| Revision as of 19:48, 20 July 2012 view sourceLifebonzza (talk | contribs)5,720 edits c/e← Previous edit | Revision as of 21:53, 20 July 2012 view source Lifebonzza (talk | contribs)5,720 edits →Early Pallavas: c/eNext edit → | ||
| Line 54: | Line 54: | ||
| ==Early Pallavas== | ==Early Pallavas== | ||
| {{Expand section|date=July 2012}} | {{Expand section|date=July 2012}} | ||
| Early Pallava script charters in Prakrit dated on paleographic grounds to 250-350 reveal that a dynasty named ''Pallava'' was active in the Tondai-Aruva region of ] in the latter stages of floruit of the Sangam period's ]. One prominent dynastic line of this clan consolidated power at the city of ] following the eclipse of the ] of ] in 220, whom the Pallavas had served as subordinates, while related family lines located around the country grew. |
Early Pallava script charters in Prakrit dated on paleographic grounds to 250-350 reveal that a dynasty named ''Pallava'' was active in the Tondai-Aruva region of ] in the latter stages of floruit of the Sangam period's ]. One prominent dynastic line of this clan consolidated power at the city of ] following the eclipse of the ] of ] in 220, whom the Pallavas had served as subordinates, while related family lines located around the country grew. In the inscriptions of the medieval ], descended from the Sangam Chola emperor ] who ruled in 180, the monarch's subordinate king Trinetra Pallava lost his third eye for refusing to carry out orders to construct the floodbanks of the ]. An ancient ]-] alliance at ] and succeeding Pallava-Naka liaisons marked the dynasty's formative years. Of this lineage, ], a younger contemporary of King ] became an independent ruler of ''Tondaimandalam'' around 200, stretching his Tondaiyar-Thiraiyar domain passed the ], ] whose construction he consecrated.<ref name="Gangoly">{{cite book|author=Ordhendra Coomar Gangoly|title=The art of the Pallavas, Volume 2 of Indian Sculpture Series|page=2|publisher=G. Wittenborn, 1957}}</ref> Centering their authority in Tondai Nadu, Ilandiraiyan's descendants gained prominence as one Pallava line ruling Kanchi from 220.<ref>The journal of the Numismatic Society of India, Volume 51, p.109</ref><ref>Alī Jāvīd and Tabassum Javeed. (2008). World heritage monuments and related edifices in India, p.107 </ref> <ref>Vakataka - Gupta Age Circa 200-550 A.D. | ||
| By R. C. Majumdar, A. S. Altekar. pp. 222-223</ref> | |||
| Under Skandavarman I (315), the greatest of the early Pallava rulers, the state extended its dominions in the early fourth century north of Aruva Nadu from the South ] to the northern Telugu districts of ] and the ], while expanding west passed the city of ]. He was crowned with the epithet ''Yuvamaharaja Shivaskandavarman'', a ruler with many subordinate chiefs who conducted several horse sacrifices. One of his inscriptions mentions the ''Vallave'' (herdsmen) and ''Govallave'' (cow herdsmen) of Pallava society. ] flourished as a great Buddhist learning centre under Pallava rule, while maritime commercial trade and cultural exchange grew. Pallava citizens settled in ] and ]. Shivaskandavarman was succeeded by Vijayaskandavarman of Kanchi. The early Pallava state grew to rule over several areas of the modern states of Andhra Pradesh and ]. | |||
| ==Middle Pallavas== | ==Middle Pallavas== | ||
Revision as of 21:53, 20 July 2012
"Pallava" redirects here. For the Pallava script, see Grantha alphabet.| Pallava dynastyபல்லவர் | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2nd -–9th century CE | |||||||||||
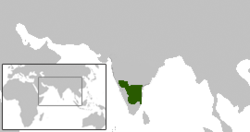 Pallava territories during Narasimhavarman I c. 645 CE. This includes the Chalukya territories occupied by the Pallavas. Pallava territories during Narasimhavarman I c. 645 CE. This includes the Chalukya territories occupied by the Pallavas. | |||||||||||
| Status | Kingdom | ||||||||||
| Capital | Kanchi | ||||||||||
| Common languages | Tamil, Sanskrit, Telugu | ||||||||||
| Religion | Hinduism | ||||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||||
| Historical era | Ancient-Middle Ages | ||||||||||
| • Established | 2nd - | ||||||||||
| • Disestablished | 9th century CE | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Today part of | |||||||||||
Pallava dynasty (Tamil: பல்லவர்), also the Tondaiyar dynasty of Tondai Nadu, was a ruling dynasty of South India from the second to the ninth century CE. Establishing themselves as a rising Tamil power in the region with the metropolis Kanchipuram of Tamil Nadu as their capital, the Pallavas emerged after the Three Crowned Kings to become one of the major states of the post-Sangam period before the rise of the medieval Chola empire. Four family dynastic lines of the Pallavas have been traced to at least the second century of the common era. An ancient Chola-Nāka alliance at Nainativu and succeeding Pallava-Naka liaisons marked the dynasty's formative years. Of this lineage, Ilandiraiyan, a contemporary of King Karikala Chola became an independent ruler of Tondaimandalam between 100-250, stretching his domain passed the Tirumala Venkateswara Temple, Tirupati whose construction he consecrated. Centering their authority in Tondai Nadu, Ilandiraiyan's descendants gained prominence after the eclipse of the Satavahana dynasty of Andhra Pradesh in 220.
