| Revision as of 16:14, 2 November 2006 editCmh (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users2,749 edits correct revert← Previous edit | Revision as of 19:30, 3 November 2006 edit undo207.156.196.242 (talk) →Presence in foodNext edit → | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
| Chemically, trans fats are made of the same building blocks as non-trans fats, but have a different shape. In trans fat ]s, the ]s between ] ]s (characteristic of all unsaturated fats) are in the '']'' rather than the '']'' configuration, resulting in a more straight rather than a kinked shape. As a result, trans fats are less fluid and have a higher melting point than the equivalent cis fats. | Chemically, trans fats are made of the same building blocks as non-trans fats, but have a different shape. In trans fat ]s, the ]s between ] ]s (characteristic of all unsaturated fats) are in the '']'' rather than the '']'' configuration, resulting in a more straight rather than a kinked shape. As a result, trans fats are less fluid and have a higher melting point than the equivalent cis fats. | ||
| Everything in here is true!!! | |||
| ==Presence in food== | ==Presence in food== | ||
Revision as of 19:30, 3 November 2006
| Types of fats in food |
|---|
| Components |
| Manufactured fats |
Trans fatty acids (commonly termed trans fats) are a type of unsaturated fat (and may be monounsaturated or polyunsaturated).
Trans fats occur naturally, in small quantities, in meat and dairy products from ruminants. Most trans fats consumed today, however, are industrially created through partial hydrogenation of plant oils and animal fats — a chemical process developed in the early 1900s and first commercialized as Crisco in 1908. Unlike other fats, trans fats are neither required nor beneficial for health. Eating trans fat increases the risk of coronary heart disease. For these reasons, health authorities worldwide recommend that consumption of trans fat be reduced to trace amounts. Trans fats from partially hydrogenated oils are generally considered to be worse than those occurring naturally.
Trans fats are increasingly being linked to chronic health conditions (see below), are tightly regulated in a few countries, are mandatory on product labels in many others, and are the central issue in several ongoing lawsuits (particularly against fast food outlets). Many companies are voluntarily removing trans fats from their products, or establishing trans-free product lines.
Chemically, trans fats are made of the same building blocks as non-trans fats, but have a different shape. In trans fat molecules, the double bonds between carbon atoms (characteristic of all unsaturated fats) are in the trans rather than the cis configuration, resulting in a more straight rather than a kinked shape. As a result, trans fats are less fluid and have a higher melting point than the equivalent cis fats.
Everything in here is true!!!
Presence in food

Trans fats occur naturally in the milk and body fat of ruminants (such as cows and sheep) at a level of 2-5% of total fat. They originate in the rumens of these animals. Animal-based fats were once the only trans fats consumed, but by far the largest amount of trans fat consumed today is created by the processed food industry by partially hydrogenating unsaturated plant fats (generally vegetable oils). These have displaced natural solid fats and liquid oils in many areas, notably in the fast food, snack food, fried food and baked good industries. Vegetable shortenings are primarily trans fats packaged for home use, and some margarines contain a large proportion of them. Foods containing artificial trans fats formed by partially hydrogenating plant fats may contain up to 45% trans fat compared to their total fat.
Benefits of hydrogenating plant-based fats for food manufacturers include an increased product shelf life and decreased refrigeration requirement. Partial hydrogenation raises the melting point of fat, producing a semi-solid material, which is much more desirable than liquid oils for use in baking. Plant-based hydrogenated vegetable oils are much less expensive than the animal fats traditionally favored by bakers, such as butter or lard, and may be more readily available or less expensive than semi-solid plant fats such as palm oil.
Because partial hydrogenation of plant oils can replace animal fats, the resulting products can be consumed (barring other ingredient and preparation violations) by adherents to Kashrut (kosher) and Halal, as well as by adherents to vegetarianism in Buddhism, ahimsa in Jainism and Hinduism, veganism, and other forms of vegetarianism.
