| Revision as of 01:07, 6 November 2014 view sourceFlyer22 Frozen (talk | contribs)365,630 edits →Layers, regions and histology: Fixes to my latest post. And removed "few layers" for epithelium bit, since, as noted on the talk page, sources can differ in describing it as having layers.← Previous edit | Revision as of 01:26, 6 November 2014 view source Flyer22 Frozen (talk | contribs)365,630 edits →Layers, regions and histology: Moved layers material up near the beginning layer material. Tweak. Fixed WP:REFNAME.Next edit → | ||
| Line 50: | Line 50: | ||
| ===Layers, regions and histology=== | ===Layers, regions and histology=== | ||
| ]) of vaginal mucosa can be seen]] | ]) of vaginal mucosa can be seen]] | ||
| ] of a ]ed slide showing a portion of vaginal |
] of a ]ed slide showing a portion of vaginal walls. ] and underling connective tissue can be seen. The deeper muscular layers are not shown. The black line points to a fold in the mucosa.]] | ||
| The |
The walls of the vagina from the lumen outwards consists of a mucosa of ] with underlying vascular connective tissue,<ref name="Konar"/><ref name="Wylie">{{cite book|last=Wylie|first=Linda|title=Essential Anatomy and Physiology in Maternity Care|accessdate=19 February 2014|year=2005|publisher=Elsevier Health Sciences|isbn=0-443-10041-1|pages=157–158|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=QgpOvSDxGGYC&pg=PA157}}</ref> a layer of ] with bundles of circular fibers internal to longitudinal fibers, and an outer layer of ] called ].<ref name="Wylie"/><ref name="Wheater">{{Cite book | editor-last=Young | editor-first=B | title=Wheater's Functional Histology: A Text and Colour Atlas | publisher=] | year=2006 | page=377 | edition=5th | isbn=978-0443068508 }}</ref> | ||
| ⚫ | Although the vaginal walls are described as being composed of three layers, a four-layer description of the vaginal walls is also common,<!-- NOTE: Sources differ when describing the number of vaginal layers; though three layers is the most common description, four layers are also sometimes described. Presenting both satisfies WP:Due weight, and takes care of any confusion presented to readers by discrepancies in the anatomical literature.--><ref name="Mulhall"/><ref name="Wylie"/><ref name="Wheater">{{Cite book | editor-last=Young | editor-first=B | title=Wheater's Functional Histology: A Text and Colour Atlas | publisher=Elsevier | year=2006 | page=377 | edition=5th | isbn=978-0443068508 }}</ref><ref name="Brown">{{cite book|last=Brown|first=Laurence|title=Pathology of the Vulva and Vagina|accessdate=February 21, 2014|year=2012|publisher=]|isbn=0857297570|pages=6–7|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=Yv2CMHoVR9wC&pg=PA6}}</ref> When described as three layers, the first layer is made up of a stratified squamous non-keratinized epithelium and is an underlying lamina propria of connective tissue (a layer of connective tissue that is highly ] under ] lining the epithelium). The second layer is the muscular layer, which is composed of smooth muscle fibers and situated longitudinally and circularly, and the third layer is the adventitia, which is a dense connective tissue that blends with the ] surrounding the area.<ref name="Mulhall"/><ref name="Wheater"/> | ||
| ⚫ | Supporting the vagina are its upper third, middle third and lower third. The upper third are the ] muscles (transcervical, ]) and the sacrocervical ligaments; these areas are also described as the ]s laterally and ] posterolaterally. The middle third of the vagina concerns the ] (also described as the paracolpos and ]). The lower third is the ]; it may be described as containing the perineal body, pelvic diaphragm and urogenital diaphragm.<ref name="Snell"/><ref name="Elsevier Obstetrics">{{Cite book |author=| title=Manual of Obstetrics. (3rd ed.) | publisher=] | year=2011 | pages=1–16 | isbn=9788131225561}}</ref> | ||
| ⚫ | For a four-layer description of the vagina walls, the first layer is an inner layer of non-keratinized squamous epithelium, which forms the folds or ] and facilitate the vagina's ability to expand large enough for child birth. The rugae are a series of ridges produced by folding of the wall of the outer third of the vagina; they are transverse epithelial ridges and their function is to provide the vagina with increased surface area for extension and stretching. The second layer of the vagina is connective tissue, which contains blood vessels. The third layer is the muscle layer; it is an outer layer of longitudinal muscle, as well as the inner layer of circular muscle. The fourth layer is an outer layer of connective tissue; it is continuous with the other pelvic organs and is made up of blood and ]s and fibers.<ref name="Wylie"/><ref name="Arulkumaran">{{cite book|authors=Sabaratnam Arulkumaran, Lesley Regan, Aris Papageorghiou, Ash Monga, David Farquharson|title=Oxford Desk Reference: Obstetrics and Gynaecology|accessdate=February 21, 2014|year=2011|publisher=]|isbn=0191620874|page=471|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=lRaWcRYx_7YC&pg=PA471}}</ref> | ||
| ⚫ | |||
| Where the vaginal ] surrounds the cervix of the uterus, it is divided into four regions of fornices (the ]); these are the anterior, posterior, and the right lateral and left lateral (the lateral fornix).<ref name="Snell"/><ref name="Konar"/> The posterior is deeper and the anterior is shallow.<ref name="Konar"/> While the anterior and posterior walls are placed together, the lateral walls, especially their middle area, are relatively more rigid; because of this, they vagina has a H-shaped cross section.<ref name="Konar"/> Behind, the upper one-fourth of the vagina is separated from the ] by the ]. Superficially, in-front of the pubic bone, a cushion of fat called the ] forms the uppermost part of the vulva. | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | Supporting the vagina are its upper third, middle third and lower third. The upper third are the ] muscles (transcervical, ]) and the sacrocervical ligaments; these areas are also described as the ]s laterally and ] posterolaterally. The middle third of the vagina concerns the ] (also described as the paracolpos and ]). The lower third is the ]; it may be described as containing the perineal body, pelvic diaphragm and urogenital diaphragm.<ref name="Snell"/><ref name="Elsevier Obstetrics">{{Cite book |author=| title=Manual of Obstetrics. (3rd ed.) | publisher=] | year=2011 | pages=1–16 | isbn=9788131225561}}</ref> | ||
