromise between the Serbian revolutionaries and the Ottoman authorities. They were the easternmost bourgeois revolutions in the 19th-century world. Likewise, Serbia was one of the first nations in the Balkans to abolish feudalism. The Convention of Ackerman in 1826, the Treaty of Adrianople in 1829 and finally, the Hatt-i Sharif, recognized the suzerainty of Serbia with Miloš Obrenović I as its hereditary Prince. The struggle for liberty, a more modern society and a nation-state in Serbia won a victory under first constitution in the Balkans on 15 February 1835. It was replaced by a more conservative Constitution in 1838. In the two following decades, temporarily ruled by the House of Karađorđević, the Principality of Serbia actively supported the neighboring Habsburg Serbs, especially during the 1848 revolutions. Interior minister Ilija Garašanin published The Draft which became the standpoint of Serbian foreign policy from the mid-19th century onwards.
Following the clashes between the Ottoman army and civilians in Belgrade in 1862, and under pressure from the Great Powers, by 1867 the last Turkish soldiers left the Principality. By enacting a new constitution without consulting the Porte, Serbian diplomats confirmed the de facto independence of the country. In 1876, Serbia declared war on the Ottoman Empire, proclaiming its unification with Bosnia. The formal independence of the country was internationally recognized at the Congress of Berlin in 1878, which formally ended the Russo-Turkish War; this treaty, however, prohibited Serbia from uniting with Bosnia by placing it under Austro-Hungarian occupation. From 1815 to 1903, Principality of Serbia was ruled by the House of Obrenović, except from 1842 to 1858, when it was led by Prince Aleksandar Karađorđević. In 1882, Serbia became a kingdom, ruled by King Milan. In 1903, following May Overthrow, the House of Karađorđević, descendants of the revolutionary leader Karađorđe Petrović assumed power. Serbia was the only country in the region that was allowed by the Great Powers to be ruled by its own domestic dynasty. The 1848 revolution in Austria lead to the establishment of the autonomous territory of Serbian Vojvodina. By 1849, the region was transformed into the Voivodeship of Serbia and Banat of Temeschwar.
Balkan Wars and World War I
Main articles: Balkan Wars and Serbian Campaign (World War I)The Balkan Wars took place between 1912 and 1913. The First Balkan War broke out when the member states of the Balkan League attacked and divided Ottoman territories in the Balkans in a seven-month campaign, resulting in the Treaty of London. For the Kingdom of Serbia, this victory enabled territorial expansion into Raška and Kosovo. The Second Balkan War soon ensued when Bulgaria, dissatisfied with its gains, turned against its former allies, Serbia and Greece. Their armies repulsed the Bulgarian offensive and counter-attacked, penetrating into Bulgaria, while Romania and the Ottomans used the favourable time to intervene against Bulgaria to win territorial gains. In the resulting Treaty of Bucharest, Bulgaria lost most of the territories gained in the First Balkan War, with Serbia annexing Vardar Macedonia. Serbia enlarged its territory by 80% and its population by 50% within just two years; it also suffered high casualties on the eve of World War I, with around 20,000 dead.

On 28 June 1914 the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria in Sarajevo by Gavrilo Princip, a Serbian Nationalist and member of the Young Bosnia organization, led to Austria-Hungary declaring war on Serbia. In defense of its ally Serbia, Russia started to mobilize its troops, which resulted in Austria-Hungary's ally Germany declaring war on Russia. The retaliation by Austria-Hungary against Serbia activated a series of military alliances that set off a chain reaction of war declarations across the continent, leading to the outbreak of World War I within a month.
Serbia won the first major battles of World War I, including the Battle of Cer and Battle of Kolubara – marking the first Allied victories against the Central Powers in World War I. Despite initial success, it was eventually overpowered by the joint forces of the German Empire, Austria-Hungary and Bulgaria in 1915. Most of its army and some people went into exile to Greece and Corfu, where they recovered, regrouped and returned to the Macedonian front to lead a final breakthrough through enemy lines on 15 September 1918, liberating Serbia and defeating the Austro-Hungarian Empire and Bulgaria. Serbia, with its campaign, was a major Balkan Entente Power which contributed significantly to the Allied victory in the Balkans in November 1918, especially by helping France force Bulgaria's capitulation. Serbia was classified as a minor Entente power. Serbia was also among the main contributors to the capitulation of Austria-Hungary in Central Europe.
Serbia's casualties accounted for 8% of the total Entente military deaths; 58% (243,600) soldiers of the Serbian army perished in the war. The total number of casualties is placed around 1,000,000, more than 25% of Serbia's prewar size, and a majority (57%) of its overall male population.
First Yugoslavia
Main article: Kingdom of YugoslaviaAt the end of World War I, the Austro-Hungarian Empire collapsed. On 29 October 1918, Syrmia became a part of the State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs. On 25 November 1918, the Assembly of Vojvodina proclaimed the unification of Vojvodina (Banat, Bačka and Baranja) with the Kingdom of Serbia. One day before this, on 24 November, the Assembly of Syrmia also proclaimed the unification of Syrmia with Serbia. On 1 December 1918, Vojvodina officially became part of the Kingdom. On 26 November 1918, the Podgorica Assembly deposed the House of Petrović-Njegoš of the Kingdom of Montenegro, opting for the House of Karađorđević, unifying the two states. Also, Bosnia declares its unification with Serbia.
On December 1, 1918, Serbian Prince Regent Alexander of Serbia proclaimed the Kingdom of the Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes. Alexander’s father, Peter I of Serbia, became king of the new state. In November 1920, with the major boundary disputes resolved, a constituent assembly was finally elected and convened and the assembly adopted a constitution in June 1921. The new kingdom was to be a highly centralized and unitary state ruled by a Serb king and predominantly Serb government. Alexander became king after Petar died in August 1921.
Serb centralists and Croat federalists clashed in the parliament, and most governments were fragile and short-lived. Nikola Pašić, leader of the Serb Radical Party and prime minister of Serbia before and during World War I, headed or dominated most governments until his death. In 1921 and 1922 Yugoslavia became a member of the Little Entente. In June 1928, a Montenegrin Radical Party deputy opened fire on the floor of the parliament. He shot and killed two Croat deputies and fatally wounded Stjepan Radić. This action completed the breach between Croats and Serbs.
King Alexander changed the name of the country to Kingdom of Yugoslavia and changed the internal divisions from the 33 oblasts to nine new banovinas. The effect of Alexander's dictatorship was to further alienate the non-Serbs from the idea of unity. The king was assassinated in Marseille during an official visit to France in 1934 by an experienced marksman from IMRO with the cooperation of the Ustaše. Alexander was succeeded by his eleven-year-old son Peter II and a regency council headed by his cousin, Prince Paul.
Prime Minister Milan Stojadinović showed growing sympathy for fascist forms of government and was dissmied by Prince Paul. The regent then encouraged the new prime minister, Dragiša Cvetković, to negotiate a solution to the Croatian problem with Vladko Macek. In August 1939 the Cvetković–Maček Agreement established an autonomous Banate of Croatia. In effect, Yugoslavia became a federation with two units: Croatia and the rest. Serb hopes of achieving similar status were put on hold by the outbreak of World War II.
World War II and Second Yugoslavia
Main articles: Yugoslav Front and Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia See also: Serbia under German occupation, Socialist Republic of Serbia, World War II persecution of Serbs, and Jasenovac concentration campIn 1941, in spite of domestically unpopular attempts by the government of Yugoslavia to appease the Axis powers, Nazi Germany, Fascist Italy, and other Axis states invaded Yugoslavia. After the invasion, the Kingdom of Yugoslavia was dissolved and Serbia was put under a German Military administration, under a joint German-Serb government with Milan Nedić as Head of the "Government of National Salvation". Serbia was the scene of a civil war between royalist chetniks commanded by Draža Mihailović and communist partisans commanded by Josip Broz Tito. Against these forces were arrayed Nedić's units of the Serbian Volunteer Corps and the Serbian State Guard.
After one year of occupation, around 16,000 Serbian Jews were murdered in Axis-occupied Serbia, or around 90% of its pre-war Jewish population. Many concentration camps were established acrros the country. Banjica concentration camp was the biggest and one of the first concentration camps for Jews in Europe. Primary victims were Serbian Jews, Roma, and Serb political prisoners.