It has been established that trans fats in human milk fluctuate with maternal consumption of trans fat, and that the amount of trans fats in the bloodstream of breastfed infants fluctuates with the amounts found in their milk. Reported percentages of trans (compared to total fats) in human milk range from 1% in Spain, 2% in France and 4% in Germany to 7% in Canada.
Nutritional guidelines
The National Academy of Sciences (NAS) advises the United States and Canadian governments on nutritional science for use in public policy and product labelling programs. Their 2002 Dietary reference intakes for Energy, Carbohydrate, Fiber, Fat, Fatty Acids, Cholesterol, Protein, and Amino Acids contains their findings and recommendations regarding consumption of Trans fat (summary).
Their recommendations are based on two key facts. First, "trans fatty acids are not essential and provide no known benefit to human health", whether of animal or plant origin. Second, while both saturated and trans fats increase levels of LDL cholesterol (so-called "bad" cholesterol), trans fats also lower levels of HDL cholesterol (so-called "good" cholesterol) ; this increases the risk of coronary heart disease (CHD). The NAS is concerned "that dietary trans fatty acids are more deleterious with respect to CHD than saturated fatty acids". This analysis is supported by a 2006 New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM) scientific review that states "from a nutritional standpoint, the consumption of trans fatty acids results in considerable potential harm but no apparent benefit."
Because of these facts and concerns, the NAS has concluded there is no safe level of trans fat consumption. There is no adequate level, recommended daily amount or tolerable upper limit for trans fats. This is because any incremental increase in trans fat intake increases the risk of coronary heart disease.
Despite this concern, the NAS dietary recommendations have not recommended the elimination of trans fat from the diet. This is because trans fat is naturally present in many animal foods, and therefore in most non-vegan diets; its removal from ordinary diets might introduce undesirable side effects and nutritional imbalances if proper nutritional planning is not undertaken. The NAS has therefore "recommended that trans fatty acid consumption be as low as possible while consuming a nutritionally adequate diet" . Like the NAS, the World Health Organization has tried to balance public health goals with a practical level of trans fat consumption, recommending in 2003 that trans fats be limited to less than 1% of overall energy intake.
The US National Dairy Council has asserted that the trans fats present in animal foods are of a different type than those in partially hydrogenated oils, and do not appear to exhibit the same negative effects . While a recent scientific review agrees with the conclusion (stating that "the sum of the current evidence suggests that the public health implications of consuming trans fats from ruminant products are relatively limited") it cautions that this may be due to the relatively low consumption of trans fats from animal sources compared to artificial ones.
History

Nobel laureate Paul Sabatier worked in the 1890s to develop the chemistry of hydrogenation which enabled the margarine, oil hydrogenation, and synthetic methanol industries. While Sabatier only considered hydrogenation of vapours, the German chemist Wilhelm Normann showed in 1901 that liquid oils could be hydrogenated and patented the process in 1902. In 1909, Procter & Gamble acquired the US rights to the Normann patent; in 1911, they began marketing the first hydrogenated shortening, Crisco (composed largely of partially hydrogenated cottonseed oil). Further success came from the marketing technique of giving away free cookbooks with every recipe calling for Crisco. Hydrogenation strongly stimulated whaling, as it made it possible to stabilize whale oil for human consumption.
Production of trans fats increased steadily until the 1960s as artificially created trans fats replaced saturated animal fats in the US and other western countries. At first, the argument was a financial one due to lower costs, however, advocates also said that the trans fats of margarine were healthier than the saturated fats of butter.
There were suggestions in the scientific literature as early as 1988 that trans fats could be a cause of the large increase in coronary artery disease. In 1994, it was estimated that trans fats caused 30,000 deaths annually in the US from heart disease.
The Center for Science in the Public Interest (CSPI) campaigned against fast foods using saturated fats starting in 1984. When fast food companies replaced the saturated fat with trans fat, CSPI's campaign against them ended. CSPI defended trans fats in their 1987 Nutrition Action newsletter. However, by 1992, CSPI began to speak against trans fats and is currently strongly against their use.
