| Revision as of 12:05, 13 May 2019 editWidefox (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Extended confirmed users, Page movers, IP block exemptions, New page reviewers, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers107,113 edits →Adverse effects: link, dubious← Previous edit | Revision as of 14:22, 13 May 2019 edit undoZefr (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, Pending changes reviewers69,656 edits →Adverse effects: rewrite, add reviewsNext edit → | ||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
| ==Adverse effects== | ==Adverse effects== | ||
| In rare cases, lavender oil in soaps, shampoos, and other skin applied medications may cause ] ] (breast development in young boys).<ref>{{Cite journal|last=Henley|first=Derek V.|last2=Lipson|first2=N|last3=Korach|first3=KS|last4=Bloch|first4=CA|date=2007|title=Prepubertal gynecomastia linked to lavender and tea tree oils|journal=New England Journal of Medicine|volume=356|issue=5|pages=479–485|doi=10.1056/NEJMoa064725|issn=0028-4793|pmid=17267908}}</ref> Other potential ]s include a ] effect and ] as an ], possibly resulting from major lavender oil constituents, ], ], ] and ].<ref name="Els">{{cite journal | last=Elshafie | first=Hazem S. | last2=Camele | first2=Ippolito | title=An overview of the biological effects of some Mediterranean essential oils on human health | journal=BioMed Research International | volume=2017 | date=5 November 2017 | issn=2314-6133 | pmid=29230418 | pmc=5694587 | doi=10.1155/2017/9268468 | pages=1–14}}</ref><ref name="Sarkic">{{cite journal | last=Sarkic | first=Asja | last2=Stappen | first2=Iris | title=Essential oils and their single compounds in cosmetics: A critical review | journal=Cosmetics | volume=5 | issue=1 | date=12 January 2018 | issn=2079-9284 | doi=10.3390/cosmetics5010011 | url=https://www.mdpi.com/2079-9284/5/1/11/htm}}</ref> | |||
| Consumption of lavender oil in conjunction with other ] can lead to detrimental effects on the body. Lavender oil taken with ] can cause chronic ] due to exponential{{dubious|reason="cumulative" would make sense from the context, "exponential" seems mathematically incongruous/exaggeration|date=May 2019}} buildup of this pharmaceutical sedative.{{medcn|date=December 2017}} | |||
| == Composition == | == Composition == | ||
Revision as of 14:22, 13 May 2019

Lavender oil is an essential oil obtained by distillation from the flower spikes of certain species of lavender. Two forms are distinguished, lavender flower oil, a colorless oil, insoluble in water, having a density of 0.885 g/mL; and lavender spike oil, a distillate from the herb Lavandula latifolia, having density 0.905 g/mL. Like all essential oils, it is not a pure compound; it is a complex mixture of phytochemicals, including linalool and linalyl acetate. As of 2011, the biggest lavender oil producer in the world is Bulgaria.
Production
Pure lavender essential oil is produced through steam distillation. This generates a greater amount of oil compared to other methods due to reduction of polar compound loss. Harvest of lavender blooms are typically around June. Lavender flowers are compacted into a still. Fewer air pockets in the still result in greater oil yield. A boiler is then used to steam the bottom of the lavender flower filled still at a very low pressure. The lavender flower pockets containing oil are broken from this heating process and a pipe of cold water is run through the center of the still. The hot lavender oil vapor condenses on the cold pipe with the cold water and is collected into a holding tank where it is allowed to settle. Due to polarity and densities of the water and oil, these two will separate in the holding tank whereupon the water is piped out, leaving just lavender essential oil.
Uses
Lavender oil has long been used in the production of perfume.
Oil of spike lavender was used as a solvent in oil painting, mainly before the use of distilled turpentine became common.
Lavender oil is used in massage therapy as a way of inducing relaxation through direct skin contact for application.
Adverse effects
In rare cases, lavender oil in soaps, shampoos, and other skin applied medications may cause prepubertal gynecomastia (breast development in young boys). Other potential adverse effects include a sedative effect and contact dermatitis as an allergic reaction, possibly resulting from major lavender oil constituents, camphor, terpinen-4-ol, linalool and linalyl acetate.
Composition
The exact composition of lavender essential oil varies from species to species but consists primarily of monoterpeneoids and sesquiterpeneoids. Of these linalool and linalyl acetate dominate, with moderate levels of lavandulyl acetate, terpinen-4-ol and lavandulol. 1,8-cineole and camphor are also present in low to moderate qualities. In all lavender oil typically contains many more than 100 compounds, although a great many of these are present at very low concentrations.