Axis puppet state of the Independent State of Croatia committed large scale persecution and genocide of Serbs, Jews, and Roma. The estimate of the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum indicates that between 330,000 and 390,000 ethnic Serb residents of Croatia, Bosnia and parts of Serbia were murdered during the Ustaše genocide campaign; same figures are supported by the Jewish Virtual Library. reports that more than 500,000 Serbs were killed overall, whereas official Yugoslav sources used to estimate more than 700,000 victims, mostly Serbs. The Jasenovac memorial so far lists 82,085 names killed at the this concentration camp alone, out of around 100,000 estimated victims (75% of whom were of Serbian origin).
Out of roughly 1,000,000 casualties in all of Yugoslavia up until 1944, around 250,000 were citizens of Serbia of different ethnicities, according to Zundhauzen. The overall number of Serb casualties in Yugoslavia was around 530,000, out of whom up to 400,000 in the Independent State of Croatia. The Republic of Užice was a short-lived liberated Yugoslav territory established by the Partisans and the first liberated territory in World War II Europe, organized as a military mini-state that existed in the autumn of 1941 in the west of occupied Serbia. By late 1944, the Belgrade Offensive swung in favour of the partisans in the civil war; the partisans subsequently gained control of Yugoslavia. The Syrmia front was the last sequence of the internal war in Serbia following the Belgrade Offensive. Between 70,000–80,000 people were killed in Serbia during the communist takeover.
The communist takeover by the Yugoslav Partisans resulted in abolition of the monarchy and a subsequent orchestrated constitutional referendum. A single-party state was soon established in Yugoslavia by the League of Communists of Yugoslavia. All opposition was repressed and people deemed to be promoting opposition to the government or promoting separatism were given harsh prison sentences or executed for sedition. Serbia became a constituent republic within the SFRY known as the Socialist Republic of Serbia and had a republic-branch of the federal Communist party, the League of Communists of Serbia.
Serbia's most powerful and influential politician in Tito-era Yugoslavia was Aleksandar Ranković, one of the "big four" Yugoslav leaders, alongside Josip Broz Tito, Edvard Kardelj, and Milovan Đilas. In 1950, Ranković as minister of interior reported that since 1945 the Yugoslav communist regime had arrested five million people. Ranković was later removed from the office because of the disagreements regarding Kosovo’s nomenklatura and the interests of Serb unity. Ranković's dismissal was highly unpopular amongst Serbs.
Pro-decentralization reformers in Yugoslavia succeeded in the late 1960s in attaining substantial decentralization of powers, creating substantial autonomy in Kosovo and Vojvodina, and recognizing a Yugoslav Muslim nationality. As a result of these reforms, there was a massive overhaul of Kosovo's nomenklatura and police, that shifted from being Serb-dominated to ethnic Albanian-dominated through firing Serbs in large scale. Further concessions were made to the ethnic Albanians of Kosovo in response to unrest, including the creation of the University of Pristina as an Albanian language institution. These changes created widespread fear amongst Serbs of being treated as second-class citizens.
Breakup of Yugoslavia and political transition
Main articles: Breakup of Yugoslavia, Yugoslav Wars, Kosovo War, and Republic of Serbia (1990–2006)In 1989 Slobodan Milošević rose to power in Serbia. Milošević promised reduction of powers for the autonomous provinces of Kosovo and Vojvodina, where his allies subsequently overtook the power, in a movement called "Anti-bureaucratic revolution". This ignited tensions with the communist leadership of the other republics, and awoke nationalism across the country, that eventually resulted in the Breakup of Yugoslavia, with Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina and Macedonia leaving one after another. In 1992, the governments of Serbia and Montenegro agreed to the creation of a new federation, called the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, which abandoned the predecessor SFRY's official endorsement of communism, and instead endorsed democracy.

Fueled by ethnic tensions, series of Yugoslav Wars broke out in Serbia's neighborhood, with most severe conflicts taking place in Croatia and Bosnia, where Serb minorities opposed their newly proclaimed independence. Serbia and Montenegro remained nominally uninvolved, with Yugoslav Army formally withdrawing in early stages of the war, but provided significant logistic, military and financial support to the Serb forces, who inherited most of the Army's resources. In response to that support, UN imposed sanctions to FR Yugoslavia in May 1992, which led to political isolation, economic decline and hyperinflation of the Yugoslav dinar. The country permanently recovered from the inflation problem in 1996.
Multiparty democracy was introduced in Serbia in 1990, officially dismantling the single-party system. Critics of Milošević claimed that the government continued to be authoritarian despite constitutional changes, as Milošević maintained strong political influence over the state media. Milošević issued media blackouts of independent media stations' coverage of protests against his government and restricted freedom of speech through reforms to the Serbian Penal Code which issued criminal sentences on anyone who "ridiculed" the government and its leaders, resulting in many people being arrested who opposed Milošević and his government.
When the ruling SPS refused to accept its defeat in municipal elections in 1996, Serbians engaged in large protests against the government. Between 1998 and 1999, peace was broken again, when the situation in Kosovo worsened with continued clashes between Yugoslav security forces and the KLA. The confrontations led to the Kosovo War.
In September 2000, opposition parties accused Milošević of electoral fraud. A campaign of civil resistance followed, led by the Democratic Opposition of Serbia, a broad coalition of anti-Milošević parties. This culminated on 5 October when half a million people from all over the country congregated in Belgrade, compelling Milošević to concede defeat. The fall of Milošević ended Yugoslavia's international isolation. Milošević was sent to the ICTY. The DOS announced that FR Yugoslavia would seek to join the European Union. In 2003, the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia was renamed Serbia and Montenegro and the EU opened negotiations with the country for the Stabilization and Association Agreement. On 21 May 2006, Montenegro held a referendum to determine whether or not to end its union with Serbia. The next day, state-certified results showed 55.4% of voters in favor of independence, which was just above the 55% required by the referendum.
Serbia's political climate has remained tense. In 2003, the prime minister Zoran Đinđić was assassinated as result of a plot originating from circles of organized crime and former security officials. Pro- and anti-EU political forces in Serbia have remained sharply divided on the political course of Serbia in regards to its relations with the European Union.
On 5 June 2006, the National Assembly of Serbia declared Serbia to be the legal successor to the former state union. In April 2008 Serbia was invited to join the intensified dialogue programme with NATO despite the diplomatic rift with the alliance over Kosovo. Serbia officially applied for the European Union membership in December 2009 and became an official candidate in March 2012.
Geography
Main article: Geography of Serbia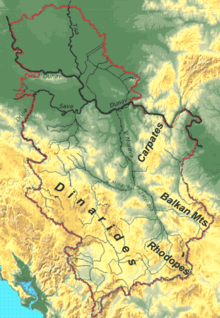