Chemistry
In a natural fatty acid, the hydrogen atoms are usually on the same side of the double bonds of the carbon chain. However, partial hydrogenation reconfigures most of the double bonds that do not become chemically saturated, twisting them so that the hydrogen atoms end up on different sides of the chain. This type of configuration is called trans, which means "across" in Latin.
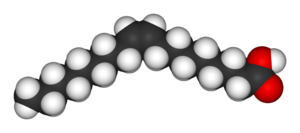
| Oleic acid | Elaidic acid |
|---|---|
| Oleic acid is a cis unsaturated fat that comprises 55-80% of olive oil. | Elaidic acid is a trans unsaturated fat and a major trans fat found in hydrogenated vegetable oils. |
 |
 |
 |
|
| These fats are geometric isomers (chemically identical except for the arrangement of the double bond). | |
The conversion from cis to trans configuration is a catalytic reaction, meaning that another atom is temporarily bonded into the fat during the conversion process and then released. The other elements used (the catalysts) are finely divided nickel, palladium, platinum or cobalt.
The amount of trans fat in the product is dependent on reaction conditions. Increasing the pressure at which an oil is hydrogenated reduces trans fat formation. Researchers at the United States Department of Agriculture applied 1400 kPa (200 psi) of pressure to soybean oil in a 2-litre vessel while heating it to between 140°C and 170°C. The standard 140 kPa (20 psi) process of hydrogenation produces a product of about 40% trans fat by weight, compared to about 17% using the high pressure method. Blended with unhydrogenated liquid soybean oil, the high pressure processed oil produced margarine containing 5 to 6% trans fat which could qualify for a label of zero grams of trans fat.
Trans fats are formed from a process described as partial hydrogenation because the reaction is not allowed to go to completion; if it were there would be no trans fat left, but the resulting material would be too solid for practical use. A notable exception is The J.M. Smucker Company's new Crisco formulation made from solid fully hydrogenated palm oil cut with soybean oil and sunflower oil. This is blended with liquid vegetable oils to yield a shortening much like the previous partially hydrogenated Crisco which was made from partially hydrogenated vegetable oil.
Health effects
Partially hydrogenated vegetable oils have been a significant part of the human diet for just over 100 years, and some deleterious effects of trans fat consumption are scientifically accepted, forming the basis of the health guidelines discussed above.
The exact biochemical methods by which trans fats produce specific health problems are a topic of continuing research. For example, the mechanisms through which trans fats contribute to coronary heart disease are fairly well understood, while the mechanism for trans fat's effect on diabetes is under investigation.
Coronary heart disease
The primary health risk identified for trans fat consumption is an elevated risk of coronary heart disease (CHD). A comprehensive review of studies of trans fats was published in 2006 in the New England Journal of Medicine that concludes that there is a strong and reliable connection between trans fats and CHD.
The major evidence for the effect of trans fat on CHD comes from the Nurses' Health Study (NHS) — a cohort study that has been following 120,000 female nurses since its inception in 1976.
Hu and colleagues analyzed data from 900 coronary events from the NHS population during 14 years of followup. He determined that a nurse's CHD risk roughly doubled (relative risk of 1.94) for each 2% increase in trans fat calories consumed (instead of carbohydrate calories). By contrast, it takes more than a 15% increase in saturated fat calories (instead of carbohydrate calories) to produce a similar increase in risk. Eating non-trans unsaturated fats instead of carbohydrates reduces the risk of CHD rather than increasing it.
Hu also reports on the benefits of reducing trans fat consumption. Replacing 2% of food energy from trans fat with non-trans unsaturated fats more than halves the risk of CHD (53%). By comparison, replacing a larger 5% of food energy from saturated fat with non-trans unsatured fats reduces the risk of CHD by 43%.