The composition of lavender essential oil as obtained by chromatography:
| Family | Composition | Lavande officinale Lavandula angustifolia |
Lavande aspic Lavandula latifolia |
|---|---|---|---|
| Terpenes / Monoterpenols |
Linalool |
28.92 % | 49.47 % |
| α-Terpineol | 0.90% | 1.08% | |
| γ-Terpineol | 0.09% | ||
| Borneol | 1.43% | ||
| Isoborneol | 0.82% | ||
| Terpinen-4-ol | 4.32% | ||
| Nerol | 0.20% | ||
| Lavandulol | 0.78% | ||
| Terpenes / Terpene esters |
 |
32.98 % | |
| Geranyl acetate | 0.60% | ||
| Neryl acetate | 0.32% | ||
| Octene-3-yl acetate | 0.65% | ||
| Lavandulyl acetate | 4.52% | ||
| Terpenes / Monoterpenes |
Myrcene | 0.46% | 0.41% |
| α-Pinene | 0.54% | ||
| β-Pinene | 0.33% | ||
| Camphene | 0.30% | ||
| (E)-β-Ocimene | 3.09% | ||
| (Z)-β-Ocimene | 4.44% | ||
| β-Phellandrene | 0.12% | ||
| Terpenes / Terpenoid oxides |
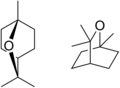 Eucalyptol (1,8-cineol) |
25.91 % | |
| Terpenes / Sesquiterpenes |
β-Caryophyllene | 4.62% | 2.10% |
| β-Farnesene | 2.73% | ||
| Germacrene | 0.27% | ||
| α-Humulene | 0.28% | ||
| Ketones |  Camphor |
0.85% | 13.00 % |
| 3-Octanone | 0.72% | ||
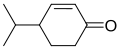 Cryptone |
0.35% |
References
- Bulgarian lavender producers worried about demand drop, China Post, 14 July 2011
- Masango, Phineas (2005-06-01). "Cleaner production of essential oils by steam distillation". Journal of Cleaner Production. 13 (8): 833–839. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2004.02.039. ISSN 0959-6526.
- Chanamai, R; Horn, G; McClements, DJ (2002). "Influence of Oil Polarity on Droplet Growth in Oil-in-Water Emulsions Stabilized by a Weakly Adsorbing Biopolymer or a Nonionic Surfactant". Journal of Colloid and Interface Science. 247 (1): 167–176. doi:10.1006/jcis.2001.8110. ISSN 0021-9797. PMID 16290453.
- N. Groom. New Perfume Handbook. Springer Science & Business Media, 1997 ISBN 9780751404036
- "Solvent", pp 605-606 in The Grove Encyclopedia of Materials and Techniques in Art, edited by Gerald W. R. Ward. Oxford University Press, 2008 ISBN 9780195313918
- Fismer, KL; Pilkington, K (2012). "Lavender and sleep: A systematic review of the evidence". European Journal of Integrative Medicine. 4 (4): e436 – e447. doi:10.1016/j.eujim.2012.08.001. ISSN 1876-3820.
- Henley, Derek V.; Lipson, N; Korach, KS; Bloch, CA (2007). "Prepubertal gynecomastia linked to lavender and tea tree oils". New England Journal of Medicine. 356 (5): 479–485. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa064725. ISSN 0028-4793. PMID 17267908.
- Elshafie, Hazem S.; Camele, Ippolito (5 November 2017). "An overview of the biological effects of some Mediterranean essential oils on human health". BioMed Research International. 2017: 1–14. doi:10.1155/2017/9268468. ISSN 2314-6133. PMC 5694587. PMID 29230418.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - Sarkic, Asja; Stappen, Iris (12 January 2018). "Essential oils and their single compounds in cosmetics: A critical review". Cosmetics. 5 (1). doi:10.3390/cosmetics5010011. ISSN 2079-9284.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - Shellie, R; Mondello, L; Marriott, P; Dugo, G (2002). "Characterisation of lavender essential oils by using gas chromatography–mass spectrometry with correlation of linear retention indices and comparison with comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography". Journal of Chromatography A. 970 (1–2): 225–234. doi:10.1016/S0021-9673(02)00653-2. ISSN 0021-9673.
External links
- http://www.webmd.com/vitamins-supplements/ingredientmono-838-lavender.aspx
- https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/002711.htm
- Lavender essential oil benefits and uses
| GABAA receptor positive modulators | |
|---|---|
| Alcohols | |
| Barbiturates |
|
| Benzodiazepines |
|
| Carbamates | |
| Flavonoids |
|
| Imidazoles | |
| Kava constituents | |
| Monoureides | |
| Neuroactive steroids |
|
| Nonbenzodiazepines | |
| Phenols | |
| Piperidinediones | |
| Pyrazolopyridines | |
| Quinazolinones | |
| Volatiles/gases |
|
| Others/unsorted |
|
| See also: Receptor/signaling modulators • GABA receptor modulators • GABA metabolism/transport modulators | |
| Androgen receptor modulators | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ARTooltip Androgen receptor |
| ||||||
| GPRC6A |
| ||||||
| Estrogen receptor modulators | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ERTooltip Estrogen receptor |
| ||||||
| GPERTooltip G protein-coupled estrogen receptor |
| ||||||