Located at the crossroads between Central and Southern Europe Serbia is found in the Balkan peninsula and the Pannonian Plain. Including Kosovo, it lies between latitudes 41° and 47° N, and longitudes 18° and 23° E. The country has several notable topographical features: the Pannonian Plain (mainly Vojvodina) and river lowlands, the Balkan and Carpathian Mountains, the Dinaric Alps, along with hillside streching across central part of Serbia. The Danube passes through Serbia with 21% of its overall length, joined by its biggest tributaries, the Sava and Tisza rivers. The province of Vojvodina covers the northern third of the country, and is entirely located within the Central European Pannonian Plain. Dinaric Alps, gradually rising towards south, cover most of western and central Serbia. The easternmost tip of Serbia extends into the Wallachian Plain. The eastern border of the country intersects with the Carpathian Mountain range, which run through the whole of Central Europe.
The Southern Carpathians meet the Balkan Mountains, following the course of the Great Morava, a 500 km long river. The Midžor peak is the highest point in eastern Serbia at 2156 m. In the southeast, the Balkan Mountains meet the Rhodope Mountains. The Šar Mountains of Kosovo form the border with Albania, with one of the highest peaks in the region, Đeravica, reaching 2656 meters at its peak. Dinaric Alps of Serbia follow the flow of the Drina river, overlooking the Dinaric peaks on the opposite shore in Bosnia and Herzegovina.
Climate
Main article: Climate of Serbia
On the macro-level, the climate of Serbia is under the influences of the Atlantic Ocean and Mediterranean Sea and the landmass of Eurasia. With mean January temperatures around 0 °C (32 °F), and mean July temperatures around 22 °C (72 °F), it can be classified as transitional between oceanic (Köppen climate classification Cfb), humid subtropical (Cfa) and humid continental (Dfa). Rainfall patterns are well-distributed and average about 50 mm/month.
In the north, the climate is more continental, with cold winters, and hot, humid summers with well distributed rainfall patterns. In the south, summers and autumns are drier, and winters are relatively cold, with heavy inland snowfall in the mountains. Differences in elevation, proximity to the Adriatic Sea and large river basins, as well as exposure to the winds account for climate variations. South and South-west Serbia are subject to Mediterranean influences. However, the Dinaric Alps and other mountain ranges contribute to the cooling of most of the warm air masses. Winters are quite harsh in the Pešter plateau, because of the mountains which encircle it.
The average annual air temperature for the period 1961–90 for the area with an altitude of up to 300 m (984 ft) is 10.9 °C (51.6 °F). The areas with an altitude of 300 to 500 m (984 to 1,640 ft) have an average annual temperature of around 10.0 °C (50.0 °F), and over 1,000 m (3,281 ft) of altitude around 6.0 °C (42.8 °F). The lowest recorded temperature in Serbia was −39.5 °C (−39.1 °F) on 13 January 1985, Karajukića Bunari in Pešter, and the highest was 44.9 °C or 112.8 °F, on 24 July 2007, recorded in Smederevska Palanka.
Biodiversity and ecology
| This section needs expansion. You can help by making an edit requestadding to it . (May 2012) |
Over 31% of Serbia is covered by forest. National parks take up 10% of the country's territory. Serbia has 5 national parks and 22 nature reserves.
The NATO bombings of 1999 caused lasting damage to the environment of Serbia, with several thousand tons of toxic chemicals stored in targeted factories being released into the soil, atmosphere and water basins affecting humans and the local wildlife (see Environmental issues in Serbia).
Recycling is still a fledgeling activity in Serbia, with only 15% of its waste being turned back for re-use.
Hydrography
Main articles: List of rivers of Serbia and List of lakes in SerbiaSpanning over 588 kilometers across Serbia, the Danube river is the largest source of fresh water. Other main rivers are Sava, Morava, Tisa, Drina and Ibar. Almost all of Serbia's rivers drain to the Black Sea, by way of the Danube river. One notable exception is the Pčinja which flows into the Aegean. The largest natural lake is Belo Jezero, located in Vojvodina, covering 25 square kilometers. The largest artificial reservoir, the Iron Gate (Đerdap), has a total area of 253 square kilometers divided by Romania and Serbia, with 163 square kilometers on the Serbian side. The largest waterfall, Jelovarnik, located in Kopaonik, is 71 meters high.
| River | Km in Serbia | Total length (km) |
Number of countries | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Danube | 588 | 2783 | 9 |
| 2 | Great Morava | 493 | 493 | 1 |
| 3 | Ibar | 250 | 272 | 2 |
| 4 | Drina | 220 | 346 | 3 |
| 5 | Sava | 206 | 945 | 4 |
| 6 | Timok | 202 | 202 | 1 |
| 7 | Tisa | 168 | 966 | 4 |
| 8 | Nišava | 151 | 218 | 2 |
| 9 | Tamiš | 118 | 359 | 2 |
| 10 | Begej | 75 | 244 | 2 |
Politics
Main article: Politics of Serbia
Serbia formally regained independence in 2006, after 88 years as part of Yugoslavia, the National Assembly drafted a new constitution which was ratified in a referendum. Serving his second term as President, Boris Tadić is the leader of the center-left Democratic Party. His second reelection was won with a narrow majority of 50.5% in the second round of the presidential election held on 4 February 2008.
The last parliamentary elections were held in May 2008. The coalition For a European Serbia led by Boris Tadic, claimed victory, but was significantly short of an absolute majority. Following the negotiations with the leftist coalition centered around the Socialist Party of Serbia, an agreement was reached to form a new government, headed by Mirko Cvetković. Present-day Serbian politics are fractiously divided on different issues, such as the European Union and the economy.
The next parliamentary, local and presidential elections will be held simultaneously on 6 May 2012.
Nationalist opposition leader, Tomislav Nikolic was elected as the president of Serbia in the 2012 presidential polls.
Kosovo has been governed since 1999 by UNMIK, a UN mission. The Provisional Institutions of Self-Government, has an assembly and a president. Although the assembly has declared independence from Serbia, Serbia does not recognise the move.
Administrative divisions
Main article: Administrative divisions of SerbiaSerbia has 5 regions: Vojvodina, Belgrade, Šumadija and Western Serbia, Southern and Eastern Serbia and Kosovo and Metohija. Two of those are autonomous provinces: Vojvodina in the north and Kosovo and Metohija in the south. Belgrade is a separate territorial unit established by the Constitution and law, while Šumadija and Western Serbia and Southern and Eastern Serbia are directly subordinated to country authorities. The area that lied between Vojvodina and Kosovo was officially called Central Serbia before 2009. Central Serbia was not an administrative division (unlike the provinces), and it had no regional authority of its own. Since 7 April 2010, the former territory of Central Serbia has officially been divided into 3 regions: Belgrade, Šumadija and Western Serbia, and Southern and Eastern Serbia.
Serbia is divided into 150 municipalities and 24 cities, which are the basic units of local self-government. Of the 150 municipalities, 47 are located in Southern and Eastern Serbia, 52 in Šumadija and Western Serbia, 39 in Vojvodina and 28 (de facto 37) in Kosovo.Of the 24 cities, 6 are in Southern and Eastern Serbia, 10 in Šumadija and Western Serbia, 6 in Vojvodina, 1 in Kosovo, and 1 (Belgrade) has a status of separate territorial unit. Municipalities and cities are gathered into districts, which are regional centers of state authority, but have no assemblies of their own; they present purely administrative divisions. Serbia is organized into 29 districts (8 in Šumadija and Western Serbia, 9 in Southern and Eastern Serbia, 7 in Vojvodina and 5 in Kosovo), while the city of Belgrade presents a district of its own.
Foreign relations
Main article: Foreign relations of Serbia See also: Accession of Serbia to the European Union and International recognition of KosovoSerbia has a network of 64 embassies, 22 Consulates-Generals in 14 countries, 3 permanent representations to the United Nations and to several other institutions, abroad. Serbia hosts 65 foreign embassies, 5 Consulates-Generals and 4 Liaison offices. Serbia also hosts representatives of the Palestinian National Authority and Sovereign Military Order of Malta and 13 Honorary Consuls, some accredited as Ambassadors. Serbia inherited about a third of the diplomatic facilities that belonged to the former Yugoslavia.

Serbia is a member of major international organizations such as: the UN, the Council of Europe, OSCE, Interpol, World Bank, Partnership for Peace, Stability Pact for South Eastern Europe, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNMIL, UNOCI, World Tourism Organization, Universal Postal Union, World Confederation of Labor, World Customs Organization, World Meteorological Organization and World Health Organization.

Foreign relations of Republic of Serbia are regulated by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs. Since 2007, ministry has been headed by Vuk Jeremić. Serbia has inherited the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, along with all of its holdings, after the dissolution of the previous state union with Montenegro. Serbian foreign ministries continue to serve citizens of the Republic of Montenegro in countries that do not have Montenegrin diplomatic presence. The President of Serbia Boris Tadić referred to relations with the European Union, Russia, United States and China as "four pillars" of foreign policy. Also, the normalization of international relations is one of the main priorities of President Boris Tadić.
On February 17, 2008, the former province of Kosovo unilaterally declared independence from Serbia, forming the Republic of Kosovo in the process. Serbia, together with Russia, China and many others do not recognize Kosovo as an independent state. Serbia has vowed to fight Kosovo's admission to international organizations. The Republic of Kosovo does not have and has not applied for United Nations membership as of yet, and has no current prospects of ever becoming a member of the United Nations at all. Serbia, in response to nations which have recognized Kosovo as an independent nation, has consistently recalled its ambassadors to these nations for some time, in an act of protest.
Serbia doesn't deal directly with the Republic of Kosovo, but only through the international intermediaries UNMIK and EULEX. As of 14 March 2012, Kosovo has received 91 diplomatic recognitions as an independent state.
Series of status neutral talks between the Republic of Serbia and partially recognised Republic of Kosovo are held in Brussels, mediated by the EU.
Serbia officially applied for European Union membership on 22 December 2009. The European Commission recommended making it an official candidate on 12 October 2011, following its successful application for the EU membership. Despite its setbacks in the political field, on 7 December 2009 the EU unfroze the trade agreement with Serbia and the Schengen countries dropped the visa requirement for Serbian citizens on 19 December 2009.
As of July 2011, Serbia has completed the cooperation with the International Criminal Tribunal for the former Yugoslavia, and Goran Hadžić became the last indicted fugitive to be arrested.
Serbia received a full candidate status on 1 March 2012. The government of Serbia has set a goal for EU accession in 2014, as per the Papandreou plan - Agenda 2014.
Military
Main article: Military of SerbiaSerbian Armed Forces are subordinate to the Ministry of Defence, and are divided into Army (includes River Flotilla on the Danube), Serbian Air Force and Air Defence and the Training Command. Established in 1912 Serbian Air Force and Air Defence, is one of the oldest air forces in the world. As a landlocked country, Serbia has no navy, but operates a river fleet as a separate service. The Chief of the General Staff, which reports to the Defence Minister, is the Chief of the General Staff of the Military of Serbia. He is appointed by the President of Serbia, who is the commander-in-chief.