There are two accepted measures of risk for coronary heart disease, both blood tests. The first considers ratios of two types of cholesterol, the other the amount a cell-signalling cytokine called C-reactive protein. The ratio test is more accepted, while the cytokine test may be more powerful but is still being studied. The effect of trans fat consumption has been documented on each as follows:
- Cholesterol ratio: This ratio compares the levels of LDL (so-called "bad" cholesterol) to HDL (so-called "good" cholesterol). Trans fat behaves like saturated fat by raising the level of LDL, but unlike saturated fat it has the additional effect of decreasing levels of HDL. The net increase in LDL/HDL ratio with trans fat is approximately double that due to saturated fat. (Higher ratios are worse.)
- C-reactive protein (CRP): A study of over 700 nurses showed that those in the highest quartile of trans fat consumption had blood levels of CRP that was 73% higher than those in the lowest quartile.
Another study considered deaths due to CHD, with consumption of trans fats being linked to an increase in mortality, and consumption of polyunsaturated fats being linked to a decrease in mortality.
Other effects
There has been suggestion that the negative consequences of trans fat consumption go beyond the cardiovascular risk. In general, there is much less scientific consensus that eating trans fat specifically increases the risk of other chronic health problems:
- Cancer: There is no scientific consensus that consumption of trans fats significantly increases cancer risks across the board. The American Cancer Society states that a relationship between trans fats and cancer "has not been determined." However, one recent study has found connections between trans fat and prostate cancer.
- Diabetes: There is a growing concern that the risk of type 2 diabetes increases with trans fat consumption. However, consensus has not been reached. For example, one study found that risk is higher for those in the highest quartile of trans fat consumption. Another study has found no diabetes risk once other factors such as total fat intake and BMI were accounted for.
- Obesity: Research with monkeys indicates that trans fat may increase weight gain and abdominal fat, despite a similar caloric intake . A 6-year experiment revealed that monkeys fed a trans-fat diet gained 7.2% of their body weight, as compared to 1.8% for monkeys on a mono-unsaturated fat diet. Although obesity is frequently linked to trans fat in the popular media, this is generally in the context of eating too many calories; there is no scientific consensus connecting trans fat and obesity.
- Liver Dysfunction: Trans fats are metabolized differently by the liver than other fats and interfere with delta 6 desaturase. Delta 6 desaturase is an enzyme involved in converting essential fatty acids to arachidonic acid and prostaglandins, both of which are important to the functioning of cells.
Public response and regulation
The lengthy political process of balancing the public health versus private profit from the public sale of processed foods containing artificially hydrogenated oils and fats continues today. Some countries are considering a complete ban against artificial hydrogenation products in food.
Canada
Canada is one of the largest consumers of trans fats in the world . The food regulator, Health Canada requires the listing of the amount of trans fats in the food described.
In November 2004, an opposition day motion seeking a ban similar to Denmark's was introduced by Jack Layton of the New Democratic Party, and passed through the House of Commons by an overwhelming 193-73 vote.
In June 2006, a task force co-chaired by Health Canada and the Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada recommended a limit of 5% trans fat (to total fat) ratio in all products sold to consumers in Canada (2% for tub margarines and spreads). The amount was selected such that "most of the industrially produced trans fats would be removed from the Canadian diet, and about half of the remaining trans fat intake would be of naturally occurring trans fats". This recommendation has been endorsed by the Canadian Restaurant and Foodservices Association and the Food and Consumer Products of Canada has congratulated the task force on the report.
KFC will switch to trans-fat free Canadian canola oil by early 2007..
Denmark
Denmark became the first country to introduce laws strictly regulating the sale of many foods containing trans fats in March 2003, a move which effectively bans partially hydrogenated oils. Naturally present trace amounts of trans fats in dairy and meat products are unaffected by these bills. The UK campaigning body tfX offers an English translation on its Denmark's trans fat law page.
European Union
The European Food Safety Authority was asked to produce a scientific opinion on trans fats.
United Kingdom
In October 2005, the Food Standards Agency (FSA) asked for better labelling in the UK. In the 29 July 2006 edition of the British Medical Journal, an editorial also called for better labelling.
Some companies such as Marks & Spencer and Waitrose have voluntarily removed or reduced trans fats from their products. Two major supermarkets will be withdrawing trans fats from their own-brand products: Sainsbury's from January 2007 and Tesco by the end of 2006.