| Maternal ], present from birth to two to four weeks, is the reason newborn females have a stratified squamous epithelium. After this age range, through to the prepubertal age and in the post-] age, the epithelium thins out.<ref name="Konar"/><ref name="Gad">{{cite book|author=Shayne Cox Gad|title=Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Handbook: Production and Processes|publisher=]|isbn=0470259809|pages=817|year=2008|accessdate=November 5, 2014|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=4c0Hp3AOi8UC&pg=PA817}}</ref> The epithelium is absent of glands, and, from puberty to menopause, the epithelial cells contain ].<ref name="Konar"/><ref name="Beckmann">{{cite book|author=Charles R. B. Beckmann|title=Obstetrics and Gynecology|publisher=]|isbn=0781788072|pages=241–245|year=2010|accessdate=November 5, 2014|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=0flWgd3OJLEC&pg=PA241}}</ref> Consisting of three different layers of cells – superficial ], intermediate cells and ] – estrogen supplies the intermediate and superficial cells with glycogen. The cells layering the vaginal area of the cervix become stable with the intermediate and superficial cells, and the intermediate and superficial cells reach to the squamocolumnar junction (the area of the cervix where the columnar epithelium takes the place of the uterus squamous lining of the vagina) at the ] (external os). The superficial cells ] continuously, especially while in an inflammatory or ] (tumorous) state. The basal cells replace the superficial cells, and ]ization results when the epithelium is exposed to the dry external atmosphere.<ref name="Konar"/><ref name="Beckmann"> | Maternal ], present from birth to two to four weeks, is the reason newborn females have a stratified squamous epithelium. After this age range, through to the prepubertal age and in the post-] age, the epithelium thins out.<ref name="Konar"/><ref name="Gad">{{cite book|author=Shayne Cox Gad|title=Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Handbook: Production and Processes|publisher=]|isbn=0470259809|pages=817|year=2008|accessdate=November 5, 2014|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=4c0Hp3AOi8UC&pg=PA817}}</ref> The epithelium is absent of glands, and, from puberty to menopause, the epithelial cells contain ].<ref name="Konar"/><ref name="Beckmann">{{cite book|author=Charles R. B. Beckmann|title=Obstetrics and Gynecology|publisher=]|isbn=0781788072|pages=241–245|year=2010|accessdate=November 5, 2014|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=0flWgd3OJLEC&pg=PA241}}</ref> Consisting of three different layers of cells – superficial ], intermediate cells and ] – estrogen supplies the intermediate and superficial cells with glycogen. The cells layering the vaginal area of the cervix become stable with the intermediate and superficial cells, and the intermediate and superficial cells reach to the squamocolumnar junction (the area of the cervix where the columnar epithelium takes the place of the uterus squamous lining of the vagina) at the ] (external os). The superficial cells ] continuously, especially while in an inflammatory or ] (tumorous) state. The basal cells replace the superficial cells, and ]ization results when the epithelium is exposed to the dry external atmosphere.<ref name="Konar"/><ref name="Beckmann"/> | ||
| For blood and nerve supply, relevant arteries are the cervicovaginal (the uterine cervix and the vagina) branch of the ], the ], ], and the ]. The veins are connected by ] (the connection of separate parts of a branching system to form a network), resulting in the formation of the ] and posterior ]. The nerve supply of the vagina is provided by the ] and ] areas of the ], with the ] supplying the lower area.<ref name="Konar"/> | For blood and nerve supply, relevant arteries are the cervicovaginal (the uterine cervix and the vagina) branch of the ], the ], ], and the ]. The veins are connected by ] (the connection of separate parts of a branching system to form a network), resulting in the formation of the ] and posterior ]. The nerve supply of the vagina is provided by the ] and ] areas of the ], with the ] supplying the lower area.<ref name="Konar"/> | ||
Revision as of 01:26, 6 November 2014
This article is about the body part. For other uses, see Vagina (disambiguation).
| Vagina | |
|---|---|
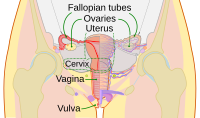 Diagram of the female human reproductive tract and ovaries Diagram of the female human reproductive tract and ovaries | |
 Vulva with vaginal opening Vulva with vaginal opening | |
| Details | |
| Precursor | urogenital sinus and paramesonephric ducts |
| Artery | superior part to uterine artery, middle and inferior parts to vaginal artery |
| Vein | uterovaginal venous plexus, vaginal vein |
| Nerve | Sympathetic: lumbar splanchnic plexus Parasympathetic: pelvic splanchnic plexus |
| Lymph | upper part to internal iliac lymph nodes, lower part to superficial inguinal lymph nodes |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Vagina |
| MeSH | D014621 |
| TA98 | A09.1.04.001 |
| TA2 | 3523 |
| FMA | 19949 |
| Anatomical terminology[edit on Wikidata] | |
The vagina is a fibromuscular tubular sex organ that is part of the female genital tract. In humans, the vagina extends from the vulva to the uterus. At the vulva, the vaginal orifice may be partly covered by a membrane called the hymen, while, at the deep end, the cervix (neck of the uterus) bulges through the anterior wall of the vagina. The vagina facilitates sexual intercourse and childbirth. It also channels the menstrual flow, consisting of blood and pieces of mucosal tissue, that occurs periodically with the shedding of lining of the uterus in menstrual cycles.
The location and structure of the vagina varies among species, and may vary in size within the same species. Unlike mammalian males, who usually have the urethral orifice as the sole external urogenital orifice, mammalian females usually have two external orifices, the urethral orifice for the urological tract and the vaginal orifice for the genital tract. The vaginal orifice is much larger than the nearby urethral opening, and both openings are protected by the labia in humans. In amphibians, birds, reptiles and monotremes an opening called the cloaca functions as a single external orifice for the gastrointestinal tract, urological tract, and reproductive tract.
The vagina plays a significant role in human female sexuality and sexual pleasure. During sexual arousal for humans and others animals, vaginal moisture increases by way of vaginal lubrication, to reduce friction and allow for smoother penetration of the vagina during sexual activity. The texture of the vaginal walls can create friction for the penis during sexual intercourse and stimulate it toward ejaculation, enabling fertilization. In addition, a variety of sexually transmitted infections (STIs/STDs) and other disorders can affect the vagina. Because of the risk of STIs/STDs, health authorities, such as the World Health Organization (WHO), and health care providers, recommend safe sex practices.