Wars and crises of the 1990s have depleted the army, which has since suffered from a lack of funding and low enrollment rates. In 2006, when there was the separation of Serbia and Montenegro, the armed forces of the federation had 65,700 troops, 110 while in 2009 their number had fallen to 30,000,111 Military spending declined from about 5% of GDP 1990. However, despite these shortfalls of the past couple of decades, the Serbian military is still the most powerful military of the region and in the higher end of European militaries.
Serbia's current defence spending stands at 2.08% of the GDP, this represents a drop in overall relation to the GDP as a percentage. Over 30% of the budget is spent on pensions alone. The continuing drive to modernize the military will add onto costs in the future. The number of active personnel has been significantly reduced from pre-2004 levels. As of 2011, over 90% of the armed forces are composed of professional soldiers and volunteers.
As of 1 January 2011, Serbia no longer practises mandatory military service. Prior to this, mandatory military service lasted 6 months for men. Conscientious objectors could however opt for 9 months of civil service instead.
Serbia participates in the Partnership for Peace program, but so far has shown no intention of full integration into NATO, due to significant social rejection, largely derived from the NATO bombing in 1999. The country has also signed the Stability Pact for South Eastern Europe and the anti-landmine treaty in Ottawa, and participate in peacekeeping missions of the UN in DR Congo, Ivory Coast, Liberia and Chad. Serbia follows the doctrine of armed neutrality. Serbia also practices the doctrine of civilian control of the military, vesting responsibility of the military in the citizens. Serbia does not maintain a military presence in the disputed territory of Kosovo. United Nations Security Council Resolution 1244 gives UNMIK temporary administrative control of Kosovo from Serbia.
Serbia is the largest exporter and producer of military hardware in the region, Serbian exports were 500 million U.S. dollars alone in 2009. Serbia exports across the world, notably to Libya, USA, Iraq and others. The Serbian military industry has seen significant growth over the years, and it is still increasing.
Demographics
Main article: Demographics of Serbia| Ethnic composition (2002) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serb | 82.9% | |||
| Hungarian | 3.9% | |||
| Bosniak | 1.8% | |||
| Roma | 1.4% | |||
| Yugoslav | 1.1% | |||
| Other | 8.9% | |||
As of January 2011, Serbia (without Kosovo) had an estimated population of 7,276,195 (not including over 200,000 internally displaced persons from Kosovo, who will be counted as a permanent population in the next census, taking place in 2011). The 2002 census was not conducted in Kosovo, which was under United Nations administration at the time. According to CIA estimates, Kosovo has around 1.8 million inhabitants, the majority of them Albanian with Kosovo Serbs coming in second.
Serbs are the largest ethnic group in Serbia, representing 83% of the total population, excluding Kosovo. With a population of 290,000, Hungarians are the second largest ethnic group in Serbia, representing 3.9% (and 14.3% of the population in Vojvodina). Other minority groups include Bosniaks, Roma, Albanians, Croats, Bulgarians, Montenegrins, Macedonians, Slovaks, Vlachs, Romanians, and Chinese. According to UN estimates, around 500,000 Roma live in Serbia. The German minority in the northern province of Vojvodina was more numerous in the past (336,430 in 1900, or 23.5% of Vojvodina's population).
Serbia has the largest refugee population in Europe. Refugees and internally displaced persons (IDPs) in Serbia form between 7% and 7.5% of its population – about half a million refugees sought refuge in the country following the series of Yugoslav wars, mainly from Croatia, and to a lesser extent from Bosnia and Herzegovina and the IDPs from Kosovo, which are currently the most numerous at over 200,000.
Meanwhile, it is estimated that 300,000 people left Serbia during the 1990s alone, and around 20% of those had college or higher education. Serbia has a comparatively old overall population (among the 10 oldest in the world), mostly due to low birth rates. In addition, Serbia has among the most negative population growth rates in the world, ranking 225th out of 233 countries overall.
Largest cities
Main article: List of cities in SerbiaTemplate:Largest cities of Serbia
Religion
Main article: Religion in SerbiaFor several centuries straddling the religious boundary between Orthodoxy and Catholicism, joined up later by Islam, Serbia remains one of the religiously more diverse countries on the continent. While formation of the nation-state and turbulent history of 19th and 20th century has left its traces on the religious landscape of the country: as of 2002, Vojvodina was 68.97% Orthodox, 19.11% Catholic and 3.55% Protestant, while Central Serbia and Belgrade regions were over 90% Orthodox Christian. Kosovo consists of an 89% Albanian Muslim majority.

| Religious groups in Serbia (excluding Kosovo) in 2002 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Orthodoxy | 84.1% | |||
| Catholicism | 6.24% | |||
| Islam | 3.42% | |||
| Protestantism | 1.44% | |||
Among the Eastern Orthodox Churches, the Serbian Orthodox Church is the largest in the country. According to the 2002 Census, 82% of the population of Serbia, excluding Kosovo, or 6,2 million people declared their nationality as Serbian, who are overwhelmingly adherents of the Serbian Orthodox Church. Other Orthodox Christian communities in Serbia include Romanians, Vlachs, Macedonians and Bulgarians. Together they comprise about 84% of the entire population.
Roman Catholicism is mostly present in Vojvodina, especially its northern part, which is home to minority ethnic groups such as Hungarians, Croats, Bunjevci, as well as to some Slovaks and Czechs. There are an estimated 388,000 baptized Roman Catholics in Serbia, roughly 6.2% of the population, mostly in northern Serbia.
Protestantism accounts for about 1.1% of the country's population, chiefly among Slovaks in Vojvodina as well as among one number of Reformist Hungarians and Vojvodinian Serbs. Islam has a strong historic following in the southern regions of Serbia – southern Raška and Preševo Valley municipalities in the south-east. Bosniaks are the largest Islamic community in Serbia with 140,000 followers or 2% of the total population, followed by Albanians.
With the exile of Jews from Spain during the Inquisition era, thousands made their way through Europe to the Balkans, some of which settled in Serbia. They were well-accepted and in the ensuing generations the majority assimilated or became secular. Later on, the wars that ravaged the region resulted in a great part of the Jewish Serbian population emigrating from the region. Today, there are approximately 1,185 Jewish Serbians living in Serbia today. The only functioning synanogue remains the Belgrade Synagogue, which was saved from destruction, at the hands of the Nazis, by the local population during World War II.
Economy
Main article: Economy of Serbia
Serbia has a transitional economy mostly dominated by services, manufacturing and agriculture. The economy is heavily reliant on exports and foreign investment. Since 2000, Serbia has attracted over $20 billion USD in foreign direct investment (FDI). Although average GDP growth over ten years has been 4.45% per year, Serbia suffers from a high unemployment rate (23.7% as of February 2012) and an unfavorable trade deficit.
GDP (PPP) for 2012 is estimated at $80.282 billion or $10,811 per capita (PPP), Serbia is an upper-middle income economy. According to Eurostat data, Serbian (PPP) GDP per capita stood at 35% of the EU average in 2010.
Serbia has free-trade agreements with the EFTA and CEFTA, a preferential trade regime with the European Union, a Generalized System of Preferences with the United States, and free-trade agreement with Russia, Belarus, Kazakhstan and Turkey.
Serbia grows about one-third of the world's raspberries and is a leading exporter of frozen fruit.
In July 2010, the credit rating agency Dun & Bradstreet rated Serbia's economy at DB4d, which remained the same since the last rating. There was expressed concern for the slower-than-expected recovery of the economy from the global financial crisis, along with the continuous high business risk due lowered credit capabilities, increasing company bankruptcy and generally poor economic prospects. The Agency also expressed concern for the high credit debt and large number of foreign banks in the financial sector, creating an increased risk of instability.
Energy
See also: Wind power in Serbia
Most of the energy is currently produced comes from coal or hydroelectric dams. Energy consumption is expected to exceed energy production by 2012 and Elektroprivreda Srbije, Serbia's largest energy producer, is expected to develop Đerdap III, a hydroelectric dam with approximately 2.4 gigawatts of power.
Naftna Industrija Srbije (NIS), Serbia's largest petroleum producer, was acquired by Russian energy giant Gazprom Neft. The two companies, are planning to build the Serbian portion of the South Stream gas pipeline. The two companies are also building a 300 million cubic meter gas storage at Banatski Dvor, located approximately 60 kilometers northeast of Novi Sad. The South Stream gas pipeline project will be the largest since the 19th century railway construction through Serbia.
Transport
Main article: Transport in SerbiaThe Morava valley route, running across the country in north-south direction, is the easiest route of travel from continental Europe to Greece and Asia Minor. European routes E65, E70, E75 and E80, as well as the E662, E761, E762, E763, E771, and E851 pass through the country. The E70 (westwards from Belgrade), E75 (from Hungarian border to Leskovac), a short segment of E80 (to Niš) as well as smaller road segments including parts of the Belgrade bypass are modern highways of motorway / autobahn standard. Many new motorways (most of which belong to the E road network) are currently being built. Serbia plans to greatly expand its motorway network in the near future. Currently the main motorway construction projects in Serbia are following the routes of Pan-European corridors.

There are four international airports in Serbia: Belgrade Nikola Tesla Airport, Niš Constantine the Great Airport, Vršac International Airport and Pristina International Airport.
As of 2010, Serbia has 1,953,061 registered cars, 40,129 motorcycles, 9,201 buses, 172,799 trucks, 23,552 special transport vehicles (2009 info), 239,295 tractors and 99,025 trailers.
Although landlocked, there are around 2000 km of navigable rivers and canals, the largest of which are: the Danube, Sava, Tisa, joined by the Timiş River and Begej, all of which connect Serbia with Northern and Western Europe through the Rhine–Main–Danube Canal and North Sea route, to Eastern Europe via the Tisa, Timiş, Begej and Danube Black Sea routes, and to Southern Europe via the Sava river. The two largest Serbian cities – Belgrade and Novi Sad, as well as Smederevo – are major regional Danubian harbours.
Telecommunication
Main article: Telecommunications in Serbia89% of households in Serbia have fixed telephone lines, and with over 9.60 million users the number of cell-phones surpasses the number of total population of Serbia itself by 30%. The largest cellphone provider is Telekom Srbija with 5.65 million subscribers, followed by Telenor with 3.1 million users and Vip mobile with just over 1 million. 52.1% of households have computers, 41.2% use the Internet, and around 45%-50% (estimate) have cable TV, which puts the country ahead of certain member states of the EU. Serbia is ranked 57th in the world in terms of Internet usage out of 216 states. 55.9% of the population uses the internet, placing Serbia ahead of all Balkan countries.
Tourism
Main article: Tourism in SerbiaTourism in Serbia mainly focuses on the villages and mountains of the country. The most famous mountain resorts are Zlatibor, Kopaonik, and the Tara. There are also many spas in Serbia, one the biggest of which is Vrnjačka Banja. Other spas include Soko Banja and Niška Banja. There is a significant amount of tourism in the largest cities like Belgrade, Novi Sad and Niš, but also in the rural parts of Serbia like the volcanic wonder of Đavolja varoš, Christian pilgrimage to the many Serbian monasteries across the country and the cruises along the Danube, Sava or Tisza. There are several popular festivals held in Serbia, such as EXIT, proclaimed to be the best European festival by UK Festival Awards 2007 and Yourope, the European Association of the 40 largest festivals in Europe and the Guča trumpet festival. 2,2 million tourists visited Serbia in 2007, a 15% increase compared to 2006.
Education
Main article: Education in Serbia
Education in Serbia is regulated by the Ministry of Science and Education. Education starts in either pre-schools or elementary schools. Children enroll in elementary schools at the age of seven, and remain there for eight years. After compulsory education students have the opportunity to either attend a high school for another four years, specialist school, for 2 to 4 years, or to enroll in vocational training, for 2 to 3 years. Following the completion of high school or a specialist school, students have the opportunity to attend university.
The largest public universities in Serbia are:
- University of Belgrade
- University of Kragujevac
- University of Niš
- University of Novi Sad
- University of Pristina
The University of Belgrade is the oldest and currently the largest university in Serbia. Established in 1808, it has 31 faculties, and since its inception, has trained an estimated 330,000 graduates. Other universities with a significant number of faculty and alumni are those of Novi Sad (founded 1960), Kragujevac (founded 1976) and Niš (founded 1965).
The roots of the Serbian education system date back to the 11th and 12th centuries when the first Catholic colleges were founded in Titel and Bač. With the establishment of the Serbian Orthodox Church and the Serbian Kingdom in 1217, education was mostly conducted through the monasteries of Sopoćani, Studenica, and Patriarchate of Peć. The oldest college faculty within the current borders dates back to 1778; founded in the city of Sombor, then Habsburg Empire, it was known under the name Norma and was the oldest Slavic Teacher's college in Southern Europe.
Science and technology
Serbia has a rich tradition of contributing to the field of science and technology. Scientist, inventor and electrical engineer Nikola Tesla patented numerous inventions and was an important contributor to the birth of commercial electricity in the United States. Other notable Serbian scientists and inventors were Mihajlo Pupin and Milutin Milanković.