United States
In May 2003, BanTransFats.com Inc., a U.S. non-profit corporation, filed a lawsuit against the food manufacturer Kraft Foods in an attempt to force Kraft to remove trans fats from the Oreo cookie. The lawsuit was withdrawn when Kraft agreed to work on ways to find a substitute for the trans fat in the Oreo. This suit was very effective at bringing the trans fat controversy to public attention.
Before 2006, consumers in the United States could not easily determine the presence (or quantity) of trans fats in food products. This information could only be inferred by reading the ingredient list on the food label. If the ingredients included the words "shortening," "partially hydrogenated vegetable oil," or "hydrogenated vegetable oil," the food probably contained trans fat. Because ingredients are listed in descending order of predominance, smaller amounts are present when the ingredient is close to the end of the list.
Some consumer advocates wanted a ban on trans fats in the US, but the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) responded with a labelling requirement instead. On July 9, 2003, the FDA issued a regulation (21 CFR 101.9 (c)(2)(ii)) requiring manufacturers to list trans fat on the Nutrition Facts panel of foods and some dietary supplements. This new information must appear below the listing of saturated fat content, which was already required. The regulation allows trans fat levels of less than 0.5 grams per serving to be labeled as 0 grams per serving, or trans fat free. (In this case, manufacturers may use the synonyms "free", "without," "no" and "zero" in their packaging claims.) However, it should be noted that small amounts may be significant, depending on how many servings are consumed. The FDA defines trans fats as containing one or more trans linkages that are not in a conjugated system. This is an important distinction, as it distinguishes synthetic trans fats from naturally occurring fatty acids with conjugated trans double bonds, such as conjugated linoleic acid, which may be beneficial.
The new labeling rule took effect January 1, 2006. The FDA created a process where companies may petition for an extension that will be reviewed on a case-by-case basis. Extensions will be granted until January 1, 2008. The FDA estimates that by 2009, trans fat labeling will have prevented from 600 to 1,200 cases of coronary heart disease and 250 to 500 deaths each year. This benefit is expected to result from consumers choosing alternative foods lower in trans fats as well as manufacturers reducing the amount of trans fats in their products.
While the FDA regulation was strictly a labeling directive, many food manufacturers used the 2006 deadline as a target date to reduce or eliminate trans fats from their products. This required some experimentation with alternative oils in an attempt to preserve the flavor and "mouth feel" of the food while maximizing shelf life. The solution for some products was a return to the saturated fats and tropical oils abandoned twenty years earlier, when saturated fats were a high-profile health concern. Another solution was the use of new soybean varieties and processing methods, which produce oils with many of the desirable characteristics of hydrogenated oils without requiring hydrogenation.
The movement away from trans fat has been seen in restaurant chains as well. In June 2006, the fast food chain Wendy's announced that they would switch to non-hydrogenated cooking oil to reduce trans fat. In June 2006, the Panera Bread food chain removed trans fats from all breads and bagels, and most of their other baked goods.
The Center for Science in the Public Interest sued KFC over its use of trans fats in fried foods. KFC reviewed alternative oil options, saying "there are a number of factors to consider including maintaining KFC's unique taste and flavor of Colonel Sanders' Original Recipe". On October 30, 2006, KFC announced that it will replace the partially hydrogenated soybean oil it currently uses with a trans-fat free low linolenic soybean oil in all restaurants in the US by April 2007: its biscuits will still contain trans-fats.
Some cities are making an effort to reduce trans fat consumption. New York City has asked all its restaurants to eliminate trans fat from their offerings, on a voluntary basis. On September 26, 2006, the New York City Board of Health voted unanimously to prohibit the city’s restaurants from serving food that contains artificial trans fats. There will be a period for written public comments, a public hearing on October 30, and a final vote in December. If approved, this would make New York the first large city in the country to strictly limit trans fats in restaurants. In May 2005, Tiburon, California, became the first American city where all restaurants voluntarily cook with trans fat-free oils. Chicago is considering banning oils containing trans fats from large chain restaurants; assuming the New York bill goes through, the ordinance would make Chicago the second American city to ban trans fat-containing oils outright.