Cultural perceptions of the vagina have persisted throughout history; these perceptions range from viewing the vagina as the focus of sexual desire, a metaphor for life via birth, an organ inferior to the penis, or as visually unappealing or otherwise vulgar. Colloquially, the word vagina is often used incorrectly to refer to the vulva.
Etymology and definition
The term vagina is from Latin vāgīnae, literally "sheath" or "scabbard." It is often referred to as the birth canal in the context of pregnancy and childbirth, though the term is, by definition, the area between the outside of the vagina and the fully dilated cervix, which is the neck of the uterus.
The Latinate plural "vaginae" is rarely used in English. Colloquially, the word vagina is often used to refer to the vulva or to the female genitals in general. However, by its dictionary and anatomical definitions, vagina refers exclusively to the specific internal structure.
Structure
Embryonic development and general structure
The vagina is derived from the embryonic Müllerian duct. During sexual differentiation (sex development of the differences between males and females), if exposed to testosterone, fusion of the urogenital folds (elongated spindle-shaped structures that contribute to the formation of the urethral groove on the belly aspect of the genital tubercle) allows the urogenital sinus to close completely and form the spongy urethra, while the labioscrotal swellings unite to form the scrotum. In the absence of testosterone, the urogenital sinus persists as the vestibule of the vagina, the two urogenital folds form the labia minora, and the labioscrotal swellings enlarge to form the labia majora.
The human vagina is an elastic muscular canal that extends from the vulva to the uterus. It, along with the inside of the vulva, is reddish pink in color, and it connects the superficial vulva to the cervix of the deep uterus. The vagina is posterior to the urethra and bladder, and reaches across the perineum superiorly and posteriorly toward the cervix; at approximately a 90 degree angle, the cervix protrudes into the vagina.
Layers, regions and histology
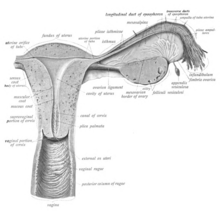
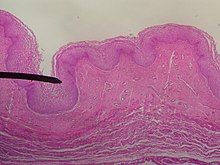
The walls of the vagina from the lumen outwards consists of a mucosa of stratified squamous epithelium with underlying vascular connective tissue, a layer of smooth muscle with bundles of circular fibers internal to longitudinal fibers, and an outer layer of connective tissue called adventitia.
Although the vaginal walls are described as being composed of three layers, a four-layer description of the vaginal walls is also common, When described as three layers, the first layer is made up of a stratified squamous non-keratinized epithelium and is an underlying lamina propria of connective tissue (a layer of connective tissue that is highly vascular under the base area lining the epithelium). The second layer is the muscular layer, which is composed of smooth muscle fibers and situated longitudinally and circularly, and the third layer is the adventitia, which is a dense connective tissue that blends with the fascia surrounding the area.
For a four-layer description of the vagina walls, the first layer is an inner layer of non-keratinized squamous epithelium, which forms the folds or rugae and facilitate the vagina's ability to expand large enough for child birth. The rugae are a series of ridges produced by folding of the wall of the outer third of the vagina; they are transverse epithelial ridges and their function is to provide the vagina with increased surface area for extension and stretching. The second layer of the vagina is connective tissue, which contains blood vessels. The third layer is the muscle layer; it is an outer layer of longitudinal muscle, as well as the inner layer of circular muscle. The fourth layer is an outer layer of connective tissue; it is continuous with the other pelvic organs and is made up of blood and lymphatic vessels and fibers.
Where the vaginal lumen surrounds the cervix of the uterus, it is divided into four regions of fornices (the vaginal fornix); these are the anterior, posterior, and the right lateral and left lateral (the lateral fornix). The posterior is deeper and the anterior is shallow. While the anterior and posterior walls are placed together, the lateral walls, especially their middle area, are relatively more rigid; because of this, they vagina has a H-shaped cross section. Behind, the upper one-fourth of the vagina is separated from the rectum by the recto-uterine pouch. Superficially, in-front of the pubic bone, a cushion of fat called the mons pubis forms the uppermost part of the vulva.
Supporting the vagina are its upper third, middle third and lower third. The upper third are the levator ani muscles (transcervical, pubocervical) and the sacrocervical ligaments; these areas are also described as the cardinal ligaments laterally and uterosacral ligaments posterolaterally. The middle third of the vagina concerns the urogenital diaphragm (also described as the paracolpos and pelvic diaphragm). The lower third is the perineal body; it may be described as containing the perineal body, pelvic diaphragm and urogenital diaphragm.
Maternal estrogen, present from birth to two to four weeks, is the reason newborn females have a stratified squamous epithelium. After this age range, through to the prepubertal age and in the post-menopause age, the epithelium thins out. The epithelium is absent of glands, and, from puberty to menopause, the epithelial cells contain glycogen. Consisting of three different layers of cells – superficial cornified cells, intermediate cells and basal cells – estrogen supplies the intermediate and superficial cells with glycogen. The cells layering the vaginal area of the cervix become stable with the intermediate and superficial cells, and the intermediate and superficial cells reach to the squamocolumnar junction (the area of the cervix where the columnar epithelium takes the place of the uterus squamous lining of the vagina) at the external orifice of the uterus (external os). The superficial cells exfoliate continuously, especially while in an inflammatory or neoplastic (tumorous) state. The basal cells replace the superficial cells, and keratinization results when the epithelium is exposed to the dry external atmosphere.
For blood and nerve supply, relevant arteries are the cervicovaginal (the uterine cervix and the vagina) branch of the uterine artery, the vaginal artery, middle rectal artery, and the internal pudendal artery. The veins are connected by anastomosis (the connection of separate parts of a branching system to form a network), resulting in the formation of the anterior and posterior azygos (unpaired) arteries. The nerve supply of the vagina is provided by the sympathetic and parasympathetic areas of the pelvic plexus, with the pudendal nerve supplying the lower area.