- Nikola Tesla was famous for developing the AC motor, the bifilar coil, various devices that used rotating magnetic fields, the alternating current polyphase power distribution systems, the fundamental devices of systems of wireless communication (legal priority for the invention of radio), radio frequency oscillators, devices for voltage magnification by standing waves, robotics, logic gates for secure radio frequency communications, devices for x-rays, apparatus for ozone generation, devices for ionized gases, devices for high field emission, devices for charged particle beams, methods for providing extremely low level of resistance to the passage of electrical current, means for increasing the intensity of electrical oscillations, voltage multiplication circuitry, devices for high voltage discharges, devices for lightning protection and VTOL aircraft. He also invented the Tesla coil and the Tesla turbine . The Tesla is the SI derived unit of magnetic flux density and was named after Tesla.
- Mihailo Petrović is known for having contributed significantly to differential equations and phenomenology, as well as inventing one of the first prototypes of an analog computer.
- Milutin Milanković is known for his theory of ice ages, suggesting a relationship between the Earth's long-term climate changes and periodic changes in its orbit, now known as Milankovitch cycles.
- Mihajlo Pupin discovered a means of means of greatly extending the range of long-distance telephone communication by placing loading coils of wire (known as Pupin coils) at predetermined intervals along the transmitting wire (known as "pupinization").
- Miodrag Radulovacki is best known for postulating the Adenosine Sleep Theory in 1984.
- Josif Pančić discovered and identified the Serbian Spruce in 1875.
- Jovan Cvijić is considered the founder of geography in Serbia. In more than 30 years of intense scientific study, Cvijić published vast number of significant works, many of which have not lost value even today. He founded the Faculty of Philosophy's Geographical institute in 1923, the first establishment of that type in Balkans.
Culture
Main articles: Serbian culture and Cultural Heritage of Serbia
For centuries straddling the boundaries between East and West, Serbia had been divided among: the Eastern and Western halves of the Roman Empire; then between Kingdom of Hungary, Bulgarian Empire, Frankish Kingdom and Byzantium; and then between the Ottoman Empire and the Austrian Empire and Austria-Hungary, as well as Venice in the south. These overlapping influences have resulted in cultural varieties throughout Serbia and the Serbian-inhabited regions; its north leaning to the profile of Central Europe, while the south being characteristic of the wider Balkans and the Mediterranean.
The Byzantine influence on Serbia was profound, firstly through the introduction of Eastern Christianity (Orthodoxy) in the Early Middle Ages. The Serbian Orthodox Church has had an enduring status in Serbia, with the many Serbian monasteries constituting the most valuable cultural monuments left from Serbia in the Middle Ages.
Serbia has a total of eight sites on the UNESCO World Heritage list: The Early Medieval capital Stari Ras and the 13th-century monastery Sopoćani, and the 12th-century monastery Studenica, and the endangered Medieval Monuments in Kosovo group, comprising the monasteries of Visoki Dečani, Our Lady of Ljeviš, Gračanica and Patriarchate of Peć (former seat of the Serbian Church, mausoleum of Serbian royalty) and finally the Roman estate of Gamzigrad–Felix Romuliana. There are two literary memorials on UNESCO's Memory of the World Programme: The 12th-century Miroslav Gospel, and scientist Nikola Tesla's valuable archive.
Serbia has a well-established theatrical tradition with many theaters. The Serbian National Theatre was established in 1861. The Belgrade International Theatre Festival, founded in 1967, is one of the oldest theatre festivals in the world, and it has become one of the five most important and biggest European festivals. The Serbian cinema is one of the oldest in the Balkans, having its foundation in 1896 with the release of the oldest movie in the Balkans, "Život i dela besmrtnog vožda Karađorđa", a biography about Karađorđe.
The most prominent museum in Serbia is the National Museum of Serbia, founded in 1844; it houses a collection of more than 400,000 exhibits, over 5,600 paintings and 8,400 drawings and prints, and includes many foreign masterpiece collections, including Miroslav Gospel. The museum is currently undergoing renovation.
The official language, Serbian, is written in both the Cyrillic and Latin alphabets.
Art
Main article: Serbian art

There were many famous royal cities and palaces in Serbia at the time of Roman Empire and early Byzantine Empire, traces of which can still be found in Sirmium, Gamzigrad and Justiniana Prima. Serbian medieval monuments, which have survived until today, are mostly monasteries and churches. Most of these monuments have walls painted with frescoes. The most original monument of Serbian medieval art is the Studenica Monastery (built around 1190). This monastery was a model for later monasteries, like: the Mileševa, Sopoćani and Visoki Dečani monasteries. The most famous Serbian medieval fresco is the "Mironosnice na Grobu" (or the "white angel") from the Mileševa monastery.
Icon-painting is also part of Serbian medieval cultural heritage. The influence of Byzantine Art increased after the fall of Constantinople into the hands of the crusaders in the year 1204, when many Byzantine artists fled to Serbia. Their influence is seen in the building of the church Our Lady of Ljeviš and many other buildings, including the Gračanica Monastery. The monastery Visoki Dečani was built between the years 1330 and 1350. Unlike other Serbian monasteries, this one was built in the Romantic style, under the authority of grand master Vita from Kotor. On the frescoes of this monastery, there are some 1,000 portraits depicting the most important episodes from the New Testament.
Another style of Architecture that followed in Serbia was that of the end of the 14th century, near the river Morava (Moravic school). A characteristic of this style was the wealthy decoration of the frontal church-walls.
During the time of Turkish occupation, Serbian art was virtually non-existent, with the exception of several Serbian artists who lived in the lands ruled by the Habsburg Monarchy. Traditional Serbian art showed some Baroque influences at the end of the 18th century as shown in the works of Nikola Nešković, Teodor Kračun, Zaharije Orfelin and Jakov Orfelin. Serbian painting showed the influence of Biedermeier, Neoclassicism, Romanticism and Realism during the 19th century. Some of the most prominent Serbian artists made their works at that time. Anastas Jovanović was a pioneering photographer in Serbia taking photographs of many leading Serbian citizens. Some of the most important Serbian painters of the 20th century were Paja Jovanović, Milan Konjović, Marko Čelebonović, Petar Lubarda, Uroš Predić, Milo Milunović, Vladimir Veličković, Mića Popović, Sava Šumanović and Milena Pavlović-Barili.
Literature
Main article: Serbian literature
The start of Serbian literacy relates to the activity of the brothers Cyril and Methodius in the Balkans. Monuments of Serbian literacy from the early 11th century can be found, written in Glagolitic. Starting in the 12th century, books were written in Cyrillic. From this epoch, the oldest Serbian Cyrillic book editorial are the Miroslav Gospels. The Miroslav Gospels are considered to be the oldest book of Serbian medieval history. Notable medieval authors include Sava Nemanjić, Nun Jefimija, Stefan Lazarević, Constantine of Kostenets and others.
Baroque trends in Serbian literature emerged in the late 17th century. Notable Baroque-influenced authors were Andrija Zmajević, Gavril Stefanović Venclović, Jovan Rajić, Zaharije Orfelin and others. Dositej Obradović was the most prominent figure of the Age of Enlightenment, while the most notable Classicist writer was Jovan Sterija Popović, although his works also contained elements of Romanticism.
In the era of national revival, in the first half of the 19th century, Vuk Stefanović Karadžić collected Serbian folk literature, reformed the Serbian language and spelling and translated the New Testament into Serbian. The first half of the 19th century was dominated by Romanticism, with Branko Radičević, Laza Kostić, Đura Jakšić and Jovan Jovanović Zmaj being the most notable representatives, while the second half of the century was marked by Realist writers such as Milovan Glišić, Laza Lazarević, Simo Matavulj, Stevan Sremac, Branislav Nušić, Radoje Domanović and Borisav Stanković. The 20th century was dominated by the prose writers Isidora Sekulić, Miloš Crnjanski, Ivo Andrić, Branko Ćopić, Meša Selimović, Borislav Pekić, Dobrica Ćosić, Danilo Kiš, Aleksandar Tišma and Milorad Pavić. There were also many valuable poetic achievements, as seen by the writings of Milan Rakić, Jovan Dučić, Desanka Maksimović, Miodrag Pavlović, Vladislav Petković Dis, Branko Miljković, Vasko Popa, and others.
In the last decade of the 20th century and the first decade of the 21st century, the most popular Serbian writers were David Albahari, Milorad Pavić, Momo Kapor, Goran Petrović, Svetlana Velmar-Janković, Svetislav Basara and Zoran Živković.
Music
Main article: Music of SerbiaSerbia has a long tradition in music. Traditional Serbian music include various kinds of bagpipes, flutes, horns, trumpets, lutes, psalteries, drums and cymbals. The kolo is the traditional collective folk dance, which has a number of varieties throughout the regions. The most popular are those from Užice and Morava region. Sung epic poetry has been an integral part of Serbian and Balkan music for centuries. In the highlands of Serbia these long poems are typically accompanied on a one-string fiddle called the gusle, and concern themselves with themes from history and mythology. There are records of gusle (гоусли) being played at the court of the 13th-century Serbian King Stefan Nemanjić.