The Walt Disney Company will begin getting rid of trans fats in meals at domestic theme parks (Disneyland, Walt Disney World, etc.) by the end of 2007. They will also be stopping the inclusion of trans fats in licensed or promotional products by 2008.
References
- ^ Nat' Academies Press, Dietary Reference Intakes for Energy, Carbohydrate, Fiber, Fat, Fatty Acids, Cholesterol, Protein, and Amino Acids (Macronutrients) (2005) page 423
- ^ Nat' Academies Press, Dietary Reference Intakes for Energy, Carbohydrate, Fiber, Fat, Fatty Acids, Cholesterol, Protein, and Amino Acids (Macronutrients) (2005) page 504
- ^ Mozaffarian D, Katan MB, Ascherio A, Stampfer MJ, Willett WC (2006). "Trans Fatty Acids and Cardiovascular Disease". New England Journal of Medicine. 354 (15): 1601–1613.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|day=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) PMID 16611951 - ^ Health Canada / Santé Canada TRANSforming the Food Supply
- Innis, Sheila M and King, D Janette (1999). "trans Fatty acids in human milk are inversely associated with concentrations of essential all-cis n-6 and n-3 fatty acids and determine trans, but not n-6 and n-3, fatty acids in plasma lipids of breast-fed infants". American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 70 (3): 383–390.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Nat' Academies Press, Dietary Reference Intakes for Energy, Carbohydrate, Fiber, Fat, Fatty Acids, Cholesterol, Protein, and Amino Acids (Macronutrients) (2005) page i
- Nat' Academies Press, Dietary Reference Intakes for Energy, Carbohydrate, Fiber, Fat, Fatty Acids, Cholesterol, Protein, and Amino Acids (Macronutrients) (2005) page 447
- Nat' Academies Press, Dietary Reference Intakes for Energy, Carbohydrate, Fiber, Fat, Fatty Acids, Cholesterol, Protein, and Amino Acids (Macronutrients) (2005) page 424
- National Dairy Council letter
- Paul Sabatier Biography at the Nobel prize site. (Reprinted from Nobel Lectures, Chemistry 1901-1921, Elsevier Publishing Company, Amsterdam, 1966.)
- HBW Patterson (2001) "Hydrogenation" SCI Lectures Paper Series
- History of Soybeans and Soyfoods: 1100 B.C. to the 1980s. Unpublished manuscript by William Shurtleff and Akiko Aoyagi
- ^ Ascherio A, Stampfer MJ, Willett WC. "Trans fatty acids and coronary heart disease". Retrieved 2006-09-14.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Booyens J, Louwrens CC, Katzeff IE (1988). "The role of unnatural dietary trans and cis unsaturated fatty acids in the epidemiology of coronary artery disease". Medical Hypotheses. 25 (3): 175–182.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) PMID 3367809 - Willett WC, Ascherio A (1995). "Trans fatty acids: are the effects only marginal?". American Journal of Public Health. 85 (3): 411–412. PMID 8179036
- Mary G. Enig, PhD. "The Tragic Legacy of Center for Science in the Public Interest (CSPI)". Retrieved 2006-05-02.
- FJ Eller (2005). "Preparation of spread oils meeting U.S. Food and Drug Administration Labeling requirements for trans fatty acids via pressure-controlled hydrogenation". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 53 (15): 5982–5984. PMID 16028984.
- Crisco nutritional facts
- ^ TRANSforming the food supply, Appendix 9iiiConsultation on the health implications of alternatives to trans fatty acids: Summary of Responses from Experts
- ^ Hu, FB (1997). "Dietary fat intake and the risk of coronary heart disease in women". New England Journal of Medicine. 337 (21): 1491–1499.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) PMID 9366580. Online Copy (free with registration). - A Ascherio (1999). "Trans fatty acids and coronary heart disease". New England Journal of Medicine. 340 (25): 1994–1998.