The rule of the Pallavas was marked by hostilities, upheaval and benign rule in Tamilakkam, as they sought to expand their country passed the northern frontiers of Aruva Nadu. Under Skandavarman I, the Pallavas extended their dominions north to the Krishna River and west to the city of Bellary, while King Vishnugopa attacked and weakened the early Chola state around Kanchi before facing defeat in 365. Emperor Simhavishnu joined Pandyan Kadungon in ending the Kalabhra Interregnum by 550, reestablishing Pallava maritime power and consolidating Tamil rule across Asia. Narasimhavarman I oversaw the long struggle for Pallava supremacy in peninsular India before their dominions eventually passed to the Chola kings in 880. The dynasty's descendants established the Kadava kingdom in the thirteenth century.
Kanchipuram, the Pallava imperial capital, developed into a city of temples to many faiths under their rule. Literary, painting and music activity spread with religious learning, where the Bhakti movement of the Vaishnava Alvars and the Saiva Nayanars flourished under Pallava royal patronage alongside Tamil Jainism, Buddhism and Native Dravidian religion. The Pallavas were largely Brahmanical Hindus, constructing Kailasanathar stone temples and sculptures, the Ekambareswarar Temple and Kamakshi Amman Temple in Kanchi. Becoming a major military, economic and cultural power in Asia, the dynasty extended their artistic prowess to the temples of Koneswaram, Ketheeswaram, Nalanda Gedige, Thiriyai and Tenavarai. Founding the school of Zen Buddhism, Pallava prince Bodhidarma transmitted his knowledge of the religion and martial arts techniques of Silambam to Silat and Kung-Fu at the Shaolin Monastery in the 5th century, attracting Chinese Buddhist pilgrims including Xuanzang to Kanchipuram in 642 to find a city of 80 Hindu shrines, 100 monasteries and 10000 monks under Narasimhavarman I. As trade with China increased, Rajasimha built the "Chinese Pagoda" of Nagapattinam to please their diplomats, merchants and monks at the Pallava court.
The Pallavas joined the Chola Dynasty in settling and asserting commercial influence in Burma, Thailand, Malaysia and Indonesia by the fourth century. Pallava royal lineages were established in the old kingdom of Kedah of the Malay Peninsula under Rudravarman I, Chenla under Bhavavarman I, Champa under Bhadravarman I and the Kaundinya-Gunavarman line of the Funan in Cambodia, eventually their rule growing to form the Khmer Empire. These dynasties' unique Dravidian architectural style was introduced to build temples such as Angor Wat while Tamil cultural norms spread across the continent, their surviving epigraphic inscriptions recording domestic societal life and their pivotal role in Asian trade routes. Direct extensive contacts with these regions were maintained from the cultural and maritime commerce port city Mamallapuram, where Mahendravarman I and his son "Mahamalla" Narasimhavarman I built the Shore Temple of the Seven Pagodas of Mahabalipuram. In the far east, the Pallavas established the South Indian doctrines of Saivism, Vaishnavism and state languages written in Pallava Grantha and Vatteluttu alphabet characters; these Tamil scripts would give rise to multiple writing systems in Asia over the next millennium, one of the Pallava's most enduring legacies.
Origins
| This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to itadding to it or making an edit request. (July 2012) |
Early Pallavas
| This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to itadding to it or making an edit request. (July 2012) |
Early Pallava script charters in Prakrit dated on paleographic grounds to 250-350 reveal that a dynasty named Pallava was active in the Tondai-Aruva region of Tamil Nadu in the latter stages of floruit of the Sangam period's Three Crowned Kings. One prominent dynastic line of this clan consolidated power at the city of Kanchipuram following the eclipse of the Satavahana dynasty of Andhra Pradesh in 220, whom the Pallavas had served as subordinates, while related family lines located around the country grew. In the inscriptions of the medieval Telugu Cholas, descended from the Sangam Chola emperor Karikala Chola who ruled in 180, the monarch's subordinate king Trinetra Pallava lost his third eye for refusing to carry out orders to construct the floodbanks of the Kaveri River. An ancient Chola-Nāka alliance at Nainativu and succeeding Pallava-Naka liaisons marked the dynasty's formative years. Of this lineage, Ilandiraiyan, a younger contemporary of King Karikala Chola became an independent ruler of Tondaimandalam around 200, stretching his Tondaiyar-Thiraiyar domain passed the Tirumala Venkateswara Temple, Tirupati whose construction he consecrated. Centering their authority in Tondai Nadu, Ilandiraiyan's descendants gained prominence as one Pallava line ruling Kanchi from 220.
Under Skandavarman I (315), the greatest of the early Pallava rulers, the state extended its dominions in the early fourth century north of Aruva Nadu from the South Penner River to the northern Telugu districts of Godavari and the Krishna River, while expanding west passed the city of Bellary. He was crowned with the epithet Yuvamaharaja Shivaskandavarman, a ruler with many subordinate chiefs who conducted several horse sacrifices. One of his inscriptions mentions the Vallave (herdsmen) and Govallave (cow herdsmen) of Pallava society. Amravati flourished as a great Buddhist learning centre under Pallava rule, while maritime commercial trade and cultural exchange grew. Pallava citizens settled in Ceylon and Far East Asia. Shivaskandavarman was succeeded by Vijayaskandavarman of Kanchi. The early Pallava state grew to rule over several areas of the modern states of Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka.