Composer and musicologist Stevan Stojanović Mokranjac is considered one of the most important founders of modern Serbian music. The Serbian composers Petar Konjović, Stevan Hristić and Miloje Milojević, all born in the 1880s, were the most eminent composers of their generation. They maintained the national expression and modernized the romanticism into the direction of impressionism. The best-known composers born around 1910 studied in Europe, mostly in Prague; Ljubica Marić, Stanojlo Rajicić, Milan Ristić who took influence from Schoenberg, Hindemith and Haba. Other famous classical Serbian composers include Isidor Bajić, Stanislav Binički and Josif Marinković.
The former Yugoslav rock scene, which Serbian rock scene was a part of during the 1960s, 1970s and 1980s, was well developed and covered in the media, which included numerous magazines, radio and TV shows. With the breakout of Yugoslav wars, former Yugoslav rock scene ceased to exist. During the 1990s popularity of rock music declined in Serbia, and although several major mainstream acts managed to sustain their popularity, an underground and independent music scene developed. The first decade of the 21st century saw the revival of the mainstream scene. The most notable Serbian rock acts include Bajaga i Instruktori, Đorđe Balašević, Disciplina Kičme, Ekatarina Velika, Električni Orgazam, Galija, Idoli, Korni Grupa, Partibrejkers, Pekinška Patka, Rambo Amadeus, Riblja Čorba, Smak, Šarlo Akrobata, YU grupa, Van Gogh, and others.

Later, many pop music performers rosed to fame. Željko Joksimović won second place at the 2004 Eurovision Song Contest and Marija Šerifović managed to win the 2007 Eurovision Song Contest with the song "Molitva", and Serbia was the host of the 2008 edition of the Contest.
The so called "novokomponovana muzika" (newly composed music) can be seen as a result of the urbanization of folk music. In its early days, it had a professional approach to performance, used accordion and clarinet and typically included love songs or other simple lyrics. At a later stage, severak popular performers used more influences from pop music, oriental music, and other genres, which led to the emergence of turbo-folk.
Turbo-folk music emerged during the breakup of Yugoslavia. Turbo-folk used Serbian folk music and "novokomponovana" as the basis, and added influences from rock, pop and electronic dance music. In the first decade of the 21st century turbo-folk featured even more pop music elements, and some of the performers were labeled as pop-folk. The most notable Turbo-folk artists include Ceca and Jelena Karleuša.
Balkan Brass, or "truba" (trumpet) is a popular genre that originated during the First Serbian Uprising (1804–1813) with military marching bands that transposed Serbian folk music. Guča trumpet festival is one of the most popular and biggest music festivals in Serbia, with over 300,000 visitors annually.
Cuisine
Main article: Serbian cuisineSerbian cuisine is a heterogeneous cuisine, sharing characteristics of the Balkans (especially former Yugoslavia), the Mediterranean (especially Greek), Turkish, and Central European (especially Austrian and Hungarian) cuisines. Each region has its own peculiarities and variations. Among traditional Serbian foods are ćevapčići, pljeskavica, sarma, pasulj, burek, gibanica, ajvar. The national drink is Slivovitz (šljivovica).
Sports
Main article: Sport in Serbia