Vaginal opening and hymen
The vaginal opening (or orifice) is at the caudal end of the vulva, behind the opening of the urethra, resting at the posterior end of the vestibule. It is closed by the labia minora in female virgins and in females who have never given birth (nulliparae), but may be exposed in females who have given birth (parous females).
The hymen is a membrane of tissue that surrounds or partially covers the vaginal opening. The effects of vaginal intercourse and childbirth on the hymen are variable. If the hymen is sufficiently elastic, it may return to nearly its original condition. In other cases, there may be remnants (carunculae myrtiformes), or it may appear completely absent after repeated penetration. Additionally, the hymen may be lacerated by disease, injury, medical examination, masturbation or physical exercise. For these reasons, it is not possible to definitively determine whether or not a girl or woman is a virgin by examining her hymen.
Variations and size
Main article: Human vaginal sizeIn its normal state, there is anatomical variation in the length of the vagina of a woman of child-bearing age. The length is approximately 7.5 cm (2.5 to 3 in) across the anterior wall (front), and 9 cm (3.5 in) long across the posterior wall (rear), making the posterior fornix deeper than the anterior. During sexual arousal, the vagina expands in both length and width.
If a woman stands upright, the vaginal tube points in an upward-backward direction and forms an angle of approximately 45 degrees with the uterus and of about 60 degrees to the horizontal.
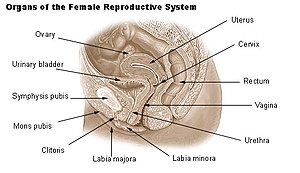
The vaginal opening and hymen can vary in size; in children, although a common appearance of the hymen is crescent-shaped, many shapes are possible.
Function
Secretions
The vagina provides a path for menstrual blood and tissue to leave the body. In industrial societies, tampons, menstrual cups and sanitary napkins may be used to absorb or capture these fluids. Vaginal secretions are primarily from the uterus, cervix, and transudation of the vaginal epithelium in addition to miniscule vaginal lubrication from the Bartholin's glands upon sexual arousal. It takes little vaginal secretion to make the vagina moist. The secretions may be minor in excess during sexual arousal, the middle of the menstrual cycle, a little prior to menstruation, or during pregnancy.
The Bartholin's glands, located near the vaginal opening and cervix, were originally thought to be the primary source for vaginal lubrication, but they provide only a few drops of mucus for vaginal lubrication; the significant majority of vaginal lubrication is generally believed to be provided by plasma seepage from the vaginal walls, which is called vaginal transudation. Vaginal transudation, which initially forms as sweat-like droplets, is caused by vascular engorgement of the vagina (vasocongestion); this results in the pressure inside the capillaries increasing the transudation of plasma through the vaginal epithelium.
Before and during ovulation, the cervix's mucus glands secrete different variations of mucus, which provides an alkaline, fertile environment in the vaginal canal that is favorable to the survival of sperm. "Vaginal lubrication typically decreases as women age, but this is a natural physical change that does not normally mean there is any physical or psychological problem. After menopause, the body produces less estrogen, which, unless compensated for with estrogen replacement therapy, causes the vaginal walls to thin out significantly."
Sexual activity
Further information: Human sexual activity and Human female sexualityIn general, the concentration of the nerve endings that lie close to the entrance of a woman's vagina (the lower third) can provide pleasurable vaginal sensations during sexual activity when stimulated, and many women additionally derive pleasure from a feeling of closeness and fullness during penetration of the vagina. The vagina as a whole, however, lacks nerve endings, which commonly hinders a woman's ability to receive sufficient sexual stimulation, including orgasm, solely from vaginal sexual activity. Although some scientific examinations of vaginal wall innervation indicate no single area with a greater density of nerve endings, or that only some women have a greater density of nerve endings in the anterior vaginal wall, heightened sensitivity in the anterior vaginal wall is common among women. These cases indicate that the outer one-third of the vagina, especially near the opening, contains the majority of the vaginal nerve endings, making it more sensitive to touch than the inner (or upper) two-thirds of the vaginal barrel. This factor is considered to make the process of child birth significantly less painful, because an increased number of nerve endings means that there is an increased possibility for pain as well as pleasure.
Besides penile penetration, there are a variety of ways that pleasure can be received from vaginal stimulation, including by masturbation, fingering, oral sex (cunnilingus), or by specific sex positions (such as the missionary position or the spoons sex position). Some women use sex toys, such as a vibrator or dildo, for vaginal pleasure. Foreplay is often used to incite sexual arousal, and may include one or more of the aforementioned sexual activities. The clitoris additionally plays a part in vaginal stimulation, as it is a sex organ of multiplanar structure containing an abundance of nerve endings, with a broad attachment to the pubic arch and extensive supporting tissue to the mons pubis and labia; it is centrally attached to the urethra, and research indicates that it forms a tissue cluster with the vagina. This tissue is perhaps more extensive in some women than in others, which may contribute to orgasms experienced vaginally.
During sexual arousal, and particularly the stimulation of the clitoris, the walls of the vagina lubricate. This begins after ten to thirty seconds of sexual arousal, and increases in amount the longer the woman is aroused. It reduces friction or injury that can be caused by insertion of the penis into the vagina or other penetration of the vagina during sexual activity. The vagina lengthens during the arousal, and can continue to lengthen in response to pressure; as the woman becomes fully aroused, the vagina expands in length and width, while the cervix retracts. With the upper two-thirds of the vagina expanding and lengthening, the uterus rises into the greater pelvis, and the cervix is elevated above the vaginal floor, resulting in "tenting" of the mid-vaginal plane. As the elastic walls of the vagina stretch or contract, with support from the pelvic muscles, to wrap around the inserted penis (or other object), this stimulates the penis and helps to cause the male to experience orgasm and ejaculation, which in turn enables fertilization.