Middle Pallavas
The Middle Pallavas ascension in the fourth century saw the dynasty adopt Sanskrit charters to chronicle its exploits, replacing Prakrit. The Cholas drove the Pallavas away from Kanchi in 340, during the reign of Vishnugopa. Records in Prakrit detail how King Vishnugopa attacked the early Chola state, but was attacked by Samudra Gupta of the Gupta Empire of North India. Taking advantage of the weakening of Pallava power, Mayurasharma a native of Talagunda launched parallel attacks on the state and eventually declared independence from Kanchi following a dispute with a Pallava guardsman, forming the Kadamba dynasty. He had travelled to Kanchi with his guru to pursue Vedic studies; his declaration of sovereign power centered on land south of the Malaprabha River. Hostilities between the Pallavas and Kadambas continued in the following decades. Twenty years later, in 360, Kumaravishnu I captured Kanchi from the Chola Dynasty as recorded in the Velurpalaiyam Plates. His son, Buddhavarman, is noted to have fought hard against the Cholas. Thereafter Kanchi developed into the capital of the imperial Pallava dynasty.
Simhavarman I's reign from 435 finds mention in the Sanskrit work Lokavibhaga. The poet Kalidasa visited his court, declaring the capital to be Nagareshu Kanchi, the world's "greatest city." Simhavarman I was succeeded by his son Skandavarman, mentioned in the Udeyindaram plates. Both kings are mentioned in the Penukonda plates of King Madhava III of the Western Ganga Dynasty as having successfully crowned two Ganga kings. The Pallavas re-captured Kanchi in the mid-6th century, possibly in the reign of Simhavishnu, the fourteenth king of the Pallava line, whom the Kasakudi plates describes as "the lion of the earth". Thereafter the Pallavas held on to Kanchi till the 9th century CE, with the last king having been Vijaya-Nripatungavarman. From sixth to eight centuries CE, the long struggle between the Pallavas and the Badami Chalukyas for the supremacy over the Tungabhadra-Krishna doab was the primary political activity in peninsular India. Chalukya ruler Pulikeshi II almost reached the Pallava capital at Kanchi, but peace was made between them by purchasing Vengi (Rayalaseema) to the Chalukyas. However Pulakeshin's second Pallava invasion ended in failure with Pallava ruler 'Vatapikonda' Narasimhavarman I occupying the Chalukya capital Vatapi. King Narasimhavarman also defeated the Pandyas, the Cholas and the Cheras. Later, in 740 CE, Badami Chalukya ruler Vikramaditya II ended the Pallava supremacy in southern India permanently and the Pallava dominions were passed to the Chola kings in 9th century CE.
Folklore traditions and later inscriptions in Telugu mention King Trilochana Pallava as the earliest Telugu king in history, a contemporary of the early Chola monarch Karikala Chola. Trilochana Pallava was punished by the Chola king for having disobeyed his orders; during his pre-Pallava reign, Karikala Chola conquered Oliya Nagas, the Aruvalar of Tondai, the Telugus and the Poduvar. His descendants formed the Telugu Cholas clan. A parallel unbroken line of contemporary Telugu Pallava kings, twenty-four of them in number and cousins to the Middle Pallava Kanchi line, appear to have ruled at a city north of Aruva Nadu following the reign of Vishnugopa in 340. Their capital was Dasanapura, which the Darsi Copper Plates state as their adhisthana. Dasanapura has been identified as Darsi, in Nellore district. The earliest inscriptions of these Pallavas were found in the districts of Bellary, Guntur and Nellore.
The royal custom of using a series of descriptive honorific titles, birudas, was particularly prevalent among the Pallavas. The birudas of Mahendravarman I are in Sanskrit, Tamil and Telugu. The Telugu birudas show that his involvement with the Andhra region continued to be strong at the time he was creating his cave-temples in the Tamil region. The suffix "Malla" was used by the Pallava rulers. Mahendravarman I used the biruda, Satrumalla, "a warrior who overthrows his enemies", and his grandson Paramesvara I was called Ekamalla "the sole warrior or wrestler". Pallavas kings, persumably exalted ones, were known by their title, Mahamalla or the "great wrestler".
| Part of a series on |
| History of Tamil Nadu |
|---|
 |
| Main |
| Sangam period |
| Medieval history |
| Categories |
| Part of a series on |
| Andhra Pradesh and Telangana |
|---|
 Chronology of the Telugu people, Andhra Pradesh, and Telangana history Chronology of the Telugu people, Andhra Pradesh, and Telangana history |
| History and Kingdoms |
Dynasties
|
Origins
Main article: Origin of PallavaChola-Naka alliance
Historically, relations between the early Chola dynasty and the Naga dynasty of Tamilakam became well established. Royals by the name Chora-Naga, Ila Naga, Cula Naga and Kunjja Naga ruled the island of Eelam (Ceylon) between 62 BCE - 196 CE. During this period, Tondai Nadu, the homeland of the Pallavas was inhabited by the Kurumbar or Aruvar/Aruvalar people (Tamil: Aruval = people with bill-hook/ Telugu name for Tamil people), one of several Tamil Naga tribes that the Kaliththokai describes as having migrated to mainland Tamilakam during the Sangam period. Ptolemy mentions the coasts of the Cholas (Soringoi) of Chola Nadu and the Aruvar (Arouarnoi) of Aruva Nadu, writing that "Orthoura" was a royal city of Soretai ruled by Sornagos, and Malanga ruled by Basaranagos of the latter. Historians have conjectured that Orthoura refers to the early Chola capital of Uraiyur while Malanga refers to Mavilanka, near Kanchipuram. "Orthoura" may refer to the northeastern Jaffna Tamil port town Uduthurai, where an early copper coin discovered carries the name Naka bumi in Tamil Brahmi, referring to the Naka Dynasty of Naka Nadu.