- Esther Lopez-Garcia (2005). "Consumption of Trans Fatty Acids Is Related to Plasma Biomarkers of Inflammation and Endothelial Dysfunction". The Journal of Nutrition. 135 (3): 562–566. PMID 15735094.
- Oh, K (2005). "Dietary fat intake and risk of coronary heart disease in women: 20 years of follow-up of the nurses' health study". American Journal of Epidemiology. 161 (7): 672–679.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) PMID 15781956 - Common questions about diet and cancer
- Chavarro et al., "A prospective study of blood trans fatty acid levels and risk of prostate cancer," Proc. Amer. Assoc. Cancer Res., Volume 47, 2006
- Hu, FB (2001). "Diet and risk of Type II diabetes: the role of types of fat and carbohydrate". Diabetologia. 44 (7): 805–817.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) PMID 11508264 - van Dam RM, Stampfer M, Willett WC, Hu FB, Rimm EB (2002). "Dietary fat and meat intake in relation to risk of type 2 diabetes in men". Diabetes care. 25 (3): 417–424.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) PMID 11874924 - Gosline, Anna Why fast foods are bad, even in moderation New Scientist 12 June 2006
- e.g. Trans Fat Press Conference by Tommy G. Thompson, US Secretary of health and human services
- M Mahfouz (1981). "Effect of dietary trans fatty acids on the delta 5, delta 6 and delta 9 desaturases of rat liver microsomes in vivo". Acta biologica et medica germanica. 40 (12): 1699–1705.
- Health Canada Trans Fat
- "Dosanjh snubs House, MP says". Retrieved 2006-05-02.
- Restaurant industry commits to Trans Fat Task Force recommendations
- Food industry congratulates Trans Fat Task Force on report
- KFC Canada phasing in zero grams trans fat menu in all 786 restaurants nationally early in the new year (press release)
- European Food Safety Authority Opinion of the Scientific Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies on a request from the Commission related to the presence of trans fatty acids in foods and the effect on human health of the consumption of trans fatty acids The EFSA Journal (2004) 81, 1-49
- Gray, Richard (February 5, 2006). "Forced to own up to the killer fat in our food". Scotsman.com.
- BBC 27 July 2006 Call to label hidden fats in food
- Clarke, Robert; Lewington, Sarah Trans fatty acids and coronary heart disease British Medical Journal 2006;333:214 (29 July), doi:10.1136/bmj.333.7561.214
- Marks & Spencer To Remove Hydrogenated Fats From All Foods By Mid 2006
- Waitrose - going trans-free
- The Guardian (Sarah Hall) Supermarket chains to curb use of trans fats 3 August 2006
- Trans Fatty Acids in Nutrition Labeling
- "FDA Acts to Provide Better Information to Consumers on Trans Fats". Food and Drug Administration. Retrieved 2005-07-26.
- Panera Bread® Product Nutrition Information
- KFC Sued for Fouling Chicken with Partially Hydrogenated Oil: Lawsuit Aimed at Eliminating, or Disclosing Use of Artery-Clogging Frying Oil
- Class Action Complaint
- The New York Times (Marian Burros) KFC Is Sued Over the Use of Trans Fats in Its Cooking 14 June 2006
- KFC announces switch to zero trans fat cooking oil following two-year test for same great taste (press release)
- BBC (Guto Harri) KFC cuts out unhealthy trans-fats 30 October 2006
- City of New York press release: HEALTH DEPARTMENT ASKS RESTAURATEURS AND FOOD SUPPLIERS TO VOLUNTARILY MAKE AN OIL CHANGE AND ELIMINATE ARTIFICIAL TRANS FAT
- New York City Plans Limits on Restaurants’ Use of Trans Fats
- Project Tiburon of Ban Trans Fats
- Burke Serves Up Another Trans Fat Plan Southwest News Herald article
- Disney to serve healthier foods at parks Yahoo! news article on plans to eliminate trans fats in Disney's theme parks