An area in the vagina that may be an erogenous zone is the G-spot (also known as the Gräfenberg spot); it is typically defined as being located at the anterior wall of the vagina, a couple or few inches in from the entrance, and some women experience intense pleasure, and sometimes an orgasm, if this area is stimulated during sexual activity. A G-spot orgasm may be responsible for female ejaculation, leading some doctors and researchers to believe that G-spot pleasure comes from the Skene's glands, a female homologue of the prostate, rather than any particular spot on the vaginal wall. Other researchers consider the connection between the Skene's glands and the G-spot area to be weak; they contend that the Skene's glands do not appear to have receptors for touch stimulation, and that there is no direct evidence for their involvement. The G-spot's existence, and existence as a distinct structure, is still under dispute, as its reported location can vary from woman to woman, appears to be nonexistent in some women, and it is hypothesized to be an extension of the clitoris and therefore the reason for orgasms experienced vaginally.
Childbirth
During childbirth, the vagina provides the channel to deliver the newborn from the uterus to its independent life outside the body of the mother. During birth, the elasticity of the vagina allows it to stretch to many times its normal diameter.
Vaginal ecosystem and acidity
Main article: Vaginal floraThe vagina is a nutrient rich environment that harbors a unique and complex microbiome. It is a dynamic ecosystem that undergoes long term changes, from neonate to puberty and from the reproductive period (menarche) to menopause. Moreover, under the influence of hormones, such as estrogen (estradiol), progesterone and follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), the vaginal ecosystem undergoes cyclic or periodic changes, i.e. during menses and pregnancy. One significant variable parameter is the vaginal pH, which varies significantly during a woman‘s lifespan, from 7.0 in premenarchal girls, to 3.8-4.4 in women of reproductive age to 6.5-7.0 during menopause without hormone therapy and 4.5-5.0 with hormone replacement therapy. Estrogen, glycogen and lactobacilli are important factors in this variation.
Clinical significance
General
The vagina is self-cleansing and therefore usually needs no special treatment. To maintain vulvovaginal health, doctors generally discourage the practice of douching. Since a healthy vagina is colonized by a mutually symbiotic flora of microorganisms that protect its host from disease-causing microbes, any attempt to upset this balance may cause many undesirable outcomes, including but not limited to abnormal discharge and yeast infection.
The vagina and cervix are examined during gynecological examinations of the pelvis, often using a speculum, which holds the vagina open for visual inspection or taking samples (see pap smear). This and other medical procedures involving the vagina, including digital internal examinations and administration of medicine, are referred to as being "per vaginam", the Latin for "via the vagina", often abbreviated to "p.v.".

The healthy vagina of a woman of child-bearing age is acidic, with a pH normally ranging between 3.8 and 4.5. This is due to the degradation of glycogen to the lactic acid by enzymes secreted by the Döderlein's bacillus. This is a normal commensal of the vagina. The acidity retards the growth of many strains of pathogenic microbes. An increased pH of the vagina (with a commonly used cut-off of pH 4.5 or higher) can be caused by bacterial overgrowth, as occurs in bacterial vaginosis and trichomoniasis, or rupture of membranes in pregnancy.
Intravaginal administration is a route of administration where the substance is applied to the inside of the vagina. Pharmacologically, it has the potential advantage to result in effects primarily in the vagina or nearby structures (such as the vaginal portion of cervix) with limited systemic adverse effects compared to other routes of administration.
Diseases
Main article: Vaginal diseaseDiseases that can affect the vagina include sexually transmitted infections (STIs/STDs) such as HIV/AIDS, human papillomavirus (HPV), genital herpes, or trichomoniasis, or other infections such as candidal vulvovaginitis. Because of STIs, health authorities and other health outlets recommend safe sex practices when engaging in sexual activity. Vaginitis is an inflammation of the vagina, and is attributed to several vaginal diseases. By contrast, vaginismus is an involuntary tightening of the vagina muscles caused by a conditioned reflex, or to disease conditions in the area, during vaginal penetration.
There can be a vaginal obstruction, such as by imperforate hymen or, less commonly, a transverse vaginal septum. Where a lump is present in the vagina, it is most commonly a Bartholin's cyst. Vaginal prolapse is characterized by a portion of the vaginal canal protruding (prolapsing) from the opening of the vagina. It may result in the case of weakened pelvic muscles, which is a common result of childbirth; in the case of this prolapse, the rectum, uterus, or bladder pushes on the vagina, and severe cases result in the vagina protruding out of the body. Kegel exercises have been used to strengthen the pelvic floor, and may help prevent or remedy vaginal prolapse. Cervical cancer may be prevented by pap smear screening and HPV vaccines. Vaginal cancer is very rare, but its symptoms include abnormal vaginal bleeding or vaginal discharge.
Modification
The vagina, including the vaginal opening, may be altered as a result of genital modification during vaginoplasty or labiaplasty; for example, alteration to the inner labia (also known as the vaginal lips or labia minora). There are two main categories of women seeking cosmetic genital surgery: those with congenital conditions such as an intersex condition, and those with no underlying condition who experience physical discomfort or wish to alter the appearance of their genitals because they believe they do not fall within a normal range.
Female genital mutilation (FGM), another aspect of female genital modification, may additionally be known as female circumcision or female genital cutting (FGC). The most severe form of FGM is infibulation, in which there is removal of all or part of the inner and outer labia (labia minora and labia majora) and the closure of the vagina; this is called Type III FGM, and it involves a small hole being left for the passage of urine and menstrual blood, with the vagina being opened up for sexual intercourse and childbirth.
Society and culture
Biological perceptions, symbolism and vulgarity
There have been various perceptions of the vagina throughout history, ranging from it being the center of sexual desire, a symbol of sexual power, a metaphor for life via birth, inferior to the penis, visually unappealing, inherently "smelly," or otherwise vulgar. In Ancient times, it was often considered equivalent (homologous) to the penis; anatomists Galen (129 AD – 200 AD) and Vesalius (1514–1564), regarded the organs as structurally the same, except for the vagina being inverted. Anatomical studies over latter centuries, however, showed the clitoris to be the penile equivalent.
The release of vaginal fluids were considered by medical practitioners to cure or remedy a number of ailments; various methods were used over the centuries to release "female seed" (via vaginal lubrication or female ejaculation) as a treatment for suffocation ex semine retento (suffocation of the womb), female hysteria or green sickness. Methods included a midwife rubbing the walls of the vagina or insertion of the penis or penis-shaped objects into the vagina. Supposed symptoms of female hysteria included faintness, nervousness, insomnia, fluid retention, heaviness in abdomen, muscle spasm, shortness of breath, irritability, loss of appetite for food or sex, and "a tendency to cause trouble". Women considered suffering from the condition would sometimes undergo "pelvic massage" — stimulation of the genitals by the doctor until the woman experienced "hysterical paroxysm" (i.e., orgasm). Paroxysm was regarded as a medical treatment, and not a sexual release. The categorization of female hysteria has ceased to be recognized as a medical condition since the 1920s.