Manimekhalai of the Sangam literature corpus describes the liaison of Princess Pilli Valai of Nāka Nadu with King Killivalavan of Chola Nadu at Nainativu; out of which union was born Prince Tondai Ilandiraiyan (Thiraiyar/sea farer of Eelam), corroborating tradition that the Pallavas were an off-shoot or branch of the Cholas and that their formation began from an ancient Chola-Nāka alliance.
The Velurpalaiyam plates, dated to 852 CE credits the Naga liaison episode, and creation of the Pallava line, to a king named Virakurcha, son of Chutapallava, while preserving its legitimizing significance:
...from him (Aśvatthāman) in order (came) Pallava, the lord of the whole earth, whose fame was bewildering. Thence, came into existence the race of Pallavas... Vīrakūrcha, of celebrated name, who simultaneously with (the hand of) the daughter of the chief of serpents grasped also the complete insignia of royalty and became famous.
The earliest Tamil literature which throws light on a region associated with the Pallavas is the Akananuru, which locates the elder Tiriyan in Gudur, Nellore district, with a kingdom extending to Tirupati or Thiruvengadam. This Tiriayan is called the elder in order to distinguish him from the younger Tiraiyan whose capital was Kanchipuram. The Sangam work, Perumbanarruppatai, traces the line of the younger Tiriyan (aka Ilam Tiriyan) to the Solar dynasty of Ikshvakus, while the later Tamil commentators identify him as the illegitimate child of a Chola king and a Naga princess.
Historically, early relations between the Nagas and Pallavas became well established. A praśasti (literally "praise"), composed in 753 CE on the dynastic eulogy in the Kasakadi plates, by the Pallava Trivikrama, traces the Pallava lineage from creation through a series of mythic progenitors, then praises the dynasty in terms of two similes hinged together by triple use of the word avatara ("descent"), as below:
From descended the powerful, spotless Pallava dynasty , which resembled a partial incarnation of Visnu, as it displayed unbroken courage in conquering the circle of the world...and which resembled the descent of the Ganges as it purified the whole world.
Simhavarman's reign from 436 CE finds mention in the Lokavibhaga.
List of Pallava monarchs
The earliest documentation on the Pallavas are copper-plate grants, belonging to Skandavarman I and written in Prakrit. Skandavarman appears to have been the first great ruler of the early Pallavas, though there are references to other early Pallavas who may have been predecessors to Skandavarman. He was heralded as Vijaya-Skandavarman or Shiva-Skandavarman.
Skandavarman extended his dominions from the Krishna in the north to the Pennar in the south and to the Bellary district in the West. He performed the Aswamedha and other Vedic sacrifices and bore the title "Supreme King of Kings devoted to dharma". According to the available inscriptions of the Pallavas, the Pallavas could be divided into four separate families or dynasties. A combination of dynastic plates and grants from the period mention their rule thus:
Early Pallavas
- Bappa - Virakurcha - married a Naga of Mavilanga (Kanchi) - The Great Founder of a Pallava lineage
- Simha Varman I (275–300 or 315–345)
- Skanda Varman I (345–355) (Shivaskandavarman)
Middle Pallavas
- Visnugopa (340–355) (Yuvamaharaja Vishnugopa)
- Kumaravisnu I (355–370)
- Skanda Varman II (370–385)
- Vira Varman (385–400)
- Skanda Varman III (400–435)
- Simha Varman II (435–460)
- Skanda Varman IV (460–480)
- Nandi Varman I (480–500)
- Kumaravisnu II (c. 500–510)
- Buddha Varman (c. 510–520)
- Kumaravisnu III (c. 520–530)
- Simha Varman III (c. 530–537)
Later Pallavas
- Simhavishnu (537-570)
- Mahendravarman I 571–630
- Narasimhavarman I (Mamalla) 630–668
- Mahendravarman II 668–672
- Paramesvaravarman I 672–700
- Narasimhavarman II (Raja Simha) 700–728
- Paramesvaravarman II 705–710
- Nandivarman II (Pallavamalla) 732–796
- Dantivarman 775–825
- Nandivarman III 825–869
- Nirupathungan (869–882)
- Aparajithavarman 882–901
Other traditions
Telugu traditions know of a certain Trilochana Pallava as the earliest Telugu King, which is confirmed by later inscriptions . Trilochana Pallava was killed by a Chalukya King near Mudivemu, Cuddapah District. A Buddhist story describes Kala the Nagaraja, resembling the Pallava Kalabhartar as a king of the region near Krishna district. The Pallava Bogga may be identified with the kingdom of Kala in Andhra which had close and early maritime and cultural relations with Ceylon. Rev Heras also identified King Bappa with Kalabhartar (aka Kalabhartri), "the head jewel of the family", whom Rev Heras proposes as the founder of the dynasty, detecting in the references to Bappa in the Hirahadagalli and Uruvapalli plates, "the flavour of antiquity and veneration which always surround the memory of the founder of a dynasty".