Sports in Serbia revolve mostly around team sports: football, basketball, volleyball, handball, water polo, and, most recently, tennis.
The two main football clubs in Serbia are Red Star Belgrade and FK Partizan, both from the capital, Belgrade. Red Star is the only Serbian and former Yugoslav club that has won a UEFA competition, winning the 1991 European Cup in Bari, Italy. The same year in Tokyo, Japan, the club won the Intercontinental Cup. Partizan is the first Eastern European football club which played in a European Cup final (in 1966). The matches between the two rival clubs are known as the "Eternal Derby". The Serbia's national football team made their first appearance during the qualifying rounds for Euro 2008 although they did not qualify for the competition. During the qualifying tournament for the 2010 FIFA World Cup, Serbia came first in its group, ahead of France and consequently qualified directly for the championship. The Serbian SuperLiga is the highest professional league in the country. The 2010/2011 season champion was FK Partizan, followed by Red Star Belgrade in second place, and FK Vojvodina in third.
Serbia is one of the traditional powerhouses of world basketball, winning various FIBA World Championships, multiple EuroBasket and Olympic medals (albeit as FR Yugoslavia). Serbia's national basketball team is the successor to the successful Yugoslavia national basketball team. Serbia has won FIBA world championships five times and won second place in the 2009 European championship. Serbian basketball players have made a deep impact in history of basketball, having success both in the top leagues of Europe and in the NBA. Serbs that have played in the NBA include: Vlade Divac (FIBA Hall of Fame), Predrag Stojaković, Željko Rebrača, Marko Jarić, Nenad Krstić, Darko Miličić, Vladimir Radmanović, and Serbian American Pete Maravich. In the domestic scene, the Basketball League of Serbia is the highest professional basketball league in Serbia. For the eighth consecutive year, KK Partizan is the reigning champion of the league, followed by rivals KK Crvena Zvezda. KK Partizan was the European champion in 1992 with the curiosity of winning the title, although playing all but one of the games (crucial quarter-final game vs. Knorr) away from home; FIBA decided not to allow teams from Former Yugoslavia play their home games at their home venues, because of the open hostilities in the region. KK Partizan was not allowed to defend their title in the 1992–1993 season, because of U.N.-imposed sanctions.
Serbian tennis players Novak Djoković, Ana Ivanović, Jelena Janković, Nenad Zimonjić, Janko Tipsarević and Viktor Troicki are very successful and their success has led to a popularisation of tennis in Serbia. Djoković, in particular, is very popular and is currently the # 1 tennis player in the ATP Rankings. He was also the founder of the first ATP tennis tournament in the country, the Serbia Open. Other well-known players are Serbian-born players are Monika Seles, Jelena Dokić and Slobodan Živojinović. The Serbia men national team won the 2010 Davis Cup.
Serbia and Italy were host nations at 2005 Men's European Volleyball Championship. The Serbia men's national volleyball team is the direct descendant of Yugoslavia men's national volleyball team. Serbia won the bronze medal at the 2007 Men's European Volleyball Championship held in Moscow, Russia.
The Serbia men's national water polo team recently won the 2009 World Championships in Rome, Italy. Serbia has won four European Championships (2001, 2003, 2006 and 2012), finished as runner-up in 2008, won two World Championships (2005 and 2009) and won bronze medal at 2008 Summer Olympics held in Beijing.
Milorad Čavić and Nađa Higl in swimming, Olivera Jevtić, Dragutin Topić in athletics, Aleksandar Karakašević in table tennis, Jasna Šekarić in shooting are also very popular athletes in Serbia.
See also
Template:Misplaced Pages books
References
- ^ "Official Results of Serbian Census 2003 – Population" (PDF) (in Serbian). p. 13.
- ^ "First Official Results of 2011 Census in Serbia". Statistical Office of Serbia. 2011. Retrieved 16 November 2011.
- ^ "Serbia". International Monetary Fund. Retrieved 20 April 2012. Cite error: The named reference "imf2" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- "Human Development Report 2011" (PDF). United Nations. 2011. Retrieved 8 November 2011.
- "The Serbian Revolution and the Serbian State". Steven W. Sowards, Michigan State University Libraries. 11 June 2009. Retrieved 28 April 2010.
- ^ "EU leaders grant Serbia candidate status". BBC News. 1 March 2012. Retrieved 2 March 2012.
- http://www.becei.org/evropski%20forumi%20u%20pdf-u/Evropski_forum_No._4,_2008.pdf
- "Projekat Rastko - Luzica / Project Rastko - Lusatia". Rastko.rs. Retrieved 19 November 2011.
- J.P. Mallory and D.Q. Adams, "Protect", The Encyclopedia of Indo-European Culture (London: Fitzroy and Dearborn, 1997).
- Nikola Tasić (1990). "Vinča and its Culture". In Vladislav Popović (ed.). Vinča: Centre of the Neolithic culture of the Danubian region. Belgrade. Retrieved 28 October 2006.
{{cite book}}: External link in|chapterurl=|chapterurl=ignored (|chapter-url=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|other=ignored (|others=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - "History (Ancient Period)". Official website. Retrieved 10 July 2007.
- "Kale – Krševica". Kale-krsevica.com. Retrieved 10 July 2011.
- Andrić, Stanko (2002). "Southern Pannonia during the age of the Great Migrations". Scrinia Slavonica. Slavonski Brod, Croatia: Croatian Historical Institute - Department of History of Slavonia, Srijem and Baranja. ISSN 1332-4853. Retrieved 27 February 2012.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - "Culture in Serbia – Tourism in Serbia, Culture travel to Serbia". VisitSerbia.org. Retrieved 28 April 2010.
- "Cyril Mango. Byzantium: The Empire of New Rome. Scribner's, 1980". Fordham.edu. Retrieved 14 November 2010.
- Ćorović 2001, Prvi Period – III
- Ćorović 2001, Drugi Period – II; Eginhartus de vita et gestis Caroli Magni, p. 192: footnote J10
- Ćorović 2001, Drugi Period – IV;
- Ćorović 2001, Drugi Period – V;
- ^ Ćorović 2001, Drugi Period – VII;
- Ćorović 2001, Drugi Period – VIII
- Ćorović 2001, Treći Period – I;
- Ćorović 2001, Treći Period – II;
- Noel Malcolm, Kosovo: a short history, London : Macmillan, 1998
- Anscombe, Frederick F. (2006). The Ottoman empire in recent international politics - II: the case of Kosovo. The International History Review 28 (4) 758-793.
- "Crucified Kosovo: Ljubisa Folic: Crucified Heritage". Пројекат Растко: Библиотека српске културе; Proјekat Rastko: Biblioteka srpske kulture. Retrieved 28 April 2010.
- P. Kitromilides, ‘“Imagined Communities” and the Origins of the National Question in the Balkans’, in P. Kitromilides, Enlightenment, National- ism, Orthodoxy: Studies in the Culture and Political Thought of South-Eastern Europe (Aldershot, 1994).
- "CEEOL Balcanica, Issue XXXVI /2005". Central and Eastern European Online Library. Retrieved 28 April 2010.
- Rados Ljusic, Knezevina Srbija
- ^ Misha Glenny. "The Balkans Nationalism, War and the Great Powers, 1804–1999". The New York Times. Retrieved 6 April 2010.
- Royal Family. "200 godina ustanka". Royalfamily.org. Retrieved 28 April 2010.
- Gordana Stokić (2003). "Bibliotekarstvo i menadžment: Moguća paralela" (PDF) (in Serbian). Narodna biblioteka Srbije.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - Ćorović 2001, Novo Doba - VIII
- L. S. Stavrianos, The Balkans since 1453 (London: Hurst and Co., 2000), pp. 248–50
- Čedomir Antić (1998). "The First Serbian Uprising". The Royal Family of Serbia.
- "The Balkan Wars and the Partition of Macedonia". Historyofmacedonia.org. Retrieved 28 April 2010.
- Balkanski ratovi Template:Sr icon
- "Typhus fever on the Eastern front of World War I". Montana State University.
- ^ "The Balkan Wars and World War I". Library of Congress Country Studies.
- "Daily Survey". Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Serbia. 23 August 2004.
- "Arhiv Srbije – osnovan 1900. godine" (in Serbian).
- Saturday, 22 August 2009 Michael Duffy (22 August 2009). "First World War.com – Primary Documents – Vasil Radoslavov on Bulgaria's Entry into the War, 11 October 1915". firstworldwar.com. Retrieved 28 April 2010.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - Највећа српска победа: Фронт који за савезнике није био битан Template:Sr icon
- Saturday, 22 August 2009 Matt Simpson (22 August 2009). "The Minor Powers During World War I – Serbia". firstworldwar.com. Retrieved 28 April 2010.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - "Serbian army, August 1914". Vojska.net. Retrieved 28 April 2010.
- "Tema nedelje: Najveća srpska pobeda: Sudnji rat: POLITIKA". Politika. 14 September 2008. Retrieved 28 April 2010.
- Тема недеље : Највећа српска победа : Сви српски тријумфи : ПОЛИТИКА Template:Sr icon
- Loti, Pierre (30 June 1918). "Fourth of Serbia's population dead". Pqasb.pqarchiver.com. Retrieved 28 April 2010.
- "Asserts Serbians face extinction". New York Times. 5 April 1918. Retrieved 14 November 2010.
- The Balkans since 1453. p. 624.
- "Jewish Heritage Europe – Serbia 2 – Jewish Heritage in Belgrade". Jewish Heritage Europe. Retrieved 28 April 2010.
- "Ustaša". Britannica OnlineEncyclopedia. Britannica.com. Retrieved 28 April 2010.
- "Jasenovac". United States Holocaust Memorial Museum. Retrieved 4 January 2010.
- Jasenovac Jewish Virtual Library. Retrieved 10 August 2008.
- "Yad Vashem" (PDF). Retrieved 10 July 2011.
- "Дан сећања на жртве усташког геноцида". Tanjug. Retrieved 20 April 2012.
- Hitler's new disorder: the Second ... – Google Books. Google Books. Retrieved 16 May 2010.
- Kočović, Žrtve II sv. rata, 65–79
- Žerjavić, Gubici stanovništva, 168
- Zundhauzen, Istorija Srbije, 370
- Kočović, Sahrana jednog mita: Žrtve II sv. rata u Jugoslaviji, 2005
- PM. "Storia del movimento partigiano bulgaro (1941–1944)". Bulgaria – Italia. Retrieved 28 April 2010.
- "Izmedju Srpa i Cekica". Scribd. 18 November 2009. Retrieved 28 April 2010.
- "RTS: Komisija za zločine iz Drugog svetskog rata" (in Template:Sr icon). RTS. 17 September 2009. Retrieved 16 May 2010.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - "I Srbija počinje s iskapanjem masovnih grobnica". Dalje.com. Retrieved 16 May 2010.
- "NIN/Sudbina pobeđenih". НИН. 25 October 2001. Retrieved 16 May 2010.
- Za i protiv ustavotvorne skupstine Srbije, Molnar Aleksandar
- ^ Melissa Katherine Bokovoy, Jill A. Irvine, Carol S. Lilly. State-society relations in Yugoslavia, 1945–1992. Scranton, Pennsylvania, USA: Palgrave Macmillan, 1997. p. 295.
- Dragnich, Alex N. (1983). The First Yugoslavia: Search for a Viable Political System. Hoover Institution Press. pp. 3–11. ISBN 0-8179-7841-0.
- ^ Melissa Katherine Bokovoy, Jill A. Irvine, Carol S. Lilly. State-society relations in Yugoslavia, 1945–1992. Scranton, Pennsylvania, USA: Palgrave Macmillan, 1997. p. 296.
- Melissa Katherine Bokovoy, Jill A. Irvine, Carol S. Lilly. State-society relations in Yugoslavia, 1945–1992. Scranton, Pennsylvania, USA: Palgrave Macmillan, 1997. p. 301.