The vagina has been termed many vulgar names, two being cunt and pussy. Cunt is used as a derogatory epithet referring to people of either sex. This usage is relatively recent, dating from the late nineteenth century. Reflecting different national usages, cunt is described as "an unpleasant or stupid person" in the Compact Oxford English Dictionary, whereas Merriam-Webster has a usage of the term as "usually disparaging and obscene: woman", noting that it is used in the U.S. as "an offensive way to refer to a woman"; and the Macquarie Dictionary of Australian English states that it is "a despicable man". When used with a positive qualifier (good, funny, clever, etc.) in Britain, New Zealand and Australia, it can convey a positive sense of the object or person referred to. Pussy, on the other hand, can indicate "cowardice or weakness", and "the human vulva or vagina" or by extension "sexual intercourse with a woman".
In contemporary art and literature
The Vagina Monologues, a 1996 episodic play by Eve Ensler, has been noted for its success in making female sexuality a topic of public discourse. It is made up of a varying number of monologues read by a number of women. Initially, Ensler performed every monologue herself, with subsequent performances featuring three actresses; latter versions feature a different actress for every role. Each of the monologues deals with an aspect of the feminine experience, touching on matters such as sexual activity, love, rape, menstruation, female genital mutilation, masturbation, birth, orgasm, the various common names for the vagina, or simply as a physical aspect of the body. A recurring theme throughout the pieces is the vagina as a tool of female empowerment, and the ultimate embodiment of individuality.
In Japan, artist Megumi Igarashi has drawn attention for her work featuring vaginas, which she considers "overly hidden" in Japan compared to male genitalia.
Reasons for vaginal modification
With the exception of voluntary vaginoplasty or labiaplasty, modification of the vagina is generally a matter of FGM. Significant controversy surrounds FGM, with the World Health Organization (WHO) being one of many health organizations that have campaigned against the procedures on behalf of human rights, stating that "FGM has no health benefits" and that it is "a violation of the human rights of girls and women" and "reflects deep-rooted inequality between the sexes". The practice has existed at one point or another in almost all human civilizations, most commonly to exert control over the sexual behavior, including masturbation, of girls and women. Custom and tradition are the most frequently cited reasons for FGM, with some cultures believing that not performing it has the possibility of disrupting the cohesiveness of their social and political systems, such as FGM also being a part of a girl's initiation into adulthood. Often, a girl is not considered an adult in a FGM-practicing society unless she has undergone FGM.
FGM is carried out in several countries, especially in Africa, and to a lesser extent in other parts of the Middle East and Southeast Asia, on girls from a few days old to mid-adolescent, often to reduce sexual desire in an effort to preserve vaginal virginity. It may also be that FGM was "practiced in ancient Egypt as a sign of distinction among the aristocracy"; there are reports that traces of infibulation are on Egyptian mummies.
Other animals
See also: Sex organs § MammalsThe vagina (along with the penis) is a general feature of animals in which the female is internally fertilised (other than by traumatic insemination). The shape of the vagina varies among different animals.
In placental mammals and marsupials, the vagina leads from the uterus to the exterior of the female body. Female marsupials have two lateral vaginas, which lead to separate uteri, but both open externally through the same orifice. The urethra and vagina of the female spotted hyena exits through the clitoris, allowing the females to urinate, copulate and give birth through the clitoris.
In birds, monotremes, and some reptiles, a homologous part of the oviduct leads from the shell gland to the cloaca. In some jawless fish, there is neither oviduct nor vagina and instead the egg travels directly through the body cavity (and is fertilised externally as in most fish and amphibians). In insects and other invertebrates, the vagina can be a part of the oviduct (see insect reproductive system).
In 2014, the scientific journal Current Biology reported that four species of Brazilian insects in the genus Neotrogla were found to have sex-reversed genitalia. The male insects of those species have vagina-like openings, while the females have penis-like organs.
See also
References
- Clinical pediatric urology: A. Barry Belman, Lowell R. King, Stephen Alan Kramer (2002)
- Kinetics, Human (15 May 2009). Health and Wellness for Life. Human Kinetics 10%. p. 221. ISBN 978-0-7360-6850-5. Retrieved 30 July 2013.
- ^ Encyclopedia of Family Health. Marshall Cavendish. 2004. p. 964. ISBN 0761474862. Retrieved 25 April 2014.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|authors=ignored (help) Cite error: The named reference "Jacoby" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page). - ^ Dianne Hales (2008). An Invitation to Health Brief 2010-2011. Cengage Learning. pp. 269–271. ISBN 0495391921. Retrieved 29 August 2013.
- ^ New Dimensions in Women's Health. Jones & Bartlett Publishers. 2011. p. 211. ISBN 1449683754. Retrieved 29 August 2013.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|authors=ignored (help) - "Global strategy for the prevention and control of sexually transmitted infections: 2006–2015. Breaking the chain of transmission" (PDF). World Health Organization. 2007. Retrieved 26 November 2011.
- "Princeton University's Wordnet search results for Birth Canal". Princeton. Retrieved 24 May 2010.
- Words meaning vulva ('vagina'), female genitalia Online Slang Dictionary
- Cai Y (2009). "Revisiting old vaginal topics: conversion of the Müllerian vagina and origin of the "sinus" vagina". Int J Dev Biol 2009; 53:925-34. 53 (7): 925–34. doi:10.1387/ijdb.082846yc. PMID 19598112.
- Merz, Eberhard; Bahlmann, F. (2004). Ultrasound in Obstetrics and Gynecology. Vol. 1. Thieme Medical Publishers. p. 129. ISBN 978-1-58890-147-7.
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help) - Schuenke, Michael; Schulte, Erik; Schumacher, Udo (2010). General Anatomy and Musculoskeletal System. Thieme Medical Publishers. p. 192. ISBN 978-1-60406-287-8. Retrieved 9 June 2014.