Etymology of Tondai
The word Tondai means a creeper and the term Pallava conveys a similar meaning. KA Nilakanta Sastri postulated that Pallavas were descendants of a North Indian dynasty of Indian origin who moved down South, adopted local traditions to their own use, and named themselves after the land called Tondai as Tondaiyar.
KP Jayaswal also proposed a North Indian origin for them, putting forward the theory that the Pallavas were a branch of the Vakatakas. The association with Vakatakas is corroborated by the fact that the Pallavas adopted imperial Vakataka heraldic marks, as is evident from Pallava insignia. The Pallavas had on their seal, the Ganga and Yamuna, known to be Vakataka insignia
The Sangam literature epic Manimekhalai describes that the first Pallava king, Ilam Thiraiyan (or younger Thiraiyan), was born of a liaison between a Naga princess named Pilli Valai (Pilivalai) and a Chola king named Killi (Killivalavan). Ilam Tiriyan was lost in a ship-wreck and found washed ashore with a twig (pallava) of the Tondai creeper, Cephalandra indica, coiled around his ankle. Hence he derived the name Tondai-man from the Tondai creeper. He became an independent ruler and the territory ruled by him came to be known as Tondaimandalam, or 'Realm of the Tondai'.
PT Srinivasa Iyengar says 'Tondaiyar' means the "tribe whose symbol was the Tondai creeper". Tondai or Coccinia indica is commonly known as Kōvai in Tamil in modern times, but the name Doṇḍe is the ordinary name for the plant in Telugu. Hence, Doṇḍe became Tonde or Tondai. Coccinia indica is also known as Cephalandra indica. See Coccinia grandis.
Politics
The Pallavas attacked and weakened the early Chola state of the ancient period. The Gupta emperor Samudragupta of Magadha brought King Vishnugopa of the Pallavas under his sway in the middle of the 4th century. At this time, the early Pallavas came into conflict with the Kadambas, the rulers of northern Karnataka and Konkan, eventually recognising Kadamba authority. During the reign of Simhavarman I, the Kalabhra Interregnum affected the dynasty; it was eventually put down by the allied efforts of Pallavas, Pandyas of Madurai and the Western Chalukyas. Emperor Simhavishnu reestablished Pallava maritime power one hundred years later, inheriting Tamil conquests of Eela Nadu, Ceylon. After the Kalabhra upheaval, the long struggle between the Pallavas and Chalukyas of Badami for supremacy in peninsular India began. Pallava ruler Narasimhavarman I occupied Vatapi following Pulakesi II's defeat in the Battle of Vatapi, defeating the Pandyas, Cholas and Cheras. The conflict resumed in the first half of the eight century with multiple Pallava setbacks, their dominions eventually passing to the Chola kings in 880 CE.
Languagues used
All the early Pallava royal inscriptions are either in Prakrit or in Sanskrit language, considered the official languages of the dynasty while the official script was Pallava grantha. The Sinhala script developed from Brahmi script but under the influence of Pallava Grantha.
Similarly, inscriptions found in Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka State are in Prakrit and not in Telugu or Kannada. The phenomenon of using Prakrit and Sanskrit as the official language in which rulers left their inscriptions and epigraphies continued till 6th century CE. It would have been in the interest of the ruling elite to protect their privileges by perpetuating their hegemony of Prakrit in order to exclude the common people from sharing power (Mahadevan 1995a: 173-188). The Pallavas in their Tamil country also adopted the same method. They used Sanskrit language and Pallava grantha scripts in their official orders.
The earliest copper-plate muniment (legal document) so far discovered in India, is by the Pallavas at an early undated time. This document was the renewal of a previous grant of a garden made by an earlier king Bappa, to twenty Brahman families of the Atreya, Harita, Bhradvaja, Kausika, Kasyapa, and Vatsya gotras, who were settled in Southern India around the date of this grant. The grant mentions certain specified shares for the Brahmans, and free from all taxes ; to which was now added a new grant of a piece of land in a neighbouring village for a threshing-floor, and of another piece for house-sites, together also with four cultivating labourers, and two other agricultural serfs attached to the soil. This endowment was created for the increase of the merit, longevity, power, and fame of the donor's family and race.
The grant was issued from Kanchipura, and it is dated on the fifth day of the sixth fortnight of the rainy season in the eight year of the donor's reign. The grant was made by the Pallava king Sivaskanda-varman, who is mentioned as a member of the spiritual guild of rishi Bharadvaja, and an offerer of the Agnishtoma, Vajapeya, and Asvamedha vedic sacrifices.
The entire body of the inscription is in an old form of Prakrit; but a short benediction in Sanskrit is added at its close, and the king's name on the seal is also written in its Sanskrit form. With regard to the date of the grant, Professor Buhler remarks that "it is impossible to say how the donor is connected with the other Pallava kings known from the sasanas as yet published, or to fix the period when he reigned", but he derives an argument for a tentative early date from the circumstance of its being written in Prakrit.