- Branka Magaš (1993). The Destruction of Yugoslavia: tracking the break-up 1980-92 (pp 165-170). Verso. ISBN 978-0-86091-593-5.
- Engelberg, Stephen (16 January 1992). "Breakup of Yugoslavia Leaves Slovenia Secure, Croatia Shaky". The New York Times. Retrieved 6 April 2010.
- Resolution 757 (1992), UN Security Council 3082nd Meeting, 30 May 1992, see United Nations Security Council Resolution 757
- "Political Propaganda and the Plan to Create a "State for all Serbs"" (PDF). Retrieved 14 November 2010.
- Wide Angle, Milosevic and the Media. "Part 3: Dictatorship on the Airwaves." PBS. Quotation from film: "...the things that happened at state TV, warmongering, things we can admit to now: false information, biased reporting. That went directly from Milošević to the head of TV".
- "Forging War: The Media in Serbia, Croatia and Bosnia-Herzegovina". International Centre Against Censorship. Article 19, May 1994. Avon, United Kingdom: The Bath Press. p. 59
- Traynor, Ian (6 June 2005). "Young democracy guerrillas join forces". The Guardian: p. 16.
{{cite journal}}:|page=has extra text (help) Available at http://www.mjaft.org/pdf/the_guardians_activism_festival.pdf - Kirkpatrick, David D.; Sanger, David E. (13 February 2011). "Egyptians and Tunisians Collaborated to Shake Arab History". The New York Times.
- "Stephen Zunes: Serbia: 10 Years Later". Huffingtonpost.com. 18 July 2009. Retrieved 19 November 2011.
- Ivan Vejvoda, ‘Civil Society versus Slobodan Milošević: Serbia 1991–2000’, in Adam Roberts and Timothy Garton Ash (eds.), Civil Resistance and Power Politics: The Experience of Non-violent Action from Gandhi to the Present. Oxford & New York: Oxford University Press, 2009, pp. 295–316. ISBN 978-0-19-955201-6.
- "Montenegro gets Serb recognition". BBC News. 15 June 2006.
- "NATO offers "intensified dialogue" to Serbia". B92. 3 April 2008. Retrieved 28 April 2010.
- "European Union wants Serbia to join". UPI.com. 26 December 2009. Retrieved 28 April 2010.
- "Serbia submits EU membership bid". BBC News. 23 December 2009. Retrieved 6 April 2010.
- "Powered by Google Docs". Google. Retrieved 28 April 2010.
- "About the Carpathians – Carpathian Heritage Society". Carpathian Heritage Society. Retrieved 28 April 2010.
- Peel, M. C., Finlayson, B. L. and McMahon, T. A. (2007.). "Updated world map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification" (PDF). Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. (11): 1641.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|year=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: year (link) - "Serbia :: Climate". Encyclopædia Britannica Online. 2007. pp. 5 of 71.
- Radovanović, M and Dučić, V, 2002, Variability of Climate in Serbia in the Second Half of the 20th century, EGS XXVII General Assembly, Nice, 21 to 26 April 2002, abstract #2283, 27:2283–, provided by the Smithsonian / NASA Astrophysics Data System
- "Basic Climate Characteristics for the Territory of Serbia". Hydrometeorological Service of Serbia.
- "Past temperature extremes since the beginning of the measurement" (PDF). Hydrometeorological Service of Serbia. Retrieved 5 November 2010.
- "Dragin obrazlozio predloge zakona u oblasti poljoprivrede". Vlada Srbije. 2005.
- "U Srbiji do 2010. godine 10% teritorije nacionalni parkovi". Poslovni Magazin – Business Surfer. Retrieved 28 April 2010.
- "Serbia recycling 15% of waste". Blic Online. Retrieved 28 April 2010.
- "Tomislav Nikolic". Retrieved 21 May 2012.
- http://media.popis2011.stat.rs/2011/prvi_rezultati.pdf
- ^ http://www.srbija.gov.rs/pages/article.php?id=20617
- ^ Law on Territorial Organization and Local Self-Government, Parliament of Serbia Template:Sr icon
- Government of Serbia: Districts of Serbia
- http://www.mfa.gov.rs/Worldframe.htm
- Diplomatic Missions in Serbia
- Tadić on Serbia's "four pillars of diplomacy"
- "Rift Emerges at the United Nations Over Kosovo". New York Sun. 19 February 2008.
- Archived (Date missing) at ekonomskitim.sr.gov.yu (Error: unknown archive URL)
- UNMIK Rule of law
- After a police protocol, EULEX and Serbian officials will intensify preparations for customs and judiciary cooperation
- "Serbia applies for EU membership". Swedish Presidency of the European Union. Archived from the original on 27 January 2010. Retrieved 25 December 2009.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - "EU unfreezes trade agreement with Serbia". Archived from the original on 8 January 2010. Retrieved 25 December 2009.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - "EU scraps visas for three Balkan states". BBC. 1 December 2009. Archived from the original on 4 December 2009. Retrieved 25 December 2009.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - "Serbia's last war crimes fugitive arrested - Europe". Al Jazeera English. Retrieved 2 March 2012.
- http://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/world/europe/EU-grants-Serbia-candidate-status/articleshow/12108156.cms
- "Cilj - Srbija u EU 2014" (in Serbian). Blic. Archived from the original on 25 December 2009. Retrieved 25 December 2009.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - "Agenda 2014: A fresh roadmap for Balkan accession to the EU". Ministry for Foreign Affairs (Greece). Retrieved 25 December 2009.
- aeroflight.co.uk
- Ministerio de Asuntos Exteriores y Cooperación. Monografía de Serbia. Consultado el 10 de noviembre de 2009.
- Nation Master. Military statistics Serbia and Montenegro. Consultado el 10 de noviembre de 2009
- Defense Ministry press conference
- Serbia's defence budget - Janes.com
- Sentinel Security Assessment
- http://www.politika.rs/rubrike/Drustvo/Vojska-Srbije-od-sutra-i-zvanicno-profesionalna.lt.html
- Amnistía Internacional. No hay justicia para las víctimas de los bombardeos de la OTAN. Consultado el 10 de noviembre de 2009.
- Bloomberg - Serbian exports
- http://www.business-dialogue.eu/vesti/1614-srbija-ponovo-izvozna-vojna-sila.html
- http://www.glas-javnosti.rs/clanak/ekonomija/glas-javnosti-11-01-2011/srpska-vojna-industrija-u-usponu
- http://www.blic.rs/Vesti/Drustvo/228348/Povratak-vojne-industrije-Srbije-na-svetsku-scenu
- "Latest Indicators". Statistical Office of Serbia. 1 January 2009.
- "CIA - The World Factbook". Cia.gov. Retrieved 19 November 2011.
- Chinese Migrants Use Serbia as Gate to Europe. ABC News. 13 July 2010.
- A young Roma woman in Serbia overcomes poverty and discrimination. UNICEF Serbia.
- According to the 1921 census, the German community was the largest non-Slavic ethnic group in Yugoslavia (505,790, or 4.22% of the population). (PDF)
- Tanjug (22 October 2007). "Serbia's refugee population largest in Europe". B92.
- "Serbia seeks to fill the 90's brain-drainage gap". EMG.rs. 5 September 2008.
- "Survey S&M 1/2003". Yugoslav Survey.
- "Country Comparison : Population growth rate". The World Factbook, CIA. 2002.
- "Statistical office of Serbia" (in Serbian).
- SIEPA - Why Serbia?
- "U Srbiji 760.000 nezaposlenih, male šanse za nova radna mesta". Blic. Retrieved 9 February 2012.
- "Upper-middle-income economies". The World Bank.
- "GDP per capita in PPS" (PDF). Eurostat. Retrieved 13 December 2011.
- SIEPA - Liberalized trade
- Borka Tomic (13 April 2006). "Rebranding Serbia". Invest in Serbia.
- "Serbia maintains rating, recovery slower". B92. 3 August 2010. Retrieved 15 May 2011.
- "Đerdap III". Večernje novosti. 25 January 2009. Retrieved 28 April 2010.
- "Registrovana vozila u Srbiji 2009/2010" (PDF) (in Serbian). Statistical Office Serbia. 2010.
- "Investing in Serbia: Modern Infrastructure, Transport". SIEPA. Retrieved 28 April 2010.
- "Business News". Balkans.com. Retrieved 28 April 2010.
- "U Srbiji baš zvoni" (in Serbian). Večernje novosti. 15 May 2007.
- "У Србији све више рачунара?". Politika. Retrieved 28 April 2010.
- http://webrzs.stat.gov.rs/WebSite/Public/PageView.aspx?pKey=2
- CIA World Handbook, Country Comparison: Internet users
- "Europe Internet Stats – Population Statistics". Internetworldstats.com. 12 April 2010. Retrieved 28 April 2010.
- "Davolja Varos, Rock Formation". New7Wonders. 7 July 2007.
- "Pilgrimage of Saint Sava". Info Hub.
- U.S. patent 462,418
- U.S. patent 568,177. The patent office classifies the patent as superconductivity technology, specifically "Dynamoelectric; liquid coolant" (310/54) and "Specific Identifiable Device, Circuit, or System; Superconductive (e.g., cryogenic, etc.) device" (327/527)
- Uth, Robert (12 December 2000). "Tesla coil". Tesla: Master of Lightning. PBS.org. Retrieved 20 May 2008.
- "Details of SI units". sizes.com. 1 July 2011. Retrieved 4 October 2011.
- Pupin, M, Art of Reducing Attenuation of Electrical Waves and Apparatus Therefor, US patent 0 652 230, filed 14 December 1899, issued 19 June 1900.
- Adenosine Sleep Theory: How I postulated it, Neurological Research, Mar 2005 by Radulovacki, Miodrag
- Rushforth, K. (1999). Trees of Britain and Europe. Collins ISBN 0-00-220013-9.
- Restauriran najstariji srpski igrani film
- http://www.netsrbija.net/srpska-kultura-film-i-kinematografija.html
- Volim te Srbijo, zapisi svetskih autora o Srbiji i Srbima kroz vekove, Ikea, 1996. godine, autor nepoznat.
- http://www.rastko.rs/isk/isk_17.html
- http://www.riznicasrpska.net/muzika/index.php?topic=60.0
- "Sabor trubača GUČA". www.guca.rs. 2 September 2007. Retrieved 14 November 2010.
Sources
- Ćorović, Vladimir (1941). "Iсторија српског народа (Istorija srpskog naroda)". Internet, 2001) (in Serbian). Пројекат Растко: Библиотека српске културе; Proјekat Rastko: Biblioteka srpske kulture.
- Ćirković, Sima M. (2004). The Serbs. Wiley-Blackwell. ISBN 0-631-20471-7.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Fine, John Van Antwerp (1991). The Early Medieval Balkans: A Critical Survey from the Sixth to the Late Twelfth Century. Michigan: The University of Michigan Press. ISBN 0-472-08149-7.
- Fine, John Van Antwerp (1991), The Early Medieval Balkans: A Critical Survey from the Sixth to the Late Twelfth Century, University of Michigan Press, ISBN 978-0-472-08149-3

This image is available from the United States Library of Congress Prints and Photographs Division under the digital ID {{{id}}}
This tag does not indicate the copyright status of the attached work. A normal copyright tag is still required. See Misplaced Pages:Copyrights for more information.
 This article incorporates public domain material from The World Factbook. CIA.
This article incorporates public domain material from The World Factbook. CIA.
External links
- Official website
- National tourist organisation of Serbia
- Template:Dmoz
 Wikimedia Atlas of Serbia
Wikimedia Atlas of Serbia- Template:Wikitravel
 Geographic data related to Serbia at OpenStreetMap
Geographic data related to Serbia at OpenStreetMap- Key Development Forecasts for Serbia from International Futures
- "Serbia". The World Factbook (2025 ed.). Central Intelligence Agency.
| Serbia articles | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| History |
|  | |||||||||
| Geography | |||||||||||
| Politics |
| ||||||||||
| Economy |
| ||||||||||
| Society |
| ||||||||||
| International organizations | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||