- ^ Snell, Richard S. (2004). Clinical Anatomy: An Illustrated Review with Questions and Explanations. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 98. ISBN 978-0-7817-4316-7. Retrieved 19 February 2014.
- ^ Hiralal Konar (2014). DC Dutta's Textbook of Gynecology. JP Medical Ltd. pp. 2–7. ISBN 9351520684. Retrieved 9 June 2014.
- ^ Mulhall, John P. (2011). Cancer and Sexual Health. Springer. pp. 13–22. ISBN 1-60761-915-6. Retrieved 21 February 2014.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|editors=ignored (|editor=suggested) (help) - ^ Wylie, Linda (2005). Essential Anatomy and Physiology in Maternity Care. Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 157–158. ISBN 0-443-10041-1. Retrieved 19 February 2014.
- ^ Young, B, ed. (2006). Wheater's Functional Histology: A Text and Colour Atlas (5th ed.). Elsevier. p. 377. ISBN 978-0443068508. Cite error: The named reference "Wheater" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- Brown, Laurence (2012). Pathology of the Vulva and Vagina. Springer Science+Business Media. pp. 6–7. ISBN 0857297570. Retrieved 21 February 2014.
- Oxford Desk Reference: Obstetrics and Gynaecology. Oxford University Press. 2011. p. 471. ISBN 0191620874. Retrieved 21 February 2014.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|authors=ignored (help) - ^ Manual of Obstetrics. (3rd ed.). Elsevier. 2011. pp. 1–16. ISBN 9788131225561.
- Shayne Cox Gad (2008). Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Handbook: Production and Processes. John Wiley & Sons. p. 817. ISBN 0470259809. Retrieved 5 November 2014.
- ^ Charles R. B. Beckmann (2010). Obstetrics and Gynecology. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 241–245. ISBN 0781788072. Retrieved 5 November 2014.
- ^ Knight, Bernard (1997). Simpson's Forensic Medicine (11th ed.). London: Arnold. p. 114. ISBN 0-7131-4452-1.
- Rogers DJ, Stark M (August 1998). "The hymen is not necessarily torn after sexual intercourse". BMJ. 317 (7155): 414. doi:10.1136/bmj.317.7155.414. PMC 1113684. PMID 9694770.
- Perlman, Sally E. (2004). Clinical protocols in pediatric and adolescent gynecology. Parthenon. p. 131. ISBN 1-84214-199-6.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Emans, S. Jean. "Physical Examination of the Child and Adolescent" (2000) in Evaluation of the Sexually Abused Child: A Medical Textbook and Photographic Atlas, Second edition, Oxford University Press. 61-65
- ^ Sloane, Ethel (2002). Biology of Women. Cengage Learning. pp. 32, 41–42. ISBN 0-7668-1142-5. Retrieved 19 February 2014.
- Bourcier, A.; McGuire, Edward J.; Abrams, Paul (2004). Pelvic Floor Disorders. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 20. ISBN 0-7216-9194-3. Retrieved 19 February 2014.
- Wiederman, Michael W.; Whitley, Jr., Bernard E. (1 August 2001). Handbook for Conducting Research on Human Sexuality. Psychology Press. p. 143. ISBN 978-1-135-66340-7. Retrieved 19 February 2014.
- "Vagina". health.discovery.com. Retrieved 11 February 2012.
- ^ Weiten, Wayne; Dunn, Dana; Hammer, Elizabeth (1 January 2011). Psychology Applied to Modern Life: Adjustment in the 21st Century. Cengage Learning. p. 386. ISBN 1-111-18663-4. Retrieved 19 February 2014.
- ^ Martha Tara Lee (2013). Love, Sex and Everything in Between. Marshall Cavendish International Asia Pte Ltd. p. 76. ISBN 9814516783. Retrieved 27 October 2014.
- ^ Sex and Society, Volume 2. Marshall Cavendish Corporation. 2009. p. 590. ISBN 9780761479079. Retrieved 17 August 2012.
- ^ Exploring the Dimensions of Human Sexuality. Jones & Bartlett Publishers. 2014. pp. 102–104. ISBN 1449648517. Retrieved 30 October 2014.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|authors=ignored (help) - ^ Hines T (August 2001). "The G-Spot: A modern gynecologic myth". Am J Obstet Gynecol. 185 (2): 359–62. doi:10.1067/mob.2001.115995. PMID 11518892.
- ^ Human Sexuality: An Encyclopedia. Routledge. 2014. pp. 229–231. ISBN 1135825092. Retrieved 30 October 2014.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|authors=ignored (help) - ^ Exploring the Dimensions of Human Sexuality. Jones & Bartlett Publishers. 2010. p. 126. ISBN 9814516783. Retrieved 27 October 2014.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|authors=ignored (help) - ^ Clinical Manual of Sexual Disorders. American Psychiatric Pub. 2009. p. 258. ISBN 1585629057. Retrieved 21 February 2014.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|authors=ignored (help) - Rosenthal, Martha (6 January 2012). Human Sexuality: From Cells to Society. Cengage Learning. p. 76. ISBN 0-618-75571-3. Retrieved 19 February 2014.
- Carroll, Janell (2012). Discovery Series: Human Sexuality. Cengage Learning. pp. 282–289. ISBN 1111841896. Retrieved 9 June 2014.
- Taormino, Tristan (2009). The Big Book of Sex Toys. Quiver. p. 52. ISBN 978-1-59233-355-4. Retrieved 9 June 2014.
- ^ O'Connell HE, Sanjeevan KV, Hutson JM (October 2005). "Anatomy of the clitoris". The Journal of Urology. 174 (4 Pt 1): 1189–95. doi:10.1097/01.ju.0000173639.38898.cd. PMID 16145367.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|laydate=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|laysource=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|laysummary=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Kilchevsky A, Vardi Y, Lowenstein L, Gruenwald I. (January 2012). "Is the Female G-Spot Truly a Distinct Anatomic Entity?". The Journal of Sexual Medicine. 2011 (3): 719–26. doi:10.1111/j.1743-6109.2011.02623.x. PMID 22240236.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|laydate=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|laysource=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|laysummary=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ The Reproductive System at a Glance. John Wiley & Sons. 2014. p. 39. ISBN 1118607015. Retrieved 30 October 2014.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|authors=ignored (help) - Color Atlas of Physiology. Thieme. 2011. p. 310. ISBN 1449648517. Retrieved 30 October 2014.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|authors=ignored (help) - ^ Danielsson, D., P. K. Teigen, and H. Moi. 2011. The genital econiche: Focus on microbiota and bacterial vaginosis" Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci 1230:48-58
- "Vaginal Problems — Home Treatment". Women's Health. WebMD, LLC. Retrieved 28 August 2009.