Assuming the correctness of the identification of the Pallavas with the pauranic Pahlavas, and of the Pahlavas with the Parthians, there are good historical grounds for supposing that Parthian colonies established themselves in the Deccan at a very early period. From the time of the separation of Bactria from Scythia in the middle of the 3rd century BC, the tendency of the Bactrians, forced by the pressure of their western and northern neighbours, was to extend themselves southwards into India. The Parthians, after their conquest of the Bactrians about a century later, followed up their successes by overrunning the Indian provinces of Bactria. The natural effect of this latter movement was to press the conquered Indo-Bactrians still further southwards and eastwards into India, with the concurrent tendency on the side of the Parthians always to follow up the retreat of their vanquished foes. After another interval, the Indo-Parthians were themselves forced out of their possessions in Afghanistan, Punjab, and Upper India by the Scythian invasion, and their only possible refuge then was in the south.
Foulkes says in the article "The Early Pallavas of Kánchípura" published in the Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society of Great Britain and Ireland as follows:
We can follow the footsteps of the refugees, by means of the inscriptions of the Kshatrapas, as far as the upper basin of the Godavari and the northern coast of the Konkans ; and when these substantial materials fail us in tracing their further progress southwards, the very natural conjecture arises that some one of the more enterprising of the defeated Parthian generals would adventure at the head of his remaining troops into the wide plains of the Dakhan (deccan) and carve out for himself a kingdom there, or, perhaps, enter into the service of the existing rulers of the Dakhan as an auxiliary defensive ally, having some frontier province committed to him for the payment of his troops, and with the ultimate inevitable result of establishing his own independent rule there. At this point of our tentative theory we are met by the Ceylonese records showing the great growth of the power of these Parthian colonists at a sufficiently early time, whatever dates may hereafter be attached to the early kings of Ceylon...
An outline of this kind, pending the discovery of more definite materials to fill in the details, quite consistently prepares us for the next succeeding historical appearance of the Pallavas in Sir Walter Elliot's Vengi copper plates of Vijaya Nandi-varman and the subsequent inscriptions of the Chalukyas, at whose arrival in the Dakhan they found the Pallavas in possession of its western districts, as far at the least as the vicinity of Badami in the middle basin of the Krishna, and of its eastern districts as far north at least as Rajahmahendri (Rajamundry) in the lower basin of the Godavari, and with their capital still at Kanchipura, where Sivaskanda-varman of our present grant reigned several centuries before.....I believe it to be, and his reign fell at any time about the end of the first century CE, or the beginning of the second..
Governance in Kanchipuram
The power of the Pallavas was well established at the time when Sivaskanda-varman is styled " supreme king of great kings," a title which implies paramount authority over other rulers subject to him ; and the circumstance of his having offered the horse-sacrifice, which indicates his own personal appreciation of his great power. His predecessor, immediate or otherwise, King Bappa, was wealthy enough to make donations to Brahmans of a 100,000 Ox ploughs, whatever the multiple of exaggeration may be, and many millions of gold coin.
Tho Pallava king was assisted in his government by 'ministers" of state and "privy councillors"; and his throne was surrounded by "royal princes." As can be ascertained from the terms of Professor Buhler's translation, they embraced "countries" governed by "prefects" distributed into " rovinces" administered by their "lords," and subdivided into "districts" under the superintendence of their "rulers". Their fiscal arrangements included "custom houses" and "officers" of customs, and "spies" or itinerant superintendents of revenue. They had also some kind of forest department with its staff of "foresters." They maintained a standing army, the brigades of which were commanded by "generals," and its minor groups of rank and file had their non-commissioned officers or "naicks".
Their village lands were occupied by ryots who paid "eighteen kinds" of contributions to the crown, partly in kind and partly in money ("taxes"). Amongst those which were paid in kind were "sweet and sour milk", "grass and wood" and "vegetables and flowers". They had to plough the crown (state) lands by turns with their "oxen in succession," and it was a part of their obligation to keep the roads and irrigation works in repair by a system of "forced labour". Salt and sugar were royal monopolies; and these not infrequently involved the ryots in "troubles".
The crown had the power to confer grants of land for religious uses, for "the increase of the merit, longevity, power, and fame of his own family and race," and to exempt the grantees and their grant-lands from the payment of the customary taxes. When such land-grants were made, the agricultural "labourers," and the "kolikas" or village staff, were transferred with the land. These "labourers" received for their remuneration "half the produce," according to the system of varam.
Village free of taxes were given to the Brahmanas.
Description
The word Pallava means "branch", in contrast with Chola meaning "new country", Pandiya meaning "old country" and Chera meaning "hill country" in Sangam Tamil lexicon.
Between 105–150 CE, the ancient capital of the Cholas, Puhar or Kaveripoompuharpatinnam, was submerged in a tsunami during Killivalavan's reign; and he moved the capital to Urayur as noted by Ptolemy. The Chola king annexed a part of his territory as Tondaimandalam and presented it to his son, Ilam Tiriyan, who ruled the kingdom between 150–175 CE. He was a contemporary of Athiyamān Nedumān Añci and Avvaiyar I.
Some of the most illustrious Tamil bhakti poets like the Nayanmars Sambandhar and Tirunavukkarasar, Sanskrit poets Bharavi and Dandin, as well as the seashore rock-cut temples of Mahabalipuram belong to the Pallava era. They developed the Pallava Grantha script, known as Grantha Tamil to write Sanskrit and Manipravalam, an alphabet that would give rise to several other southeast Asian scripts. Chinese traveller Hiuen Tsang visited Kanchipuram during Pallava rule and extolled their benign rule..
Pallava Chronology
The rule of the Pallavas apparently starts as early as 275 CE, but their greatest epoch corresponds to the 7th and 8th century.
Early Pallavas
The history of the early Pallavas has not yet been satisfactorily settled. The earliest documentation on the Pallavas is the three copper-plate grants, belonging to Skandavarman I and written in Prakrit. Skandavarman appears to have been the first great ruler of the early Pallavas, though there are references to other early Pallavas who were probably predecessors of Skandavarman.
Skandavarman extended his dominions from the Krishna in the north to the Pennar in the south and to the Bellary district in the West. He performed the Aswamedha and other Vedic sacrifices and bore the title of 'Supreme King of Kings devoted to dharma'.
In the reign of Simhavarman IV, who ascended the throne in 436 CE, the fallen prestige of the Pallavas was restored. He recovered the territories lost to the Vishnukundins in the north up to the mouth of the Krishna. The early Pallava history from this period onwards is furnished by a dozen or so copper-plate grants in Sanskrit. They are all dated in the regnal years of the kings.
With the accession of Nandivarman I (480–500 CE), the decline of the early Pallava family was seen. The Kadambas had their aggressions and attacked even the headquarters of the Pallavas with the Pallavas taking retaliatory measures by expelling and invading Kadamba territories in Karnataka. In coastal Andhra the Vishnukundins established their ascendency. The Pallava authority was confined to Tondaimandalam.
With the accession of Simhavishnu, father of Mahendravarman I, (c. 575 CE), the Pallava revival began in the south.
Later Pallavas


The incursion of the Kalabhras and the confusion in the Tamil country was broken by the Pandya Kadungon and the Pallava Simhavishnu. The King Mahendravarman I re-established the Pallava Kingdom after defeating the Kalabhras. Some of the most ornate monuments at Mamallapuram, were constructed under the rule of King Mahendravarman I. The Pallava kingdom began to gain both in territory and influence over the South Indian peninsula and were a regional power by the end of the 6th century, defeating kings of Ceylon and mainland Tamilakkam. The Pallavas exercised control over their southern neighbours of Cholas and Pandyas. But their history is marked by the continuous conflict with the Badami Chalukyas.
Narasimhavarman I and Paramesvaravarman I were the kings who stand out with glorious achievements in both military and architectural spheres. Narasimhavarman II built the Shore Temple.
- Simhavishnu 555–590 CE
- Mahendravarman I 590–630 CE
- Narasimhavarman I (Mamalla) 630–668 CE
- Mahendravarman II 668–672 CE
- Paramesvaravarman I 672–700 CE
- Narasimhavarman II (Raja Simha) 700–728 CE
- Paramesvaravarman II 705–710 CE
- Nandivarman II (Pallavamalla) 732–796 CE
- Dantivarman 775–825 CE
- Nandivarman III 825–869 CE
- Aparajithavarman 882–901 CE
Kadava kingdom
Main article: KadavaDuring the thirteenth and the fourteenth centuries CE, a small principality of the Kadava dynasty came into brief prominence. These rulers claimed descent from the Pallavas. The notable rulers of this dynasty are Kopperunchinga I (reigned c. 1216–1242 CE), and his son and successor Kopperunchinga II (c. 1243–1279 CE). Together they extended the influence of their kingdom and played a major part in the ultimate demise of the Chola dynasty.
Religion
Pallavas were followers of Hinduism and made gifts of land to gods and Brahmins. In line with the prevalent customs, some of the rulers performed the Aswamedha and other Vedic sacrifices. They were, however, tolerant of other faiths. The Chinese monk Xuanzang who visited Kanchipuram during the reign of Narasimhavarman I reported that there were 100 Buddhist monasteries, and 80 temples in Kanchipuram.
Mahendravarman I was initially a patron of the Jain faith. He later re-converted to Hinduism under the influence of the Saiva saint Appar with the revival of Hinduism during the Bhakti movement in South India.
Pallava architecture

The Pallavas were instrumental in the transition from rock-cut architecture to stone temples. The earliest examples of Pallava constructions are rock-cut temples dating from 610–690 CE and structural temples between 690–900 CE. A number of rock-cut cave temples bear the inscription of the Pallava king, Mahendravarman I and his successors.
The greatest accomplishments of the Pallava architecture are the rock-cut temples at Mahabalipuram. There are excavated pillared halls and monolithic shrines known as rathas in Mahabalipuram. Early temples were mostly dedicated to Shiva. The Kailasanatha temple in Kanchipuram and the Shore Temple built by Narasimhavarman II, rock cut temple in Mahendravadi by Mahendravarman are fine examples of the Pallava style temples. The temple of Nalanda Gedige in Kandy, Sri Lanka is another. The famous Tondeswaram temple of Tenavarai and the ancient Koneswaram temple of Trincomalee were patronized and structurally developed by the Pallavas in the 7th century.