- ^ "The Vagina (Human Anatomy)". WebMD. Retrieved 27 April 2014.
- ^ See, e.g., Colin Hinrichsen, Peter Lisowski, Anatomy Workbook (2007), p. 101: "Digital examination per vaginam are made by placing one or two fingers in the vagina".
- Anderson, Douglas M, ed. (2002). Mosby's Medical, Nursing & Allied Health Dictionary (6th UK ed.). St. Louis, Missouri, USA: Mosby. p. 1324. ISBN 0-7234-3225-2.
- ^ Vaginal pH Test from Point of Care Testing, July 2009, at: University of California, San Francisco – Department of Laboratory Medicine. Prepared by: Patricia Nassos, PhD, MT and Clayton Hooper, RN.
- Todar, Kenneth (2008). "The Nature of Bacterial Host-Parasite Relationships in Humans". Online Textbook of Bacteriology. Retrieved 28 August 2009.
- "Bartholin cyst". Mayo Clinic.com. 19 January 2010. Retrieved 18 August 2011.
- Hagen S, Stark D (2011). "Conservative prevention and management of pelvic organ prolapse in women". Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 12: CD003882. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003882.pub4. PMID 22161382.
- ^ Lloyd, Jillian et al. "Female genital appearance: 'normality' unfolds", British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, May 2005, 112(5), pp. 643–646. PMID 15842291
- ^ Crooks, Robert; Baur, Karla (2010). Our Sexuality. Cengage Learning. pp. 55–56. ISBN 978-0-495-81294-4. Retrieved 9 June 2014.
- ^ "Female genital mutilation". World Health Organization. Retrieved 22 August 2012.
- Stone, Linda (2002). New Directions in Anthropological Kinship. Rowman & Littlefield Publishers. p. 164. ISBN 058538424X. Retrieved 9 June 2014.
- Hutcherson, Hilda (2003). What Your Mother Never Told You about Sex. Penguin. p. 8. ISBN 0399528539. Retrieved 9 June 2014.
- LaFont, Suzanne (2003). Constructing Sexualities: Readings in Sexuality, Gender, and Culture. Prentice Hall. p. 145. ISBN 013009661X. Retrieved 9 June 2014.
- Angier, Natalie (1999). Woman: An Intimate Geography. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. p. 92. ISBN 978-0-395-69130-4. Retrieved 9 June 2014.
- ^ Maines, Rachel P. (1998). The Technology of Orgasm: "Hysteria", the Vibrator, and Women's Sexual Satisfaction. Baltimore: The Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 0-8018-6646-4.
- ^ Ensler, Eve (2001). The Vagina Monologues: The V-Day Edition. Random House LLC. ISBN 0375506586. Retrieved 9 June 2014.
- Morton, Mark (2004). The Lover's Tongue: A Merry Romp Through the Language of Love and Sex. Toronto, Canada: Insomniac Press. ISBN 978-1-894663-51-9.
- "Definition of CUNT". Dictionary – Merriam-Webster online. Merriam-Webster. Retrieved 9 June 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - "cunt". Merriam-Webster's Learner's Dictionary. Merriam-Webster. Retrieved 13 September 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - For example, Glue by Irvine Welsh, p.266, "Billy can be a funny cunt, a great guy..."
- "pussy, n. and adj.". Oxford English Dictionary (third ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. 2007.
- Coleman, Christine (2006). Coming to Read "The Vagina Monologues": A Biomythographical Unravelling of the Narrative. University of New Brunswick. ISBN 0494466553. Retrieved 9 June 2014.
- McCurry, Justin (15 July 2014). "Vagina selfie for 3D printers lands Japanese artist in trouble". The Guardian. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- ^ Momoh, Comfort (2005). "Female Genital Mutation". In Momoh, Comfort (ed.). Female Genital Mutilation. Radcliffe Publishing. pp. 5–12. ISBN 978-1-85775-693-7.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Luckett, W.P. 1977. Ontogeny of amniote fetal membranes and their application to phylogeny. Major patterns in Vertebrate Evolution. New York, London: Plenum Publishing Corporation. p 439-516
- Szykman. M., Van Horn, R. C., Engh, A.L. Boydston, E. E. & Holekamp, K. E. (2007) Courtship and mating in free-living spotted hyenas. Behaviour. 144: 815–846.
- Iannaccone, Philip (1997). Biological Aspects of Disease. CRC Press. pp. 315–316. ISBN 3718606135. Retrieved 9 June 2014.
- Comparative Anatomy: Manual of Vertebrate Dissection. Morton Publishing Company. 2012. pp. 66–68. ISBN 1617310042. Retrieved 9 June 2014.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|authors=ignored (help) - The Insects: Structure and Function. Cambridge University Press. 2013. pp. 314–316. ISBN 052111389X. Retrieved 9 June 2014.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|authors=ignored (help) - http://www.theverge.com/2014/4/17/5617766/scientists-discover-insect-with-female-penis
- Kazunori Yoshizawae; Rodrigo L. Ferreira; Yoshitaka Kamimura; Charles Lienhard (17 April 2014). "Female Penis, Male Vagina, and Their Correlated Evolution in a Cave Insect". Current Biology. Retrieved 27 April 2014.
- Cell Press (17 April 2014). "In sex-reversed cave insects, females have the penises". Science Daily. Retrieved 27 April 2014.
External links
- [REDACTED] Media related to Vaginas at Wikimedia Commons
- [REDACTED] The dictionary definition of vagina at Wiktionary
| Female reproductive system | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Internal |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Blood supply | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Human regional anatomy | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body | Skin | ||||
| Head | |||||
| Neck | |||||
| Torso (Trunk) | |||||
| Limbs |
| ||||