See also
| Middle kingdoms of India | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Notes
- Ancient India, A History Textbook for Class XI, Ram Sharan Sharma, National Council of Educational Research and Training, India pp 209
- ^ Ordhendra Coomar Gangoly. The art of the Pallavas, Volume 2 of Indian Sculpture Series. G. Wittenborn, 1957. p. 2.
- The journal of the Numismatic Society of India, Volume 51, p.109
- Alī Jāvīd and Tabassum Javeed. (2008). World heritage monuments and related edifices in India, p.107
- International Tamil Language Foundation (2000). The Handbook of Tamil Culture and Heritage. Chicago: International Tamil Language Foundation. p. 877.
- Sastri, K.A. Nilakanta (1949). South Indian Influences in the Far East. Bombay: Hind Kitab Ltd. pp. 28 & 48.
- The journal of the Numismatic Society of India, Volume 51, p.109
- Alī Jāvīd and Tabassum Javeed. (2008). World heritage monuments and related edifices in India, p.107
- Vakataka - Gupta Age Circa 200-550 A.D. By R. C. Majumdar, A. S. Altekar. pp. 222-223
- ^ Rev. H Heras, SJ (1931) Pallava Genealogy: An attempt to unify the Pallava Pedigrees of the Inscriptions, Indian Historical Research Institute
- Ancient India, A History Textbook for Class XI, Ram Sharan Sharma, National Council of Educational Research and Training, India pp 211-215
- KR Subramanian. (1989). Buddhist remains in Āndhra and the history of Āndhra between 224 & 610 A.D, p.71:
- Paramanand Gupta. (1973). Geography in ancient Indian inscriptions, up to 650 A.D, p.69
- Bharatiya Vidya Bhavan, Bhāratīya Itihāsa Samiti. (2009). The History and Culture of the Indian People: The classical age, p.279
- ^ KR Subramanian. (1989). Buddhist remains in Āndhra and the history of Āndhra between 224 & 610 A.D, p.71
- ^ Marilyn Hirsh (1987) Mahendravarman I Pallava: Artist and Patron of Māmallapuram, Artibus Asiae, Vol. 48, Number 1/2 (1987), pp. 109-130
- Michael D Rabe. (1997). The Māmallapuram Praśasti: A Panegyric in Figures, Artibus Asiae, Vol. 57, Number 3/4 (1997), pp. 189-241
- ^ Michael D Rabe. (1997). The Māmallapuram Praśasti: A Panegyric in Figures, Artibus Asiae, Vol. 57, No. 3/4 (1997), pp. 189-241.
- ^ KR Subramanian. (1989). Buddhist remains in Āndhra and the history of Āndhra between 224 & 610 A.D, p.72
- Perumpāṇāṟṟuppaṭai 29-30, 454
- ^ Now referred to as the Mayidavolu, Hirahadagalli and the British Museum plates – Durga Prasad (1988)
- ^ Nilakanta Sastri, A History of South India, p91
- Nilakanta Sastri, A History of South India, pp91–92
- http://chestofbooks.com/history/india/South-India-Culture/Chapter-VIII-Early-History-Of-The-Pallavas.html
- ^ South Indian History Congress. (February 15–17). Proceedings of the First Annual Conference. The Congress, 1980.
{{cite book}}: Check date values in:|date=and|year=/|date=mismatch (help); Unknown parameter|Volume=ignored (|volume=suggested) (help) - A.Krishnaswami. Topics in South Indian history: from early times upto 1565 A.D. Krishnaswami, 1975. pp. 89–90.
- Bihar Research Society (1933). The Journal of the Bihar Research Society. Vol. 19. pp. 183–184.
- P. T. Srinivasa Iyengar (1929). History of the Tamils: from the earliest times to 600 A.D. Asian Educational Services. p. 401. ISBN 81-206-0145-9, 9788120601451.
{{cite book}}: Check|isbn=value: invalid character (help) - ^ Rajan K. (Jan-Feb 2008). Situating the Beginning of Early Historic Times in Tamil Nadu: Some Issues and Reflections, Social Scientist, Vol. 36, Number 1/2, pp. 40-78
- ^ Foulkes T (Oct 1889) The Early Pallavas of Kánchípura, Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society of Great Britain and Ireland, New Series, Volume 21, Number 4, pp. 1111-1124
- Avari, p186
- Nilakanta Sastri, A History of South India, pp91–92
- ^ Nilakanta Sastri, A History of South India, p92
- Kulke and Rothermund, p105
- Kulke and Rothermund, p120
- ^ Kulke and Rothermund, p111
- Kulke and Rothermund, pp121–122
- Appar
- Nilakanta Sastri, pp412–413
- Nilakanta Sastri, p139
References
- Avari, Burjor (2007). India: The Ancient Past. New York: Routledge.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - Dubreuil, G. Jouveau (1995). The Pallavas. India: Asian Educational Services. ISBN 81-206-0574-8.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Hermann, Kulke (2001) . A History of India. Routledge. ISBN 0-415-32920-5.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Minakshi, Cadambi (1938). Administration and Social Life Under the Pallavas. Madras: University of Madras.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - Nilakanta Sastri, K.A (2002) . A History of South India. New Delhi: OUP.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - Prasad, Durga (1988). History of the Andhras up to 1565 A.D. Guntur, India: P.G. Publishers.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - "South Indian Inscriptions". Archaeological Survey of India. What Is India Publishers (P) Ltd. Retrieved 2008-05-30.
